Multimode fiber is suitable for many applications when transmitting data over a limited distance. Multimode fiber is widely used in data centers and local area networks (LANs) because it can transmit multiple signals over the same cable. Multimode fiber uses light waves to transfer data, allowing for high speeds. In a multimode fiber cable, the weak signals travel down the line’s core, bouncing off the cladding and back towards the body until they reach the end of the line.
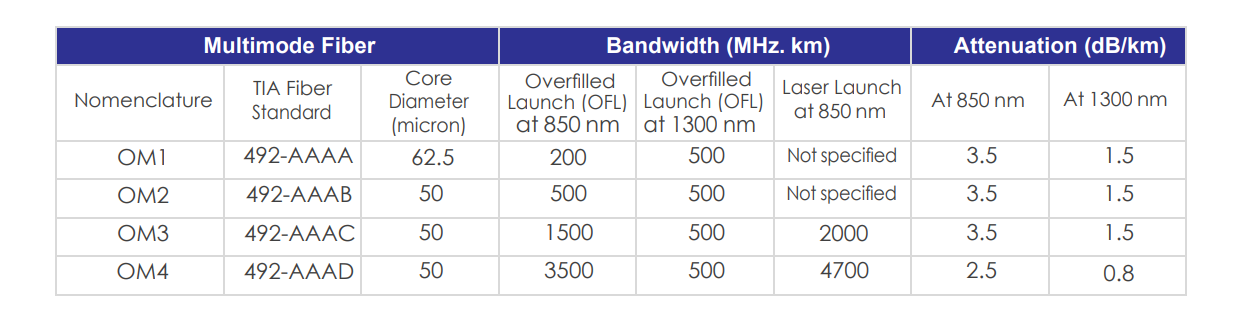
Multimode fiber has a large core diameter, which allows multiple modes or light paths to propagate through the body. This means that the different light paths travel over the same distance but have different lengths, which can cause some distortion and dispersion in the signal. This effect is known as modal dispersion. Multimode fiber is categorized into several types based on performance, including OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5.
OM3 multimode fiber has a core diameter of 50 micrometers and can support data transmissions up to 10 Gigabits per second (Gbps) at 300 meters. OM3 fiber has a 2000 megahertz bandwidth, supporting longer link lengths than OM2 fiber. This type of fiber is ideal for transmitting data over short distances, such as within a data center or building. It is commonly used for high-speed applications like backbone cabling and storage area networks.
OM4 multimode fiber is similar to OM3 fiber in core diameter but has a higher bandwidth and can support longer distances. OM4 fiber has a 4700 megahertz bandwidth, double that of OM3 fiber. OM4 fiber can help data transmissions up to 10 Gbps at 550 meters and 100 Gbps at 150 meters. It also offers better performance over longer distances compared to OM3 fiber. OM4 fiber is commonly used in 40 Gbps and 100 Gbps Ethernet applications in data centers.
Bandwidth measures the amount of data transmitted over a given period. OM4 fiber has a higher bandwidth than OM3 fiber due to its design and construction. OM3 fiber has a bandwidth of 2000 megahertz, while OM4 fiber has a bandwidth of 4700 megahertz. The higher bandwidth of OM4 fiber allows it to support longer transmission distances and higher data rates.
The transmission distance of multimode fiber depends on its bandwidth and the speed of the data being transmitted. OM3 fiber can support data transmissions up to 10 Gbps at 300 meters, while OM4 fiber can support data transmissions up to 10 Gbps at a distance of 550 meters. OM4 fiber can also help data transmissions up to 100 Gbps at a distance of 150 meters. The transmission distance of each type of fiber varies depending on the specific application and network requirements.
Choosing the appropriate fiber type ensures high-performance data transmission for applications like data centers and LANs. OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers are two commonly used fiber types with unique features and characteristics. OM3 fiber can support short-distance transmission at high speeds, while OM4 fiber is suitable for longer transmission distances at higher speeds. Determining which type of fiber to use depends on each application’s network requirements, data transmission distance, and bandwidth requirements.
Before diving into a detailed comparison of OM3 and OM4 fiber optic cables, it is essential to understand the critical factors that can influence your decision. These factors include bandwidth requirements, distance limitations, budget, and applications. OM3 and OM4 cables have similarities in design, including core diameter, cladding diameter, and color-coded jackets. However, OM4 cables have improved attenuation rates and reach longer distances than OM3 cables. Therefore, if you require high bandwidth capacity and extended reach, OM4 cables would be an ideal choice, but you need to consider the cost implications.
OM3 and OM4 fiber optic cables have different performance characteristics. OM3 cables have a bandwidth capacity of 10 Gbps per channel at 300-meter distances, while OM4 cables can achieve 10 Gbps at 550-meter distances. OM4’s lower attenuation rate allows for extended reach, resulting in significantly higher bandwidth capacity. OM4 cables can support 40 Gbps and 100 Gbps data rates over longer distances than OM3 cables, making them ideal for data centers and future optical networks.
Compatibility with existing infrastructure is a significant consideration when upgrading or installing fiber optic cables. OM3 and OM4 cables are backward compatible with OM1 and OM2 cables, which have a smaller core diameter, making them ideal for multimode applications. It is worth noting that OM4 cable can support higher transmission rates, but to enjoy the benefits, your equipment must be OM4-compatible.
Cost is often a decisive factor when choosing between OM3 and OM4 fiber optic cables. OM3 cables are less expensive than OM4 cables but offer lower performance and shorter transmission distances. OM4 cables, on the other hand, have higher performance characteristics, such as extended reach and higher bandwidth capacity, making them more expensive than OM3 cables. It is essential to consider your budget and the performance requirements of your application when choosing between the two.
In addition to cost, you should also consider the future-proofing capabilities of your fiber optic cable. OM3 cables can support up to 10 Gbps transmission rates, while OM4 cables can support up to 100 Gbps and beyond, making them an ideal choice for future applications. If you are considering upgrading your infrastructure, investing in OM4 cables would be a cost-effective choice as you will not need to replace them altogether when upgrading your network.
Modal bandwidth refers to the maximum data-carrying capacity of an optical fiber. It determines the data transmission rate and the range of the fiber optic communication system. The fiber optic link’s efficiency and integrity depend on the fiber’s modal bandwidth. The system can operate at higher speeds and longer distances with higher modal bandwidth. Modal bandwidth also determines the number of modes that can propagate in the fiber and affect the dispersion of the optical signal.
OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers are fiber optic cables for high-speed data transmission in local area networks (LANs), data centers, and backbone networks. OM4 has a higher modal bandwidth than OM3, meaning it can transmit data over longer distances and at higher speeds. The modal bandwidth of OM3 is 2000 MHz/km, and that of OM4 is 4700 MHz/km. OM4 is backward compatible with OM3, which means OM4 cables can replace old OM3 cables and work seamlessly.
Modal dispersion is a phenomenon where the signals transmitted through the fiber optic cable disperse over time due to the different propagation times of various modes. It causes a temporal spreading of the optical signal, which reduces bandwidth and limits the data transmission rate. If not managed, modal dispersion can lead to errors or even communication link failure. To minimize modal dispersion, fiber optic cables with higher modal bandwidth, such as OM4, are used to improve performance.
Laser-optimized OM3 and OM4 multimode fibers are designed to enhance fiber optic communication performance by reducing modal dispersion effects. They achieve this by using a more focused laser source with a narrower spectral width and increased power to minimize modal dispersion. Laser-optimized fibers also allow for higher speeds and more extended distances, improving the efficiency of fiber optic networks. Laser-optimized OM3 and OM4 fibers offer up to 40% higher bandwidth and enhanced stability and reliability than traditional multimode fibers.
The bandwidth of a fiber optic cable plays a crucial role in determining its suitability for specific applications. In data centers where high-speed data transfer is critical, OM4 cables are preferred due to their higher bandwidth. In contrast, OM3 cables are sufficient and more cost-effective in short-distance applications such as LANs. The bandwidth requirements also vary depending on the type of data transmitted, with video and multimedia applications requiring higher bandwidth than simple data transfer. Therefore, selecting a suitable fiber optic cable with proper bandwidth is essential to meet the application’s specific requirements.

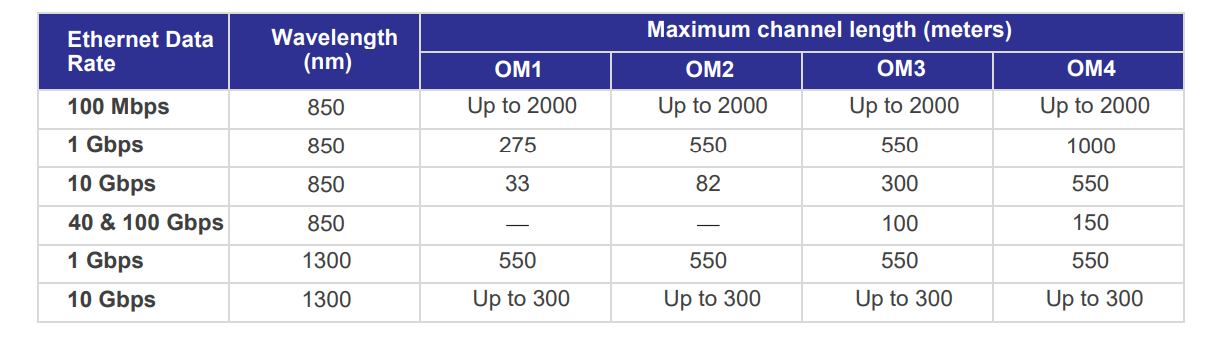
The distance that multimode fiber can transmit data depends on various factors, including the type of fiber, the bandwidth, the connector type, and the network design. For example, OM1 fiber has a core diameter of 62.5 microns and a maximum transmission distance of up to 550 meters for Ethernet applications. OM2 fiber has a core diameter of 50 microns and can transmit data up to 2 kilometers at 10 Gbps. OM3 and OM4 fibers have even larger cores, with diameters of 50 and 62.5 microns, respectively, and can transmit data up to 300 and 550 meters at 10 Gbps speeds.
OM3 multimode fiber is a high-bandwidth fiber with a core diameter of 50 microns. It can support 10 Gbps Ethernet connections up to 300 meters long, making it ideal for high-speed data center applications. However, the maximum transmission distance of OM3 fiber can be affected by factors such as attenuation, dispersion, and modal noise, which can degrade signal quality and reduce transmission performance. To overcome these issues, it is essential to use high-quality connectors, patch cords, and network equipment optimized for OM3 fiber.
OM4 multimode fiber is a newer fiber type with a larger core diameter of 62.5 microns. It is designed to support higher-bandwidth applications and can transmit data up to 550 meters at 10 Gbps speeds. However, the extended transmission distance of OM4 fiber is due to its lower attenuation and dispersion values, which allow it to maintain signal quality over longer distances. Compared to OM3 fiber, OM4 fiber has a higher bandwidth and lower modal noise, further enhancing its transmission performance.
Attenuation is a critical factor affecting multimode fiber’s transmission distance and performance. It measures signal loss over a space caused by absorption, scattering, and reflection. OM3 and OM4 fibers have different attenuation characteristics, with OM4 fiber having a lower value than OM3 fiber. OM4 fiber can transmit data over longer distances without significant signal loss, making it more suitable for high-bandwidth applications requiring longer transmission distances.
Several other factors can affect the transmission distance of multimode fiber, including connector type, patch cords, network design, and signal quality. For example, low-quality connectors or excessive patch cords can increase attenuation and reduce transmission distances. Similarly, network design can play a role in determining the overall transmission performance of multimode fiber, with factors such as backplane bandwidth, switch port buffers, and packet latency affecting signal quality. To ensure optimal transmission performance, it is essential to use high-quality equipment and follow best practices for multimode fiber installation and maintenance.

OM3 multimode fiber is the older of the two fiber types, and it supports transmission speeds of up to 10 Gbps for distances of up to 300 meters. OM3 fiber optic cables are a popular choice due to their economical cost, making them an ideal solution for many enterprise networks. However, OM3 fiber optic cables have a lower range and data transmission rate than OM4 fiber, requiring multiple repeaters for longer distances.
OM4 multimode fiber is newer than OM3 and offers higher bandwidth and faster data transmission rates of up to 40 Gbps. The primary benefit of OM4 fiber optics is that it can transmit data over longer distances of up to 550 meters without repeaters. However, compared to OM3, OM4 fiber optic cables have a higher cost due to their manufacturing complexity, making them less economical for smaller networks and shorter distances.
When comparing the cost implications of OM3 and OM4 fiber optic cables, the primary consideration is the length of the wires required. For shorter distances of up to 300 meters, OM3 fiber optic cables remain a more cost-effective solution. However, if longer distances of up to 550 meters are required, OM4 fiber optic cables become the more economical choice due to their more extended range and fewer repeaters required.
As data transmission speeds continue to increase, OM4 fiber optic cables will likely become the more prominent fiber type due to their higher bandwidth and extended range capabilities. However, for current applications that require shorter distances and lower transmission speeds, OM3 fiber optic cables still offer a suitable solution at a lower cost. Choosing a fiber type that can be upgraded in the future as network requirements grow is essential.
OM3 and OM4 fiber optic cables are backward compatible with older equipment designed for OM1 and OM2 fiber types. However, if fiber optic cables are being upgraded from OM1 or OM2 to OM3 or OM4, it is necessary to change the multimode fiber optic transceivers and switches to ensure compatibility. Choosing a compatible fiber type that will work well with existing equipment is essential for proper network optimization.

A: OM3 and OM4 are multimode fiber types, but OM4 has a higher bandwidth and can support longer distances than OM3.
A: OM3 and OM4 refer to the different versions of multimode fiber optic cables.
A: Multimode fiber is an optical fiber that allows multiple light modes or paths to travel simultaneously. It can transmit data at relatively shorter distances than single-mode fiber.
A: The modal bandwidth refers to the capacity of a fiber cable to carry multiple modes of light signals simultaneously.
A: OM3 fiber has a higher bandwidth and can support longer distances than OM1 and OM2 fibers.
A: OM2, OM3, and OM4 are versions of multimode fiber with varying bandwidths and distance capabilities. OM2 has a lower bandwidth than OM3 and OM4, while OM4 has the highest bandwidth and can transmit data over longer distances.
A: Yes, OM3 and OM4 fibers are generally compatible. However, using the same type of fiber is recommended for optimal performance.
A: OM4 fiber optic cables are commonly used in high-speed data transmission applications, such as data centers, enterprise networks, and telecommunications networks.
A: OM3 fiber can support distances of up to 300 meters for 10 Gigabit Ethernet, while OM4 fiber can support distances of up to 550 meters for the same data rate.
A: OM4 fiber provides higher bandwidth, longer transmission distances, and better performance than lower-grade fibers like OM1 and OM2.