The need for secure and private communication has grown exponentially as the world becomes increasingly digital. This has led to the rise of Virtual Private Networks (VPN), which allow users to connect to the internet through a private, encrypted tunnel using a remote server.
A VPN is a network that provides a secure and private connection between a user’s computer and the Internet. It does so by routing the user’s internet traffic through a remote server in a different location, masking the user’s IP address. The encrypted connection ensures no one can intercept the user’s traffic or spy on their online activities.
VPN technology has several advantages, making it an essential tool in the modern digital landscape. Firstly, a VPN significantly increases security when browsing the internet or accessing sensitive information. This is done by encrypting the user’s data, which ensures that hackers cannot intercept communication. Secondly, VPN allows for increased privacy, as it hides the user’s IP address and location from internet service providers, advertisers, and other agencies that may try to track user activity. Thirdly, VPN enables users to access the internet remotely, which is crucial for remote workers, freelancers, and business travelers. Last but not least, VPN helps users avoid geo-restrictions, enabling them to access content that may be restricted in certain countries or regions.
Despite its many advantages, VPN technology also has its potential drawbacks. The most common fault is slow connection speeds, resulting from the encryption process VPN uses to secure internet traffic. Another potential problem is limited server options, which can limit the location from which users can access the internet. There are also concerns over trust and reliability as some VPN providers have been known to log user data, which defeats the purpose for which the technology was designed.
One of the significant advantages of MPLS is its efficiency, as it can improve network performance significantly by reducing network congestion. With MPLS, network operators can establish Quality of Service (QoS) parameters that prioritize specific types of traffic, resulting in reduced data transfer times and excellent network performance. Additionally, MPLS can enhance security by reducing external threats and safeguarding sensitive data.
However, there are some negative aspects to consider when implementing MPLS. The significant drawback is that MPLS is more expensive than traditional routing protocols. This is because MPLS requires sophisticated hardware and software and specialized expertise to manage and maintain. Moreover, installing MPLS technology can lead to delays and potential risks for projects. Finally, MPLS technology might not be compatible with older networking equipment or software applications.
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) and VPN (Virtual Private Network) are two commonly used technologies that aim to secure and speed up data transmission across networks. While both have their benefits and drawbacks, it’s essential to understand the differences between each technology’s speed, security, and cost. In this article, we will compare and contrast MPLS and VPN, examining their unique features and which technology suits specific use cases.
Speed is a crucial aspect of network transmission, and selecting a technology that matches the demands of the network’s end-users is essential. MPLS is known for its fast and efficient data transmission, making it the better option for large organizations with high bandwidth requirements. Unlike VPN, MPLS uses a physical connection between locations, which makes it possible to guarantee the quality of service. On the other hand, VPN operates over the public internet, which means it could be subject to delay and lag. Although VPN can be a cost-effective solution for small organizations, it may not be the best for those that require high-speed connectivity.
Security is also an essential aspect of network transmission, and it’s crucial to understand how each technology approaches it. MPLS is more secure than VPN because it relies on dedicated connections between locations to ensure data privacy. MPLS also uses labels to route traffic, so data is not visible to other devices on the network. However, VPN operates over the public internet, making it susceptible to hacks and data breaches. Although VPN uses encryption to secure data, it doesn’t have the same level of security as MPLS. Therefore, MPLS is the better option for organizations that prioritize security above all else.
Cost is always a determining factor when selecting a technology solution. MPLS is a more expensive solution than VPN because it requires extensive equipment and infrastructure. Additionally, MPLS is an entirely managed solution, which means organizations must pay for all maintenance and upgrades. VPN, on the other hand, is a cost-effective solution because it requires minimal equipment and infrastructure. Although organizations may need to pay for VPN software licenses, it’s often less expensive than MPLS. Consequently, for small organizations with a limited budget, VPN is the better option.
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a secure and encrypted connection between two networks or devices over the internet. In many instances, MPLS and VPN are used in a converged network to leverage and complement each other’s strengths.
When VPN and MPLS are utilized together in a converged network, they can enhance network performance and minimize downtime. Combining MPLS’s reliability and speed with VPN’s security and manageability allows for a more robust and scalable network. For example, a bank may use MPLS to transport critical financial data between branches and use VPN to connect remote users securely. The bank can create a secure and efficient network that serves internal and external users by converging MPLS and VPN.
MPLS and VPN are highly complementary technologies that can be used together to create a more secure, efficient, and robust network. MPLS provides a highly reliable and scalable transport mechanism for data-intensive applications. On the other hand, VPN offers a secure and encrypted connection over the internet, providing remote access or connecting remote sites without the need for dedicated connections. By harmonizing MPLS and VPN, enterprises can achieve greater flexibility, security, and scalability while reducing costs associated with dedicated circuits.
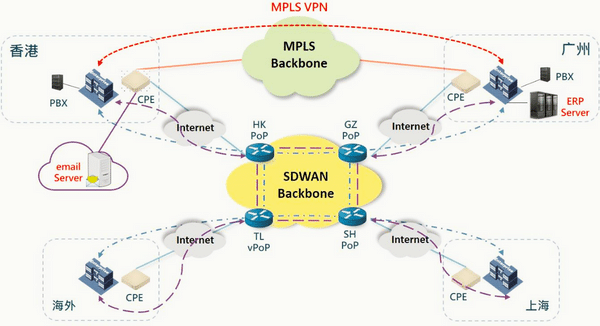
SD-WAN is a relatively new technology that is disrupting traditional networking. SD-WAN stands for Software-Defined Wide Area Network, designed to provide a more flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional VPN and MPLS networks.
SD-WAN offers several advantages over traditional VPN and MPLS networks. It enables businesses to prioritize and route traffic dynamically based on application needs, ensuring that critical traffic gets the necessary bandwidth and quality of service. SD-WAN also allows businesses to use cheaper broadband internet connections, replacing expensive MPLS circuits. However, it is crucial to note that SD-WAN is not without its disadvantages, including security concerns and complexity.
In conclusion, the decision to choose between MPLS, VPN, or SD-WAN is not a straightforward one. Each option has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on your business needs. If you require a secure and reliable network and are willing to pay a premium, then MPLS is the way to go. If cost-effectiveness is your main concern, then a VPN is ideal. However, SD-WAN may be the best choice if you are looking for a network that balances performance and cost. The decision rests on your specific business needs and budget.
MPLS and VPN differ in several ways. MPLS prioritizes traffic based on labels assigned by the service provider, ensuring reliable and efficient data delivery. On the other hand, VPN uses encryption to protect data and keep it secure over the internet. MPLS is generally faster and more efficient because the labels reduce the time it takes for the router to look up and match IP addresses. VPN, however, can be accessed from any location with an internet connection, making it more accessible for businesses with remote workers or multiple locations.
When deciding between MPLS and VPN, several essential factors must be considered. To choose between the two, you must weigh the costs associated with each, including upfront and maintenance costs. MPLS typically requires a more significant upfront investment but can be cost-effective in the long run because it provides higher speeds, lower latency, and better reliability. VPN, on the other hand, is generally more affordable to set up and maintain but can be slower and less reliable.
Other critical factors include network complexity, bandwidth requirements, and security needs. MPLS is generally more complex to configure and maintain, requiring skilled IT personnel. It may also provide limited bandwidth, making it challenging for businesses that need to support high-bandwidth applications. On the other hand, a VPN can offer unlimited bandwidth, making it ideal for businesses with high bandwidth requirements. However, a VPN may not provide the same level of security as MPLS, making it a less suitable option for businesses that handle sensitive data.
A: The choice between VPN and MPLS depends on your specific requirements and network infrastructure. Both technologies have their advantages and disadvantages. VPNs are generally more cost-effective and easier to set up, making them popular for small to medium-sized businesses. On the other hand, MPLS offers faster speeds and more excellent reliability, making it a better option for large organizations that require high-performance networks.
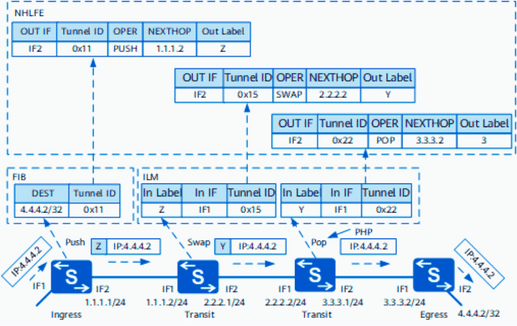
A: MPLS adds a label (or tag) to each packet entering the network. This label contains routing information that allows routers to make fast and efficient forwarding decisions. Instead of analyzing each hop’s packet header, routers can read the MPLS label and determine the next hop based on preconfigured label-switching tables. This results in faster data transmission and reduced network congestion.
A: Yes, a VPN and MPLS in a hybrid network setup is possible. This allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both technologies. For example, you can use MPLS for high-speed and reliable backbone connectivity between your main office and branch locations while using VPNs to provide secure remote access for individual users or smaller branch offices.
A: MPLS and VPNs can provide secure connectivity over a wide area network. VPNs use encryption protocols (IPsec) to secure data transmitted over a public network. Conversely, MPLS relies on the provider network’s physical security, as packets are not encrypted by default. However, MPLS offers a more controlled and isolated network environment, which can enhance security when combined with appropriate access controls.
A: The choice between VPN and MPLS depends on your specific requirements and priorities. If cost-effectiveness, ease of deployment, and remote access for individual users are important factors, then VPN may be the better choice. If speed, reliability, and efficient traffic management are the primary concerns, then MPLS may be a better fit for your organization. It is recommended to carefully evaluate your needs and consult a network professional to determine the best solution.
A: In general, MPLS is faster than traditional VPNs. MPLS networks utilize label-switching technology, allowing faster packet forwarding and reducing network congestion. This makes MPLS ideal for applications that require low latency and real-time data transmission, such as voice and video conferencing. However, the actual performance may vary depending on network infrastructure, provider capabilities, and configuration factors.