To choose the suitable Ethernet cable for your networking needs, it’s essential to understand the differences between Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat7 cables. These categories distinguish the performance characteristics and capabilities of the lines. The primary factors to consider include speed, bandwidth, maximum distance, and cost. In this section, we will delve into the specifics of Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat7 cables, evaluating their suitability for 10Gb networks.
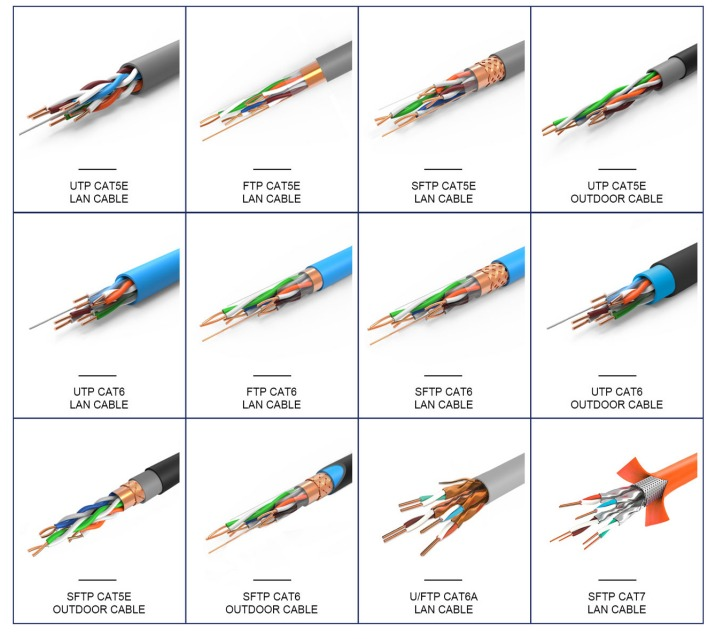

Cat6, or Category 6, Ethernet cables are a significant upgrade from their predecessor, Cat5. They are designed to support Gigabit Ethernet data rates of 1 gigabit per second (Gbps) over a maximum distance of up to 100 meters. However, for lengths above 55 meters, the speed is reduced to 250 megahertz (MHz). They feature more stringent specifications for reducing system noise and crosstalk interference. Cat6 cables also come in shielded twisted pair (STP) variants for environments with high electromagnetic interference. However, their limitation lies in the bandwidth support for 10Gb networks, making them less suitable for ultra-high-speed applications.
Cat6a, or Category 6 augmented, Ethernet cables pick up where Cat6 cables leave off. They are engineered to accommodate 10 Gigabit Ethernet data rates over a maximum distance of up to 100 meters without any signal degradation. This marks them as a substantial improvement over Cat6 cables, which see a dip in speed beyond 55 meters. Cat6a cables operate at a frequency of 500 MHz, which is double that of Cat6 cables, providing greater bandwidth and, therefore, higher data transfer rates. Their design includes thicker sheathing to eliminate crosstalk interference, ensuring high-speed data transfer without interruptions. This makes Cat6a cables an ideal choice for 10Gb networks in modern data centers and business environments seeking faster, more reliable connections. However, the increased performance comes with a slightly higher cost and larger physical size due to enhanced shielding.
Cat7, also known as Category 7, represents the next evolution in the Ethernet cable hierarchy. Built to support an impressive bandwidth of up to 600 MHz, these cables are capable of delivering 10 Gigabit Ethernet data rates over a maximum distance of 100 meters, similar to Cat6a. However, the standout feature of Cat7 cables is their extensive shielding, which significantly reduces crosstalk and improves overall performance. Each wire pair within the cable is shielded, in addition to a comprehensive shield around the cable itself. This design provides a significant boost in data transmission quality, ensuring a swift, uninterrupted, high-speed data flow. Despite their increased performance capabilities, Cat7 cables are thicker and more rigid than their predecessors, which may present an installation challenge in some scenarios. Moreover, their higher cost can be a deterrent for some users. Nonetheless, for environments requiring high-speed, high-quality data transmission, Cat7 cables offer an effective solution.
When it comes to bandwidth and data transmission capabilities, the differences between Cat6 and Cat6a cables are pretty pronounced. Cat6 cables, which support bandwidth frequencies of up to 250 MHz, are often sufficient for most home network and small business applications. They can deliver data at speeds of up to 10 Gigabits per second but only over a short distance of up to 55 meters. On the other hand, Cat6a cables, where ‘a’ stands for ‘augmented,’ provide enhanced performance characteristics. They double the bandwidth of their Cat6 counterparts to an entire 500 MHz and can maintain data transfer speeds of 10 Gigabits per second over a considerably longer distance of up to 100 meters. This makes Cat6a a superior choice for businesses and data centers that require higher data transmission rates over longer distances and are prepared to invest in a slightly more expensive cabling solution.
In the realm of 10GBASE-T networking, where data transmission rates of up to 10 Gigabits per second are required, both Cat6a and Cat7 cables come into the picture. Cat6a cables, as aforementioned, can maintain these data transfer speeds over a distance of up to 100 meters. This is generally adequate for most business and data center applications. However, Cat7 cables take it a notch further. They offer a bandwidth of up to 600 MHz and are also efficient in carrying 10 gigabits per second of data over the same 100-meter distance. However, it’s worth noting that Cat7 cables utilize a different connector type, known as a GG45, which is backward compatible with RJ45 connectors. Although Cat7 cables offer marginally better performance, their higher cost, coupled with their unique connector requirement, often renders Cat6a cables a more practical choice for 10GBASE-T networking.
When choosing between Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat7 cables for your networking needs, compatibility, and application play pivotal roles in the decision. Cat6 cables are widely compatible and offer reasonable performance for small to medium-sized businesses, making them a cost-effective solution in less-demand-intensive settings. However, for enterprises or data centers requiring higher data transfer rates over longer distances, Cat6a cables are an excellent choice, offering faster speeds and higher frequency. They are also backward compatible with older Ethernet standards, ensuring smooth integration with existing network infrastructure. Cat7 cables, while providing the highest performance in terms of speed and frequency, have a unique connector type, the GG45, which is not as universally compatible as the RJ45 found on Cat6 and Cat6a cables. The higher cost and compatibility issues make Cat7 a less practical choice unless the highest level of performance is essential. Therefore, while each cable category has its strengths, the best choice largely depends on your specific networking requirements and budget constraints.

When selecting between Cat6 and Cat6a cables for your structured cabling system, it’s essential to consider both present and future needs. Though Cat6 cables may be a more affordable option, they have a shorter maximum distance for 10Gb/s data transmission and lower resistance to electromagnetic interference. Conversely, Cat6a cables, while more expensive and thicker, provide superior performance that can sustain higher-speed data transmission over longer distances. They also offer better shielding, making them more suitable for environments with significant electrical equipment. Therefore, if you anticipate an increase in data demand or plan for network expansion in the future, investing in Cat6a cables could provide a more cost-effective solution in the long run. It’s crucial to balance these considerations with your budget constraints and infrastructure compatibility to make an informed decision.
If your network requirements exceed what Cat6 or Cat6a cables can provide, you might consider deploying Cat7 cables for your 10GbE networks. Cat7 cables are designed to handle frequencies up to 600 MHz and provide a higher data transmission speed, making them well-suited for ultra-fast, high-bandwidth operations. However, keep in mind that Cat7 cables are more expensive and require special GG45 connectors to utilize their capabilities thoroughly.
When planning for Cat7 cable deployment, take into account the following factors:
Remember, the selection of the correct cable type should align with your current needs, budget, and future expansion plans to ensure an efficient, scalable, and resilient network infrastructure.

Cat6 cables are a reliable choice for many networking scenarios, offering high-speed data transfer capabilities of up to 10 Gigabits per second (Gb/s) over a range of 55 meters. With a standard frequency of 250 MHz, they are well-suited for networks that require high-speed internet and less interference.
Use Cases of Cat6 Cables:
However, it’s crucial to note that while Cat6 cables offer impressive speeds, they may not be the best choice for environments demanding higher data transmission rates or long-distance applications, where Cat6a or Cat7 might be more appropriate choices.
Cat6a cables, also known as Category 6a cables, are an enhanced version of their predecessor, Cat6. They deliver superior performance for 10 Gigabit Ethernet applications, with several key advantages.
In summary, for installations that require 10 Gigabit Ethernet, Cat6a cables are a robust and future-forward choice, providing high-speed, reliable connections over more considerable distances and with less interference.
Like Cat6a, Cat7 cables (Category 7) represent a step up in network cabling performance. Here are some of the key features and benefits of Cat7 cables:
In conclusion, Cat7 cables represent an excellent choice for applications that require high-speed data transmission and superior interference mitigation. They are robust, versatile, and future-ready, ensuring they will serve the needs of advanced network technologies as they emerge.

These are some key factors to consider when choosing the suitable Ethernet cable for your network. It’s crucial to evaluate your current and future network demands to make the most appropriate selection.
When it comes to 10GbE switches and connectivity, the compatibility with Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat7 cables varies. While all three cable types can support 10GbE connections, the maximum transmission distance and overall performance differ significantly.
Cat6 cables, although initially designed for Gigabit Ethernet, can support 10GbE up to a distance of 55 meters, making them suitable for short-range connections. However, for more extensive networks or data centers, Cat6 may not be the most efficient choice due to its limited range in supporting 10GbE.
On the other hand, Cat6a cables, designed with 10GbE in mind, can readily support these connections up to 100 meters. They also offer improved alien crosstalk characteristics, making them a more reliable option for 10GbE networks.
Cat7 cables, being the most advanced, can support 10GbE up to 100 meters and are equipped with superior shielding, thus providing the highest level of protection against electromagnetic interference. However, their higher cost and thickness might make them less desirable for specific applications.
In conclusion, while all three cable types are technically compatible with 10GbE switches, the choice between Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat7 should be primarily determined by the specific network requirements, including transmission distance, interference level, budget, and future-proofing considerations.
When examining Power over Ethernet (PoE) support, Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat7 cables each demonstrate unique capabilities:
These sources provide a diverse and in-depth look into the topic of thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), covering various aspects such as types, uses, properties, and recent advancements. They offer valuable information for readers interested in understanding this versatile material.
Recommend reading: Understanding the difference between Cat5e and Cat6 Ethernet Cables

A: Cat6 cables support up to 10Gbps and are suitable for most home and office networks. Cat6a cables are an improved version with better insulation and higher speeds, supporting up to 10Gbps at longer distances. Cat7 cables are designed to support even higher rates and have shielding to reduce crosstalk and interference.
A: Yes, Cat6 cables can support 10Gbps Ethernet, but the maximum distance for reliable performance is limited to 55 meters.
A: Cat6a cables can support bandwidths of up to 500MHz, allowing for high-speed data transfer and network performance.
A: Yes, Cat6 cables are compatible with Cat6a connectors, as both use the same RJ45 connectors for termination.
A: When deciding on which structured cabling system to use, consider factors such as the number of users, maximum bandwidth requirements, and the potential for future upgrades to higher speeds.
A: When choosing Ethernet cables, look for specifications such as the cable category (Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7), maximum supported speed (e.g., 10Gbps), and whether the cable supports Power over Ethernet (PoE).
A: Yes, Cat6 cables are suitable for smart home applications, providing reliable connectivity for devices such as smart TVs, security cameras, and home automation systems.
A: Yes, Cat6a cables are suitable for 10GBASE-T networking, offering the necessary performance and throughput for high-speed data transfers.
A: You can find recommendations for loading Cat6, Cat6a, or Cat7 Ethernet cables from reputable retailers such as Amazon.com, which offer a wide selection of lines suitable for various applications.
A: Yes, Cat7 Ethernet cables can support Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications, providing both data and power transmission for devices such as IP cameras, access points, and VoIP phones.