A server CPU, short for Central Processing Unit, is a specialized computer chip designed to power enterprise-level applications and manage heavy workloads in a server environment. Unlike consumer-grade CPUs in desktop or laptop computers, a server CPU is engineered to handle multiple tasks simultaneously and operate more efficiently over prolonged periods.
A server CPU acts as the system’s brain and is responsible for processing and executing the various instructions and tasks submitted by users and applications. It handles resource-intensive activities such as data processing, storage, and transmission. A server CPU differs from traditional CPUs because it generally has more cores, cache memory, and a higher clock speed. This design allows it to handle multiple applications and services running simultaneously, providing the computing power necessary to support the needs of an enterprise.
The key features that make a server CPU optimized for running heavy workloads are:
• Higher Core Counts – Server CPUs have many cores that combine to split requests into multiple threads simultaneously.
• Hyper-Threading – This technology optimizes CPU utilization by allowing multiple threads to simultaneously work on the same core.
• High Clock Speed – Server CPUs double the clock speed of a consumer-grade CPU, which helps handle heavy workloads and calculations.
• More Cache Memory – Server CPUs contain more cache memory than consumer-grade CPUs. Cache memory is faster than regular memory, which allows the CPU to access data faster.
Different types of server CPUs are available on the market today, such as Intel Xeon, AMD EPYC, and Qualcomm Centriq. Intel Xeon is the most common server CPU, designed for high-performance computing, data processing, and storage. AMD EPYC is designed for high-performance computing workloads and features a high core count and memory capacity. Qualcomm Centriq is intended for cloud computing and integrated with an AI-based platform.
Intel Xeon is known for its performance and reliability, but can be expensive. AMD EPYC performs similarly to Intel Xeon but comes at a lower price. However, it has a lower market share. Qualcomm Centriq is relatively new and offers powerful computing for cloud services, but it is not as established compared to Intel and AMD.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of a server and is responsible for executing most of the server’s operations. A server CPU is designed to handle multiple tasks simultaneously and efficiently. Therefore, the performance of a Data Center largely depends on the quality and reliability of its server CPUs. The CPU determines the processing speed of the system, which directly impacts the overall efficiency of the Data Center.
The most essential attributes of a Server CPU in a Data Center are its clock speed, number of cores, and cache memory. Clock speed refers to the number of cycles a CPU can execute per second. The higher the clock speed, the faster the server can process data. The number of cores determines the number of tasks a server can handle simultaneously. Cache memory is a small amount of high-speed memory used to store frequently accessed data.
Cloud computing relies heavily on servers, and server CPUs play a vital role in the performance of Cloud Computing. A cloud-based infrastructure requires a robust and reliable CPU to handle multiple user requests. The Server CPU should be able to process many requests and allocate resources efficiently to multiple virtual machines. This ensures that the Cloud Computing system can deliver a seamless and high-quality experience to the end-users.
The most essential attributes of a Server CPU in Cloud Computing are its performance and power efficiency. A high-performance CPU can handle complex applications and workloads and provide faster response time. Power efficiency is crucial in Cloud Computing as it reduces energy consumption and allows the system to run at a lower temperature.
Choosing a high-quality server CPU can enhance the efficiency and productivity of Data Centers and Cloud Computing systems. A high-quality CPU can process data faster, handle complex applications and workloads, and allocate resources more efficiently. A high-quality CPU can also reduce energy consumption, which means lower operating costs, improved reliability, and a longer hardware lifespan.

CPU cores refer to the number of central processing units in a CPU. A CPU with more cores can process more data simultaneously, increasing server performance. For instance, a server with a 16-core CPU will perform better than a server with a 4-core CPU. However, the number of CPU cores needed will depend on the server’s intended use, with more bodies being essential for servers used for resource-intensive applications such as virtualization or hosting.
Another crucial factor to consider when selecting a server CPU is clock speed. Clock speed measures the rate at which the CPU executes instructions, estimated in Gigahertz (GHz). A higher clock speed means a faster CPU, which enhances server performance. However, it is essential to note that clock speed alone does not always translate to higher performance on a server. Other factors like the number of CPU cores and the server’s intended use must also be considered.
Threads refer to the number of processes that a CPU can execute simultaneously. Hyper-threading technology enables CPUs to run multiple lines simultaneously, which enhances server performance by increasing CPU utilization. Thread count is essential when selecting a CPU for multi-threaded server applications.
A CPU cache is a high-speed memory that stores frequently used data to speed up CPU operations. The larger the CPU cache, the faster the CPU can access frequently used data. A larger stock translates to increased CPU performance and improved overall server efficiency.
The motherboard is the main circuit board of a server that connects all its components. The motherboard’s compatibility with a particular CPU is essential when choosing a server CPU. Different CPUs require different motherboard socket types, and selecting an incompatible motherboard may render the CPU useless. Therefore, verifying a CPU’s compatibility with the motherboard beforehand is of utmost importance to ensure reliable server performance.

One trend that will continue to shape the server CPU landscape in 2023 is the focus on power efficiency and performance. With data centers consuming significant energy and generating heat, server CPU manufacturers invest in developing CPUs that consume less energy and produce less heat while delivering high-performance computing power. Some notable technologies in this space include Intel’s 14 nm Broadwell-EP, AMD’s 7 nm Epyc, and Arm-based processors such as the Ampere Altra.
As the use of AI continues to grow, server CPUs that can handle AI workloads will become more prevalent in 2023. AI workloads require specialized hardware and software, and server CPUs are designed and optimized to support such workloads. Examples of AI-focused server CPUs include Nvidia’s Ampere Altra and Intel’s Nervana Neural Network Processor.
With increased cyber threats and attacks, server CPUs with advanced security features will be a top priority in 2023. Some CPU manufacturers integrate security features into their offerings to protect servers from attacks. Examples of security-focused server CPUs include AMD’s Epyc and Intel’s Xeon.
When selecting the most suitable server CPU in 2023, businesses and organizations should consider their specific needs and requirements. For example, if energy efficiency is a top priority, CPUs such as Intel’s 14 nm Broadwell-EP or AMD’s 7 nm Epyc may be the best choice. On the other hand, organizations that need high-performance computing power may opt for CPUs such as the Ampere Altra or Intel’s Nervana Neural Network Processor, which are well-suited for AI workloads. Lastly, CPUs with advanced security features like AMD’s Epyc and Intel’s Xeon are essential for organizations prioritizing server security.
When comparing different brands and models of server CPUs, factors include processing power, energy efficiency, security features, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. For example, the Intel Xeon Scalable Processor family offers high-performance computing power and advanced security features. AMD’s Epyc processors, on the other hand, are known for their energy efficiency and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Lastly, the Ampere Altra, an Arm-based processor, is designed to handle AI workloads while consuming less power and generating less heat.
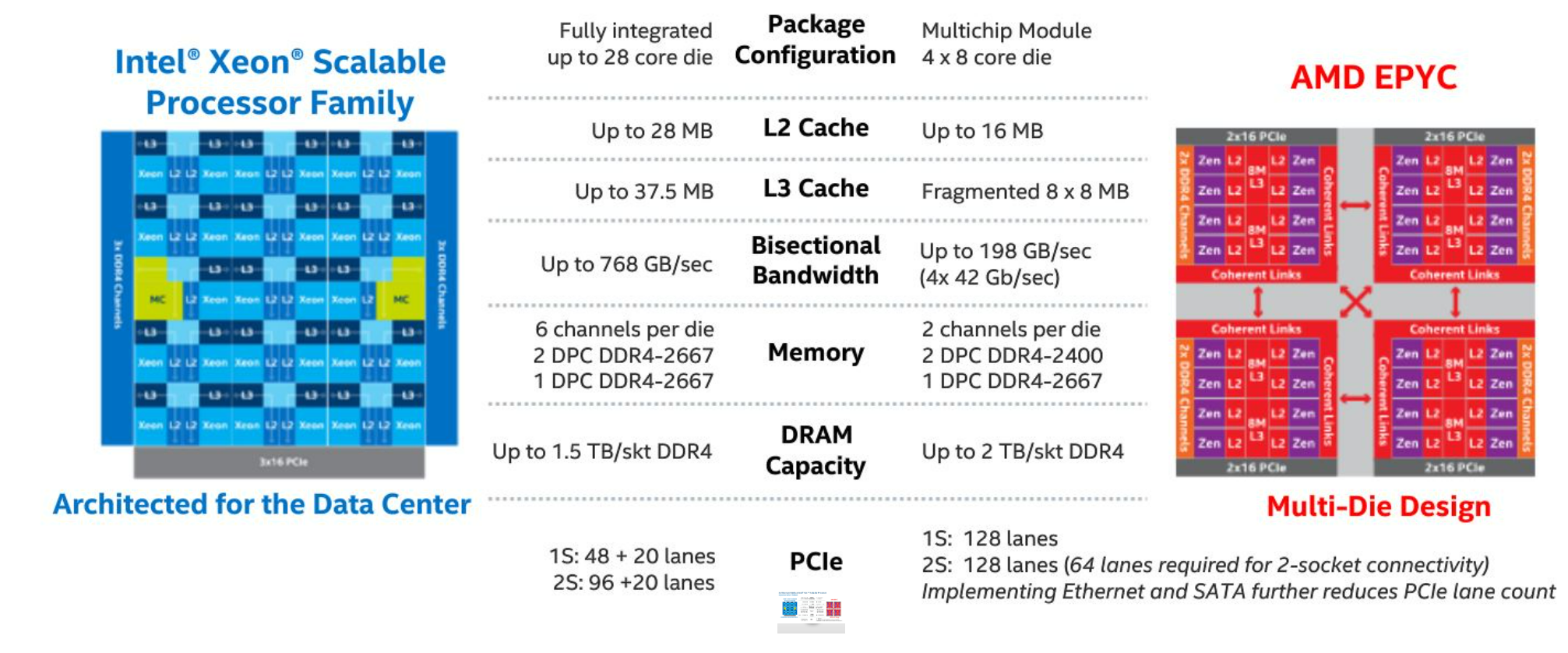
Regarding server CPUs, Intel and AMD are two of the most prominent players in the market. Intel offers various server CPU lines, including Xeon Scalable, Xeon E7/E5/E3, and Atom processors, each tailored to different business needs. On the other hand, AMD’s server CPU lines, such as EPYC, Ryzen, and Opteron, offer high performance and cost-effectiveness, making them particularly popular among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Both companies use different architectures, cache sizes, clock speeds, and core counts that differentiate their products. As a result, businesses need to understand these aspects to make the right purchasing decisions thoroughly.
Intel’s Xeon Scalable processor series offers powerful CPUs for data-center class workloads. These processors come in Gold, Silver, and Bronze tiers, delivering up to 28 cores and a base speed 1.7GHz with Turbo Boost Technology. They also come with Intel QuickAssist Technology, which enhances packet processing throughput and cryptography acceleration. The Xeon E7 processors provide high scalability, reliability, and availability to support mission-critical workloads. Intel’s Atom processors are designed for low-power and density-optimized workloads, with features such as error-correction code (ECC) memory support for enhanced data reliability.
The EPYC processor series from AMD offers exceptional performance, scalability, and security. The AMD EPYC 7003 series, or Milan,’ is the latest server CPU line and uses the Zen 3 architecture. These processors offer up to 64 cores, a base clock speed of 2.2GHz, and a maximum boost speed of 3.9GHz. Additionally, AMD’s Opteron processors are designed for SMBs to provide high performance, low power consumption, and cost-effectiveness. Finally, the Ryzen Pro processors offer reliable and secure CPUs for desktop workloads.
To compare the performance between Intel and AMD server CPUs, looking at benchmarks and real-world usage is essential. Several benchmarking programs, such as Geekbench, SPEC, and AnTuTu, can help compare performance across CPU models. In recent years, AMD has gained momentum in the performance segment, with their EPYC processors outperforming comparable Intel Xeon processors in many benchmarks. For example, the AMD EPYC 7763 processor scored an impressive 44,815 in SPECint_rate benchmark tests, while the equal Intel Xeon Platinum 8380 scored 32,733. However, Intel processors tend to offer better performance when it comes to specific workloads such as gaming or single-threaded applications.
Another critical aspect to consider is energy efficiency, which can impact operational costs and the environmental footprint of businesses. AMD’s EPYC processors have a reputation for energy efficiency compared to Intel’s counterparts, thanks to their design enhancements. EPYC CPUs use less power, generate less heat, and require less cooling capacity overall, decreasing electricity consumption and costs. Additionally, AMD’s SenseMI technology enhances power management by dynamically adjusting CPU power consumption based on usage, further improving energy efficiency. Conversely, Intel’s Xeon processors tend to deliver better performance per watt in single-threaded workloads. Still, they may lag in multi-threaded tasks, leading to higher energy consumption and operating costs.
The workload requirements of your server refer to the amount of processing power and resources needed to carry out specific tasks and applications. It is essential to select a CPU that can handle the workload requirements of your server effectively. For example, if your server performs tasks like data processing or runs heavy applications, you’ll need a powerful CPU that can handle it. Some of the factors you should consider when analyzing the workload requirements of your server include the number of users, concurrent tasks, and the complexity of applications that will be running on the server.
Today, virtualization technology is widely used in server environments to enable multiple operating systems and applications to operate independently on a single physical server. When selecting a CPU, IT professionals must ensure that it supports virtualization technology. A processor that has virtualization support will improve server efficiency, flexibility, and scalability while reducing overall hardware costs.
The scalability of your CPU is another essential factor to consider. Scalability refers to the ability of the server to handle an increasing workload as the business expands. By selecting a scalable CPU, IT professionals can easily add more processing power and resources to the server without replacing the entire system. Scalable CPUs are ideal for businesses that experience high growth rates, as they enable the server to keep up with the increased demand.
Power consumption is a critical factor that needs to be considered when selecting a CPU for your server. High-performance CPUs that draw a lot of power can lead to increased energy costs and a higher carbon footprint for the company. With energy efficiency becoming a top priority for businesses, IT professionals should consider CPUs that consume less power while still providing high performance. A CPU’s power consumption directly impacts the total cost of ownership for the server.
When selecting a CPU for your server, IT professionals must decide between a single processor or dual processor configuration. A single processor configuration is ideal for entry-level servers that do not require a lot of processing power. Dual processor configurations, conversely, are better suited for mid-to-large businesses that need high-performance servers. A dual-processor design provides better processing power and overall server performance but comes at a higher cost.
A: Choosing the right server CPU is crucial because it directly affects your server’s performance, efficiency, and scalability. The CPU is the brain of a server and determines how fast and efficiently it can handle tasks and workloads.
A: Server processors, also known as server CPUs, are specifically designed for server platforms and are optimized for performance, reliability, and scalability. Desktop processors, on the other hand, are intended for consumer desktops and offer a balance between performance and power consumption.
A: Intel Xeon processors are widely considered the industry standard for server CPUs. They offer a range of features and capabilities specifically tailored for server workloads, such as support for virtualization, scalability, and low power consumption.
A: AMD EPYC processors are a solid alternative to Intel Xeon processors. They offer exceptional performance, more cores, and competitive pricing. If you require a high-performance server CPU for virtualization, video editing, or other demanding tasks, AMD EPYC processors are worth considering.
A: To choose the right CPU for your server, you must consider factors such as your workload, power consumption requirements, scalability needs, and budget. It is recommended to consult with a knowledgeable professional or refer to the specifications provided by the CPU manufacturer.
A: Yes, server CPUs are specifically optimized for server workloads and can deliver higher performance than desktop CPUs. They are designed to handle multiple simultaneous tasks and have enhanced features like higher core counts and support for advanced technologies like PCIe.
A: The CPU, or central processing unit, is the primary component responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations in a server. It handles tasks such as data processing, application execution, and overall system performance.
A: The number of CPU cores directly impacts server performance. More bodies allow for parallel processing and can handle multiple tasks simultaneously, resulting in improved performance and faster response times.
A: A server CPU’s power consumption directly contributes to a server’s overall energy efficiency. Lower power consumption means reduced electricity costs and environmental impact. Therefore, choosing a server CPU with lower power consumption can result in long-term savings.
A: Yes, server processors can also be used in workstation setups. Server processors, such as Intel Xeon or AMD EPYC, offer powerful performance and reliability, making them suitable for demanding workloads in workstations.
Everything You Need to Know About Network Servers
10G DAC High-Speed Cable VS 10G AOC Active Optical Cable: Who is better?