Multimode fiber is a type of optical fiber that is used for transmitting light signals. Unlike single-mode fiber, which has a small core size (around 8-10 microns), multimode fiber has larger core sizes (ranging from 50-100 microns). This means it can support multiple modes or paths of light travel, making it ideal for short-distance communication applications.

Multimode fiber is a type of optical fiber with a larger core diameter than single-mode fiber. It is designed to support multiple transmission modes, allowing it to propagate light over short distances. Multimode fiber is commonly used in local area networks (LANs), data centers, and other short-distance communication applications.
Multimode fiber has several characteristics that make it suitable for short-distance communication applications. Firstly, it has a larger core diameter, which allows more light to be transmitted through the fiber. This results in higher data rates and greater bandwidth availability than single-mode thread. Secondly, multimode fiber is more flexible and easier to install than other fiber types, making it a popular choice for LANs. Lastly, it is relatively inexpensive compared to different fiber types, making it ideal for cost-sensitive applications.
Multimode fiber works by allowing multiple modes of light to travel through the fiber simultaneously. This is achieved by using a larger core diameter, which reduces the likelihood of signal attenuation and distortion. When a signal is transmitted through a multimode fiber, it bounces around between the different modes of light, which ensures that the password is transmitted over a wider area. This results in a lower density of light in the fiber, reducing signal distortion likelihood.
There are several different types of multimode fiber, each of which has other performance characteristics. OM1 fiber, for example, is the oldest type of multimode fiber and can support data rates up to 1 Gbps over distances of up to 300 meters. OM2 fiber, on the other hand, has a larger core diameter and can support data rates up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 600 meters. OM3 and OM4 fibers have even larger core diameters and can support data rates up to 40 Gbps and 100 Gbps, respectively, over distances of up to 350 meters.
Users need to understand the different types of multimode fiber and their performance characteristics, as this can significantly impact the performance and cost of their applications. For example, using OM1 fiber in a high-speed application would result in poor performance, while using OM4 fiber in a low-speed application would be unnecessary and expensive. By understanding the different types of multimode fiber and their performance characteristics, users can select the correct kind of fiber for their application, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.

OM1 fiber, also known as 62.5/125 µm fiber, is a multimode fiber widely used in LANs (Local Area Networks) and data center applications. This fiber type is constructed using two types of materials – a core made of high-quality silica glass with a diameter of 62.5µm and a cladding layer made of a lower refractive index material with a diameter of 125µm.
OM1 fiber can support IEEE 802.3 Ethernet transmission standards, and it has a maximum bandwidth of 200 MHz*Km at 850nm wavelength. It can transmit data at speeds up to 10 gigabits per second, with a maximum transmission distance of 33 meters using the 10GBASE-SR transmission standard. It has a typical attenuation of 3.5 dB/km at 850 nm and 1.5 dB/km at 1310 nm wavelength. OM1 fiber is also resistant to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation caused by bending or twisting.
OM1 fiber cable is used for both indoor and outdoor applications. It is widely used in data centers, high-speed LANs, and security systems. OM1 fiber is also suitable for fiber optic patch cables, fiber optic pigtails, and fiber optic Connectors.
Compared to OM2, OM3, and OM4, OM1 fiber has a lower bandwidth and shorter distance capabilities. While OM2 offers a bandwidth of 500 MHzKm, OM3 and OM4 can support up to 2000 MHzKm bandwidth. OM3 and OM4 fibers also offer longer transmission distances, up to 550 and 400 meters, respectively.
When working with OM1 fiber, it is essential to ensure that the core diameter of the fiber optic cable matches the equipment you are using. It is also necessary to ensure that the connector plugs are cleaned and inspected before connecting to prevent dust, fiber breakage, or contamination. It is important to note that whenever OM1 fiber is spliced, the splicing loss must be measured and kept below the acceptable range of 0.1 to 0.5 dB. Finally, the installation must be carried out properly to avoid damaging the fiber cable.

OM2 Multimode Fiber is an optical fiber used for short-range data transmission at high speeds. It is designed to be a cost-effective alternative to more expensive single-mode fibers while offering high-quality performance. OM2 fiber is an excellent choice for local area networks (LANs) and data centers, providing reliable and efficient data transmission over short distances.
OM2 Multimode Fiber has a core diameter of 50 microns, allowing it to transmit data faster than OM1 fiber. It also has a higher bandwidth than OM1, meaning it can transmit more data over a given distance. Moreover, OM2 fiber supports multiple light paths, which enables it to support duplex transmission. This means that data can be transmitted in both directions simultaneously, which enhances the fiber’s transmission capabilities.
OM2 Multimode Fiber is characterized by its excellent transmission performance due to its large core diameter and high bandwidth. Together, these features allow for high data transmission speeds of up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 550 meters. This makes OM2 fiber an ideal choice for LANs, data centers, and other short-range applications.
OM2 fiber also features a tight-buffered design, which makes it highly durable and resistant to external factors such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, and physical impact. Additionally, OM2 fiber is compatible with various connector types, including the popular LC and ST connectors, which ensure easy installation and maintenance.
While OM1 and OM2 fibers have a core diameter of 50 microns, there are several key differences between the two. One of the most significant differences is the bandwidth, as OM2 fiber has a higher bandwidth than OM1. This means that OM2 can carry more data over a given distance, which increases its efficiency and reliability.
Another difference between OM1 and OM2 fibers is their maximum cable distances. OM1 fiber can transmit data over distances of up to 275 meters, while OM2 can transmit data over distances of up to 550 meters. This means that OM2 fiber is a more suitable for larger networking projects.

OM3 Multimode Fiber is a type of optical fiber designed for high-speed computer networking applications. As the name implies, this type of fiber allows multiple modes of light to be transmitted through the cable, which enables the thread to be used to transmit both digital and analog signals. This technology was introduced in the early 2000s as an upgrade to the previously used OM1 and OM2 fiber types.
OM3 Multimode Fiber is made up of a core surrounded by a cladding material, which in turn is surrounded by a protective coating. The core diameter is about 50 micrometers, with a cladding diameter of 125 micrometers. The protective layer is typically made of a polymer material, such as silicone or acrylate, which provides mechanical protection to the fiber.
One of the critical benefits of OM3 Multimode Fiber is its ability to transmit large amounts of data over long distances. This is due to the fiber’s high bandwidth and low attenuation characteristics. The thread can transmit data at speeds of up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 300 meters and at speeds of up to 40 Gbps over distances of up to 100 meters.
OM3 Multimode Fiber has several essential characteristics and features that make it ideal for high-speed data communications networks. One of the key features is its high bandwidth, which enables it to carry large amounts of data over long distances. In addition, the fiber is highly resistant to signal attenuation and distortion, which ensures that the data transmitted over the fiber arrives at its destination intact and with minimal errors.
Another essential feature of OM3 Multimode Fiber is its versatility and cost-effectiveness. The fiber is compatible with various industry-standard networking equipment, including switches, routers, and optical transceivers. Additionally, the thread is relatively inexpensive to manufacture, making it an affordable option for many organizations.
OM3 Multimode Fiber has several advantages over other types of fiber optic cabling. One of the key advantages is its ability to transmit large amounts of data at high speeds over long distances. This makes the fiber ideal for data centers, enterprise networks, and other high-speed data communications applications.
However, there are also some potential disadvantages to using OM3 Multimode Fiber. One of the drawbacks is signal attenuation, which can occur when the signal on the fiber degrades over a distance. In addition, there are limitations to the space the thread can transmit data without signal amplification or regeneration.
Despite these potential disadvantages, OM3 Multimode Fiber remains a popular choice for many organizations that require high-speed, reliable data communications. As technology continues to advance, likely, the demand for this type of fiber optic cabling will only continue to grow.
OM4 Fiber is an optical fiber cabling that has been gaining popularity in recent years. It is a multimode fiber cable capable of transmitting data over longer distances, at faster speeds, and with better bandwidth than its predecessor, OM3 Fiber. OM4 Fiber is designed to meet the increasing demand for high-speed data transmission in data centers, LANs, and SANs.
OM4 Fiber is a type of multimode fiber that features a higher bandwidth and supports Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology. It is designed to transmit data over distances of up to 550 meters at speeds of 10 Gbps or 400 meters at 40 Gbps, making it the perfect choice for high-speed data transmission in data centers and other high-density environments.
One of the critical characteristics of OM4 Fiber is its high bandwidth. This fiber cable can support data transmission at a bandwidth of 4700 MHz*km, almost twice that of OM3 Fiber. OM4 Fiber is also optimized for WDM technology, allowing the cable to transmit multiple signals over different wavelengths simultaneously. OM4 Fiber can support more data traffic while maintaining high data rates and low latency.
OM4 Fiber is the successor to OM3 Fiber, offering several significant advantages over its predecessor. One of the main advantages of OM4 Fiber is that it supports higher data rates over longer distances. While OM3 Fiber can transmit data at speeds of 10 Gbps over distances of up to 300 meters, OM4 Fiber can share the same amount of data at the same pace over distances of up to 550 meters. Additionally, OM4 Fiber can support data rates of 40 Gbps over distances of up to 400 meters, which is impossible with OM3 Fiber.
OM4 Fiber is ideal for various applications, including data centers, LANs, and SANs. It is commonly used in high-density environments where there is a need to transmit large amounts of data over long distances at high speeds. OM4 Fiber is also ideal for use in the backbone of networks, where it can provide high bandwidth connections between switches and routers.

OM5 fiber is a type of multimode fiber specifically designed to enhance high-speed data transmission over short and medium distances, up to 3km. Compared to other multimode fibers, OM5 has a broader range of wavelengths, which enables it to offer higher bandwidth capabilities. OM5 is also designed to work seamlessly with traditional multimode fibers and is backward compatible with OM4 and OM3 cabling, which is a significant advantage for users upgrading their systems.
OM5 fibers are available as 50-micron diameter cores with Aqua-colored jackets. They can support a range of wavelengths from 850nm to 953nm and have an increased bandwidth of 50 GHz over longer distances than other multimode fibers. Additionally, OM5 fibers support a range of applications, including Ethernet, Fiber Channel, InfiniBand, and others. Because of its higher bandwidth capabilities, OM5 fiber can achieve data transmission speeds of up to 100Gbps or even 400Gbps in duplex mode.
OM5 fiber has a more complex fiber structure with a graded index (GI) profile that helps reduce modal dispersion and increase the fiber’s bandwidth. In addition, OM5 fibers can be used with mode conditioning patch cables, which minimize signal distortion and help improve the fiber’s transmitted bandwidth.
OM5 fibers offer advantages over other multimode fibers, including cost-effectiveness, compatibility with existing multimode fiber cabling, and increased capacity and flexibility. OM5 fibers are more affordable than single-mode fibers but provide high transmission speeds and bandwidth capabilities. They are also compatible with OM3 and OM4 cabling, allowing seamless upgrades without needing expensive equipment replacements.
OM5 fiber’s increased bandwidth and distance capabilities make it an excellent choice for high-performance data centers, campuses, buildings, and other environments that require intensive network demand. Its ability to support different applications and data transmission speeds is a significant advantage for users in various industries. OM5 fiber is also future-proof, supporting future upgrades and bandwidth demands.
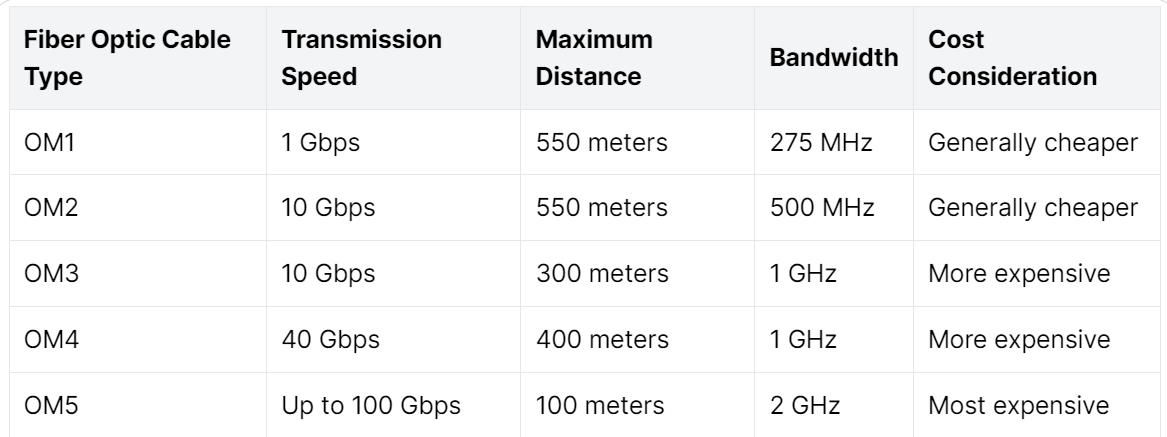
A fiber optic cable’s transmission speed and distance refer to its ability to carry data at high rates over long distances. OM1 fiber optic cables have a transmission speed of 1 Gbps and can transmit data up to 550 meters. OM2 cables offer a faster transmission speed of 10 Gbps and support data transmission up to 550 meters. On the other hand, OM3 cables have a transmission speed of 10 Gbps and can support data transmission up to 300 meters. OM4 fiber optic cables offer an enhanced rate of 40 Gbps and support data transmission up to 400 meters. Finally, OM5 cables are optimized for short-range link lengths of 100 meters but can support faster speeds of up to 100 Gbps.
Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data transmitted through a cable in a given time frame. OM1 cables offer a maximum bandwidth of 275 MHz, while OM2 cables have a bandwidth of 500 MHz. On the other hand, OM3 and OM4 cables support a maximum bandwidth of 1 GHz, while OM5 fiber optics have the highest bandwidth of 2 GHz. To understand this in layperson’s terms, bandwidth can be compared to a pipeline that carries data- the more comprehensive the channel, the higher the amount of data that can pass through at a given time.
The cost of fiber optic cables is a significant consideration in choosing the right option. The price of OM1 and OM2 cables is usually lower compared to OM3, OM4, and OM5 cables, which have higher performance capabilities. Additionally, newer technologies such as OM4 and OM5 can be more expensive due to their unique features. The adoption of fiber optic cables varies based on the specific application, with some industries opting for higher-performance options while others may prioritize cost-effectiveness. For instance, OM3 and OM4 are used in high-performance applications such as data centers, while OM1 and OM2 cables are preferred for shorter distances or lower data rates.
In conclusion, the differences between OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5 are significant, and the choice of a specific fiber optic cable should be based on the required transmission speed and distance, bandwidth requirements, cost, and application. As technology advances, it is essential to stay informed on the latest fiber optic cable options to make informed choices that meet specific requirements.

One of the crucial factors to consider when selecting a multimode fiber type is the distance the signal needs to travel. Multimode fibers are available at various lengths, ranging from 220 to 550 meters. Choosing the right fiber type can help avoid signal loss and interference issues that degrade network performance. If the distance is short and the data rate is low, then OM1 (62.5 µm) fiber is a suitable choice. If the space is longer, up to 500 meters, then OM3 (50 µm) fiber is recommended because of its superior bandwidth.
Data rate is another factor when choosing the right multimode fiber type. The higher the data rate, the more bandwidth is required to avoid signal distortion and loss. OM3 (50 µm) multimode fiber can transmit at speeds of up to 10 Gbps at distances up to 300 meters, while OM4 (50 µm) can transfer at speeds of up to 100 Gbps at distances up to 150 meters.
The connector type is another crucial factor to consider when selecting multimode fiber. Various connectors are available, such as LC, SC, ST, and MPO. However, choosing the correct connector type is critical to ensure compatibility with the network equipment and devices it will use. LC and SC are the most popular connector types for multimode fiber because of their compact design and compatibility with most network devices.
While deploying multimode fiber, several best practices must be followed to achieve the desired network performance. First, ensure the fibers are appropriately labeled and labeled throughout the installation process. This helps in troubleshooting and maintenance in the future. Second, avoid sharp bends in the thread, which can cause signal loss and attenuation. Third, use high-quality splicing and termination materials to minimize signal loss and ensure proper connectivity.
While there is no ideal type of multimode fiber for all applications, the differences between OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5 can often make a big difference in how people use them. There have been considerable advancements in the evolution of fiber optics over the years,, enabling consumers to access more excellent capabilities than was previously available. It is currently being used widely in many industries like telecoms, data centers, and consumer homes. The need for faster data transfer speeds and increased bandwidth requirements will only ever grow more so as technology increases its reach. With that being said, it is safe to say that what’s important now is understanding the differences from one multimode type to another, and staying up-to-date with new trends as soon as possible. If you want to stay ahead of the curve, familiarizing yourself with today’s current industry standards will ensure you are ready for any future developments that may come your way!
Recommend Reading: What is OM3 Multimode Fiber?
A: OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5 are different types of multimode fiber that vary in bandwidth capabilities and maximum transmission distances. OM1 fiber has a core size of 62.5 microns and can support network speeds of up to 10 Gbps over short distances. OM2 fiber also has a 62.5-micron core, but it offers higher bandwidth and can support network speeds of up to 10 Gbps over longer distances than OM1. OM3 fiber has a smaller core size of 50 microns and can help network speeds of up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 300 meters. OM4 fiber, explicitly developed for high-speed data transmission, has a core size of 50 microns and can support network speeds of up to 40 Gbps over distances of up to 400 meters. Finally, OM5 is the newest type of multimode fiber with a core size of 50 microns and is designed for wideband multimode fiber applications, supporting multiple wavelengths to support higher-capacity networks.
A: The main difference between single-mode fiber and multimode fiber lies in the size of the core, which is the central part of the fiber optic cable that carries the light signals. Single-mode fiber has a much smaller core size, usually around 9 microns, allowing for transmitting a single ray of light or mode. This results in longer transmission distances and higher bandwidth capabilities than multimode fiber. On the other hand, Multimode fiber has a larger core size, typically ranging from 50 to 62.5 microns. It can transmit multiple rays of light, or modes, simultaneously, but over shorter distances and with lower bandwidth capabilities compared to single-mode fiber.
A: Multimode fiber offers several advantages in specific network applications. It is more affordable than single-mode fiber, making it a cost-effective choice for short-distance and lower bandwidth requirements. It is also easier to install and terminate, which can reduce installation time and costs. Additionally, multimode fiber supports using lower-cost LED light sources instead of more expensive laser-based light sources used in single-mode fiber systems. Overall, multimode fiber is a versatile and reliable option for various network setups.
A: OM3 multimode fiber can support network speeds of up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 300 meters. Its higher bandwidth and dispersion characteristics make it suitable for use in data centers, enterprise networks, and other applications that require high-speed data transmission over intermediate distances.
A: OM4 multimode fiber offers improved performance compared to OM3. It can support network speeds of up to 40 Gbps over distances of up to 400 meters, providing better bandwidth and longer transmission distances than OM3 fiber. OM4 fiber is especially suitable for applications that require higher data rates and longer link lengths, such as high-performance computing, data centers, and backbone infrastructure.
A: OM1 and OM2 multimode fibers have the same core size of 62.5 microns but differ in bandwidth capabilities and transmission distances. OM2 fiber provides higher bandwidth and can support network speeds of up to 10 Gbps over longer distances than OM1 fiber, which is limited to shorter transmission distances. OM2 fiber is commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and other applications that require higher data rates and longer link lengths.
A: OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers are commonly used in optical fiber networks due to their high bandwidth capabilities and ability to support high-speed data transmission over intermediate distances. These fibers are widely deployed in data centers, enterprise networks, and other applications that require reliable and efficient optical communication.
A: OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers differ in bandwidth and maximum transmission distances. OM3 fiber has a core size of 50 microns and can support network speeds of up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 300 meters. OM4 fiber, on the other hand, has the same core size but offers increased bandwidth, enabling network speeds of up to 40 Gbps over distances of up to 400 meters. OM4 fiber is designed for high-performance applications requiring higher data rates and longer link lengths than OM3.
A: OM3/OM4 and OM5 multimode fibers differ in their bandwidth and range of supported wavelengths. Both OM3/OM4 and OM5 fibers have a core size of 50 microns, but OM5 fiber is designed explicitly for wideband multimode fiber applications. OM5 fiber can support multiple wavelengths, allowing higher capacity networks and improved spectral transmission. It is suitable for applications that require increased bandwidth and support for emerging technologies like wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) and vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers (VCSELs).
A: There are different fiber connectors for single-mode and multimode fibers. Single-mode fiber connectors have a narrower ferrule size to align with the smaller core size of single-mode threads. Common single-mode fiber connectors include LC (Lucent Connector) and SC (Subscriber Connector). Multimode fiber connectors, on the other hand, typically have a larger ferrule size to accommodate the larger core size of multimode fibers. Examples of multimode fiber connectors include ST (Straight Tip) and SC connectors. It is essential to use the appropriate connector type for the thread to ensure proper alignment and optimal performance.