As data demands skyrocket due to AI workloads, big data analytics, and 5G applications, data centers require transceivers capable of handling massive throughput with minimal latency. 800G OSFP InfiniBand transceivers address these needs by providing unprecedented bandwidth, enabling efficient data transfer across servers, storage, and networking equipment. Their role in reducing bottlenecks and enhancing scalability is critical for enterprises aiming to stay competitive in data-intensive industries.
This article explores the core technologies, key features, typical use cases, and the critical role of 800G NDR OSFP modules in the evolution of future network infrastructures—offering readers a comprehensive understanding of this cutting-edge optical communication solution.
800G NDR OSFP (Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable) transceivers are cutting-edge optical modules designed to deliver ultra-high-speed data transmission at 800 gigabits per second (Gbps). Built for next-generation data centers, these transceivers leverage NVIDIA’s InfiniBand NDR (Next Data Rate) protocol to support high-performance computing (HPC), artificial intelligence (AI), and hyperscale cloud environments. The OSFP form factor, with its eight-lane configuration, enables compact, high-density connectivity, making it a cornerstone for modern networking infrastructure.
As the demand for higher network bandwidth and low-latency connectivity grows rapidly with the rise of AI, big data, cloud computing, and high-performance computing (HPC), data centers are accelerating their transition to the 800G era. The 800G OSFP optical module, a key enabler of this shift, is gaining widespread adoption in next-generation network architectures thanks to its high density, ultra-high bandwidth, and energy-efficient performance.
An 800G OSFP module typically includes advanced components like high-speed lasers, photodetectors, and digital signal processors (DSPs). These modules support PAM4 (Pulse Amplitude Modulation with 4 levels) signaling, which doubles data capacity per lane compared to traditional NRZ modulation. The OSFP design also incorporates robust thermal management to handle the high power consumption of 800G operations, often exceeding 15W per module.
The NDR protocol, part of NVIDIA’s InfiniBand family, operates at 100 Gbps per lane, allowing 800G transceivers to achieve full capacity across eight lanes. NDR introduces enhancements like improved error correction and adaptive routing, ensuring reliable data transmission in demanding environments. This protocol is optimized for low-latency, high-throughput applications, making it ideal for AI training clusters and scientific simulations.
800G OSFP transceivers support various optical configurations, such as 800G SR8 (short-range, multimode fiber) and 800G-DR8 (data center reach, single-mode fiber). They typically operate over distances from 100 meters to 2 kilometers, depending on the fiber type. Electrically, they comply with IEEE 802.3 standards, ensuring compatibility with modern Ethernet switches and routers.
The OSFP form factor is larger than its predecessor, QSFP-DD, to accommodate advanced cooling and higher power requirements. Common connector types include MPO-12/APC for multimode fiber, supporting parallel optics for short-range applications. These connectors ensure high-density port configurations, maximizing rack space efficiency in data centers.
Role in High-Performance Computing (HPC)
HPC environments, such as those used in scientific research and financial modeling, rely on 800G NDR OSFP transceivers to handle massive datasets. These transceivers enable rapid data exchange between compute nodes, reducing processing times for complex simulations and analyses.
Supporting AI and Machine Learning Workloads
AI and machine learning workloads, particularly deep learning training, demand high-bandwidth, low-latency interconnects. 800G NDR OSFP transceivers facilitate the rapid transfer of large datasets between GPUs, accelerating model training and inference in AI clusters.
Ethernet and InfiniBand Network Integration
These transceivers support both InfiniBand and Ethernet protocols, allowing seamless integration into diverse network architectures. This flexibility makes them suitable for hybrid environments where data centers combine HPC and cloud workloads.
Enhanced Bandwidth and Low Latency
With a capacity of 800 Gbps, these transceivers deliver unmatched bandwidth, enabling data centers to handle growing traffic demands. Their low-latency design ensures minimal delays, critical for real-time applications like autonomous driving and online gaming.
Scalability for Future Network Demands
800G OSFP modules are designed with scalability in mind, supporting the transition to multi-terabit networks. Their backward compatibility with lower-speed OSFP modules ensures a smooth upgrade path for data centers.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Despite their high performance, 800G transceivers incorporate power-efficient designs, reducing energy costs per bit transmitted. This efficiency translates to lower operational expenses, making them a cost-effective solution for large-scale deployments.
Support for NVIDIA Quantum-2 and Spectrum-4 Platforms
800G NDR OSFP transceivers are optimized for NVIDIA’s Quantum-2 InfiniBand switches and Spectrum-4 Ethernet switches, ensuring seamless integration with NVIDIA’s ecosystem. This compatibility maximizes performance in AI and HPC environments.
Compliance with Industry Standards (OSFP MSA, IEEE 802.3)
These transceivers adhere to the OSFP Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) and IEEE 802.3 standards, ensuring broad compatibility with third-party equipment. This standardization reduces vendor lock-in and enhances deployment flexibility.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure
800G OSFP modules can coexist with legacy systems, supporting gradual upgrades. Their ability to operate with existing fiber infrastructure minimizes the need for costly overhauls, making them a practical choice for data center operators.
As AI, HPC, and hyperscale data centers demand increasingly higher bandwidth and lower latency, 800G InfiniBand NDR (Next Data Rate) has emerged as a cornerstone technology for next-generation high-performance interconnects. Below are its core application scenarios and typical deployment topologies.
Quantum-2 InfiniBand Switches (e.g., QM9700/QM9790):
ConnectX-7 Smart NICs:
Optical Modules and Cables:
1.Switch-to-Switch (800G to 800G):
Scenario: High-speed interconnects between Quantum-2 switches.
Solution: Use OSFP-800G-2xSR4H modules with MPO-12 direct-attach cables (≤50m).
Example: Two QM9700 switches connected via OSFP-800G-2xSR4H modules for full 800G bandwidth.
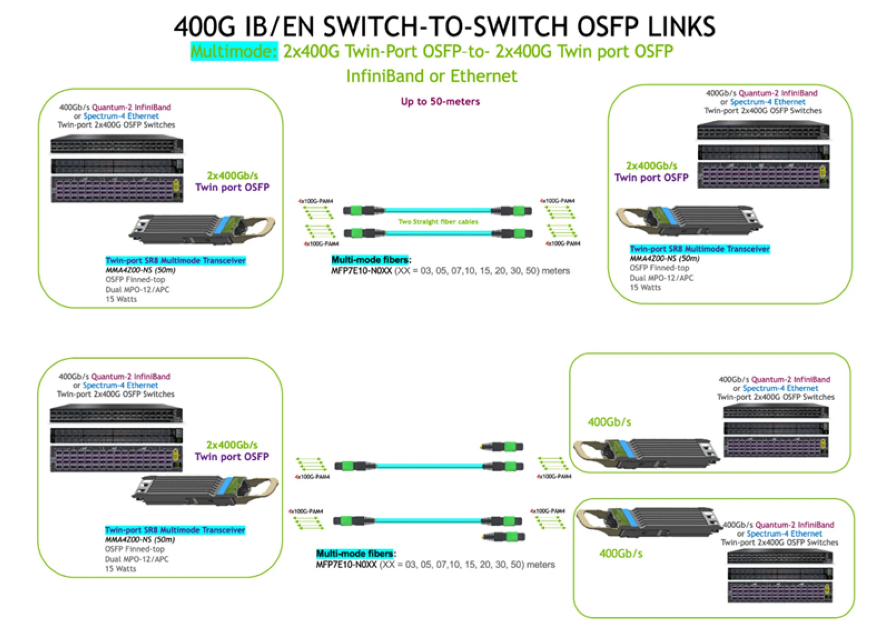
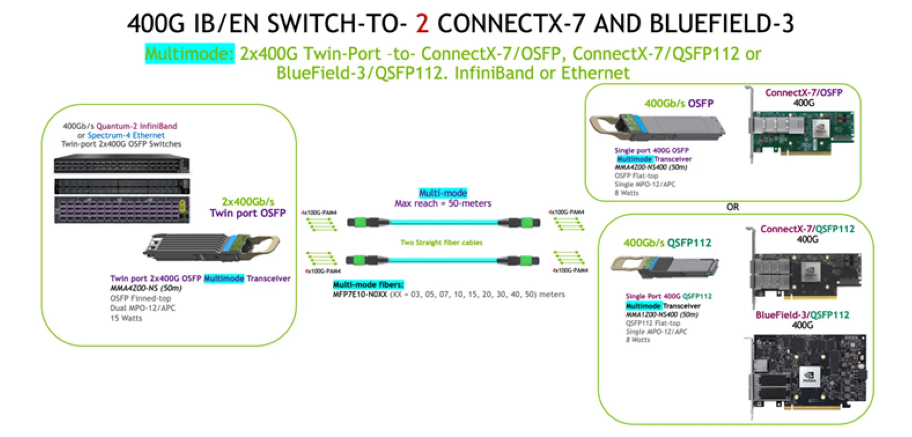
2. Switch-to-Server/HCA Interconnects
800G to 2×400G:
Switch Side: OSFP-800G-2xSR4H module.
Server Side: Breakout DAC (e.g., MCP7Y00-Nxxx) connecting two 400G ConnectX-7 NICs.
Use Case: AI training nodes (e.g., NVIDIA DGX H100) supporting AllReduce with high bandwidth demands.
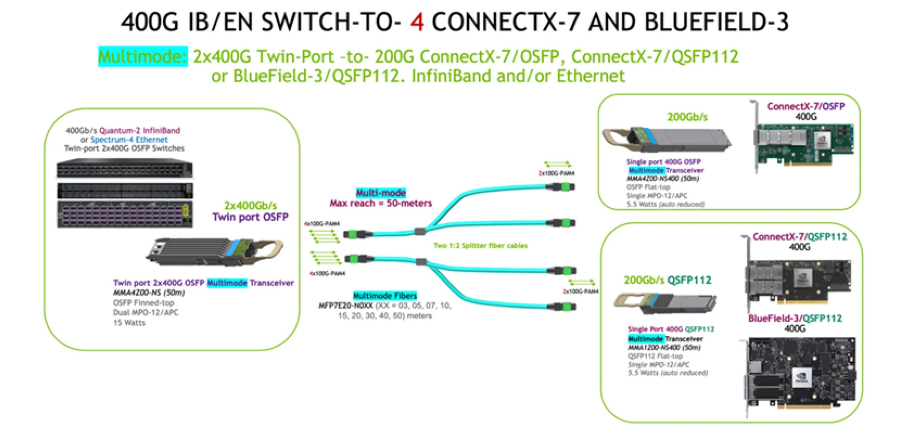
3. 800G to 4×200G:
Switch Side: OSFP-800G-2xSR4H module.
Breakout Cable: 1:4 cable (e.g., MCP7Y50-Nxxx) to four 200G NICs (in NDR200 mode).
Use Case: Distributed storage or GPU clusters, optimized for metadata synchronization.
4. Long-Distance Single-Mode Connectivity
Scenario: Inter-rack or inter-DC links (>100m).
Solution: Use OSFP-800G-2DR4 modules with OS2 single-mode fiber for up to 500m reach.
The 800G InfiniBand NDR solution, built on the Quantum-2 platform and flexible optical interconnects, delivers high bandwidth and ultra-low latency for AI, HPC, and cloud data centers—while lowering complexity and total cost of ownership (TCO). Choosing the right mix of modules and cables depends on topology distance and speed requirements.
The rise of cloud computing, AI, and IoT has fueled demand for 800G transceivers. Industry analysts predict widespread adoption in hyperscale data centers by 2026, driven by the need for higher bandwidth and faster data processing.
Innovations in silicon photonics are reducing the size and cost of 800G transceivers while improving performance. These advancements are paving the way for more compact and efficient optical modules.
As 800G becomes mainstream, the industry is already eyeing 1.6T transceivers. The OSFP form factor is designed to support these future speeds, ensuring long-term relevance for current deployments.
In summary, the 800G OSFP infiniBand NDR series optical modules and cables offer excellent bandwidth, low latency, and high energy efficiency. These features make them a key technology for advancing next-generation data centers and high-performance computing environments. They are highly valuable in high-demand applications such as AI training, cloud computing, and scientific research.
As the need for faster networks continues to grow, 800G NDR OSFP modules not only address current challenges but also provide a strong foundation for future network upgrades and expansions. With ongoing technological progress, we expect 800G OSFP to be adopted more widely across the globe, helping data centers operate more efficiently and sustainably.
A: OSFP modules offer better thermal management and higher power capacity than QSFP-DD, making them better suited for 800G applications. However, QSFP-DD is more compact, appealing for space-constrained environments.
A: NDR doubles the per-lane speed of HDR (50 Gbps) and quadruples that of EDR (25 Gbps), offering significantly higher throughput and lower latency, ideal for next-generation workloads.
A: Challenges include managing high power consumption, ensuring adequate cooling, and upgrading cabling infrastructure to support 800G speeds. Proper planning is essential to avoid performance bottlenecks.
A: Yes, 800G OSFP modules require advanced cooling solutions, such as high-capacity fans or liquid cooling, due to their power consumption, which can exceed 15W per module.
A: While initial costs are high, 800G transceivers reduce cost per bit through energy efficiency and higher port density, leading to long-term savings in large-scale deployments.