In the era of the digital world, computer networking has become an essential component of almost all businesses, educational institutions, and homes. Computer networking enables multiple computers to communicate and share resources, such as data, applications, and hardware. However, managing this network can be challenging, especially if you are unfamiliar with the differences between hubs, switches, and routers. This article’ll discuss these three devices, their functions, and how to choose the best device for your network.

A hub is a simple networking device connecting multiple Ethernet devices, such as computers, printers, and servers. Hubs operate by replicating the data the devices send to each other, meaning that any data received on one port is broadcast to all other ports connected to the hub. However, this broadcast technique results in a lower network performance, as every device connected to the hub receives all the traffic, even if it is not intended for them.
A switch operates similarly to a hub, allowing multiple Ethernet devices to connect. However, unlike a seat, a button can identify the intended recipient and only forward the data to the designated device. This capability leads to a higher network performance as the amount of redundant traffic on the network is significantly reduced. Therefore, switches boost the network performance in comparison to hubs.
A router is a device that connects multiple networks, enabling communication between different subnets. A router operates similarly to a switch as it can identify the intended recipient; however, it also can forward data between other networks, such as a LAN and a WAN. Additionally, routers provide the function of Network Address Translation (NAT), which allows private IP addresses to be translated into public IP addresses for internet access.
The primary difference between hubs, switches, and routers is their functionality and how they forward data. Hubs broadcast data to every connected device, resulting in a low network performance. Switches forward data to the intended recipient, significantly reducing redundant traffic and improving the network performance. Routers connect different networks,, enabling communication between them, and offering NAT for internet access.
Hubs have simplicity, low cost, and ease of installation advantages but can result in lower network performance and high traffic congestion. Switches offer improved network performance and reduce unnecessary traffic but are slightly more expensive than hubs. Routers connect different networks and enable communication with NAT functionality, but they can be very costly.
Choosing the best device for your network setup or need can be challenging. A hub is suitable for small networks as it is cheap and easy to use, but it may not be appropriate for more extensive networks where performance is a priority. Switches are more expensive than hubs but perform better, making them ideal for medium to large networks.
Routers are essential for large networks that require communication between multiple subnets. They can also integrate with firewalls to provide network security, making them the best option for businesses where security and performance are concerned. Before choosing a device, it’s essential to consider the network size, requirements, and budget.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between hubs, switches, and routers is essential to building and maintaining a network. Each device has advantages and disadvantages, and selecting the suitable machine for your network setup or need is crucial to achieving optimal network performance. Always consider the size of your network, the traffic requirements, and the budget before deciding. With the proper knowledge, you can select the best device for your network needs and enjoy smooth and efficient networking.
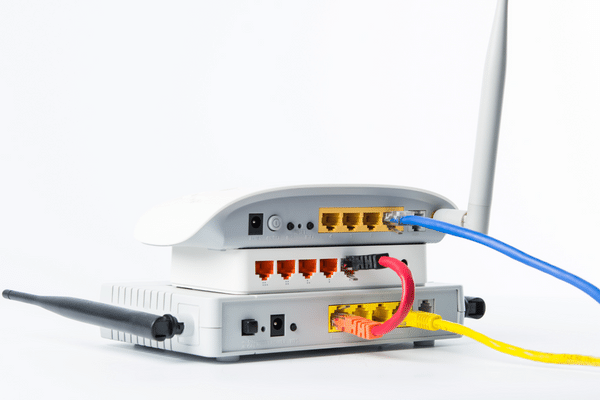
A hub, in the context of computer networking, is a networking device that connects multiple devices and allows them to communicate with each other. It operates at the OSI model’s physical layer and can transmit data to all connected devices on the network.
A hub acts as a central connection point for devices in a network, allowing multiple devices to share the same network segment. The corner receives data from one device and broadcasts it to all other devices connected to it, regardless of the destination of the data. This results in inefficient use of network bandwidth and can lead to collisions and data errors in high-traffic networks.
While hubs and switches perform similar functions, there are some critical differences between them. Unlike a seat, a controller operates at the OSI model’s data link layer and can analyze data packets to determine their source and destination addresses. This allows a switch to forward data packets only to the intended recipient, resulting in improved network performance and reduced collisions.
Due to its limitations in network performance and potential for collisions, a hub is generally only recommended for use in small networks with low traffic volume. A switch is the recommended networking device in more extensive networks where the bandwidth is critical. Hubs are also more commonly used in home networking applications where the number of connected devices is limited.

A switch is a networking device that operates within a local area network (LAN) to help connect devices and facilitate data exchange between them. Generally, a switch’s primary function is to learn and store connected devices’ Media Access Control (MAC) addresses, enabling it to direct traffic between devices within a LAN. When a device sends data to another device in the same network, the switch forwards the data directly to the recipient device based on the MAC address, resulting in faster transmission and reduced network congestion.
Unlike a switch, a router is a device designed to manage and direct traffic between networks, such as LANs and Wide Area Networks (WANs). While a button works mainly to connect devices within a network, a router uses different protocols to connect and communicate between separate networks, including maintaining tables of device IP addresses for better navigation. Unlike switches, routers can direct traffic to their respective destinations across different networks, block unauthorized access, perform Network Address Translation (NAT), and handle much higher bandwidth capabilities. However, routers can be more costly than switches and are better suited for more complex network deployments.
Switches are ideal for setups that involve heavy traffic between devices within one LAN-based network. They are cost-effective, offer higher bandwidth capacity than traditional hubs, and deliver better performance and connectivity by isolating network traffic to optimize data flow between connected devices. A switch is perfect for small to medium-sized businesses with low to medium internet usage or when a more straightforward network setup is the focus. For instance, in a retail store with several point-of-sale (POS) terminals, a switch can provide fast and reliable connectivity for the POS system and any other devices within the store’s local network setting. In this way, a button can help build a dependable and efficient local network environment that suits the business’s specific needs.

A router is a networking device that directs data packets from one network to another. Its primary function is determining the best path for data between multiple networks. Routers use IP addresses to identify each network and send data packets based on those addresses to their respective destinations. A router acts as a traffic director, ensuring that data travels efficiently and securely between devices and networks.
While routers and switches are networking devices, they have different functionalities and uses. A switch is a device that connects multiple devices on a single network, allowing them to communicate with one another. In contrast, a router connects multiple networks, allowing devices on different networks to communicate. A router uses IP addresses to identify each network and determine the best path for data to travel. In contrast, a switch uses MAC addresses to identify the devices on a single network and direct data packets between them. While switches are helpful for local network communication, routers are necessary for communication between networks.
A router is necessary whenever devices on different networks need to communicate with one another. For example, if a company has multiple branch locations that need to share data and resources, a router must create a vast area network (WAN) to connect those locations. Additionally, if an individual wants to connect to the internet using a home network, a router must direct data packets between the local network and the internet service provider (ISP). Routers are also essential for network security, as they can be configured to block unauthorized access and protect against cyber threats.
| Parameter | Hub | Switch | Router |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Ports | 4月24日 | Up to 48 | |
| Memory Size | Low | Moderate | High |
| Processor Speed | Low | Moderate | High |
| Bandwidth | Low | High | High |
| Switching Capacity | Low | High | Moderate |
| MAC Address Table Size | Small | Large | Large |
| Packet Forwarding Rate | Low | Moderate | High |
| Latency | High | Low | Low |
| Cost | Low | Moderate | High |
| Complexity | Low | Moderate | High |
The differences between a hub, switch, and router lie primarily in their functions, features, and technical capabilities. A seat is the most straightforward device with no intelligence or decision-making capabilities. A switch is more advanced and can decide where to forward data to reduce network traffic. A router is the most intelligent device and can decide how to route data between networks.
The similarities between these devices lie in their essential functions. All three devices are used to connect devices and enable data transmission. They act as intermediaries between devices and help to ensure that data is sent to the correct destination on the network.
Choosing the best device for your network depends on your specific needs and budget. A hub may be sufficient if you have a small network with only a few devices. However, a switch is a better option if you have more devices or need better performance. A router is the best choice if you have multiple networks or need to connect to the internet.
When selecting a device, consider data transmission speed, network size, security, and cost. A hub or a primary switch may be a cost-effective solution for a small network. For more extensive networks, a more advanced switch or router may be required. It’s also important to consider the potential for future growth and scalability.
In conclusion, understanding the differences and similarities between a hub, switch, and router is essential for making informed decisions about which device is best for your network. By considering your specific needs and budget, you can choose a device that will provide the necessary functionality and performance for your network now and in the future.
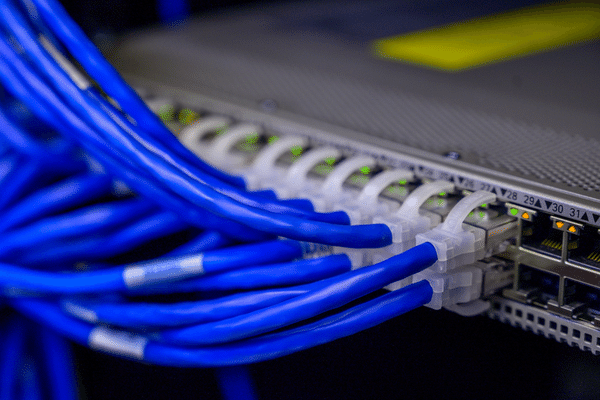

Ethernet is a technology that connects computers and other devices to form a local area network (LAN). This protocol was initially developed in the 1970s by Xerox Corporation, and it has since become the most widely used LAN technology. Ethernet allows multiple devices to share a common communication medium, known as a physical layer, that can carry data in the form of packets.
Ethernet operates on the principles of networking and is based on implementing a set of rules and protocols that allow for reliable data transfer between devices. Data sent over Ethernet comprises a sequence of packets, each containing a header and a payload. The title includes information on the destination address, source address, and other metadata, while the load carries the data sent.
Ports are physical connectors on a device that allowsconnect different peripherals and devices to the network. Each port has a unique number assigned to it, which allows for communication between devices and the web. Ports can be used for various purposes, including internet access, file sharing, printing, and gaming.
Many types of ports are available, and each port serves its unique function. Some of the most common types of ports include USB, Ethernet, HDMI, VGA, and DisplayPort. These ports are essential for connecting different types of peripherals and devices to the network and for seamless communication between devices.
Ethernet and ports work in conjunction to allow for data transfer between devices over the local network. Ethernet provides the communication medium for data transfer, while ports provide the physical connection between devices and the web. Ethernet and ports have greatly simplified the data transfer process between devices, making it faster, more reliable, and more efficient.
As technology continues to evolve, Local Area Networks (LAN) and Internet Protocol (IP) addresses have become crucial components in the world of networking. A LAN is a network of connected devices within a specific area, like an office building or a campus. The primary purpose of a LAN is to enable devices to communicate with each other and share resources such as files, printers, and servers.
LANs operate faster than Wide Area Networks (WANs) and are more secure since they are limited to a specific area. They also offer significant cost advantages over WANs because they do not require external network resources. In a LAN, data is transmitted through interconnected devices using copper or fiber-optic cables, wireless connections, or a combination of both.
Key elements and components of a LAN include network interface cards (NICs), switches, routers, hubs, and various cables such as twisted pair, coaxial, and fiber-optic cables. NICs are responsible for enabling devices to connect to the LAN, while switches and routers help manage data flow among devices. Hubs, on the other hand, act as the center of the network by connecting various devices.
An IP address is a unique numerical identifier that identifies devices connected to a network. This address enables devices to communicate with each other across the internet. Like a street address, an IP address determines where data packets are sent and received and allows data to travel through different networks and routers.
As internet usage has increased, the demand for IP addresses has increased, leading to a shortage of available IP addresses. There are two IP addresses: IPv4, the most commonly used IP address type, and IPv6, which was developed to address the shortage of IPv4 addresses. IPv6 offers a significantly larger address space, allowing more devices to be connected to the internet.
IP addresses are assigned to devices either statically or dynamically. Static IP addresses are manually assigned to an apparatus and do not change, while dynamic IP addresses are set automatically and can change periodically.
In LANs, IP addresses are utilized in communication between devices and systems. Devices in a LAN are assigned unique IP addresses, allowing them to communicate with other devices in the network. IP addresses are also used for routing, which sends packets from one network to another, creating a path for data packets to reach their intended destination.
In summary, a LAN is a network of devices within a specific area, while IP addresses are unique identifiers used to identify devices connected to a web. Understanding the roles of LAN and IP addresses is essential in ensuring effective network communication and management. As technology continues to evolve, it is essential to stay up-to-date and informed on the latest advancements in networking.

Wireless networks are computer networks that use radio waves to connect multiple devices without physical cables or wires. They are increasingly becoming important in today’s digital age due to their flexibility, scalability, and ease of use. Wireless networks provide mobility and location independence, enabling devices to connect to the network from any location within range, making it possible to work remotely, collaborate easily, and access information anywhere. Wireless networks are crucial in our everyday lives, from homes to businesses and educational institutions in [variable city/town] and beyond.
A router is an electronic device that allows multiple devices to connect to a network and exchange data. A router is essential in setting up and using a wireless network because it acts as a central point for connecting devices to the internet and controlling the data flow between them. A router provides security features, such as network address translation (NAT), firewall, and port forwarding, which protect the network from intruders and secure private information. Furthermore, a router provides a stable and reliable connection to the internet, ensuring that devices connected to the network can enjoy a high-speed internet connection.
Selecting the appropriate wireless router ensures a reliable and efficient network connection. When choosing a wireless router, several essential factors need to be considered. These include network speed, range, security features, and device compatibility. Network speed is a critical factor to consider, especially when streaming videos or playing online games. A router with higher speeds ensures that data is transmitted quickly, providing an uninterrupted experience. Range is another factor to consider, especially when setting up a network in an ample space. A router with a longer range can extend the network coverage, providing a stable connection throughout the area. Security features are of utmost importance, and choosing a router that offers robust encryption protocols and firewall protection is crucial in ensuring that private information is secure. Lastly, compatibility with devices should be considered, and choosing a router that supports the latest Wi-Fi standards ensures that all devices connected to the network can enjoy a high-speed connection.

Despite its usefulness, creating and maintaining a WAN can be a challenging task. One of the primary challenges of a WAN is the need to navigate a combination of different networks and protocols. This challenge creates the need for a router, an essential tool in directing data packets from one network to another. A router is a device that connects multiple networks and enables communication between them. It identifies the optimal path for data to travel and forwards the data packets to the appropriate device or network.
A router plays a crucial role in WAN, providing essential functionalities such as packet filtering, network address translation, and access control. Packet filtering ensures that only authorized traffic is allowed in or out of a network. In contrast, network address translation maps addresses from a local network to a unique public IP address. Access control lets administrators control user access to network resources and prioritize network traffic. These functionalities help ensure that data gets to its destination effectively while maintaining the network’s security.
Several types of routers are commonly used in WAN networks, including edge routers, core routers, and distribution routers. Edge routers connect users to the internet, providing boundary protection and enforcing policies that govern network access. Core routers are responsible for high-speed data transfer between different networks, functioning as the backbone of the WAN. Distribution routers connect the different LAN segments and intermediate networks in a WAN, routing traffic to the core routers through designated paths.
As networks have become more sophisticated, various devices have been developed to help users manage and optimize their connections. Three of the most critical network devices are hubs, switches, and routers. In this article, we have explained the key differences between these devices and outlined some of the advantages and disadvantages of each one for different network scenarios.
A hub is a simple and inexpensive device connecting many devices in a network. It operates in a broadcast network, meaning that it sends all data packets to all connected devices. This can lead to network congestion, slower speeds, and decreased security as all devices receive sensitive data. Hubs are suitable for small networks with limited devices and a low budget.
A switch is a more advanced device that improves network efficiency by forwarding data packets only to the destination device. It creates a point-to-point network and can manage traffic flow, reducing network congestion and increasing speed. Switches also offer better security as they forward only necessary data. They are ideal for networks that need high speed and security, such as large businesses.
A router is the most complex device of the three and can connect multiple networks, even those with different architectures and protocols. It directs data packets to other networks and devices and can optimize traffic flow, providing both security and speed. Routers can also perform network address translation (NAT) and firewall functions, making them suitable for larger organizations or Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
Choosing the best device depends on several factors, including budget, network size, and connectivity needs. A hub is the most affordable but works best for small networks with little traffic. A switch offers better speed and security for large networks but costs more. A router is expensive but provides the most advanced features, making it ideal for organizations with high traffic and complex network architectures.
In conclusion, each device has unique advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right one depends on your needs. Consider your budget, network size, and connectivity needs when deciding. Youyou can optimize your network performance, improve security, and ensure smooth data f with the right devicelow.
A: A hub, switch, and router are all devices used in computer networks, but they serve different purposes. A seat is the least intelligent device, simply allowing multiple devices to connect and share data simultaneously. A switch is a more intelligent device that reads the destination address of incoming data and sends it only to the intended device. Conversely, a router connects two or more networks and directs data packets from one network to another.
A: You need a router when you want to connect two or more networks. A switch can only connect devices within a single web, while a router can direct data between networks. If you have multiple networks, such as a home network and an office network, you would need a router to connect them.
A: A network switch is a device that operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the network layer model. It allows multiple devices to connect to a network and share data simultaneously. A switch reads the destination address of incoming data and sends it only to the intended device, improving network efficiency and reducing unnecessary network traffic.
A: A switch is a more intelligent device compared to a hub. While a seat simply allows multiple devices to connect and share data simultaneously, a controller reads the destination address of incoming data and sends it only to the intended device. This helps improve network efficiency and reduces unnecessary network traffic. In other words, a switch can direct data to the specific device it is intended for, while a hub broadcasts data to all connected devices.
A: The type of switch you need depends on the specific requirements of your network. There are managed switches and unmanaged switches. Managed switches offer more control and flexibility, allowing you to configure settings and monitor network traffic. On the other hand, unmanaged switches are more basic and require less maintenance but offer limited control over the network.
A: When data arrives at a switch, it reads the packet’s destination address and checks its internal lookup table to determine which port to send the data to. The controller sends the data to that specific port, ensuring it reaches the intended device. This process, called switching, allows for efficient data transmission within a network.
A: The main difference between a switch and a router is their functionality. While both devices connect devices in a network, a switch operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) and directs data within a network. Conversely, a router works at the network layer (Layer 3) and requires data between networks. In simpler terms, a switch connects devices within a network, while a router connects networks.
A: It depends on your network setup. If you only have a single network with wired devices, a switch may be sufficient for connecting and sharing data among those devices. However, if you want to connect your wired network to another network, such as the Internet, you need a router to perform the necessary routing functions.
A: No, a switch operates at the data link layer and can only read the destination address within a single network. It cannot read the destination address across multiple networks. For routing packets between different networks, a router is required.
A: In general, routers tend to be more expensive than switches. Routers are more complex devices that perform additional functions, such as network routing and firewall capabilities. On the other hand, switches are relatively more straightforward devices primarily focusing on connecting devices within a network and directing data.
Fiber optic access network WAN connection topology design
The Complete Guide to Different Types of Network Switches for Your Network