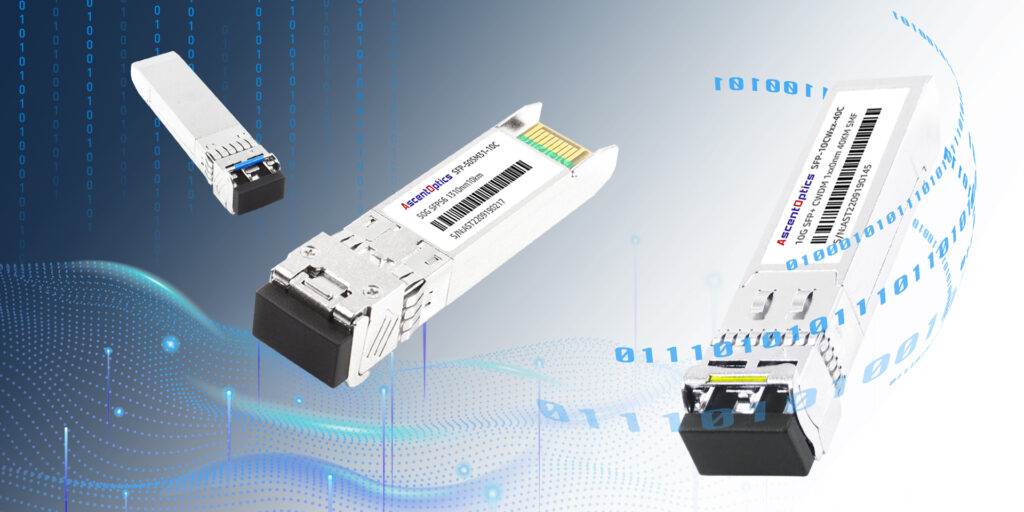

SFP modules, or Small Form-factor pluggable modules, are hot-swappable hardware components that allow network devices to connect with fiber optics or copper cables. SFP modules operate at high data rates, making them ideal for transmitting data in short and long distances. They are essential in IT because they make it easier for IT professionals to configure and maintain their network equipment.
One of the key advantages of using SFP modules is their ease of use. They can be easily inserted into a network device’s SFP port without requiring a system reboot. This makes them a quick and efficient way to improve network connectivity. SFP modules also offer performance benefits, particularly regarding network speed, reliability, and scalability. This is because they allow for flexible networking and make it possible to upgrade and customize network equipment to suit specific requirements.
Compatibility is vital when it comes to SFP modules. It is essential to use the right SFP module that is compatible with the network device in question and the type of cable being used. Mismatched equipment can result in network downtime or poor performance, which can hurt business operations. For this reason, it is essential only to use SFP modules certified for use with specific network devices, cables, and other equipment.
The MSA, or Multi-Source Agreement, is an industry-standard defining SFP module characteristics. Adherence to this standard ensures that SFP modules are interchangeable between different manufacturers, making it easier for organizations to upgrade or customize their network equipment without fear of compatibility issues. The MSA standard specifies critical parameters, such as electrical, mechanical, and environmental specifications, which manufacturers must follow to ensure that their SFP modules are interoperable.
Choosing the suitable SFP module depends on various factors, including the type of network device being used, the location of the data transmission, and the type of cable being used. It is essential to consider the data rate, wavelength, distance, and interface type when choosing an SFP module. IT professionals must also consider the need for redundancy, power consumption, and heat dissipation when selecting an SFP module. Consulting with networking professionals and adhering to industry standards can help ensure that the suitable SFP modules are chosen and that the network runs smoothly and efficiently.

The two most commonly used types of SFP modules are copper and fiber modules. Copper SFP modules are designed for copper cables and have RJ-45 ports. They can connect switches or routers to servers or other networking devices. Fiber SFP modules, however, are used with fiber optic cables and have different mechanical dimensions than copper modules. Fiber modules come in different types, such as single-mode and multimode. The usage of fiber modules depends on the length and quality of the cables, which may vary depending on the requirements of the network setup.
SFP modules are small and compact, measuring only 8.5mm in width and 13.4mm in depth. They are built with a modular design, so they can be easily swapped out and replaced in the field if necessary. They are also designed to be compatible with various manufacturer’s equipment, making integrating them into a wide range of network setups easy. SFP modules are available with different connector types, such as LC, SC, and ST, making it easy to connect them to different kinds of cables.
QSFP modules (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable modules) are an evolution of the SFP modules and offer more advanced capabilities. They are designed to support higher bandwidth applications, making them well-suited for use in data centers that require fast and efficient processing. QSFP modules are also used in Ethernet networking to help achieve more efficient data transmission over long distances. They are available in different configurations, such as QSFP+ and QSFP28, and can support data rates of up to 100 Gbps.

SFP modules are widely used in Ethernet networking for their versatility, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. They are used in data centers, enterprise networks, and service provider networks to provide network connectivity between different devices. SFP modules support a range of Ethernet standards, including 10/100/1000BASE-T, 100BASE-FX, and 1000BASE-SX/LX/BX, allowing them to be used in various network setups. The ability to hot-swap SFP modules also makes it easy to upgrade or replace components of an Ethernet network on the fly without downtime.
While other optical networking solutions are available, SFP modules offer unique benefits that set them apart from competitors. For example, unlike other solutions that require complex installation and configuration processes, SFP modules are easy to install and can be used with various equipment. They are also cost-effective and modular, which means they can be quickly and easily replaced or upgraded. Additionally, SFP modules offer the ability to support a wide range of Ethernet standards, making them a versatile and flexible option for various networking setups.
The first consideration when selecting an SFP module is the type of fiber optic cable used. There are two main types of fiber optic cables: single-mode and multimode. Single-mode SFP modules are used for long-range connections and can transmit data over distances up to 10 kilometers or more. Multimode SFP modules are used for shorter-range connections, typically within or between campus buildings. They are capable of transmitting data up to distances of 550 meters. The decision to choose between single-mode and multimode SFP modules depends on the space that needs to be covered by the network connection and the type of fiber optic cable being used.
The second consideration when selecting an SFP module is the wavelength of light being used to transmit data. Different wavelengths of light have other properties, which can affect the performance of the SFP module. The most common wavelength for SFP modules is 850 nanometers, used for multimode fiber optic connections. Single-mode fiber optic connections typically use wavelengths of 1310 nanometers or 1550 nanometers. The decision to choose between these wavelengths depends on the type of fiber optic cable being used and the distance that needs to be covered by the network connection.
The third consideration when selecting an SFP module is compatibility with network equipment. SFP modules are designed to work with a wide range of network products, including switches, routers, and other devices. However, ensuring that the SFP module is compatible with the network product being used is important. Compatibility issues can cause the SFP module not to work or cause problems with the overall performance of the network.
The fourth consideration when selecting an SFP module is the network’s bandwidth requirements and distance limitations. SFP modules are available in a wide range of speeds, from 100Mbps to 100Gbps. The decision to choose a specific rate depends on the bandwidth requirements of the network. Additionally, the distance limitations of the SFP module should be considered. SFP modules have a maximum distance limitation, beyond which the signal degrades. It is essential to choose an SFP module that can cover the distance required by the network while maintaining signal integrity.

One of the most significant advantages of using hot-pluggable SFP modules is their ease of use and flexibility. They can be easily inserted and removed without power down the device, allowing for simple maintenance and upgrades. Additionally, SFP modules can support multiple networking technologies, such as Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and SONET/SDH, making them versatile options for various applications. Their hot-pluggable nature also eliminates the need for labor-intensive installations and time-consuming shutdowns.
SFP modules offer a significant advantage in environments where space is limited, such as data centers and server rooms. Their small form factor allows for greater port density, enabling users to connect more networking devices in less space. This compact size also makes SFP modules lighter and easier to manage and transport. In addition, SFPs can be used with modules that feature Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus (SFP+) technology, doubling the maximum available bandwidth.
SFP modules can increase network port density, which can help save space, reduce cabling, and enhance network scalability. A switch that supports SFP interfaces can accommodate a variety of fiber or copper interfaces by using the appropriate SFP module. This ability to support different interfaces enables users to mix and match the appropriate cabling for each device without purchasing additional switches, helping to reduce costs.
SFP modules can also support other optical networking technologies, such as Gigabit Ethernet, 10 Gigabit Ethernet, and Fibre Channel. By integrating these technologies, users can create a versatile and flexible network that supports various applications and configurations. When combiniproperles with other optical networking technologies, it is essential to ensure their compatibility, including the wavelength, mode, and link length supported.
While SFP modules offer many benefits, they may also encounter common issues like power consumption, temperature, and compatibility. Users should choose high-quality modules that meet industry standards to overcome these issues. They should also ensure the device meets the required specifications, such as power, wavelength, and link length. In case of any issues, users should consult the device manual or vendor support for troubleshooting tips.
As technology advances, the demand for high-speed and reliable networking solutions grows. SFP modules, known as small form-factor pluggable modules, play a crucial role in modern networks. Whether you require gigabit Ethernet connections or optical networking capabilities, choosing the suitable SFP module is vital for optimal network performance. By understanding the different types, compatibility considerations, and critical factors in selecting an SFP module, you can ensure a seamless and efficient networking experience. So, explore the diverse range of SFP modules available and select the one that best suits your network requirements.

A: When choosing an SFP module, there are several factors to consider, such as compatibility with your device, the type of network you are connecting to (copper or fiber), the required data transmission speed (1G or 10G), and the distance the module needs to cover. Additionally, you should ensure that the SFP module complies with the SFP Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) to guarantee compatibility with different manufacturers.
A: In most cases, mixing and matching SFP brands is possible. However, using SFP modules from the same brand or ensuring MSA compatibility is recommended to avoid any compatibility issues and ensure optimal performance.
A: Copper SFP modules use copper cables to transmit data, offering a cost-effective solution for short-range connections. Fiber SFP modules, on the other hand, utilize fiber-optic cables and are suitable for long-distance communication with their higher bandwidth and immunity to electrical interference.
A: The maximum distance an SFP module can cover depends on the specific module and type of network. For example, a single-mode fiber module can cover distances of up to 20km, while a multimode fiber module typically covers spaces up to 550m.
A: SFP modules have a small form factor designed to fit into the SFP socket of a networking device. They typically measure 8.5mm in width, 13.4mm in height, and 56.5mm in length.
A: No, an SFP module is designed to work either with single-mode or multimode fiber. The type of fiber used should be selected based on the network requirements and the distance the module needs to cover.
A: The SFP MSA (Multi-Source Agreement) is a standard that defines the mechanical, electrical, and signaling specifications for SFP modules. It ensures compatibility between different manufacturers’ SFP modules, allowing users to select the appropriate transceiver for their networking needs.
A: Yes, an SFP module can provide fast communication between switches or between switches and necessary network devices, such as servers, routers, or firewalls. It enables high-speed data transmission and enhances network connectivity.
A: SFP modules offer several advantages, including small form factor, hot-pluggable design, low power consumption, and compatibility with various network types. They are widely used in most networks due to their flexibility, scalability, and compatibility with different networking devices.