In addition to 10G network structured cabling solutions, which typically use SFP+ optical modules and fiber optic patch cords, 10G DAC high-speed cables and 10G AOC active optical cables are also a cost-effective alternative due to their high performance and low cost features. In this article, we will introduce 10G SFP+ DAC high-speed cable and 10G SFP+ AOC active optical cable in detail and compare them.
Introduction of 10G DAC/AOC Active Optical Cable
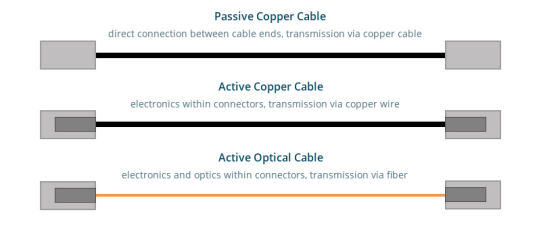
The 10G DAC high-speed cable consists of a dual-core copper cable with SFP+ connectors on both ends, which can be directly connected to active devices. Passive DAC and Active DAC Both can transmit electrical signals directly over the copper wire. The difference is that the former can be transmitted without signal modulation, while the latter has electronic components inside the optical transceiver to enhance the signal. Typically, 10G DAC high-speed cables are used to connect switches, servers, and storage devices between cabling racks.
10G AOC Active Optical Cable consists of multi-mode fiber optic patch cords and SFP+ connectors connected at both ends. It requires an external power to complete the conversion of optical/electrical signals, first from electrical to optical signals and then back to electrical signals. Similar to 10G DAC high-speed cables, 10G AOC active optical cables are mainly used for interconnecting storage devices, switches, and switches to servers between data center cabling racks.
What is the difference between 10G DAC high-speed cable and 10G AOC active optical cable?
By understanding the above, it is clear that 10G DAC high-speed cable is different from 10G AOC active optical cable in the following ways.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) refers to the interference generated by external power sources on the circuit. As mentioned earlier, 10G AOC active optical cables contain optical fiber, which is a dielectric material that does not conduct electricity. Therefore, AOC active fiber optic cables are not susceptible to EMI and can be used in most scenarios. However, 10G DAC high-speed cables contain copper, which is susceptible to electromagnetic interference due to its ability to transmit electrical signals. In order to avoid a series of problems such as system crashes and failures, it is important to consider the electromagnetic interference environment during use of these cables.
Typically, the power consumption of a 10G AOC active optical cable is 1-2W, which is higher than that of a DAC high-speed cable. The power consumption of a 10G active DAC high-speed cable is generally less than 1w, while a passive DAC high-speed cable can have a power consumption as low as 0.15w due to its special thermal design, which can be considered as almost zero power consumption. Therefore, using a DAC high-speed cable solution can help reduce operating costs generated by power consumption.
As mentioned above, the power consumption of a 10G DAC high speed cable is very low, and the passive DAC cables have almost zero power consumption and heat. Therefore, DAC high-speed cables are suitable for use in a wider range of ambient temperatures. In comparison, 10G AOC active optical cables have a limited operating temperature range, but due to the greater flexibility, they may help accelerate airflow cooling.
The 10G AOC active optical cable uses fiber optic technology, which has a maximum transmission distance of 100m, while the 10G DAC high-speed cable has a maximum transmission distance of 10m (passive DAC: 7m; active DAC: 10m). Note that the maximum distance for information transmission via DAC high-speed cable can vary with the data rate. When the rate increases, the transmission distance will be reduced, for example, 100G DAC high-speed cable can only transmit a maximum of 5 meters. The transmission distance limitation also reflects the common application of DAC high-speed cable: usually connecting devices located in the same rack, such as connecting a server to a TOR switch. In short, DAC high-speed cables are suitable for short-distance transmission, while AOC active optical cables are suitable for long-distance network connection.
Overall, 10G DAC high-speed cable is less expensive than 10G AOC active fiber optic cable because 10G DAC high-speed cable has fewer internal components, is relatively simple in construction, and is much cheaper to use copper than fiber. In other words, when deploying a network in a large data center, a large number of DAC high-speed cables will save more money than AOC active fiber optic cables. For short distance transmission, 10G DAC high-speed cable does provide a more cost-effective solution than AOC active optical cable, but for long distance transmission, it is necessary to compare the overall cost of the two solutions.
What are the application environments for 10G DAC high-speed cable and AOC active optical cable?
Due to the above factors, 10G DAC high-speed cables and 10G AOC active optical cables are usually used in different operating environments.
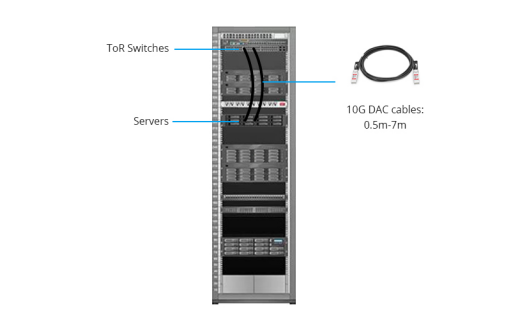
10G DAC High-Speed Cable The primary use is to connect a switch/server to a switch located in the same rack or an adjacent rack, for example, for 10GToR switch and server rack ToR switch interconnections or 10G switch stacking. Since the 10G SFP+ DAC high-speed cable typically supports 7m links while offering low power consumption, low latency, and low cost, this DAC high-speed cable solution is ideal for short-distance connections.
In addition, a 10G DAC high-speed cable solution can also be employed in high-density ToR scenarios where there are a large number of access layer devices. Such distributed access makes the connection look clear and straightforward, but also increases the difficulty of centralized maintenance and management of the switch.
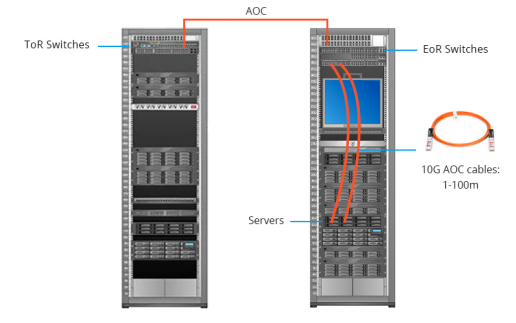
10G AOC active fiber optic cable is commonly used in data centers for ToR, EoR and MoR applications. Similar to DAC high-speed cables, the 10G AOC active optical cable can be used to connect ToR switches between network and server racks, as well as switches within racks, with the maximum distance of up to 100 meters.
For example, in EoR cabling, servers are connected to switches via 10G AOC active optical cables, which allows a large number of cable connections from multiple server cabinets to converge at the side network cabinets. This approach can make cable management more difficult, but it also simplifies centralized maintenance. The solution of using AOC active optical cables in MoR cabling is similar to the EoR solution while simplifying the connection and centralizing the management.
Conclusion
In summary, when selecting a 10G network deployment solution, it is important to consider various factors such as the application environment, cabling space, distance requirements, power consumption limitations, budget and other factors. When the transmission distance is within 7 meters, power consumption is limited and the cost requirement is high, it is suitable to choose 10G DAC high-speed cables. On the other hand, in data centers (within 30 meters) or environments with high electromagnetic interference, 10G AOC active optical cables are a more appropriate solution.