The 200G QSFP56 transceiver is a hot-pluggable optical module that supports data transmission at up to 200 Gbps. It is designed as a small form-factor pluggable (SFP) interface for high-speed networking applications like data centers, enterprise networks, cloud computing, and telecommunications networks. The QSFP56 transceiver is compatible with various fiber types, including single-mode and multimode fibers.
The 200G QSFP56 transceiver offers several benefits for modern networking equipment. It provides high-speed data transmission with low power consumption, which makes it an efficient solution for data centers and enterprise networks. The QSFP56 transceiver also supports modulation techniques, such as PAM4 and NRZ, to improve signal integrity and reduce noise. Additionally, the QSFP56 transceiver allows easy upgrades and replacements without interrupting the network operation.
Related product:200G QSFP56 for sale
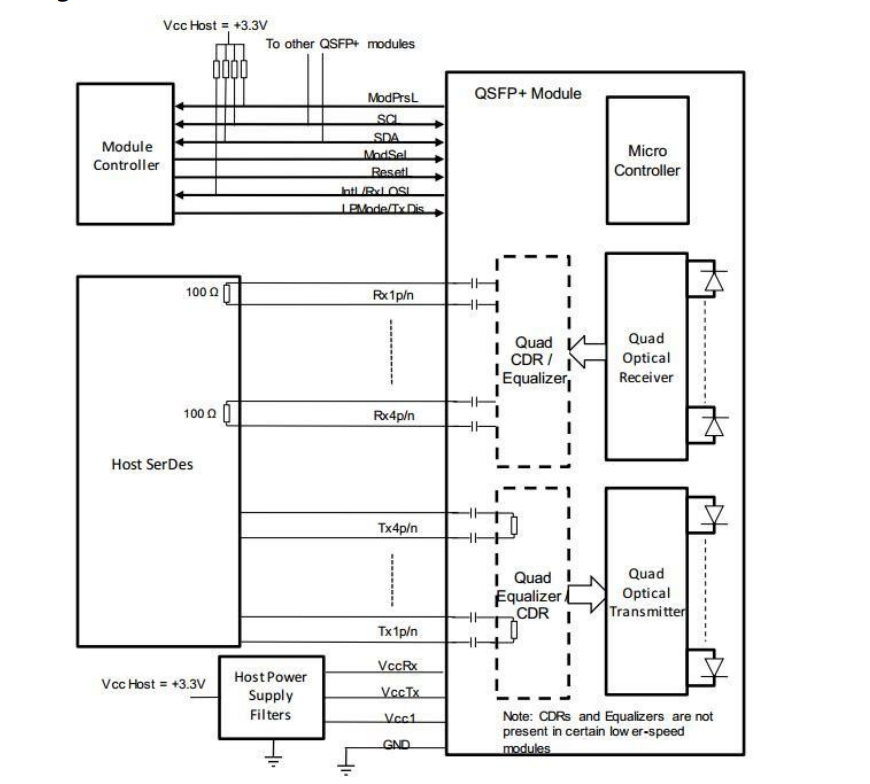
The QSFP56 transceiver uses a combination of optical and electrical interfaces to transmit and receive data signals. On the visual side, the transceiver converts electrical signals into optical signals using a laser or LED light source and a modulator. The optical signals are then transmitted through a fiber optic cable to the receiving end, where they are converted back into electrical signals. On the electrical side, the QSFP56 transceiver uses a high-speed electrical interface to send and receive calls from the host equipment.
The QSFP56 transceiver uses a Multimode Fiber (MMF) or Single-Mode Fiber (SMF) optical interface to transmit and receive data signals. The MMF interface supports up to 70m of transmission distance, while the SMF interface supports up to 10km. The optical interface also supports various wavelengths and channels to handle different types of data traffic, such as Ethernet, InfiniBand, and Fibre Channel.
The QSFP56 transceiver uses a high-speed electrical interface to connect to the host equipment, such as a switch or a router. The electrical interface supports up to four data transmission lanes, and each route can operate at a speed of up to 50Gbps. Therefore, the QSFP56 transceiver can support data transmission at up to 200Gbps. The electrical interface also complies with various industry standards, such as the IEEE 802.3bs and InfiniBand EDR.
The QSFP56 transceiver supports various modulation techniques to improve signal integrity and reduce noise. The most commonly used modulation techniques include Pulse Amplitude Modulation-4 (PAM4) and Non-Return-to-Zero (NRZ). PAM4 is a four-level signaling scheme that doubles the data rate while reducing the signal-to-noise ratio. NRZ is a two-level signaling scheme that preserves the data rate but is more susceptible to signal degradation and noise. Therefore, the choice of modulation technique depends on the specific application requirements.
200G QSFP56 product portfolio includes SR4 and FR4. Here is a detailed comparative analysis of the 200G QSFP56 SR4 and 200G QSFP56 FR4 optical modules, covering key technical parameters such as transmission distance, modulation format, application scenarios, and fiber types.
200G QSFP56 SR4:
“SR” stands for Short Reach, supporting 200Gbps transmission over multimode fiber (MMF). It uses 4 parallel channels, each at 50Gbps with PAM4 modulation.

200G QSFP56 FR4:
“FR” stands for 200GBASE-FR4 (Forward Reach), supporting up to 2 km over single-mode fiber (SMF). It uses 4 CWDM lanes, each running at 50Gbps PAM4.

| Feature | 200G QSFP56 SR4 | 200G QSFP56 FR4 |
|---|---|---|
| Form Factor | QSFP56 | QSFP56 |
| Line Rate | 200Gbps (4 × 50Gbps PAM4) | 200Gbps (4 × 50Gbps PAM4) |
| Modulation | PAM4 | PAM4 |
| Fiber Type | MMF | Single-Mode Fiber (SMF) |
| Optical Connector | MPO-12 | Duplex LC |
| Max Transmission | Up to 100m (OM4) / 150m (OM5) | Up to 2km (SMF) |
| Typical Use Case | Rack-to-rack, intra-data center connections | Inter-rack/core switch or inter-DC links |
| Power Consumption | ~3.5W–4W | ~4W–5W |
200G QSFP56 SR4 is ideal for short-reach, high-speed connections within data centers, including links between Top-of-Rack (ToR) switches and servers, as well as high-bandwidth interconnects in GPU or AI clusters.
200G QSFP56 FR4 is suitable for medium-distance data center interconnects of up to 2 kilometers. It is ideal for spine-leaf architectures, core network aggregation, and high-performance routing over single-mode fiber (SMF) with simplified duplex cabling.
Use 200G QSFP56 SR4 when your deployment is confined to short distances within the same room or rack, and cost and density are key concerns.
Use 200G QSFP56 FR4 when you need longer reach (up to 2 km) and want to save on cabling complexity using duplex single-mode fiber.
This transceiver module is designed to operate at a data rate of 200Gbps and is compatible with various network devices.
The 200G QSFP56 transceiver is compatible with many devices, such as Ethernet switches, routers, servers, and storage devices. The form factors of these devices vary, but the transceiver module can seamlessly connect with them using a compatible connector. For instance, the QSFP56 transceiver can link with Ethernet switches featuring QSFP56 ports.
The 200G QSFP56 transceiver can be connected to other devices using different interconnection options such as direct attach copper, active optical cables, and fiber optic cabling. Direct attach copper (DAC) is a cost-effective solution that transmits data over copper wires, while active optical cables (AOC) consist of fiber optics and offers better heat dissipation. Fiber optic cabling utilizes glass or plastic fibers to transmit data longer distances. One of these interconnection options may be more suitable depending on the network application.
Recommend reading: Passive WDM technology and its application in 4G/5G forward transmission
The 200G QSFP56 transceiver can be configured in breakout modes, allowing for more flexible and customized networking setups. The two primary breakout configurations for the QSFP56 transceiver are 4x50G and 2x100G. The 4x50G configuration splits data into four 50Gbps channels, enabling the module to connect with four different network devices. The 2x100G configuration divides the data into two 100Gbps channels, increasing the connection range and providing more incredible data transmission speed.
When integrating 200G QSFP56 transceivers, it’s essential to ensure that the devices and interconnects are compatible. Network administrators and data center operators must verify the compatibility of the connectors, form factors used, and the interconnect option employed. It’s also crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines carefully during the installation and testing of the transceivers. Proper handling, cleaning, and maintenance of the transceiver modules are also necessary to ensure optimal performance.
Data centers require high-speed connectivity for their mission-critical applications. The 200G QSFP56 transceiver is ideal due to its high bandwidth and low latency. It can be used for applications such as server-to-switch interconnects, storage area networks, and high-performance computing clusters. Additionally, QSFP56 transceivers can be used for 50G and 100G data transmission, making them a versatile option for data center networks.
The demand for faster and more efficient communication networks drives the adoption of 200G Ethernet networks. The QSFP56 transceiver is the preferred option for these networks due to its compatibility with 200G Ethernet standards. They can be used for various applications, such as switches, routers, and servers. The QSFP56 transceivers are also backward compatible with existing 100G Ethernet networks, making them an ideal choice for network upgrades.
The deployment of QSFP56 transceivers is gaining momentum in various industries. In telecommunications, companies such as AT&T and Verizon leverage these transceivers to upgrade their 5G networks. The financial services industry also uses QSFP56 transceivers for their high-speed trading platforms. Cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud use QSFP56 transceivers for their data center networks.
As data rates continue to increase, there will be a growing need for higher-speed optical modules. The QSFP-DD and OSFP form factors are expected to become the standard for 400G Ethernet networks, but QSFP56 transceivers will remain the preferred option for 200G Ethernet networks. Advances in silicon photonics and new manufacturing techniques will continue to improve the performance and reliability of QSFP56 transceivers. In the coming years, we expect to see increased adoption of QSFP56 transceivers in various industries.
It is essential to adhere to industry standards and specifications when using the 200g qsfp56 transceiver. Following these standards ensures the transceiver performs optimally and provides a reliable and secure network connection. Industry standards such as IEEE 802.3 standards and Multi-source Agreements (MSAs) ensure interoperability between different vendors’ devices, reducing the risk of compatibility issues.
The 200g qsfp56 transceiver supports various wavelengths, ranging from 850nm to 1550nm. Each wavelength has its unique range and distance limitation. Choosing the right wavelength depends on the application’s requirements, including distance and bandwidth. The supported cable types include copper, multimode fiber (MMF), and single-mode fiber (SMF). Copper cables typically have a shorter range but provide high data rates at a low cost. On the other hand, fiber cables offer longer transmission distances and higher data rates, albeit at a higher price.
Recommend reading: What is data center CWDM4 transmission technology?
Several challenges may arise when using the 200g qsfp56 transceiver, including signal distortion, electromagnetic interference, temperature, and power control. Signal distortion can occur due to different cable lengths and connectors. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) may occur with inadequate shielding, resulting in signal degradation. Temperature and power control are crucial considerations since they affect the transceiver’s reliability and can cause the device to malfunction.
Several troubleshooting strategies can be employed to resolve any potential issues with the 200g qsfp56 transceiver. First, ensure the device’s firmware is up-to-date and that all the required drivers are installed. Also, check for any physical damages to the connector, cable, or transceiver. It could be that the cable connections are not secure, resulting in signal dropouts. Sometimes, a software error or a mismatch in the configuration can cause problems. In such instances, resetting the configuration parameters can solve the issue.
A: Choosing a 200g qsfp56 optical transceiver offers several advantages. It provides a high-speed connection of 200Gbps, making it ideal for data center applications. Additionally, it is compatible with various visual transceiver standards and offers a cost-effective solution for upgrading your network.
A: An optical transceiver is a device that converts electrical signals into optical signals and vice versa. It is used in network communication systems to transmit data over fiber-optic cables.
A: MSA stands for Multi-Source Agreement. It is an industry-standard that ensures compatibility and interoperability between different manufacturers’ products. MSA standards are widely used in the optical transceiver industry.
A: QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable Double Density) is an enhanced version of the QSFP transceiver. It provides higher density and bandwidth, allowing for transmitting up to 400Gbps data rates.
A: The 200G Ethernet interface is a high-speed interface that supports data transmission at 200 Gbps. It is commonly used in data center networks to meet the increasing demand for higher bandwidth.
A: An electrical interface uses electrical signals to transmit and receive data, while an optical interface uses light signals transmitted through fiber-optic cables. Visual interfaces are known for their higher data transfer rates and longer transmission distances.
A: The 200g qsfp56 optical transceiver is compatible with 400G networks. It can be used to connect devices that support both 200G and 400G data rates.
A: The 200gbase-sr4 QSFP56 MSA standard defines the specifications for a 200G Ethernet optical transceiver with a short reach (SR) interface. It uses four lanes of multimode fiber and operates at a wavelength of 850nm.
A: Several manufacturers offer 200g qsfp56 optical transceivers, including Mellanox, Innolight, and other reputable brands. It is essential to choose a reliable manufacturer to ensure compatibility and performance.
A: Yes, the 200g qsfp56 optical transceiver typically comes with a lifetime warranty to give customers peace of mind and product quality assurance.