What is Fiber Color Code, and Why is it Important?
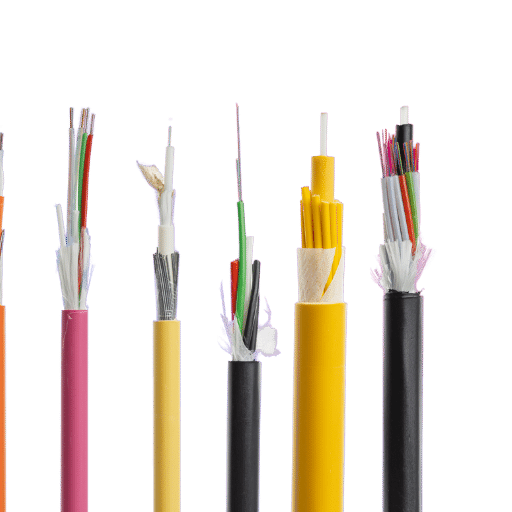

Fiber Color Code (FCC) is a standardized method used to identify and organize optical fibers in a cable. This system employs distinct colors to label individual fibers, tubes, and groups in a structured and sequential manner, aiding in the efficient management and maintenance of complex fiber optic networks. The importance of the FCC lies in its ability to prevent confusion and errors during network setup or troubleshooting. It facilitates quick identification of different fibers, ensuring proper connections, thus maintaining the integrity of the network, reducing downtime, and enhancing overall efficiency.
Understanding the basics of fiber color coding
In understanding the basics of fiber color coding, there are several vital points to be aware of:
- Standard Color Coding: The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) has defined a traditional color coding system for fiber optics. The sequence starts with Blue, Orange, Green, Brown, Slate, White, Red, Black, Yellow, Violet, Rose, and Aqua. This sequence is followed repeatedly for larger fiber counts.
- First and Second Level of Color Coding: The first level of color coding applies to the fiber itself. The second level applies to the 12-fiber group or the tube holding the threads. Each 12-fiber group uses the same color sequence as the fibers.
- Super Units: For fiber counts above 144, excellent units are used. These are bundles of tubes, typically assembled in groups of six or twelve. Each amazing team is bound by a specific color based on the color code sequence.
- Loose Tube Cables and Ribbon Cables: In flexible tube cables, each fiber is covered by a color-coded plastic tube. In ribbon cables, each thread in the ribbon has a printed number for identification, while the ribbons themselves are color-coded.
- Importance of Consistency: It’s crucial to maintain consistency in color coding across the entire network infrastructure. Any deviation can lead to confusion and potential errors during system configuration or maintenance.
The significance of fiber color code in identifying cables
The importance of fiber color coding in identifying lines extends across multiple aspects of telecommunications infrastructure management:
- Speedy Identification: The color coding of the fibers enables quick and easy identification of individual fibers within a string. This can significantly reduce time spent on manual sorting and identification during installation or maintenance activities.
- Reduced Errors: Consistency in color coding reduces the risk of errors during cable installation and maintenance. Mistakes can lead to network downtime or even damage to the infrastructure, resulting in financial loss and operational disruption.
- Efficient Troubleshooting: In the event of a network failure or disruption, color coding enables efficient and accurate identification of the problem fiber. This can dramatically speed up the troubleshooting process and minimize network downtime.
- Scalability: The color coding system is designed to accommodate large fiber counts, making it scalable for future network expansions. This prevents the need for retraining or introducing new color schemes as the network grows.
- Universal Standardization: The adherence to an internationally recognized standard, such as the TIA color code, ensures that the color coding remains consistent across different regions and organizations. This is particularly beneficial for multinational companies that operate data centers in other locations.
How fiber color code aids in quick recognition of fiber optic cables
The fiber color code plays a crucial role in the swift recognition of fiber optic cables, particularly in densely wired environments. Each fiber in a multi-fiber line is encased in a uniquely colored buffer, assigned according to the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) standard. This color code system allows technicians to quickly differentiate individual fibers within a cable, thereby simplifying tasks like network installations, troubleshooting, and maintenance. The use of distinct colors reduces the likelihood of fiber misidentification, which can lead to network performance issues or accidental cross-connection. Essentially, the fiber color code serves as a visual language, enhancing operational efficiency and accuracy in the management of fiber optic infrastructure.
Importance of maintaining a consistent color code system
Maintaining a uniform color code system in a fiber optic infrastructure is vital for several reasons:
- Efficiency: A uniform color code system aids in quickly identifying and distinguishing between different cables, which can significantly save time during installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance.
- Accuracy: Consistency in color coding lessens the risk of mistakes, preventing potential damage or performance issues caused by incorrect cable connections.
- Safety: Adhering to a consistent color code system can ensure safety by correctly identifying different cables and their functions, thereby minimizing the risk of accidents.
- Training: A standardized, consistent color code system simplifies the training process, as technicians only need to learn and remember one set of codes.
- Interoperability: Consistency in color codes promotes interoperability between different departments, companies, or even countries, especially if everyone adheres to the same international standard. This can be particularly beneficial in collaborative or shared environments.
Applications of fiber color code in cable management and installations
The fiber color code system proves its utility in several areas of cable management and buildings:
- Cable Identification: By adhering to a standardized color code, technicians can easily distinguish between different cables, streamlining the identification process during installation or maintenance.
- Buffer Tube Recognition: In multi-fiber cables, each buffer tube is color-coded, making it easier to identify individual lines and their corresponding fibers.
- Fiber Tracing: Color coding allows for efficient fiber tracing, simplifying the process of tracking a fiber’s path from start to end.
- System Classification: Color codes are often used to differentiate between systems or subsystems within a more extensive network infrastructure, enhancing organization and management.
- Fault Detection: By simplifying identification and tracing, color codes expedite the process of detecting and fixing faults in a cable network.
- Safety Compliance: The use of color codes can indicate different safety levels or precautions required, assisting in the prevention of accidents or mishandling.
Remember, the utility of a fiber color code system in cable management and installations largely depends on maintaining consistency and adhering to set standards.
How to Identify and Interpret Fiber Color Codes
Deciphering the color codes of fiber optic cables
Deciphering color codes in fiber optic cables is a straightforward process once you familiarize yourself with the standard color scheme. The Universal Color Code, adopted by most manufacturers, follows a 12-color sequence: Blue, Orange, Green, Brown, Slate, White, Red, Black, Yellow, Violet, Rose, and Aqua. This order repeats after the 12th fiber.
For multi-fiber cables, each fiber within a buffer tube follows this color sequence. The buffer tubes themselves are also color-coded, following the same line. The first buffer tube starts with Blue, the second with Orange, and so on.
In ribbon cables, the ribbons follow this 12-color pattern, and fibers within each ribbon are numbered.
Remember, these color standards become more complex when dealing with different types of cables or fibers above 24, requiring a more detailed understanding. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for specific color coding rules and exceptions.
Common fiber color code standards and systems used in the industry
In the fiber optic cabling industry, several color code standards and procedures are in widespread use.
- The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) Standards: TIA-598C is perhaps the most recognized standard, providing guidelines for optical fiber cable color coding. This regulation prescribes both the color scheme and the identification methods for individual fibers, buffer tubes, and ribbon units in a cable.
- The Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) Standards: Similar to TIA, the EIA employs a 25-pair color code scheme traditionally used in telecommunications. It utilizes a combination of five primary colors – White, Red, Black, Yellow, and Violet.
- International Color Code (IEC) Standards: IEC 60304 is an international standard that defines color coding for resistors and capacitors. It is also utilized for fiber optic cables.
Each of these systems offers its distinct advantages, and the choice between them often depends on the specific needs of the network, the nature of the cabling project, and the regulations of the region. Always ensure that you refer to the appropriate standard documentation or consult with a fiber optic professional for accurate information and guidance.
Interpreting connector color codes in fiber optic cables
Just as with fiber optic cables, connectors also follow a color-coding system that helps in identifying and distinguishing different types of connectors and their applications.
- Blue: This color is typically used for connectors attached to Single-Mode fiber, which is designed for long-distance data transmission.
- Green: Green connectors denote APC (Angled Physical Contact) connectors. These connectors are used in high-precision networks as they have a lower return loss.
- Beige or Black: These colors are often used for connectors attached to Multi-Mode fiber, which is designed for short-distance data transmission.
- Aqua or Light Blue: These colors represent connectors of the OM3 or OM4 type, which are used for higher-speed data transmission over a relatively short distance.
These color codes are standardized to ensure consistency across the industry, allowing professionals to identify the type and application of a connector quickly. As always, consult the manufacturer’s documentation or a fiber optic professional for exact details.
Understanding cable jacket color coding and its implications
Fiber optic cable jacket color coding offers a quick and easy way to identify the type of fiber optic cable in use, which is crucial when setting up or maintaining a network. Here are some of the standard color codes for fiber optic cables:
- Yellow jacket: Typically associated with Single-Mode fiber, which is primarily used in long-distance data transmission due to its ability to maintain the integrity of the light signal over great distances.
- Orange or Aqua jacket: These colors usually represent Multi-Mode fiber cables, specifically OM1 and OM2 for Orange and OM3 and OM4 for Aqua. These are designed for short-distance data transmission and are commonly used within data centers or between nearby buildings.
- Green jacket: This color is often used for APC (Angled Physical Contact) armored cables, signifying a higher level of physical protection.
- Violet jacket: This is associated with OM4+ or OM5 Multi-Mode fiber cables, which support higher-speed data transmission over a relatively short distance.
Always remember that while these colors are globally recognized standards, variations may occur. Always check the manufacturer’s documentation to confirm the exact specifications of the cable. Understanding the implications of cable jacket color coding aids in accurate network design and efficient troubleshooting.
Using fiber color code as a guide to identifying fiber types and classifications
The color coding of fiber optic cables extends beyond the outer jacket and also includes the individual fibers within the line. This internal color-coding plays a crucial role in identifying fiber types and classifications. As a rule of thumb, the color sequence starts with blue and progresses in a specific order: blue, orange, green, brown, slate, white, red, black, yellow, violet, rose, and aqua.
Let’s take a closer look at the significance of these internal color codes.
- Blue and Orange fibers: Traditionally used to identify primary and secondary connections, respectively. However, the significance of these colors may vary depending on the specific network configuration and the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Green Fiber: Often signifies the grounding connection.
- Brown and Slate fibers: Commonly used in reserve or for future upgrades.
Moreover, the combination of the outer jacket color and internal fiber color can provide more detailed information about the cable type, mode, and classification. For instance, a cable with a yellow jacket (indicating Single-Mode fiber) containing blue and orange fibers can denote a duplex Single-Mode fiber optic cable.
Remember, color codes are a guide but always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications or the TIA-598C standard (the most recent color-coding standard) to ensure precise identification. Understanding the color code system can significantly simplify network installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Practical Applications and Considerations of Fiber Color Code
Importance of adhering to fiber optics cable color code standards
Adherence to fiber optics cable color code standards is of utmost importance in the design, installation, and maintenance of fiber optic networks.
Firstly, it facilitates easier identification of fibers, hence streamlining the process of connecting and testing them. Proper color coding also drastically reduces the risk of errors during installation, which could otherwise lead to connection issues, performance degradation, or even system downtime.
Furthermore, adhering to standardized color coding ensures compatibility and interoperability across different network systems and components, enhancing the overall efficiency and reliability of the network infrastructure.
Lastly, it enables future network upgrades or expansions to be more accessible, as technicians can readily identify specific cables based on their color. Thus, strict adherence to the TIA-598C standard or specific manufacturer’s color code guidelines optimizes the operational efficiency and longevity of fiber optic networks.
Utilizing fiber color codes for identifying different parts of the fiber optic cable
Fiber optic color codes are used not only for identifying individual fibers but also for identifying different parts of the fiber optic cable.
To begin with, the outer jacket (or sheath) color indicates the type of cable. For instance, yellow typically denotes single-mode line, Orange is used for multimode cables, and aqua signifies OM3 or OM4-type multimode cables. These jacket colors assist in quickly distinguishing different types of wires in a network setup.
Further inside the cable, the strength members (central elements that provide mechanical strength) might also be color-coded.
Finally, within the cable, each fiber is color-coded as per the TIA-598C standard to facilitate easy identification. This color-coding of the threads applies regardless of whether the lines are tight-buffered or loose tube construction.
Thus, understanding these color codes can greatly simplify cable identification during installation and maintenance, enhancing overall network management efficiency.
Implementing color coding for connectors and its impact on connectivity
Color coding of connectors in fiber optic networks is crucial for optimal performance. Different colors indicate the type of cable they are compatible with. Matching the connector color with the appropriate line minimizes errors, reduces signal loss, and improves data transmission efficiency. It also simplifies maintenance and troubleshooting. Color coding enhances overall network connectivity and performance.
Practical considerations for using fiber color codes in different fiber optic installations
Practical considerations should be taken into account when using fiber color codes in fiber optic installations. These include the installation environment, type of installation, complexity of the network, and adherence to industry standards. Considering these factors is crucial for the effective implementation and utilization of fiber color codes.
Challenges and solutions in maintaining accurate fiber color code systems
Maintaining proper fiber color code systems is not without its challenges. However, these can be mitigated with careful planning and the application of practical solutions.
- Fading Colors: Over time and under certain environmental conditions, the colors of fiber optic cables may fade, making it difficult to distinguish between them. One solution is to use high-quality cables with fade-resistant colors, especially for long-term outdoor installations.
- Inconsistent Color Interpretations: Different manufacturers may interpret color standards differently, leading to confusion and potential errors. This can be resolved by strictly adhering to universally accepted industry standards, such as the TIA-598C.
- Training and Human Error: Not everyone involved in fiber optics is familiar with color codes, and there is always a risk of human error. Implementing thorough training programs and regular refresher courses can help ensure all staff members are knowledgeable and up-to-date.
- Complex Networks: As networks become more complex, the need for more detailed color coding systems might be necessary. Systematic planning and the use of advanced color coding systems can facilitate easy identification and prevent errors in these situations.
By addressing these challenges head-on and implementing these solutions, it is possible to maintain an efficient and accurate fiber color code system.
Understanding Different Fiber Types and Their Color Codes
Exploring the color codes for single-mode and multimode fiber optics
Single-mode and multimode fiber optics, two distinct types of optical fiber, employ different color codes for easy differentiation and organization:
- Single-Mode Fiber Optics: These fibers are usually color-coded in yellow. Single-mode fibers are designed to carry light directly down the thread. They are used for long-distance transmission, such as telephony and television networks.
- Multimode Fiber Optics: These are typically orange or aqua color-coded. Multimode fiber allows multiple light signals to pass through at the same time, but each at a different reflection angle. They are commonly used for short distances, such as within a building or on a campus.
Understanding these color codes is essential in the management of fiber optic networks, contributing to their efficient operation and maintenance. These color identifications serve as an industry-standard guide to help prevent errors in fiber optic handling, installation, and troubleshooting.
Interpreting color coding based on the types of fiber used in premises cables
In premises cables, color-coding serves as an essential tool for distinguishing between different types of fibers used. The fiber type and construction of the line significantly determine this color coding system:
- OM1 and OM2 Fiber: These multimode fibers are typically used in premises applications and are traditionally color-coded Orange. They are optimized for operation at the 850nm wavelength and are often employed for distances up to 2 km.
- OM3 and OM4 Fiber: These are laser-optimized multimode fibers used for higher bandwidth applications, typically color-coded in aqua. They operate optimally at 850nm and can carry 10 Gigabit Ethernet over distances up to 300 meters (OM3) or 550 meters (OM4).
- OM5 Fiber: The latest wideband multimode fiber (WBMMF) is usually color-coded in lime green. OM5 fiber is designed to support short wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM), which reduces parallel fiber count by at least a factor of four to allow continued use of just two fibers (rather than eight) for transmitting 40 Gb and 100 Gb Ethernet signals.
- OS1 and OS2 Fiber: Single-mode fibers used in premises applications are usually color-coded yellow. They are designed for long-haul networks, supporting distances of up to 100 km, and are optimized for wavelengths of 1310nm and 1550nm.
Understanding these color codes is crucial as it enables efficient cable management, accurate installation, and troubleshooting, thereby ensuring the smooth operation of the fiber optic network within the premises.
Identifying the color codes and standards for various fiber optic connector types
In fiber optic systems, connectors play an integral role, and they, too, follow color coding standards for easier identification and optimal network performance.
- LC Connectors: Lucent Connectors, commonly known as LC connectors, are often color-coded beige for multimode, blue for single mode, and green for APC (Angled Physical Contact) terminations.
- SC Connectors: Standard Connectors or SC connectors can be identified by their beige color for multimode, blue for single mode, and green for APC terminations.
- ST Connectors: Straight Tip or ST connectors, a common choice for multimode fiber, are typically black.
- FC Connectors: Ferrule Connectors, also known as FC connectors, come in a metallic body with color-coded quick-release nuts – black for multimode, blue for single mode, and green for APC.
Understanding these color codes ensures correct connector identification, facilitating efficient installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of a fiber optic network.
Implications of color coding in identifying fiber types and classifications
Color coding serves as a vital tool in categorizing and identifying fiber types and classifications, playing a pivotal role in the entire lifecycle of a fiber optic network. It aids in the prevention of potential network errors and downtime by ensuring the correct fiber types are being installed and maintained. Furthermore, color coding streamlines the process of network expansion and upgrade, as technicians can easily distinguish between different fibers, eliminating the risk of misconnections. Ultimately, consistent adherence to color coding standards contributes significantly to the overall efficiency, reliability, and performance of fiber optic networks.
Using color codes for quick identification of fiber strands and cable types
Color codes are used to identify fiber strands in a cable, with each color representing a specific strand number. This systematic coding method allows technicians to quickly pinpoint strands, improving the speed and accuracy of fiber identification. The outer jacket of fiber optic cables also follows a color coding system, enabling quick identification of cable types for different network scenarios.
Best Practices and Implementation of Fiber Color Code System
Steps to ensure continuity of color codes throughout a cable run
- Designate Standard Color Code: The first step involves setting a global standard for the color code system to be followed throughout the cable run. This standard should adhere to established industry guidelines.
- Training: Technicians should be adequately trained in the standard color code system. This includes understanding the color representation for each fiber type and strand number, as well as cable types.
- Consistency: Consistency is crucial in maintaining the continuity of color codes. Ensure that the same color codes are used throughout the network.
- Documentation: Proper documentation should be maintained for all fiber optic cables, outlining their color code, type, and location. This facilitates easy reference and troubleshooting.
- Inspection and Audit: Regular review and audit of the fiber optic network should be carried out to ensure adherence to the color code system. This will help identify and rectify any deviations at an early stage.
- Labeling: Use clear and durable labels on all hardware and cable runs. Labels should correctly reflect the color coding system used.
Utilizing color codes for cable jackets to maintain consistency and standards
Utilizing color codes for fiber optic cable jackets helps maintain consistency and standards across networks. The color acts as a visual identifier for different cable types, reducing errors and downtime. Educating team members, documenting codes, and conducting inspections ensure efficient network functioning.
Best practices for using fiber color code for visual identification of fiber types
It is crucial to use fiber color coding best practices for visual identification of fiber types to ensure a well-organized, efficient, and error-free network. Here are a few essential rules:
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Adhere to industry-accepted color coding standards such as those defined by the TIA-598C standard. This assures interoperability and seamless maintenance.
- Training and Education: Ensure that all network technicians and staff members are thoroughly trained and educated about the color coding system. This includes understanding the meaning of each color and its corresponding fiber type.
- Systematic Implementation: Apply color coding uniformly across all cables, regardless of their function or location within the network. This will ensure consistency and make it easier to identify specific wires when needed.
- Clear Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of the color code system used. This should include a chart or reference guide that clearly shows the color associated with each fiber type.
- Regular Auditing: Conduct regular audits to ensure the color coding system is being adhered to correctly. Any errors or discrepancies should be rectified as soon as they are identified to prevent confusion or mistakes in the future.
By adopting these best practices, you can ensure that your fiber color coding system is effective, easily understood, and reliable, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of your network.
Ensuring accuracy in identifying fiber types through color codes throughout installations
Accuracy in identifying fiber types through color codes is crucial during installations. This is how you can ensure proper system organization and prevent potential issues linked to incorrect cabling. To achieve this, you should do the following:
- Use of Proper Tools: Invest in high-quality tools designed explicitly for handling fiber optic cabling, such as fiber identifiers or optical cable testers. These tools can confirm whether the color coding corresponds to the correct fiber type.
- Double-Checking Connections: Always double-check connections during installation. Misconnections due to incorrect identification of fiber types can lead to system malfunctions or even damage the hardware.
- Quality Control: Implement a robust quality control process that includes checking the color coding before, during, and after the installation. This will help to catch any mistakes early on and rectify them promptly.
By prioritizing accuracy during the color coding process, you can avoid potential errors and ensure the reliability and efficiency of your fiber optic network.
Benefits and challenges of using color code systems in optical fiber installations
Implementing color code systems in optical fiber installations presents both benefits and challenges.
Benefits
- Efficiency: Color coding can significantly increase efficiency during installation and maintenance. It allows quick identification of specific cables, reducing time spent on tracing and testing.
- Order and Organization: Color coding helps maintain a neat and organized cable management system. It simplifies the process of distinguishing between different cables and fiber types.
- Reduced Errors: With a color code system, the likelihood of errors due to misconnections can be minimized. This increases the overall reliability of the network.
Challenges
- Training: To effectively implement and maintain a color coding system, staff need to be adequately trained. This requires time and resources.
- Consistency: Maintaining consistency in the color coding system can be a challenge, especially in large installations. Inconsistencies may lead to confusion and potential errors.
- Cost: While color coding can improve efficiency and reduce errors, it also comes with an additional charge for color-coded cables and the necessary tools.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of a color-coded system in optical fiber installations typically outweigh the difficulties, particularly in terms of long-term network management and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is fiber optic color coding?
A: Fiber optic color coding is a method of identifying different types of fiber optic cables and components based on the colors present in their design. This system helps distinguish fiber types visually and aids in the identification and maintenance of fiber optic networks.
Q: How does the fiber optic color code system work?
A: The fiber optic color code system uses specific outer jacket colors for different fiber types. For instance, single-mode fibers are often designated by yellow outer jackets, while aqua cables are commonly used for multimode fibers. Additionally, the color code runs from 1 to 12, helping to work with and identify threads within a line or inside each tube.
Q: Why is it essential to remember fiber optic color codes?
A: It is essential to remember fiber optic color codes as they are crucial for correctly identifying and working with fiber optic cables and connectors. Understanding the color coding system allows for smooth installation and maintenance processes, preventing errors and confusion.
Q: What are the applications of the fiber optic color code?
A: The fiber optic color code system finds applications in various areas, such as telecommunications, data centers, and networking. It helps in the organization and management of complex fiber optic networks, making it easier to distinguish and handle different fiber types.
Q: How are fibers color-coded for identification?
A: Fibers are color-coded for identification by using specific colors for individual fiber strands. This color-coding enables technicians and engineers to easily distinguish between different fibers when working with fiber optic cables and connectors.
Q: What is the significance of the 12-fiber color code?
A: The 12-fiber color code is a standardized system that allows for the identification and organization of up to 12 strands of fiber within a single cable. This coding simplifies the management and maintenance of fiber optic networks containing multiple threads.
Q: How do I remember fiber optic color codes?
A: A helpful mnemonic to remember fiber optic color codes is to associate each color with its corresponding fiber type and position in the coding system. Creating visual or mental cues can aid in recalling the associations and applying the color codes accurately.
Q: What are the outer jacket colors for other fiber types?
A: While yellow and aqua are standard outer jacket colors for single-mode and multimode fibers, respectively, other fiber types may be considered. For example, orange jackets are often used for OM2 multimode fibers, and blue may be employed for fiber cable or inside each tube in specific applications.
Q: How does the fiber optic color coding help in cable management?
A: Fiber optic color coding assists in cable management by enabling easy identification of individual fibers within a cable. This simplifies the installation and maintenance of fiber optic networks as technicians can quickly distinguish and work with specific threads as needed.
Q: Are there any tools available to work with and identify fiber optic colors?
A: Yes, there are specialized tools and resources designed to assist in working with and identifying fiber optic colors. These may include color code reference charts, fiber optic patch cords with color-coded connectors, and visual aids to help technicians accurately handle and manage colored fibers.
References
- Optcore: This source provides a simple guide for beginners, helping to clarify fiber color codes commonly used in the industry.
- The Fiber Optic Association: This source offers detailed information on how color codes are used in fiber optics to identify fibers, cables, and connectors.
- Sopto: Sopto gives a detailed explanation of how to identify the fiber color code, including the EIA/TIA-598 standard.
- DAEnotes: This site deciphers the color code for fiber optic cables and explains how connector colors often signify their type and application.
- Beyond tech: Beyondtech discusses the standard color codes for different types of fiber optic cables, such as yellow for single-mode lines and Orange for multimode cables.
- Utilities One: This source explains how color coding simplifies fiber identification and the importance of following industry color standards.
- YouTube – Fiber Optic Cable Colors: This YouTube video provides a visual guide to understanding fiber optic cable colors and their applications.
- AndCable: AndCable provides a whitepaper that offers an in-depth understanding of fiber optic cables and connectors, including the use of color codes.
- Network Installers: This blog post provides a guide to the standardized fiber optic cable color code system and how it works.
- Corning: This manufacturer’s website provides detailed information about fiber color coding in fiber to the premises (FTTP) modules and components.
Post Views: 6,029


