WDM, the full English name is Wavelength Division Multiplexing. It is a technology that combines multiple optical signals of different wavelengths through a combiner and couples them into the same fiber for data transmission.
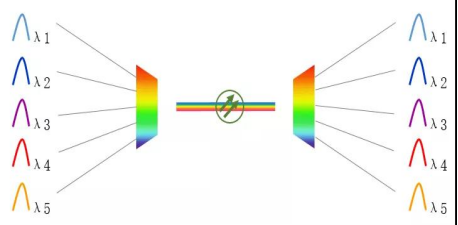
How WDM works
Wavelength x frequency = speed of light (constant value), so WDM is actually frequency division multiplexing
In simple terms, we can also think of WDM as a highway where different types of vehicles gather and then go their separate ways when they reach their destination.
The role of WDM is to enhance the transmission capacity of fibers and improve the efficiency of fiber resource utilization.
For a WDM system, it is obvious that the wavelength (frequency) of each optical signal must be controlled in order to function properly. If the wavelength interval is too short, collisions are likely to occur. If the wavelength interval is too long, the utilization rate is very low.
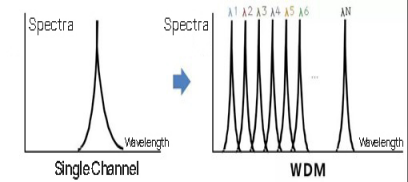
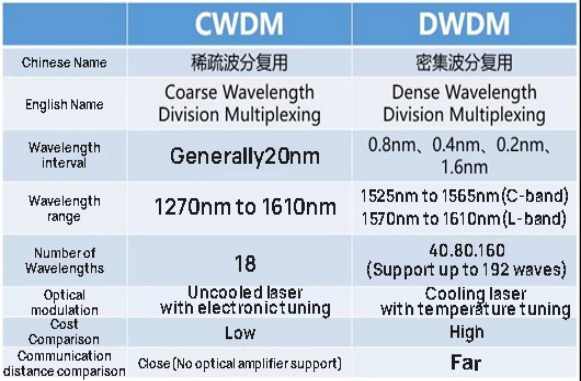
In the early days, due to technical limitations, the wavelength spacing was typically controlled to a few tens of nm. This more dispersed form of WDM is called Sparse WDM, or CWDM (Coarse WDM).
Later, the technology became more and more advanced, the wavelength spacing pressed shorter and shorter, compressed to the level of a few nm, resulting in a compact form of WDM known as Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing(DWDM).
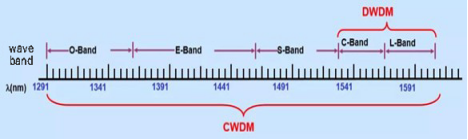
CWDM has a wavelength spacing of 20nm and a wavelength range of 18 bands from 1270nm to 1610nm.
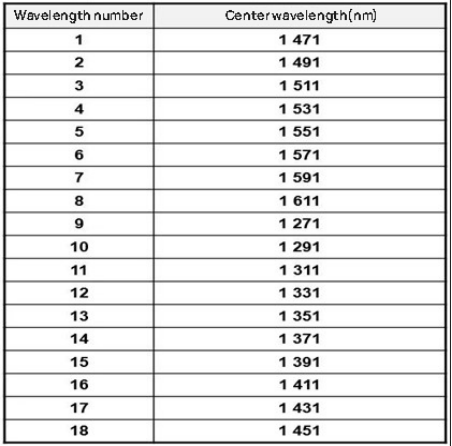
At the very beginning, the wavelength range specified by ITU for CWDM (ITU-T G.694.2) was 1270 to 1610 nm.
Later the ITU made a change to shift the center of the channel by 1nm, so the center wavelength range is 1271 to 1611nm.
However, because there is a significant increase in attenuation in the 1270-1470nm band, many older fibers cannot be used properly, so CWDM generally prioritizes the use of the 8 bands from 1470 to 1610nm.
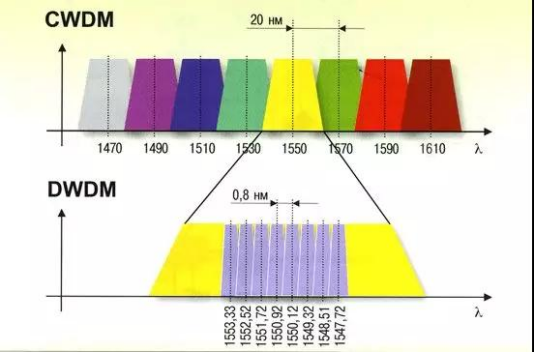
And the wavelength interval of DWDM can be 1.6nm, 0.8nm, 0.4nm, 0.2nm, which can accommodate 40, 80, 160 waves (up to 192 waves can be supported.) The wavelength range of DWDM is 1525nm to 1565nm (C-band) and 1570nm to 1610nm (L-band).
DWDM commonly used C-band, wavelength interval 0.4nm, channel frequency interval 50GHz
A summary comparison would be this.
CWDM and DWDM are more common, next I will talk about MWDM and LWDM.
MWDM, which is medium wavelength division multiplexing. It is a preferred technology of China Mobile and was proposed along with its semi-active forwarding scheme (also known as Open WDM).
As I mentioned yesterday when introducing the 5G forward pass, all current 5G forward passes now require at least 12 wavelength channels. There the three major operators have programs that aim to achieve 12 waves.
The principle of MWDM is to reuse the first 6 wavelengths of 25G CWDM and offset the wavelengths by 3.5nm to the left and right, forming 12 wavelengths by incorporating TEC (Thermal Electronic Cooler) for temperature control. The specific scheme is as follows.
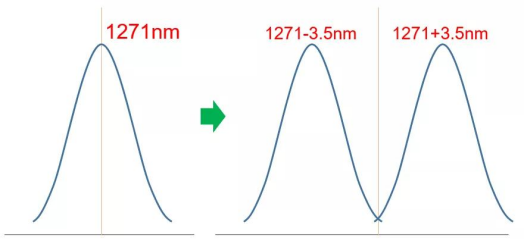
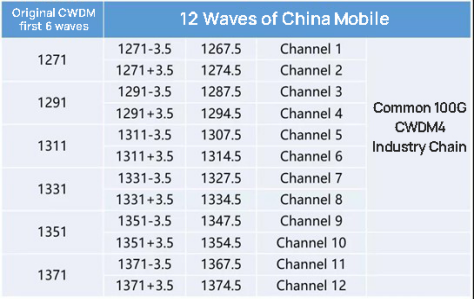
This solution not only reuses the CWDM industry chain, but also can meet CMCC’s own 10km forward transmission distance demand, and at the same time saves a lot of fiber resources, which is a multi-benefit.
Let’s look at LWDM again.
LWDM is based on Ethernet channel wavelength division multiplexing (LAN WDM), which is also referred to as fine wavelength division multiplexing by some.
It is extended from the existing 8 waves to 12 waves according to the channel spacing of 800 GHz. The wavelengths are shown in the following figure.
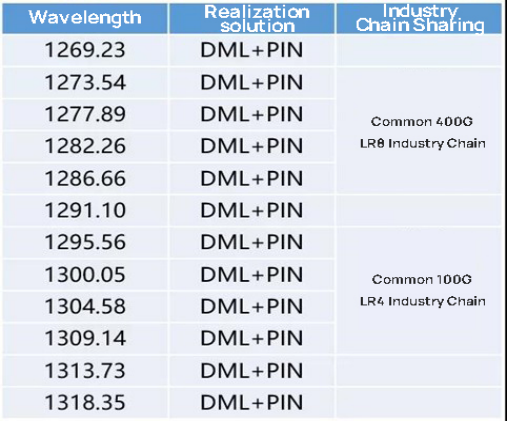
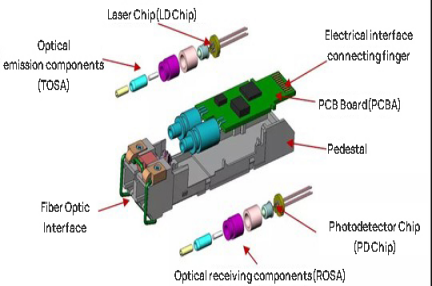
The DML refers to the Directly Modulated Laser (DML) on the TOSA(Transmitter Optical Sub-Assembly) transmitter side of the optical module, while its counterpart is the EML (Electro-absorption Modulated Laser) Diode.
LWDM is the preferred technology of China Telecom (While China Unicom focuses on DWDM). Currently, China Telecom is organizing the upstream and downstream of the industry chain for discussion and development, and it is in the sampling stage.