SFP stands for Small Form-factor Pluggable, a hot-swappable transceiver module used in network switches, routers, and network interface cards (NICs). An SFP port is an interface on networking devices designed to support SFP modules. Everything you need to know about SFP Ports will now be described in detail.

SFP ports are utilized to connect network devices to either fiber optic or copper cabling and communicate over Ethernet, SONET and Fibre channel protocols. They are a small form factor and hot swappable.
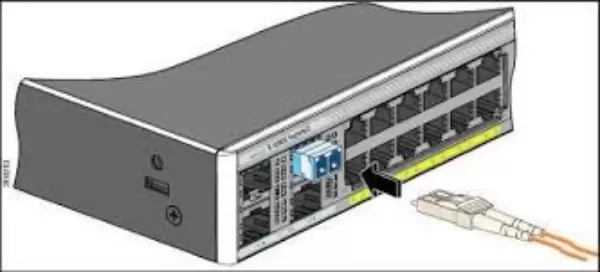
Network administrators can utilize SFP ports with different types of fiber and copper cables. A specific device does not need to be turned off to be maintained during the changing of interfaces. Applications that support the use of SFP Connectors send digital signals which are converted into either optical or electrical ones to be sent over the network.
There are advantages that SFP ports have over traditional Ethernet ports such as expansion capabilities. One of the most important things however is the flexibility provided by SFP ports. They are hot swappable, thus with ease one can alter the type of connection and speed by simply swapping out the module without having to replace the entire device.
One more benefit of SFP ports is the accessibility it provides to multimode and single-mode fiber optic cables that can be used for long-distance network links. More so, SFP ports are also impressively compatible with diverse protocols and therefore are more functional than out ports types.
SFP ports finds application in various fields like healthcare, finance, education, etc. They are quite useful in instances like large data centers and enterprise networks that require high levels of flexibility, reliability and scalability.
In the SFP port sphere, the Cisco Small Business SFP Modules series makes for the most remarkable product. This product has many SFP transceivers that are Gigabit Ethernet capable and can transmit data at rates up to 10 Gbps. Other reputable brands in the SFP port market include Netgear, TP-Link, and Mikrotik.
Recommended Reading: SFP+ Module: Everything You Need to Know
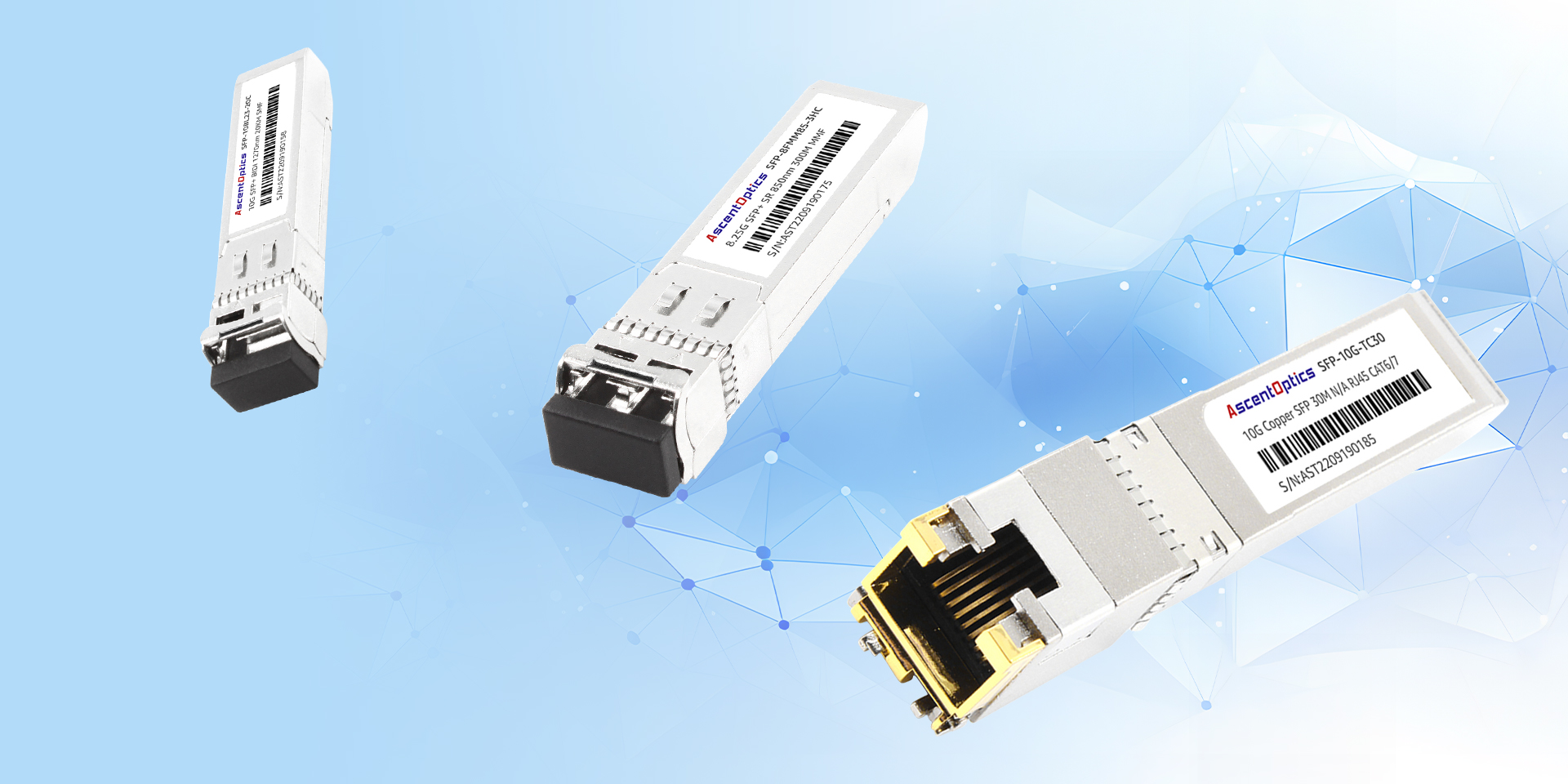

SFP modules or Small Form-Factor Pluggable modules connect via standard SFP ports on various network devices such as routers and switches. They allow for the transmission of data through a variety of media types, be it copper or fiber optic cables. Copper SFP Modules, for example, these modules are utilized in short-distance LAN links and use copper cables to relay signals. Fiber SFP Modules can be used to transmit at greater distances by employing fiber optic cables or for more rapid signal transmission. Bi-Directional SFP Modules employ a single fiber optic cable and transmit in both directions. In addition, CWDM and DWDM SFP Modules utilize Wavelength Routers do what its capable of regarding fiber optics – sending more data across thicker bands in thicker optics.
There are various types of Copper SFP modules, with 10/100/1000Mbps and 10Gbps speeds. Fiber SFP modules include single-mode and multimode varieties and are available in various other rates like 1G to 100G. Other types include Bi-Directional SFP which also come in various speeds and are either single-mode or multimode. CWDM and DWDM SFP modules allow long distance and high speed data transfer.
While selecting an SFP module for your network, it is important to consider the type of media that you plan to use, be it copper or fiber optic, the length of the data transmission and speed requirements. It is also very crucial that the SFP module works with the switch or router that is going to be employed. Before buying it is a good practice to check with the manufacturer’s specifications and compatibility lists.
As much as general assumptions can be made that all SFP Modules serve the same purpose, such assumptions can be misleading as not all SFP Modules are the same nor are they suitable for every device out there, which is why it’s advisable to always buy SFP Modules produced by the same manufacturer of the router or switch. If getting a compatible switch is not possible, it is vital to look at the compatibility matrix and specifications of both devices to make sure they will work together seamlessly.
The case for fitting an SFP Module is pretty cut and dry, as users only need to plug the device in the SFP port of either the switch or router. After the SFP Module has been inserted, users must be able to see and configure the module just like every other interface that is available on the device. Configuration may include speed, duplex, or VLAN tagging among other things. In case a user is unsure, they may look at the guidelines provided by the SFP Module manufacturer.
People encounter issues using SFP modules when connecting them such as speed , performance and different device compatibility range. To begin resolving these issues, a good way of proceeding would be to check the device logs for any SFP module hardware related errors. Also examine the cables and connectors whether they might be loosely connected or damaged. If this does not solve the problem, you might consider removing the SFP module and replacing it with a similar working SFP module. Also check whether the SFP module and also the device are using the same speed and duplex settings. Here goes the last option. All of the foregoing failed, you may indeed have to seek service from the manufacturer.
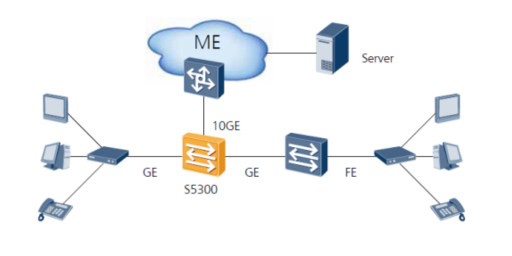
SFP ports are one of the most interconnected connections with switches, routers, and servers, as well as having a great impact on overall performance of the architecture of the network.
The setup of SFP ports in a network switch depends on the brand of the switch and SFP modules used. Apart from these aspects, the configuration procedure generally starts with determining the SFP port number and type, followed by setting the speed and duplex parameters, and then VLAN and port security configurations.
In order to improve the network performance with SFP ports, it is recommended to use quality SFP modules in accordance with the specifications of the switch. Moreover, the SFP ports may also be set to auto negotiation for better optimization of bandwidth. Improving network performance can also be achieved through link aggregation where a number of SFP ports are combined, thereby giving a higher amount of bandwidth.
SFP ports are always on the line of having issues with either of the two tools being utilized, which are the SFP module and the switch. Such burden can be avoided by refraining from these connections due to the SFP modules not being aligned to switches. Another well known SFP module issue arises amongst switches which is solved through SFP replacement.
Interconnectivity issues are best solved by the use of SFP ports in any device due to the various functions SFPs can provide. Thanks to SFP ports, network engineers are able to link switches and devices over longer distances utilizing different cabling methods, such as copper, multimode fiber, single-mode fiber, and even direct attach cables. There are cases, Traditional RJ45 ports may not handle that kind of heavy load and will not be sufficient, where such feature comes in handy.
There are similarities that can be found in SFP and RJ45 ports which is they get to be found in network switches as connection ports or interfaces. RJ45 ports are generally used for close range connection between devices and make use of copper cables. Other than that, SFP offers a variety of ways of connecting equipment over long distances- different cables including fibre optic cables and direct attach cables could be used. Furthermore, SFP enjoys faster speeds and greater bandwidth than RJ45 ports.
Recommended Reading: Data Center Network Architecture
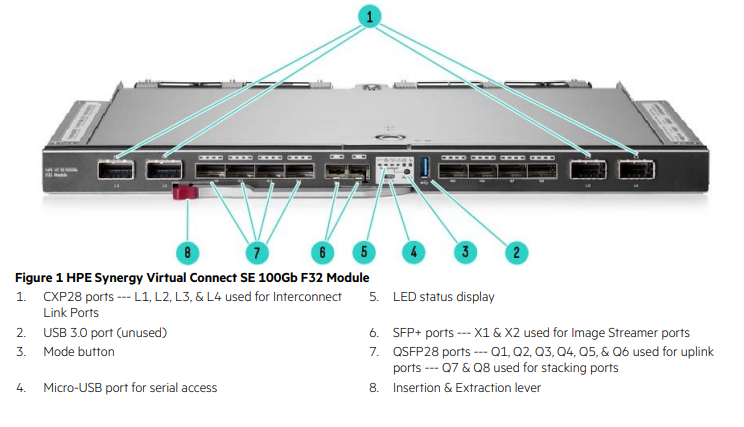
Uplink SFP ports are special kind of ports used for connecting final switches or routers to a larger size network. Such ports are high speed, supporting data rates ranging from 1 Gbps to 100 Gbps. SFP as a small form-factor pluggable transmission media, uplink SFP ports use SFP ports instead of normal Ethernet ports to connect with different networks or other media.
On the other hand, downlink ports also refer to Ethernet ports but use it to connect the network equipment to the switch. Similarly to uplink SFP ports, downlink ports tend to have lower speed but don’t use specialized hardware. Moreover, downlink ports are used to link the computer, printers, IP phone or any other last devices to the switch.
End devices are configured to communicate with the network infrastructure using downlink ports. Such ports may be configured to be able to support several other settings such as Quality of Services (QoS), VLANs, and Link Aggregation Control Protocols (LACP) for improved network performance. It is worth mentioning that the number of ports supported by downlink ports is limited in nature, which would mean that excessive usage of devices with these ports would mean network congestion and lower speed as all the ports would be used at once.
There’s a need to understand the configuration of uplink and downlink ports correctly so as to enhance the switch’s performance. An example would be setting the switch’s proper speed and duplex mode when connecting an uplink SFP port and a switch. One may also need to make the necessary adjustments on the switch to facilitate the advanced processes such as LACP or even VLAN tagging.
For the switches to perform better, uplink ports should have the switch adjustments to satisfy the needs of QoS and VLAN as well. It is also needed to keep in mind the necessary number of dowlink ports so as to eliminate the chances of oversubscription of ports which causes network congestion. The uplink ports and the downlink ports if configured correctly allow the switch to function efficiently at every level of the network.
Combining uplink and downlink ports allow maximum network design flexibility a switches have uplink ports that connect other networking devices which enables the creation of wider networks. And using downlink ports at the other end of a switch uplink, allows you to connect the end devices directly to the switch itself. With the integration of these ports, the structure of the network design can be modified as several including the formation of star, tree and even mesh networks layouts. Other methods that would sufficie include trunking and even link aggregation.
However, it is crucial for the thinker to assess where the potential problem areas could lie in terms of combining uplink and downlink ports. For instance, if all ports are set as downlink ports, bottlenecks and congestion may occur while, if all the ports are set as uplink ports, it will cause end devices to have limited options for connectivity. Hence, the number of uplink and downlink ports must be distributed such as to satisfy certain requirements of the network.
When defining the optimal ratio of uplink and downlink ports, the topology of a particular network and individual product specifications certain corner devices’ invoices should be accounted for. As an example, the network with more terminal devices should have more down-link ports than up-link ports while a sparsely deployed device network that requires heaps of data transfer among switches or routers should have the reverse, lots of uplink ports rather than downlink ports. Also, the employment of sophisticated technologies such as VLANs, QoS or LACP will stipulate particular settings on the ports.
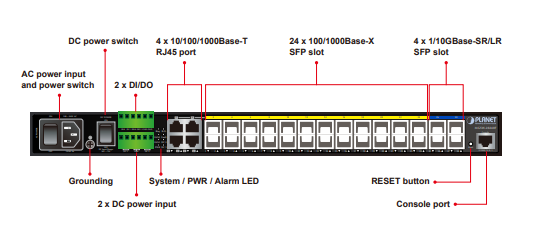
The connectivity, error messages, speed and performance troubles, errors, module faults are the most complained occurrences. With the right understanding of these concerns and a proper troubleshooting approach, SFP-related difficulties can be handled in a timely and effective manner by network engineers.
SFP ports suffer from connectivity issues, due to cable problems, incorrect configurations or even network problems, which are very common. To solve any reasons behind connectivity issues, one will have to diagnose the devices and cabling within their network. Start the process by confirming whether the SFP module and the primary equipment have any connection. Confirm that SFP is properly placed in its case, and that the wires are functional. Confirm that the SFP link status indicatives are present and get the speed and duplex settings right. If the link indicator lamp does not light up, use an alternate cable or narrow your cabling in order to change the settings. Improper VLAN assignments or wrong switch port assignments are also one more common reason for the SFP connections issue. Keeping those connectivity issues in check will help you maintain a successful communication between devices within your network.
A network can be encumbered as a result of performance degradation resulting from SFP ports’ errant email transports and SFP ports. Usually, such messages are a sign that some of the network hardware or even the network settings need some correction. Such error messages as “SFP module not readable,”, “SFP module not present,” and “SFP module error” are most regular offense committed. In little or no time, these error messages are said to be resolved if the SFP module status indicates that it sitting and powered properly. Refer to the SFP module’s data sheet and investigate as per the data sheet’s guidelines. In addition, another common cause of SFP network problems is network configurations errors. Due to this, it is preferable to manage the check of a network configuration periodically to make sure the right one is deployed.
It is a common problem encountered with SFP ports to experience speed and performance troubles as well. Certainly, they affect the productivity of your network and even worse, the end-user experience. When there are such issues, speed and performance issues, go through the data sheet of the SFP module to check its compatibility with the network equipment used. Furthermore, verify the configuration of the network equipment, that the speed settings correspond with SFP module and the physical cabling. In the end, take a look at your network topology to ensure that there are no uneven loop artifacts which could jeopardize the network speed.
When the problem with an SFP port persists even after all attempts of troubleshooting, an SFP module replacement may then be warranted. But first, ensure that you have found the root of the problem. Manufacturer guidelines should be followed when installing new SFP modules. It is always most appropriate to replace the SFP module with as close a version as possible of the failed one removed.
Best Practices for Maintaining Proper Working Conditions for SFP Ports
There are some best practices that need to be observed in order to prevent SFP ports from underperforming:
• In a dry, cool and well-ventilated area, store SFP modules.
• Do not expose SFP module to extreme temperature or humidity.
• Do not contact the optical parts of the SFP module.
• Over time dirt and dust will affect performance, so it is advisable to clean connectors on a regular basis.
• Use a connector cleaning kit to get rid of dirt, dust, and clean connectors.
• SFP modules’ status should be checked on a regular basis.
This way, you will ensure increased lifespan of your SFP ports as well as their effective operation.

A: On the other hand, SFP ports have a bigger range since they support various transceiver modules such as ethernet, Fibre channel and even SONET which means wider deployment options. This is unlike RJ45 connectors which are ethernet interface connectors.
A: Yes, in most cases, amperes are also equipped with SFP ports along with other gorges. These ports serve as supplementary ports connected to other switches and to devices that need fiber optics.
A: Depending on the switch model and brand, there may be different numbers of SFP ports on a gigabit switch. Some switches have at least one or two SFP ports, while others have numerous ports available for multiple switching configurations.
A: For a SFP port gigabit switch to work, the port allows for the attachment of different transceiver modules which would allow other forms of connectivity such as fiber optics which therefore enhances and broadens the range of the switching capabilities in the network configurations.
A: A gigabit switch can support both SFP and RJ45 ports at the same time. This gives a mix of fiber and ethernet connectivity which can change according to the network needs.
A: SFP ports are generally utilized in the connection of network elements that are used for long range or very fast networking. Most of the times they are used for uplinks between switches or for connecting other networking elements which use fiber optics.
A: A number of SFP ports for ethernet connections include single-mode, multimode fiber and copper ports. The type of SFP port that you will be using is governed by the need and the purpose of the network.
A: No, console ports are not SFP ports per se. A console port is a separate dedicated port found on a network device which is solely meant for initial configuration and diagnostic functions.
A: No, it cannot. For a valid link to be established, an SFP port must have a transceiver module inserted in it. The transceiver module connects the SFP port to the network cable and allows data transfer.