Fiber to the Room (FTTR) is an advanced communication technology that delivers high-speed internet and data services to multiple endpoints within a building. This technology is designed to meet the growing demand for faster and more reliable internet connectivity in densely populated areas such as office buildings, hotels, and apartments.
Unlike traditional copper-based communication networks, FTTR uses fiber-optic cables to transmit data signals from a central location to various endpoints within a building. The fiber-optic cables can deliver much higher speeds and bandwidth than copper cables and are less susceptible to interference and signal degradation.
In FTTR, a central point of control known as the distribution point is established within a building. This point is the central hub where all fiber-optic cables converge, and the signals are transmitted to different endpoints within the building. Each endpoint, known as a room unit, is connected to the distribution point through fiber-optic cables, allowing for high-speed data transmission.
To ensure that different endpoints can be identified and their signals transmitted without a mix-up, FTTR employs a technology called wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). This technology enables signals to be sent over different wavelengths or colors of light, allowing for multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously over a single fiber-optic cable.
Overall, FTTR provides a dedicated fiber-optic cable connection from the distribution point to each room unit, thus enabling high-speed and reliable connectivity to multiple endpoints within a building.
Fiber to the Room (FTTR) has several benefits that make it a superior technology for delivering high-speed internet connectivity and data services within buildings. These benefits include:
High-speed connectivity: FTTR provides high-speed internet with speeds of up to 1 Gbps, making it ideal for applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and video conferencing.
Greater bandwidth: FTTR has a larger bandwidth capacity compared to traditional copper-based communication networks, allowing for more data to be transmitted at once and enabling faster downloads and uploads.
Improved reliability: Fiber-optic cables are less susceptible to signal interference and degradation, resulting in more excellent reliability and reduced downtime than copper cables.
Enhanced security: FTTR is a secure system less prone to hacking and cyber-attacks, making it a better choice for organizations that handle sensitive data.
Fiber to the Home (FTTH) and Fiber to the Room (FTTR) are similar but distinct technologies that deliver fiber-optic connectivity to different endpoints. FTTH is designed to provide fiber-optic connectivity directly to homes, while FTTR focuses on providing high-speed and reliable connectivity to multiple endpoints within a building.
One of the main differences between FTTH and FTTR is the number of endpoints they can serve. FTTH is designed to help a single endpoint, while FTTR can serve multiple endpoints, making it ideal for densely populated areas such as office buildings and hotels.
Additionally, FTTH requires the installation of fiber-optic cables from a community’s central location to individual homes. In contrast, FTTR only involves the installation of lines within a building, minimizing costs and installation time.
Recommended Reading: Traditional Data Center Network Architecture
Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology allows multiple signals to be transmitted over a single fiber-optic cable.
Dedicated fiber-optic cables from the distribution point to each room unit ensure high-speed and reliable connectivity.
FTTR can serve multiple endpoints within a building, making it ideal for densely populated areas.
Fiber-optic cables are less susceptible to interference and signal degradation, resulting in improved reliability and reduced downtime.
Enhanced security makes FTTR a better choice for organizations that handle sensitive data.
Fiber To The Room (FTTR) technology can benefit several industries and organizations. These include:
Hotels: FTTR can provide high-speed internet connectivity to hotel guests, enabling them to stream movies and videos and stay connected while traveling.
Conference Centers: FTTR can provide reliable and high-speed internet connectivity during conferences, seminars, and meetings, enabling attendees to access online resources and participate in virtual discussions.
Apartments: FTTR can provide high-speed internet connectivity to apartment residents, enabling them to access online resources and stay connected with family and friends.
Office Buildings: FTTR can provide high-speed internet connectivity to businesses within an office building, enabling them to access online resources and collaborate with colleagues remotely.
In today’s internet-connected world, Fiber To The Room (FTTR) has emerged as a preferred option to provide high-speed internet to residential and commercial spaces. With the increasing demand for faster internet and full coverage in every room, FTTR is critical to improving network status and bandwidth.
Recommended Reading: SFP+ Module: Everything You Need to Know
Compared to other popular alternatives, such as Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) or cable connections, FTTR offers several benefits. The most significant advantage is its ability to deliver faster internet speeds and greater bandwidth. This is possible as FTTR uses fiber-optic cables that transmit data faster than traditional copper wires.
Another critical advantage of FTTR is its ability to provide full coverage in every room. Traditional internet connections often suffer from signal loss when the distance from the source increases. However, with FTTR, data travels through fiber-optic cables that can cover long distances without signal loss. This means that every room in a house or office can access high-speed internet without compromising speed or connectivity.
Improved network status is another advantage of FTTR. Unlike traditional internet infrastructures that use copper or coaxial cables, fiber-optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference. FTTR is less prone to network interruptions and downtime caused by external factors such as weather or electromagnetic interference.
In addition to these benefits, FTTR has gained popularity due to its ability to support online education and remote work. Recently, there has been an upsurge in online learners and remote workers. With FTTR, learners and workers can access high-speed internet and complete tasks without delay or interruption.
Fiber-optics technology enhances the performance of several applications and services, such as online gaming and virtual reality. These applications require high-speed internet and greater bandwidth to provide a seamless experience. In online gaming, fiber-optic internet delivers the lowest latency possible, making games run smoother and faster. Virtual reality also benefits from fiber-optic internet, providing high-quality, immersive experiences with little to no lag.
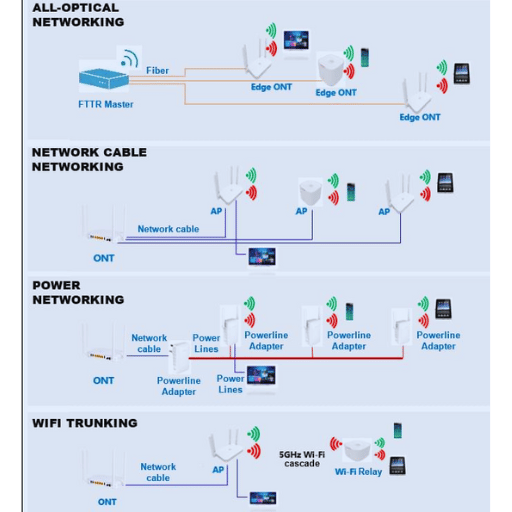
Fiber to the room (FTTR) is a cutting-edge technology that offers high-speed broadband connectivity to individual rooms within a building. With its all-optical networking mode, FTTR provides a faster and more reliable connection, making it an ideal solution for hotels, student accommodations, and other multi-dwelling units.
The FTTR network solution differs from other broadband options, such as Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) and Cable Internet, in that it offers a dedicated fiber optic connection to each room. This allows for higher bandwidth capacity, superior data transmission quality, and negligible signal degradation. It also eliminates the need for shared infrastructure, making it a more secure and efficient solution.
Deploying an FTTR network requires a series of crucial steps and considerations to ensure a seamless installation process. One of the first steps in the installation process is extending Fiber with fiber optic cables to each room. This involves laying the necessary fiber optic cables and connecting them to optical network units (ONUs) in each room.
The ONUs are responsible for converting the optical signal into an electrical signal that the user’s device can recognize. During installation, technicians must verife that each ONU is set up correctly and connected to the fiber optic network.
The final step in FTTR deployment is the operation and maintenance of the network. This includes regularly monitoring network performance, troubleshooting issues, and upgrading the system when necessary. To ensure successful operation and maintenance of the web, it is essential to follow best practices and consider potential challenges that may arise.
Deploying an FTTR network solution requires careful consideration and expert planning. By following best practices and considering various challenges that may arise, the installation of ONUs, deployment of all-optical networking mode, configuring enslaver and enslaved person FTTR units, and operation/maintenance of the FTTR network can be achieved efficiently, helping to ensure speedy deployment and a successful project outcome.
While traditional networking setups have served us well, Fiber to the Room (FTTR) technology promises to advance our network connectivity.
The first advantage of FTTR technology is its high-speed and low-latency network. FTTR technology utilizes fiber optic cables, which enable data to travel at lightning speeds compared to traditional copper cables. In addition, the low latency of FTTR technology provides a near-instant connection to the internet without buffering or delays, making it perfect for streaming or gaming.
FTTR technology offers full coverage and high bandwidth capabilities, making it highly advantageous over traditional networking solutions. With FTTR technology, users can enjoy seamless connectivity in every home or office room. Moreover, FTTR technology provides sufficient bandwidth to accommodate numerous devices and heavy internet usage without compromising speed or connectivity.
Another benefit of FTTR technology is the availability of gigabit Wi-Fi coverage in every room. This ensures maximum connectivity and speed for each device connected to the network, enabling users to enjoy faster downloads, higher-quality video conferencing, and lag-free gaming experiences. Additionally, with FTTR technology, users can expect wall-to-wall Wi-Fi coverage without any dead zones, enhancing the quality and reliability of the network.
FTTR technology provides a stable and reliable network connection, making it ideal for residential and commercial spaces. Being built on fiber optics, FTTR technology offers unparalleled stability and consistently high performance, ensuring no lag or downtime during usage. This stability and reliability make FTTR technology an excellent choice for those who require uninterrupted network connectivity.
Finally, FTTR technology supports gigabit Ethernet and Wi-Fi 6, making it a future-proof technology. As technology evolves, FTTR technology ensures that your network can handle the latest advancements while maintaining maximum speed and connectivity. You can rest assured that your network is ready for the future.

Fiber to the Room (FTTR) deployment is a technology that involves laying fiber optic cables directly to individual rooms or homes. This technology offers a range of benefits, including faster speeds, greater bandwidth, and more reliable connectivity. However, achieving a successful FTTR deployment requires considering various challenges and considerations.
One significant challenge when deploying FTTR is the cost of laying fiber optic cables. Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optic cables require specialized equipment and expertise, which can significantly increase costs. Moreover, FTTR typically requires laying fiber optic cables from the service provider to each room, which can also add to the overall deployment costs.
Another significant consideration is integrating FTTR with existing network cables and Wi-Fi networks. This can be a complex process, particularly when upgrading from older technologies. FTTR typically requires replacing existing copper cables with fiber optic cables, which can be challenging in buildings with limited space or complex wiring systems. Moreover, integrating new fiber optic networks with existing Wi-Fi infrastructure also requires careful planning and implementation.
Another challenge to consider is ensuring compatibility with different terminal devices. FTTR technology requires using compatible modems and routers to connect to the fiber optic cables. However, not all terminal devices are compatible with FTTR, which can be particularly problematic in older buildings with outdated wiring systems. Therefore, it is essential to consider the compatibility of different terminal devices when deploying FTTR.
Selecting the right router and Optical Line Terminal (OLT) is also crucial when deploying FTTR. The OLT connects to the service provider’s network and converts optical signals to electrical signals for distribution to individual rooms. Different routers offer varying speeds, bandwidths, and other features that can impact the overall performance of the FTTR network. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the specific needs of the deployment when selecting routers and OLT devices.
Recommended Reading: 10G DAC High Speed Cable VS 10G AOC Active Optical Cable: Who is better?
Finally, ensuring all-optical connectivity and minimizing latency is critical to the successful deployment of FTTR. FTTR networks offer faster speeds and more reliable connectivity than traditional copper networks. However, latency can still be an issue. Moreover, ensuring all-optical connectivity requires careful planning and testing to ensure all fiber optic cables connect correctly.

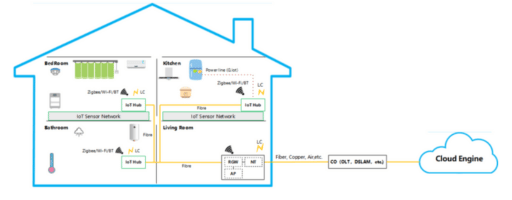
A: Fiber to the room (FTTR) is a new coverage solution that provides high-speed gigabit optical network access to every room in a building. It uses optical fiber cables to deliver high-quality network services directly to the room.
A: FTTR uses optical fiber cables to establish a direct connection between the central optical modem and each room in a building. This allows each room to have dedicated gigabit optical network access, achieving full coverage and high-speed internet connectivity.
A: FTTR provides numerous benefits, including:
A: GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) is a technology used in FTTR solutions to deliver high-speed optical network access. It allows the sharing of fiber infrastructure among multiple users, providing efficient and cost-effective network solutions.
A: FTTR improves network coverage by extending the optical fiber network directly to each room in a building. This eliminates traditional network cables and ensures every room can reach high-quality network services.
A: FTTR (Fiber to the Room) and FTTP (Fiber to the Premises) are optical fiber network solutio thatey differ in coverage. FTTR focuses on providing gigabit optical network access to individual rooms in a building, while FTTP aims to deliver the same access to the entire premises.
A: A fiber patch in FTTR refers to the optical fiber cable that connects the central optical modem or network switch to the optical network terminal in each room. It serves as the physical medium for transmitting high-speed optical signals.
A: Yes, FTTR can be used for home networks. It provides gigabit optical network access to every room in a house, ensuring that all devices and appliances can connect to a high-quality and high-speed network.
A: The advantage of FTTR over traditional network cables is the use of optical Fiber, which allows for much higher speeds and greater bandwidth. FTTR eliminates network congestion and ensures a high-quality, high-speed network connection throughout the building.
A: Yes, FTTR is suitable for online offices and businesses. It provides a reliable and high-quality network infrastructure supporting various online activities, such as video conferencing, data transfer, and cloud computing.