——
A Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier allocated to a network interface controller (NIC). This identifier is crucial for communication within a network segment at the data link layer. It’s a fundamental component of network infrastructure and plays a significant role in facilitating efficient data transmission between various devices.
In technical terms, a MAC address is a unique identifier assigned to a Network Interface Controller (NIC). Its primary function is to facilitate communication within a network segment at the data link layer. This 12-digit hexadecimal number is globally unique and is usually stored in the device’s hardware, like the NIC or Wi-Fi card.
The Nintendo Switch gaming console utilizes MAC addresses in its networking capabilities. The MAC address allows the Nintendo Switch to be uniquely identified on a network, enabling it to effectively communicate with other devices and access internet services such as online multiplayer games and content updates.
Locating the MAC address of a Nintendo Switch involves a simple process. From the main menu of the device, users need to navigate to ‘System Settings,’ then ‘Internet,’ and finally ‘Internet Settings’. Under the details of the currently connected network, the MAC address is listed.
Setting up the MAC address for network functionality involves several steps:
The MAC address plays a pivotal role in network setup. It’s instrumental in directing packets of data to the correct destination, ensuring all devices within a network can communicate effectively. Without a MAC address, devices would not be identifiable on a network, severely hindering their ability to send or receive data.
——
A MAC address table in a network switch is a fundamental component in network management and data transmission. This table contains the unique identifiers of all devices connected to the switch, facilitating efficient routing and forwarding of data packets. It is an integral part of the switch’s operational mechanics and aids in maintaining smooth and accurate network communication.
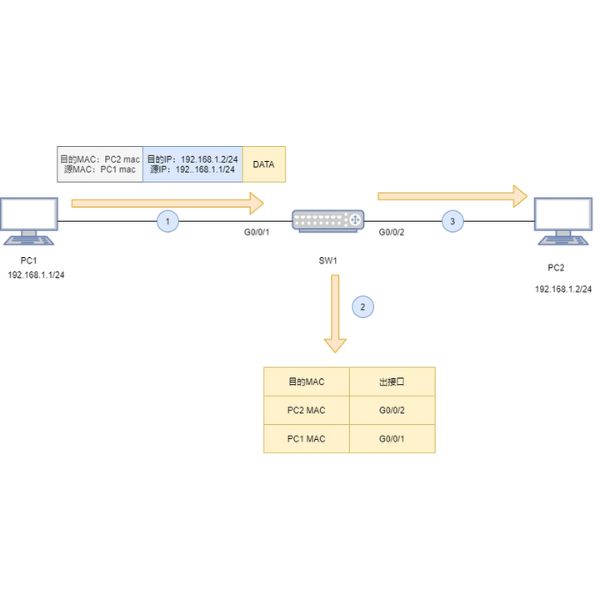
The MAC address table serves as a directory within a network switch, associating each device’s MAC address with the corresponding port on the switch. Its primary function is to guide the switch in forwarding data packets. By consulting the MAC address table, the switch can determine the specific port to which a data packet needs to be sent, ensuring efficient and targeted data transmission.
A network switch learns MAC addresses through a process known as “MAC learning.” When a data packet arrives at a switch port, the switch examines the packet’s source MAC address. If the address is not already present in the MAC address table, the switch adds it, associating it with the port where the packet arrived. This continuous updating allows the switch to ‘learn’ and remember the MAC addresses of all devices connected to it.
When a data packet arrives at a switch port, the switch checks the destination MAC address within the packet header against its MAC address table. If the destination MAC address is found within the table, the switch forwards the packet to the corresponding port. If the address is not found, the packet is sent to all ports, a process known as “flooding.”
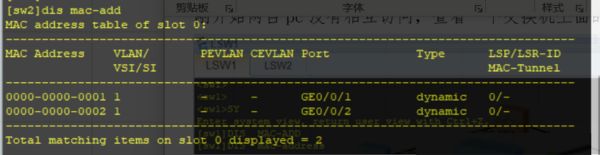
To display the MAC address table on a network switch, one usually needs to access the switch’s management interface, often through a command-line interface (CLI) or a web-based GUI. The specific command or navigation steps may vary based on the switch model and manufacturer, but generally, it involves a command such as ‘show mac-address-table’ or similar.
Updating the MAC address table on a network switch is typically an automatic process driven by MAC learning. Each time a data packet is received, the switch checks the source MAC address and updates the table if necessary. However, in some cases, manual intervention may be required. This could involve entering specific commands in the switch’s management interface to add, remove, or modify entries in the MAC address table.
——
In the realm of network management, understanding the role and implications of dynamic Media Access Control (MAC) addresses is vital. A dynamic MAC address, unlike its static counterpart, is not permanently assigned and can change over time. This characteristic can significantly influence how a network switch operates, affecting aspects like data packet forwarding, VLAN configuration, and overall network security.
A dynamic MAC address may change over time, usually assigned by the system or network upon device connection. In contrast, a static MAC address is a fixed identifier manually assigned to a device and remains constant over time. In the context of a network switch, dynamic MAC addresses can offer more flexibility, while static MAC addresses provide predictability and control.
VLANs, or Virtual Local Area Networks, divide a physical network into multiple logical networks, providing segmentation and isolation. Dynamic MAC addresses play a crucial role within VLANs as they allow devices to join or leave a VLAN without manual reconfiguration. The network switch automatically learns and assigns dynamic MAC addresses to the appropriate VLANs, facilitating efficient network management.
When a device changes both its IP address and MAC address, the network switch reacts by updating its address tables. The switch identifies the new MAC address as a unique device and associates it with the specific port it’s connected to. If the switch’s security settings permit, the device can continue communicating on the network with its new addresses.
Specifying a static MAC address for a specific port on a network switch typically involves accessing the switch’s configuration settings. Through the switch’s command-line interface or web-based management interface, users can manually assign a static MAC address to the desired port. This process ensures that the specified port will always communicate using the assigned MAC address.
A network switch handles dynamic MAC addresses based on its MAC address learning function. In general scenarios, when a device connects to a switch port, the switch learns the device’s MAC address and updates its MAC address table accordingly. If a device disconnects or if its MAC address changes, the switch updates the table to reflect the change. This dynamic handling allows the switch to maintain accurate information for efficient data packet forwarding.
——
The Switch MAC Address is a vital part of network functionality. It operates as a unique identifier for every device on the network. Its role is to indicate where to direct data packets, ensuring the information arrives at the right destination.
You can generally locate your device’s MAC Address within the network settings or configuration menu. For detailed instructions, refer to your device’s user manual or contact the manufacturer for help.
In general, altering the MAC Address is not advisable as it could disrupt network communication and create connectivity problems. The MAC Address is meant to be a unique identifier – changing it may have unintended side effects.
In VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) configuration, the Switch MAC Address plays a pivotal role. It assists in segmenting and guiding network traffic based on the devices’ MAC Addresses. The result is efficient data transmission within the VLAN.
While generally associated with wired Ethernet connections, the Switch MAC Address is equally important in wireless networks. Wireless devices have unique MAC Addresses used for communication and network management.
The Switch MAC Address is instrumental in network traffic filtering. The switch can selectively forward data packets based on the MAC Address, optimizing network traffic flow.
Incorrect Switch MAC Address settings could lead to network connectivity problems, data transmission errors, and potential network security vulnerabilities. It’s vital to ensure accurate and properly configured MAC Address settings.
Typically, the Switch MAC Address is hardcoded into the device’s network interface and remains unchanged in regular situations. However, certain advanced network configurations might involve MAC Address spoofing and dynamic MAC assignments.
The Switch MAC Address enhances network security by enabling device authentication and authorization based on their MAC Addresses. This process helps ward off unauthorized access and strengthens network security protocols.
If you’re experiencing Switch MAC Address-related problems, it’s recommended to check your network configuration settings, confirm MAC Address entries, and verify the correct network device connections. If issues persist, contact network support professionals for assistance.
——