Switches are electronic devices designed to connect multiple devices in a network or system and direct the data flow between them. Put, switches are the gatekeepers of data, ensuring that information gets to its destination accurately and efficiently. Depending on their features, switches can manage different types of data traffic, such as voice, video, and data packets, making them an essential component of modern communication networks.
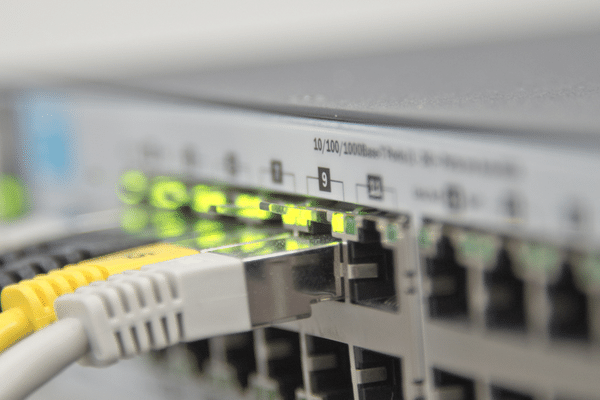

To better comprehend the inner workings of switches, it’s essential to understand their essential components and how they function. Controls typically consist of a central processing unit (CPU), multiple ports, and, in some cases, storage memory for configuration settings. The ports are where devices are connected, and the CPU analyzes incoming data packets, determining which port should transmit each box to its intended destination. Switches can be configured and managed remotely or locally, depending on their model and features.
Switches operate by forwarding data packets between ports based on the destination address. Once a controller receives data, it examines the source and destination addresses to determine where it needs to be directed. For instance, switches can divide bandwidth based on QoS settings, ensuring that high-priority data (such as streaming video or voice calls) gets transmitted with the best quality possible. Switches also play a crucial role in automation systems, where they control the flow of information between sensors, controllers, and actuators. In manufacturing, switches help coordinate the movement of robots and other machinery, ensuring that tasks are performed safely and efficiently.
Networking is perhaps the most evident and widespread application of switches, with millions of businesses and individuals relying on these devices to connect to the internet and other networks. Controls help organizations manage network congestion, improve reliability, and boost security. In automation systems, buttons enable devices and sensors to communicate with one another, helping to automate processes, increase efficiency, and reduce costs. Industrial controllers are designed to withstand harsh environments and operate in hazardous locations.
Switches play a critical role in modern communication networks, enabling data to be transmitted quickly and reliably. They help organizations manage increasing data traffic and prioritize high-priority applications while ensuring optimal network performance. Besides, switches are easy to install and operate, making them an ideal networking solution for small and large enterprises. Whether in networking, automation, or electronics, switches are essential components that offer a versatile and resilient solution for managing data traffic and optimizing communication systems.

Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology that enables transmitting electrical power and data over a single Ethernet cable. It is commonly used in networking and telecommunications to power devices that need low voltage, such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points. PoE eliminates the need for separate power cables, simplifying installation and reducing costs.
PoE works by injecting electrical power onto an Ethernet cable, along with data signals, from the power sourcing equipment (PSE) to a powered device (PD). The PSE can be a network switch or a midspan device, whereas the PD can be any PoE-enabled device. The PSE detects whether the PD is PoE-compatible and provides power up to a specific wattage over the Ethernet cable, based on its classification. PoE requires two wires in an Ethernet cable, whereas PoE+ and PoE++ need all four teams.
PoE, PoE+, and PoE++ differ in the amount of power they can provide to a powered device over an Ethernet cable. PoE can provide up to 15.4 watts of power, PoE+ can provide up to 30 watts, and PoE++ can provide up to 100 watts. Moreover, PoE+ and PoE++ use all four pairs in an Ethernet cable, enabling more efficient power transmission and reducing power loss. PoE++, also known as 4PPoE, stands for four-pair Power over Ethernet. Additionally, PoE+ and PoE++ support features such as power priority, which enables power to be allocated to critical devices first, and device discovery, which allows the PSE to to detect and authenticate connected devices.
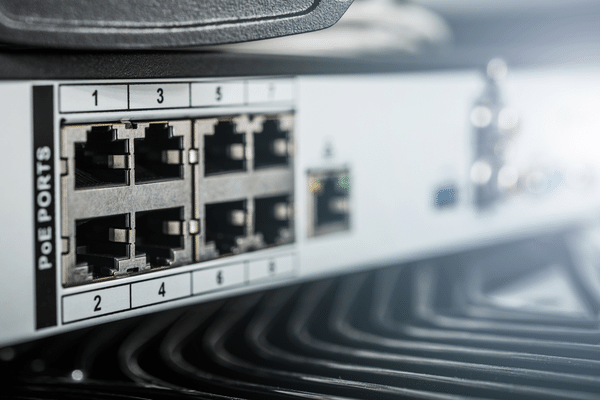

One of the most crucial factors to consider when selecting a PoE switch is its power budget. A power budget refers to the total power the controller can provide to connected devices. Therefore, it’s crucial to determine the power requirements of the devices connected to the controller and select a button with a power budget that can accommodate those needs.
Another factor to consider is the number of ports that the switch has. A port represents an Ethernet connection point. Therefore, choosing a PoE switch with the correct number of ports is crucial. For example, a controller with 24 ports would be suitable for small- to medium-sized businesses, while a switch with 48 ports would be suitable for a more extensive enterprise.
Switch management features are also crucial when choosing a PoE switch. Managed switches provide greater control over the network than unmanaged switches. Therefore, it’s essential to consider whether the controller needs to support advanced features such as VLANs, QoS, and port mirroring or if a more straightforward unmanaged switch will suffice.
PoE switches have a wide range of applications in different industries and contexts. For example, they are commonly used in surveillance systems for powering IP cameras and providing network connectivity. PoE switches are also used in the healthcare industry to power medical devices such as telemedicine and bedside monitors. Additionally, PoE switches are utilized in Wi-Fi access points, VoIP phones, and point-of-sale systems.
There are three main types of PoE switches: unmanaged, managed, and fully managed. Unmanaged switches are the most basic and provide only basic network connectivity. Managed switches offer more control over the network and are typically used in more extensive networks. Fully managed switches provide the most excellent control over the web and are suitable for large enterprises with complex networks. Additionally, PoE switches are available in different classes that determine the amount of power they can provide. Class 1 provides the least power, while Class 4 provides the most energy.

PoE switches offer increased flexibility and scalability by enabling the deployment of network devices in locations that may lack access to power outlets. This makes it easier to install and manage network devices in various areas, including warehouses, parking lots, and outdoor spaces, without additional power infrastructure. PoE switches also provide up to 100 meters of deployment distance, enabling network devices to be installed in more accessible locations. Moreover, PoE switches offer flexibility and scalability through their simple configuration processes and remote management features.
PoE switches offer a cost-effective solution for network installation and maintenance. One of the primary advantages of PoE switches is their ability to eliminate the need for additional wiring or power outlets. This significantly reduces installation time and costs associated with deploying network devices in remote or underdeveloped areas. Additionally, PoE switches are designed to manage power more efficiently, reducing overall power consumption and cutting energy costs. This translates into significant cost savings over time and contributes to the overall economic feasibility of using PoE switches.
PoE switches streamline installation and maintenance processes through their simple and centralized management systems. Rather than tasking IT personnel with installing and maintaining multiple cables and power outlets, PoE switches allow for a single cable installation optimized for data and power transfer. This also means that network devices can be remotely managed and configured from one central location, saving time and labor costs. Maintenance requirements are also simplified with fewer cables and power outlets to maintain, the need for complex equipment, and the risk of human error.
Recommend reading: The Complete Guide to Different Types of Network Switches for Your Network
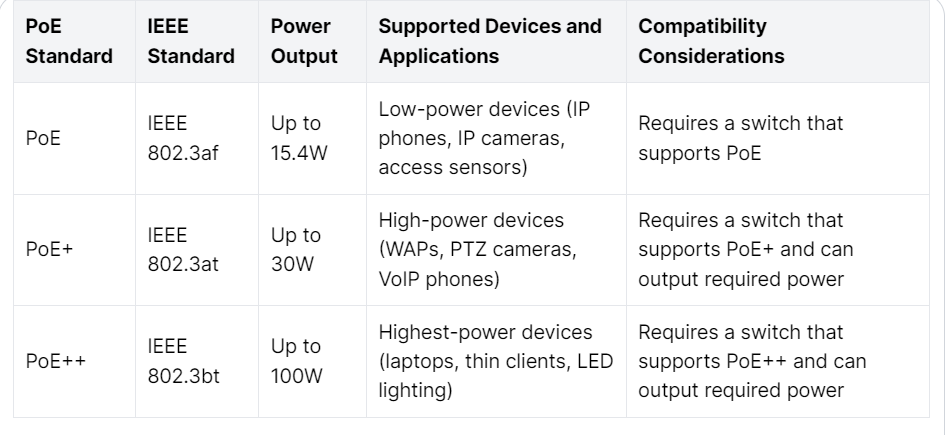
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology that allows network cables to transmit power and data. PoE systems require a power source and a powered device (PD) and are categorized by power output. PoE, PoE+, and PoE++ differ in how much power they can deliver.
PoE provides up to 15.4 watts of power per port and is sufficient for low-power devices such as IP phones and cameras. PoE+ or IEEE 802.3at delivers up to 30 watts, which is ideal for higher-powered devices like wireless access points (WAPs), pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) cameras, and voice-over-IP (VoIP) phones. PoE++, or IEEE 802.3bt, delivers up to 100 watts of power, making it ideal for high-powered devices such as laptops and thin clients.
The devices supported by PoE, PoE+, and PoE++ depend on the power output they can deliver. PoE is suitable for low-powered devices such as VoIP phones, IP cameras, and access sensors. PoE+ is appropriate for high-powered devices like WAPs, PTZ cameras, and video phones. PoE++ is designed for even higher-powered devices such as thin clients, laptops, and LED lighting.
When integrating PoE into an existing infrastructure, compatibility is crucial. PoE devices require a switch that supports PoE and the output of power needed. Incompatibility can result in devices not receiving enough power, leading to system errors and, in some cases, damage to the device. It is essential to ensure that the switch and devices to be used with PoE are compatible.
PoE+ is a good choice for businesses that need to support high-power devices such as WAPs and PTZ cameras while keeping the infrastructure cost-effective. PoE++ is ideal for larger companies or data centers that need to invest even higher-powered devices such as laptops and thin clients. It is essential to ensure compatibility with existing infrastructure before making changes to the system. Overall, the selection of PoE, PoE+, or PoE++ depends on the intended use case, the power requirements of the devices, and compatibility with existing infrastructure.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technologies, such as PoE, PoE+, and PoE++, provide a practical and cost-effective solution for data transmission and power supply across the network infrastructure. These technologies vary in the power they deliver, making them suitable for different devices and applications. PoE is ideal for low-power devices, while PoE+ and PoE++ are more appropriate for high-power and very high-power devices, respectively. It’s also crucial to ensure compatibility of these PoE technologies with your existing infrastructure before adoption. Whether unmanaged or fully managed, PoE switches offer flexibility and scalability, streamlining network installation and maintenance processes. Moreover, they significantly reduce costs by eliminating the need for additional wiring or power outlets while managing power efficiently.
Recommend reading: What Is Poe Switch: Everything You Need to Know

A: PoE, PoE+, and PoE++ are different standards for power over Ethernet. PoE (Power over Ethernet) refers to the IEEE 802.3af standard, which provides up to 15.4 watts of power. PoE+ (Power over Ethernet Plus) refers to the IEEE 802.3at standard, which provides up to 30 watts of power. PoE++ (Power over Ethernet Plus Plus), also known as 802.3bt, provides up to 60 watts of power.
A: Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology that allows for the delivery of electrical power along with data over an Ethernet cable. It eliminates the need for separate power cables, making installing and power network devices easier.
A: PoE switches send power and data over a single Ethernet cable. The PoE switch detects if a connected device supports PoE; if it does, it delivers power accordingly. This simplifies the installation and reduces the number of cables needed.
A: The specifications for PoE, PoE+, and PoE++ are as follows:
A: PoE can power a wide range of devices, including IP phones, wireless access points, network cameras, and IoT devices. It is beneficial in situations where it’s difficult to provide power outlets.
A: The main difference between PoE and PoE+ is the amount of power they provide. PoE offers up to 15.4 watts, while PoE+ offers up to 30 watts. This additional power capacity of PoE+ enables it to support devices that require higher power, such as pan-tilt-zoom cameras and access points with multiple radios.
A: PoE++ provides even more power than PoE+ and can deliver up to 60 watts of power. This makes it suitable for powering devices with high power requirements, such as high-performance access points and PTZ cameras with heaters and blowers.
A: Not all switches support all types of PoE. Some buttons may only support PoE, while others may support PoE+ or PoE++ as well. It is essential to check the specifications of a button to ensure it supports the desired type of PoE.
A: PoE has a wide range of applications, including powering IP phones in offices, providing power to wireless access points in large-scale networks, powering network cameras for surveillance systems, and enabling connectivity for IoT devices.
A: Industrial PoE switches are specifically designed for use in harsh environments, such as industrial settings, outdoor installations, or areas with extreme temperatures. They are built to withstand rugged conditions and provide reliable power and data transmission.