An aggregation switch consolidates data traffic from multiple network access switches into a single high-bandwidth link directed toward a core network or data center. The primary function of an aggregation switch is to aggregate and forward data from multiple network devices, such as access switches, wireless access points, servers, and storage devices, to higher-level switches or routers.
Aggregation switches are typically deployed in enterprise networks, central network connectivity, and data transfer points. They are designed to handle large volumes of network traffic and provide high-speed, reliable connectivity between the various network segments.

An aggregation switch operates at Layer 2 or Layer 3 of the OSI model, depending on the configuration and topology of the network. The controller uses protocols, such as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) or Static Link Aggregation, to combine physical links into a single logical link. This increases bandwidth and redundancy, as data can be transmitted over multiple paths simultaneously.
The aggregation switch also uses the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent network loops and ensure that data is transmitted only through the most efficient path. Additionally, the button supports VLAN tagging, which enables traffic isolation into separate broadcast domains, improving security and network performance.
Recommended Reading: TD-SCDMA optical transmission network network construction idea discussion
Link aggregation, or port trunking, involves combining multiple physical network links into a single logical link. This technique increases bandwidth, improves network redundancy, and provides failover capabilities. Aggregation switches handle link aggregation by using LACP or Static Link Aggregation protocols.
LACP is a dynamic protocol that automatically discovering and configures aggregated links between switches. It monitors the state of each physical connection and reconfigures them as necessary to maintain consistent bandwidth and uptime.
Static Link Aggregation, conversely, is a manual configuration combining multiple physical links into a single logical connection. This mode does not dynamically adjust the link configuration, but it provides a more straightforward setup and is suitable for networks with fixed topology.
Aggregation switches provide several benefits to Layer 2 networks, including:
Increased bandwidth: Aggregation switches consolidate traffic from multiple devices into a single high-bandwidth link, improving network performance and reducing packet loss.
Improved redundancy: Aggregated links offer redundancy, enabling data to be transmitted even if one or more physical connections fail. This reduces network downtime and improves overall network reliability.
Simplified network management: Aggregation switches provide a centralized point for network connectivity, making it easier to manage and troubleshoot network issues.
Aggregation switches are the logical choice for a core switch in enterprise networks. They provide high-speed connectivity between access switches, servers, and other network devices. The aggregation switch can handle large traffic volumes without impacting network performance, ensuring the network runs smoothly. It also provides advanced features such as VLAN tagging and link aggregation, which enable network administrators to manage traffic flows and increase network performance.
The Unifi Aggregation Switch is a high-performance aggregation switch designed for enterprise networks. It offers several advantages and features, including:
High-speed connectivity: The Unifi Aggregation Switch provides 10G and 40G connectivity, enabling high-speed data transfer between network devices.
Advanced management features: The switch offers advanced management features, such as VLAN tagging, Storm Control, and Quality of Service (QoS), which enable IT admins to manage traffic flows and prioritize mission-critical applications.
Redundancy and failover: The Unifi Aggregation Switch supports LACP and Static Link Aggregation, which provides network redundancy and failover capabilities.
Simplified management: The Unifi Controller software can manage the switch, which offers a single-pane-of-glass management interface that simplifies network management and monitoring.
Scalability: The Unifi Aggregation Switch can be easily expanded to meet the needs of growing networks by adding additional switches and physical links.
Aggregation switches are essential for enterprise networks, providing high-speed connectivity between multiple switches and devices. They collect data traffic from various access switches and forward it to the appropriate destination. However, selecting the right aggregation switch can be challenging. We have outlined several factors to help you choose the best solution for your enterprise network.
Recommended Reading: Everything You Need to Know about SFP Ports
Compatibility: One critical factor to consider when selecting an aggregation switch is compatibility with the existing network infrastructure. Ensure the controller is compatible with the access switches, networking protocols, and network management systems.
Port Density: Aggregation switches should have adequate port density to accommodate high-traffic volumes from different access switches.
Bandwidth: The switch’s maximum throughput and bandwidth are another crucial factor. It should be capable of handling the network traffic without causing a bottleneck.
Scalability: The aggregation switch should be scalable, allowing you to add new controls and devices without affecting the network’s performance.
Manageability: Choose a switch that can be easily managed through a graphical user interface (GUI) or command-line interface (CLI).
Consider the number of users and the volume of data traffic that will pass through the switch.
Choose a switch that supports various networking protocols, including VLAN, QoS, and OSPF.
Consider the physical size of the switch, rack space, and power consumption.
Invest in switches that have redundancy features to ensure high availability.
Understanding the Importance of Network Security Policies for Aggregation Switches:
Network security policies are crucial for aggregation switches as they help to safeguard the network against unauthorized access and cyber-attacks. Access control lists (ACLs), port security, and Virtual Private Networks (VPN) are some security measures that should be implemented. Unauthorized access to an aggregation switch could result in a security breach, leading to data loss or system downtime.
Scalability and high bandwidth are critical considerations when selecting an aggregation switch. Scalability ensures the button can grow with the network and accommodate new devices. High bandwidth ensures that the controller can handle the increasing data traffic volume without causing network speed degradation. When controls experience high traffic volumes, packets can be lost, causing dropped connections and network slowdowns.
Cisco provides enterprise-level aggregation switch solutions that are reliable, scalable, and secure. The Cisco Nexus series, such as the Nexus 9000 and 7000, are potent switches that offer high-performance and low-latency connectivity for enterprise data centers. They are designed for aggregation, core, edge deployments, and support protocols like Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and FCoE. The Cisco Nexus switches also have various security features, such as ACLs, Cisco TrustSec, and SNMPv3.
In conclusion, selecting the right aggregation switch is critical to your enterprise network’s performance, scalability, and security. Consider compatibility, port density, bandwidth, scalability, and manageability when choosing. Invest in switches that have redundancy features to ensure high availability. Ensuring your network is secure through security policies is as important as selecting the right button. Choose a button-scalable switch with high-bandwidth capabilities to accommodate the growing volume of data traffic. For superior performance, reliability, and security, consider Cisco’s enterprise-level aggregation switch solutions, such as the Nexus 9000 and 7000.
Recommended Reading: Data Center Network Architecture
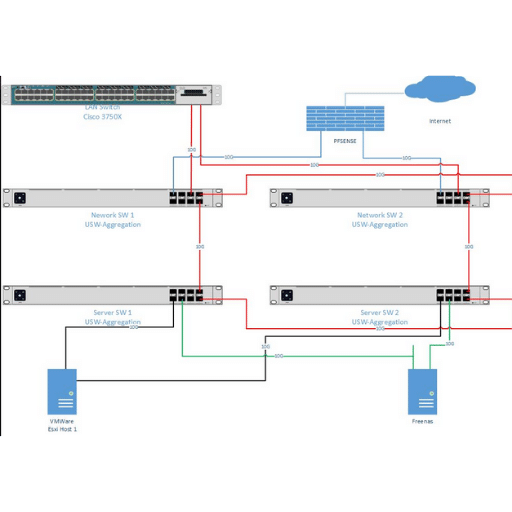
Link aggregation is grouping multiple network interfaces to increase bandwidth and provide redundancy. LACP, also known as IEEE 802.3ad, is a protocol used to automate the process of link aggregation configuration between switches. Here are the steps to set up LACP on an aggregation switch:
Log into the control using the console or web interface.
Navigate to the network interfaces configuration page.
Select the interfaces you want to aggregate.
Configure the LACP mode to active or passive.
Set the LACP timeout according to your needs.
Save the configuration and apply it to the switch.
Virtual LANs (VLANs) segment the network into smaller groups for better traffic management and security. You can use VLANs to segregate different types of traffic, such as voice, video, and data. Here are the steps to configure VLANs on an aggregation switch:
Log into the control using the console or web interface.
Navigate to the VLAN configuration page.
Create your VLANs and assign each interface to a corresponding VLAN.
Set VLAN tagging on interfaces that will carry VLAN traffic.
Configure VLAN trunking between switches.
Save the configuration and apply it to the controller.
Quality of Service (QoS) is a way to manage and prioritize network traffic based on application type, user group, or traffic throughput. QoS helps ensure that critical traffic, such as VoIP or video, receives higher priority than less important traffic, such as web browsing. Here are the steps to optimize QoS settings on an aggregation switch:
Log into the control using the console or web interface.
Navigate to the QoS configuration page.
Create QoS policies based on application type, user group, or traffic throughput.
Assign priority levels to each approach.
Set bandwidth limits for each procedure.
Save the configuration and apply it to the switch.
An uplink is a connection from a switch to another device, such as a router or controller. Uplinks can be configured automatically or manually, depending on the network topology and requirements. Here are the steps to configure an uplink on an aggregation switch:
Log into the control using the console or web interface.
Navigate to the interface configuration page.
Select the interface you want to use as an uplink.
Configure the interface as either a trunk or access port.
Set the speed and duplex settings for the interface.
Save the configuration and apply it to the switch.
An aggregation switch with 10 Gigabit Ethernet and SFP ports provides several benefits, such as faster data transfer, flexibility, and scalability. Here are some key advantages of using 10 Gigabit Ethernet and SFP ports on an aggregation switch:
Faster data transfer – 10 Gigabit Ethernet provides up to 10 times more immediate than Gigabit Ethernet, which is crucial for applications with high bandwidth requirements, such as video streaming or data center storage.
Flexibility – 10 Gigabit Ethernet and SFP ports allow for more flexible network topologies, as they support longer distances and various media types, including copper and fiber optic cables.
Scalability – 10 Gigabit Ethernet enables seamless network expansion and growth as the need for more bandwidth arises without compromising network performance.
An aggregation switch is a crucial element of modern enterprise networks. Its primary function is aggregating and combining traffic from multiple access switches, making network management more accessible and efficient. Without an aggregation switch, managing and directing network traffic from the access layer would be challenging, leading to congestion, slow network speeds, and potential downtime.

An aggregation switch enhances network performance in the access layer by reducing the number of direct connections between access switches and network servers. With an aggregation switch, traffic from multiple access switches is combined and streamlined, leading to better network performance and reduced downtime. Additionally, an aggregation switch can help load balancing so traffic is evenly distributed across the network, maximizing bandwidth usage and ensuring all devices receive high-speed and reliable connectivity.
An aggregation switch is different from a core switch. While both switches direct traffic on a network, a core switch handles traffic between other subnetworks and ensures bandwidth availability. In contrast, an aggregation switch is responsible for combining and streamlining traffic from multiple access switches. An aggregation switch is typically between the access and core switches, making it essential for efficient network management.
Data flow from the access switch to the aggregation switch follows a specific path. The access switch collects data from network devices such as computers, printers, and servers and sends it to the aggregation switch for further processing. Once received, the aggregation switch aggregates the data and streamlines it for efficient transmission to the core switch, where it is then sent to its final destination. This flow ensures efficient network performance and reduces the likelihood of network congestion or downtime.
Aggregation switches play a critical role in redundancy and failover scenarios. An aggregation switch with redundant components can maintain network functionality and ensure minimum downtime in a network failure. Additionally, an aggregation switch can help balance traffic loads across multiple links, ensuring that if one link fails, traffic is automatically redirected to another link. This functionality ensures network uptime and prevents costly downtime.
When selecting an aggregation switch, it’s essential to consider the network’s forwarding rate and bandwidth requirements. The forwarding rate refers to the speed at which the controller can process data and direct it to its destination. In contrast, bandwidth refers to the total capacity the controller can handle. As businesses grow and require more data-intensive solutions, selecting an aggregation switch with a high forwarding rate and sufficient bandwidth to drive that growth is essential.
Aggregation switches play a crucial role in connecting multiple buttons at the core level of a computer network. These switches act as a central hub, allowing numerous devices to communicate with each other across the web. They are designed to facilitate network traffic by creating a single aggregation point for all connected devices. The market is currently saturated with numerous aggregation switch models from different manufacturers.
Ubiquiti is a well-known name in the network device industry, and their Unifi aggregation switch solutions are no different. Their aggregation switches are a set of managed, high-bandwidth switches that specialize in optimizing data transfer speeds and reducing network congestion.
Ubiquiti’s Unifi aggregation switch solutions are designed to provide centralized management and configuration options for the entire network. Their switches offer scalability to accommodate growth in the network while ensuring seamless connectivity across all devices. Additionally, they support high bandwidth connectivity, enabling uninterrupted data transfer and reliable network performance.
Cisco is another big player in the network device industry, and its range of aggregation switches is also noteworthy. Cisco’s aggregation switches come in a wide range of sizes and configurations, making them suitable for networks of all sizes and complexities.
Cisco’s aggregation switches have advanced features, including extensive security protocols, multicast and Quality of Service (QoS) optimizations, and an intuitive user interface. Additionally, their switches provide granular control over the network, allowing administrators to manage the network traffic efficiently.
Other notable manufacturers in the aggregation switch market include Juniper Networks, Arista Networks, and HPE. Juniper Networks, for example, offers a range of highly scalable switches, ideal for large enterprise networks. Arista Networks specializes in low-latency switches that come in various configurations for different types of networks. HPE provides highly modular aggregation switches designed to address complex network requirements effectively.
Managed layer 2 switches bring several benefits to aggregation networks. They offer efficient traffic management functionalities, including packet filtering, Quality of Service (QoS), and VLAN support. Additionally, they allow for granular control over the network, allowing network administrators to optimize traffic flow and manage network security protocols effectively.
Scalable and high-bandwidth aggregation switches provide high-speed connectivity and seamless performance even under heavy network loads. The controls are designed to accommodate increasing traffic volumes and adaptability should the network grow. They offer efficient traffic aggregation, enabling multiple devices to send and receive data without network slowdowns. With these switches, businesses can expect optimal network performance, fast data transfers, and trouble-free connectivity, even under heavy network loads.
Recommended Reading: What is a Data Center Network? How to manage a data center network

A: An aggregation switch, also known as a network switch, is a device that combines multiple network connections into a single, high-bandwidth connection.
A: The primary purpose of an aggregation switch is to connect multiple access switches to a core layer switch, allowing for efficient data flow and network management.
A: Ubiquiti UniFi is a brand of networking equipment, including aggregation switches, that offers high-performance and easy-to-manage solutions for home and business networks.
A: The aggregation layer is a network layer with multiple access switches connected to a core layer switch.
A: An access switch is a network switch that connects end devices, such as computers or IP phones, to the rest of the network.
A: Layer 3 refers to the network layer in the OSI model, which is responsible for routing and forwarding data packets between different networks.
A: A switch port is a physical connector on a network switch that allows devices to connect to the network.
A: QoS, or Quality of Service, is a set of techniques to prioritize certain types of network traffic to ensure better performance for applications such as voice or video streaming.
A: An uplink is a network switch or router connection that connects to a higher-level device, such as a core layer switch or ISP.
A: 10GbE, or 10 Gigabit Ethernet, is a high-speed Ethernet standard that provides 10 gigabits per second data transfer.