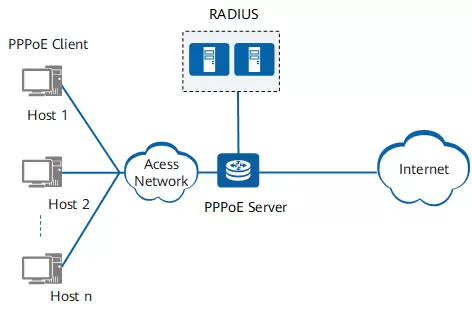
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a networking protocol that enables the formation and management of secure, point-to-point connections across Ethernet-based networks. This protocol is mainly used to provide secure and reliable internet access, particularly in areas where digital subscriber lines (DSL) or cable systems are the primary means of internet connectivity. PPPoE encapsulates Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) frames within Ethernet frames, which allows for the creation of logical network connections over physical connections.
PPPoE has several applications, including internet service providers (ISPs), remote access servers, and point-to-point connections between businesses or homes. The PPPoE protocol ensures the authentication of users before granting access to the internet by verifying user credentials such as login name and password.
One notable difference between PPPoE and other networking protocols is that it offers users flexible authentication options. Users can authenticate through a Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) session, Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS), or a local database such as Active Directory.
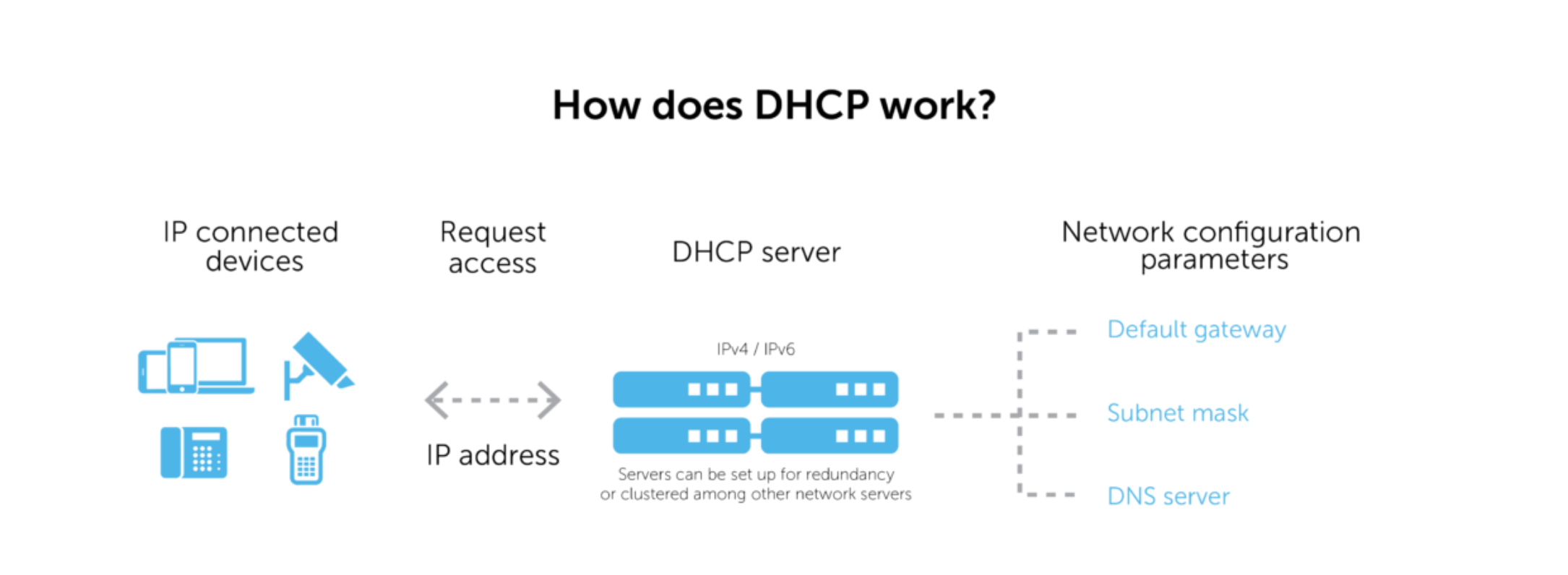
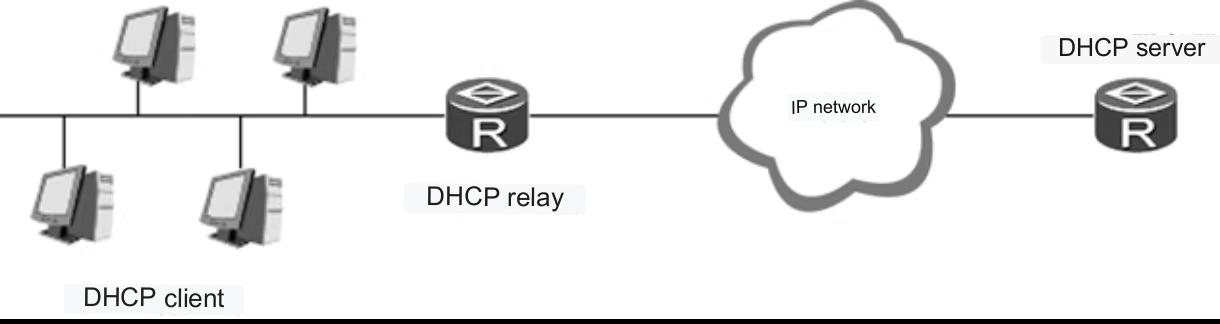
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a networking protocol that allows network administrators to automate the process of assigning IP addresses to devices connected to the network. DHCP is designed to reduce the administrative burden associated with manual IP address allocation in large networking environments. DHCP operates using a client-server architecture. A DHCP server is responsible for assigning IP addresses, while a DHCP client requests IP address assignments.
DHCP has two modes of operation: static and dynamic IP address assignment. In static IP address assignment mode, the network administrator manually assigns a predetermined IP address to a device. In dynamic assignment mode, the DHCP server automatically assigns an IP address to a device when the client requests for one.
DHCP is typically used in corporate environments, internet cafes, and other areas where there are a large number of devices connected to the network. DHCP simplifies network management by optimizing the use of IP addresses and eliminating the need for manual allocation.
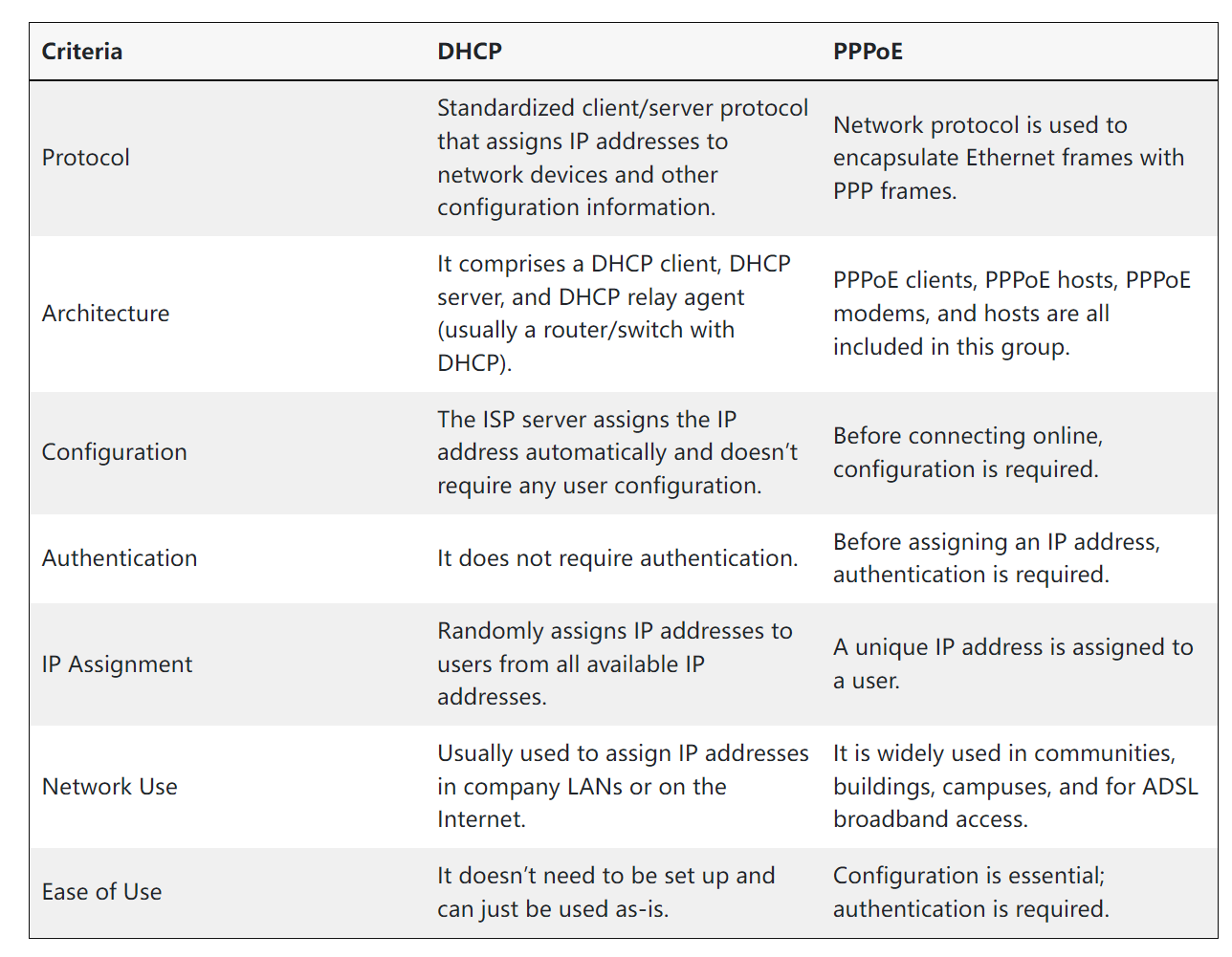
PPPoE and DHCP differ in how they assign IP addresses to devices on a network. PPPoE assigns IP addresses on a per-user basis, while DHCP assigns IP addresses on a per-device basis. PPPoE provides access authentication at the point of connection, making it more secure than DHCP. In contrast, DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network, which can be less secure.
IP addresses can be either static or dynamic. A static IP address is a fixed IP address assigned to a device that ensures it always has the same address. In contrast, a dynamic IP address is assigned to a device by the DHCP server, and the address changes each time the device renews its DHCP lease. PPPoE is used for assigning static IP addresses, which are required for some applications that require devices to have a specific address. Dynamic IP addresses are commonly used in home and office networks and are assigned by DHCP.
The configuration process for PPPoE and DHCP is different. PPPoE requires users to enter their username and password before they establish a connection, while DHCP does not have this requirement. DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network without any manual intervention. PPPoE, on the other hand, requires users to input their credentials during the setup process and then manually configure their device’s network settings to connect to the network.
PPPoE requires a username and password for authentication before an IP address is assigned to the device. This credential is unique for each user and must be entered each time that user connects to the network. The requirement for a username and password makes PPPoE more secure than DHCP. DHCP, on the other hand, does not require a username or password for devices to connect to the network. This makes it easier for unauthorized devices to access the network but can be more convenient for users.
PPPoE is typically used in internet service provider (ISP) environments where users have to connect via a modem. The username and password ensure that only registered users can access the ISP’s internet services. PPPoE is also commonly used in VPNs, which require static IP addresses to function properly.
DHCP is widely used in home and office networks for managing IP addresses. It dynamically assigns IP addresses to devices on the network, which eliminates the need for manual configuration. DHCP also simplifies network management by assigning IP addresses and network settings to devices automatically.
In conclusion, PPPoE and DHCP differ in how they assign IP addresses to devices on a network, the types of IP addresses, the configuration process, the requirements for username and password, and the common usage scenarios. While PPPoE is more secure, it requires manual configuration and a username and password for each user. DHCP is more convenient and makes network management easier but is less secure, as it does not require users to input credentials for access. Choosing between these protocols depends on specific network requirements, network size, and security needs.
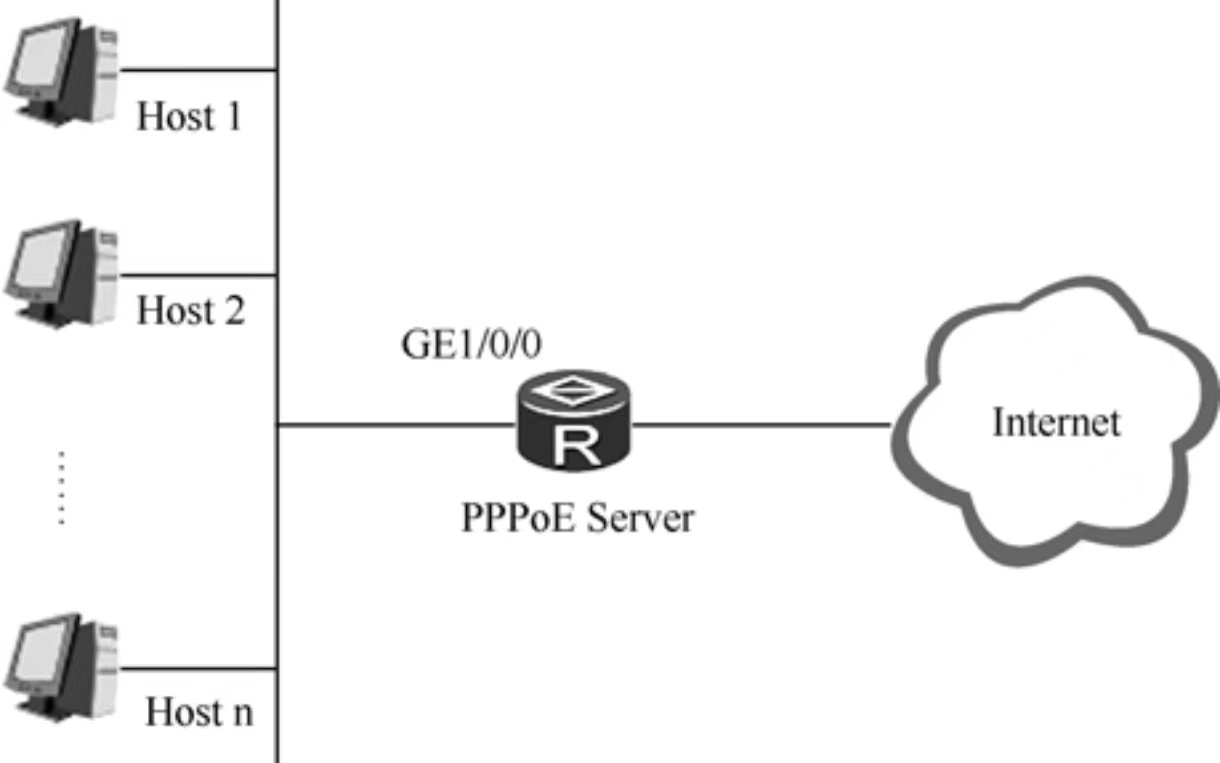
When it comes to connecting to the internet, both PPPoE and DHCP serve crucial roles. PPPoE establishes a secure connection between the devices and the internet service provider, ensuring encryption of data, authentication, and access control. As such, PPPoE is ideal for use in situations where security is a priority such as enterprises and remote work settings. Meanwhile, DHCP automates the process of obtaining an IP address, the network mask, and default gateway for a device, making it simpler to connect to the internet. DHCP is more suitable for small-size networks such as home networks or branch offices where security is not a significant concern.
The process of assigning IP addresses to devices can be daunting, especially in large networks. Here is where DHCP comes in handy. DHCP automates the assignment of IP addresses and ensures the devices have a correct and unique IP address, which is crucial for communication with other devices and accessing the internet. On the other hand, PPPoE does not assign IP addresses but instead allows an authenticated device to connect to the internet via its established connection.
Network configuration refers to the setup and management of network devices such as routers, switches, and servers. Both PPPoE and DHCP protocols play crucial roles in network configuration. In configurations where traffic needs to be segregated, PPPoE is an excellent choice since it allows for logical division through virtual circuits. In contrast, DHCP-enabled servers simplify network administration by automatically assigning unique IP addresses, which reduces the need for manual configuration and saves time.
ISPs typically prescribe the protocol they want their clients to use to connect to the internet. If the ISP recommends PPPoE, you must use the protocol to access their services. Conversely, DHCP is widely available and is used by most internet service providers to allocate IP addresses to devices.
Routing refers to how data packets travel between networks. In most cases, PPPoE is used when an internet service provider uses multiple IP addresses routed to different clients. In this case, a router can direct each number to a different destination. Conversely, DHCP is suitable for use in server setups where there is a need to manage IP addresses in a network.
1. Connect the router to the DSL modem via an Ethernet cable.
2. Access the router’s web interface and click on the WAN tab.
3. Choose PPPoE from the WAN Connection Type drop-down menu.
4. Enter your PPPoE username and password provided by your internet service provider (ISP).
5. Click Save Settings.
1. Connect your router to the modem via an Ethernet cable.
2. Access your router’s web interface and click on the DHCP Server option.
3. Make sure the DHCP server is enabled.
4. Set the starting IP address and ending IP address for the range of addresses to be assigned to devices.
5. Configure the subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers.
6. Click Save Settings.
One common issue with PPPoE is the need to enter the correct PPPoE username and password provided by your ISP. Failure to do so can result in a failed connection. In such cases, double-check the username and password entered, and ensure they are correct. Another issue is the presence of interference on the DSL line, which can result in disconnects or a slow connection. Troubleshooting this issue involves contacting your ISP to troubleshoot the line.
For DHCP, an issue that often crops up is IP address conflicts. This issue arises when two or more devices are assigned the same IP address. To resolve this issue, ensure that the device being assigned the IP address has a unique MAC address. Alternatively, you can configure your router to assign IP addresses based on the device’s MAC address.
To ensure optimal performance of both PPPoE and DHCP, it is essential to follow the following best practices.
1. Use a strong and unique password for PPPoE to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Regularly change the password for PPPoE.
3. Assign static IP addresses to critical devices to avoid IP address conflicts.
4. Enable DHCP reservation to assign a specific IP address to a specific device.
For more advanced configurations, you can customize your PPPoE and DHCP settings to suit your specific networking needs. For instance, you can configure DNS settings, enable MAC address filtering, and configure QoS settings to prioritize specific types of traffic over others.
Configuring PPPoE and DHCP may seem daunting at first, but with the right instructions and troubleshooting tips, the process becomes straightforward. Following the best practices outlined above will help you create a reliable and efficient network that meets your specific needs. By understanding and configuring these protocols correctly, you can enjoy fast and seamless internet connectivity for your organization or home.
A: PPPoE and DHCP are both protocols used to connect devices to the internet, however, they serve different purposes. PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) is commonly used for establishing a connection between a client device and an ISP server. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is used to dynamically assign IP addresses to devices on a network.
A: DHCP works by having a DHCP server on the network that holds a pool of available IP addresses. When a device connects to the network and requests an IP address, the DHCP server will assign an available address to that device for a specified lease period. This way, IP addresses are assigned dynamically rather than manually.
A: A static IP address is an IP address that is manually assigned to a device and does not change. Unlike dynamic IP addresses which are assigned by DHCP, a static IP address must be configured on the device itself or on the DHCP server to ensure that the device always uses the same IP address.
A: A DHCP server is a network server that is responsible for dynamically assigning IP addresses to devices on a network. It holds a pool of available IP addresses and leases them out to devices as they connect to the network.
A: PPPoE works by encapsulating PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) frames within Ethernet frames. This allows authentication and session management to take place between the client device and the ISP server, enabling the establishment of a connection.
A: Yes, DHCP is a protocol – it stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It is used to dynamically assign IP addresses, along with other configuration information, to devices on a network.
A: The purpose of PPPoE and DHCP is to facilitate the connection of devices to the internet. PPPoE is commonly used in DSL connections, while DHCP is used in various network setups to assign IP addresses automatically.
A: A DHCP client uses the DHCP protocol to send a request to the DHCP server on the network. The client requests an IP address and other configuration information, and the DHCP server responds with the assigned IP address and lease duration.
A: PPPoE stands for Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet. It is a protocol used to establish a connection between a client device and an ISP server in order to access the internet.
A: PPPoE servers handle the authentication and session management for PPPoE connections. They verify the credentials of the client device, establish a session, and manage the data transmission between the client and the server.
Understanding the Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6