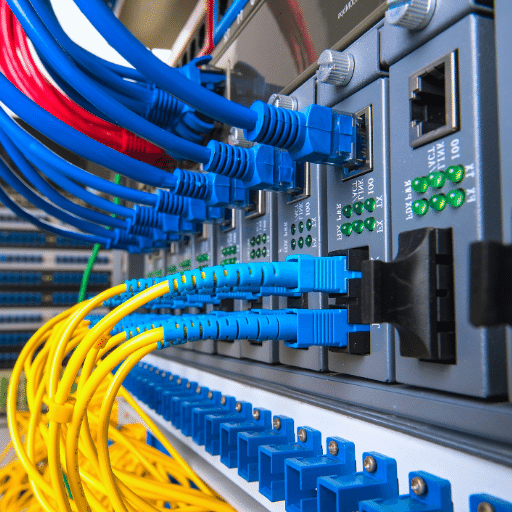
Horizontal cabling is a distinct component of a structured cabling system that connects the telecommunications room to the individual outlet or work area. It is the central cabling infrastructure responsible for data transmission on a specific floor or area within a building. Structurally, it includes the cabling components, such as copper or fiber cables, patch panels, and cross-connects, laid out horizontally, hence the name. It is of paramount importance in telecommunications as it facilitates the efficient transmission of data, voice, and video signals across the network.
The importance of horizontal cabling in telecommunications cannot be overstated. Here are some reasons why it is so crucial:
There are several types of cables used in horizontal cabling to cater to different networking needs:
Each type has its own set of advantages and is suited to specific applications, network size, and environmental considerations. It’s crucial to choose the right kind of cable to ensure optimal network performance.
Standards and regulations govern the design and installation of horizontal cabling systems to ensure consistency, reliability, and performance. Vital regulatory bodies such as the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) have developed specific standards for horizontal cabling:
These standards outline requirements for the maximum length of horizontal cables (typically 90 meters for permanent links), the types of wires used, the maximum number of outlets per area, and other critical parameters. Compliance with these standards can help ensure that the cabling network can support a wide variety of existing and future applications without requiring a significant overhaul of the physical cabling infrastructure.
When it comes to horizontal cabling installation, following best practices is paramount to overall network performance and longevity. Here are some of the key considerations:
Remember, the longevity and performance of a network heavily depend on the quality of the cabling installation. As such, it’s essential to adhere to these best practices for a reliable and efficient network.

Backbone cabling, also known as vertical cabling, is a critical component of a structured cabling system. It serves crucial roles in network infrastructure:
Understanding the role of backbone cabling is essential for designing and implementing a robust, scalable, and efficient network.
Twisted pair and fiber optic cables are the two principal types of cables utilized in horizontal cabling systems.
Twisted pair cables are a type of wiring in which two conductors are twisted together to cancel out electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources. These cables are widely used due to their affordability and ease of installation. They come in two variants: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). UTPs are common in office environments, while STPs are used in environments with potential electromagnetic interference. The twisting pattern of the wires helps prevent interference between pairs, ensuring a steady transmission rate.
Fiber optic cables, on the other hand, transmit information as light pulses. They provide several significant benefits: high-speed data transmission, broader bandwidth than twisted pair cables, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Their ability to maintain signal strength over long distances makes them an ideal choice for connecting different buildings on a campus or for high-speed data transmission across extensive facilities.
Both twisted pair and fiber optic cables play significant roles in horizontal cabling, supporting various applications, from data and voice services to video and building management systems. Understanding the characteristics and benefits of these cables is crucial when planning and implementing a structured cabling system.
A structured cabling system is an integral component of any horizontal cabling system due to the following reasons:
These points highlight the significance of a well-planned and implemented structured cabling system in a horizontal cabling setup. Considering these benefits, it is clear that structured cabling plays a pivotal role in optimizing an organization’s IT infrastructure.
The Telecommunications Room is the central hub for managing and organizing the cabling system in a building. It houses equipment for cable termination, network connections, and signal distribution. Proper cable management in the Telecommunications Room ensures clean and organized cabling, promotes better air circulation, and simplifies maintenance. Cable labels, color codes, cable trays, and cable ties are commonly used for cable management.
Below are some best practices for Telecommunications Room and cable management in horizontal cabling:
By adhering to these best practices, an organization can ensure a robust and efficient cabling infrastructure that caters to its present and future networking needs.
Vertical Cable Management refers to the organization and management of cables that run vertically in server racks or cabinets in a data center or telecommunications room. Its significance is multi-fold:
Therefore, Vertical Cable Management is an integral part of a well-functioning and efficient telecommunications infrastructure.
By following this guide, the organization can establish a reliable and efficient horizontal cabling system that supports its current and future network requirements.
When installing copper and fiber optic cables in horizontal cabling systems, several best practices should be adhered to:
By adhering to these best practices, you can ensure the reliability and longevity of your copper and fiber optic cabling system.
Patch Panels and Patch Cords serve critical functions in horizontal cabling systems.
Patch Panels: These are crucial elements in structured cabling, acting as the central hub for network connections. They enable the routing of data to and from different network devices, such as servers and switches. Patch panels consist of ports where network cables from the workspace outlet are terminated. Their inherent organization aids in easy management of the network, facilitating quick identification of cable routing, simplifying troubleshooting, and minimizing downtime in case of connectivity issues.
Patch Cords: These are relatively short, flexible cables used for patching—an essential process of connecting one network device to another or linking a device to a network signal. Patch cords provide the flexibility needed for network alterations and rerouting signals as required. They are typically used in conjunction with patch panels, connecting ports on the panel to network devices. As an integral component of the network infrastructure, the quality of patch cords directly impacts data transmission quality and overall network performance.
In summary, patch panels and patch cords play vital roles in ensuring efficient and effective data communication in horizontal cabling systems. They contribute to network organization, flexibility, and reliability.
Conduits and cable pathways are crucial elements in horizontal cabling systems. Conduits, such as PVC, steel, or aluminum tubes, protect network cables from damage and interference. Cable pathways, including conduits, trays, and raceways, define the routes cables follow within a building. Proper planning and installation of these components ensure organized, protected, and easily accessible cables, enhancing network system longevity and performance.
Testing and certifying horizontal cabling systems is crucial for ensuring reliable and high-performance networks. It involves verifying compliance with industry standards and checking physical parameters like length and continuity. Certification assesses the system’s ability to carry specific signals. By using specialized equipment, technicians can identify and fix potential issues before they affect network performance. Overall, testing and certification guarantee optimal performance and longevity for cabling systems.
Horizontal and Backbone cabling systems are integral parts of structured cabling solutions, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Below is a comparison of the two systems:
This comparative analysis underscores the importance of both horizontal and backbone cabling in creating a robust and reliable network infrastructure.
Many fallacies persist in the understanding of horizontal and backbone cabling that can often lead to inefficiencies in network infrastructure. Here, we aim to debunk some of the most prevalent misconceptions.
By understanding these misconceptions, one can make informed decisions when setting up or upgrading a network infrastructure.
The decision to use horizontal cabling or backbone cabling is contingent upon the specific network requirements and layout of a building or campus.
Horizontal Cabling: This type of cabling is most commonly used to connect workstations, equipment, and outlets within a single floor or throughout a small building. If you need to connect multiple devices over shorter distances, horizontal cabling is an excellent choice. It has a maximum distance of 100 meters, including the length of patch cables.
Backbone Cabling: On the other hand, backbone cabling is ideal for interconnecting telecommunications rooms, equipment rooms, and entrance facilities. When there’s a need to connect different floors in a building or buildings within a campus, backbone cabling should be employed. The maximum length of backbone cabling varies depending on the media type and application, but it can exceed the reach of horizontal cabling.
The impact of cabling infrastructure on network performance cannot be overstated. The type, quality, and layout of cables directly influence the speed, reliability, and scalability of a network.
Speed and Reliability: High-quality, well-structured cabling provides an optimal path for data transmission, ensuring maximum speed and preventing data loss or corruption. Conversely, low-quality cables or poor cabling infrastructure can cause packet loss, increase latency, and lead to frequent network downtime.
Scalability: A well-planned cabling infrastructure offers scalability, a vital factor for businesses expecting to grow in the future. With a scalable network, companies can add new devices or upgrade systems without significant disruption to the existing setup, thereby reducing costs and minimizing potential downtime.
Security and Compliance: A robust cabling infrastructure also contributes to network security. Shielded cables and organized, well-managed cabling can reduce the risk of data theft or interception. Furthermore, following industry standards and regulations in cabling ensures compliance, which can be a crucial factor for businesses operating in specific sectors.
In conclusion, cabling infrastructure is a critical element that dictates the performance and efficiency of a network. Thus, it is essential to consider it carefully during the planning and installation phases of a network setup.
When future-proofing your cabling infrastructure, especially in terms of horizontal cabling, several considerations come into play to ensure longevity, efficiency, and scalability.
Material and Category: The choice of cable type (e.g., Cat5e, Cat6, Cat7) and the material of the cable (e.g., copper, fiber optic) significantly influences the speed, bandwidth, and distance that the network can handle. Therefore, choosing the right category and material based on your current and projected future needs is crucial.
Cable Management: Proper cable management is essential to maintain the performance and longevity of your cabling infrastructure. Effective organization, labeling, and routing of cables prevent tangling and make future modifications easier and less disruptive.
Standards Compliance: Adhering to industry standards, such as those set by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), is essential for compatibility and safety. It also ensures that your cabling infrastructure can accommodate future technological advancements.
Consideration for Future Growth: Designing extra capacity into your horizontal cabling infrastructure can support future growth. This might involve installing more cable runs than currently needed or considering the potential for more advanced connectivity technologies.
By taking these factors into account during the planning and installation stages, you can future-proof your horizontal cabling infrastructure, ensuring it meets both your present and future networking requirements.
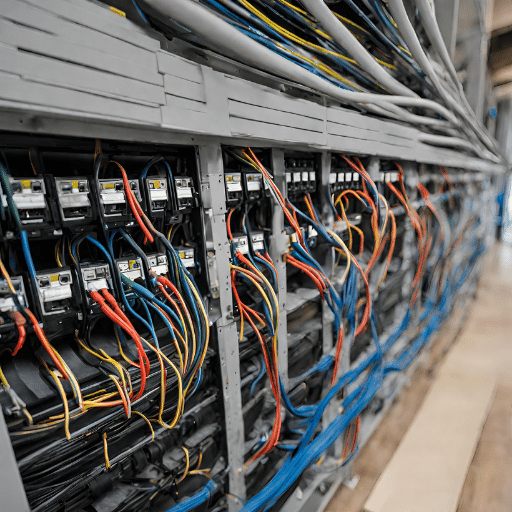
Cable support and management are crucial for maintaining efficiency and reliability in a horizontal cabling system. Proper support prevents physical damage and ensures a neat infrastructure, minimizing interference. Effective management involves routing, labeling, and maintenance, enabling quick issue resolution and facilitating future modifications. Overall, cable support and management play a significant role in ensuring network efficiency and reliability.
Throughout the installation process of a horizontal cabling system, several common challenges may arise, but each can be effectively managed with appropriate planning and considerations.
Congestion: As cabling systems expand, cable congestion can become a significant issue. Utilizing effective cable management, such as cable trays, can help organize the cables and reduce congestion.
Interference: Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can affect network performance. Selecting appropriate cable types, such as shielded twisted pair (STP) cables, can help prevent interference.
Cost: The cost of cabling materials and installation can be substantial. Careful budgeting and long-term planning, taking into consideration future growth and technology advancements, can help optimize expenses.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to local codes and standards is critical. Working with certified professionals and conducting regular audits can ensure compliance.
By considering these challenges from the onset of your project, you can efficiently manage your horizontal cabling installation and ensure optimal network performance.
Adherence to industry standards and best practices in the installation of horizontal cabling is paramount to achieving optimal network performance. The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) publish widely recognized standards for structured cabling systems.
Cable Types: Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 6a cables are commonly used for horizontal cabling in accordance with TIA standards. The selection of the cable type depends on the required network speed, distance, and budget.
Cable Length: The maximum length for horizontal cables as per TIA standards is 100 meters, including patch cables at the workstation and telecommunications room end.
Cabling Pathways: The installation of cabling pathways such as conduits, cable trays, and raceways should allow for easy insertion, removal, and maintenance of cables.
Cable Termination: The termination of cables at both ends should follow the T568A or T568B wiring schemes as per TIA/EIA-568-B standard.
Testing: Post-installation, it’s vital to carry out comprehensive testing, including wiretap, length, propagation delay, delay skew, and crosstalk. This ensures that the installed system meets the required performance specifications.
By incorporating these standards and best practices, you can ensure efficient, reliable, and compliant horizontal cabling installations.
Regular inspections, maintenance, and upgrades are crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of horizontal cabling systems. This involves visually checking for physical damage, organizing and clearing obstructions, cleaning patch panels and outlets, and verifying cable pathways. Upgrades may be necessary to support higher network speeds or increased data traffic. By committing to these practices, you can maintain the long-term reliability and performance of your cabling infrastructure.
Partnering with certified cabling partners for horizontal cabling solutions brings numerous advantages. These professionals possess extensive knowledge, industry certifications, and a commitment to best practices. They ensure optimal performance, strict adherence to standards, and reliable installations. From design to maintenance, they offer comprehensive services and thorough testing. Collaborating with certified cabling partners safeguards your investment and ensures long-term reliability and efficiency.
A: Understanding horizontal cabling is crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable telecommunication networks within buildings.
A: Backbone cabling generally refers to the inter-building or intra-building cable connections, while horizontal cabling connects telecommunications rooms to individual work area outlets on a single floor.
A: The function of the backbone cabling is to provide interconnection between telecommunication rooms, equipment rooms, and entrance facilities in a building.
A: The main cabling methods for horizontal cabling include star topology, where each work area outlet is directly connected to a central telecommunication room.
A: Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) copper cables are commonly used in horizontal cabling to connect network devices within a single floor.
A: A structured cabling partner can provide expertise in designing, installing, and maintaining horizontal cabling systems to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
A: Cable support hardware is essential in maintaining the organization and support of horizontal cabling within buildings, ensuring proper cable management and protection.
A: Backbone cabling typically spans multiple floors or buildings, while horizontal cabling is limited to connecting within a single floor or building.
A: A cabling contractor is responsible for the installation and maintenance of horizontal cabling systems, ensuring proper connectivity and adherence to industry standards.
A: Horizontal cabling systems utilize various types of cabling, including UTP copper cables and fiber optic cables, to meet the specific networking requirements of buildings.
She recommended Reading:10G DAC High-Speed Cable VS 10G AOC Active Optical Cable: Who is better?