The adoption of Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Ethernet is a vital element in the development of modern communication systems because it facilitates networking in complex enterprise systems and even simple office projects. Yet, what makes UTP Ethernet so crucial, and what role does it play in the ever-evolving network technology landscape? The purpose of this guide is to explain UTP Ethernet by highlighting its components, operation, and functions. As an IT expert, this article will further broaden your already existing knowledge, while for a novice, it will eloquently express concepts that shape the functioning of communication systems to help build an appreciation for the necessity of UTP Ethernet-supported communication networks and data systems. Be ready to learn the important information that supports network systems around the world.

UTP Ethernet, commonly known as Unshielded Twisted Pair Ethernet, is a popular network technology that enables data transfer between devices. It employs unshielded twisted pair cables which are composed of pairs of protective copper wires twisted together to minimize signal interference. This design allows cost-effective production while making reliable communication possible. UTP Ethernet functions by sending data signals over these cables while adhering to various industry standards, such as IEEE 802.3, to guarantee smooth operation and efficiency. Because of its ease, flexibility, and inexpensive use, it serves as the main component of local area networks (LANs) globally.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) technology has many popular advantages, which is why it’s widely used as a network infrastructure. One of its advantages is its cost-effectiveness since UTP cables are relatively cheaper to manufacture and install than other cabling options. Moreover, its lightweight and flexible design permits easy installation and maintenance. UTP is supported by most networking standards like Ethernet and facilitates high data transfer rates that are compatible with most LAN applications. Though it renders sufficient performance in environments with low electromagnetic interference, the cost-effectiveness and efficiency make it ideal for numerous commercial and residential networking requirements.
For wired data communication in computer networking, ethernet cables are of utmost importance. Cables that connect computers to routers and switches enable rapid transfer and undisturbed data flow through various devices, allowing seamless communication. These cables are commonplace in homes and businesses because of the unwavering infrastructure they provide for low-latency networks. Moreover, ethernet cables are reliable because they work with elementary networking protocols which makes the construction of local area networks secure and efficient.
As a result of the absence of shielding around their wiring, unshielded Ethernet cables (UTP) tend to be lighter, more flexible, and easier to install compared to their shielded counterparts. UTP cables do not protect against EMI, but their flexibility makes them ideal for most standard home and office networks where EMI is minimal. On the contrary, shielded Ethernet cables (STP) use layers of shielding such as foil or braided metal to protect against EMI, making them suitable for environments like industrial settings that have high interference from electronic equipment. The balance of unshielded and shielded cables is best determined by the network’s environmental conditions and performance requirements.
It’s critical to differentiate between Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a when selecting Ethernet cables in order to achieve optimum performance for your network needs. These categories are differentiated by the levels of speed, bandwidth, and interference offered. Here’s a breakdown.
Cat5e (Category 5 Enhanced)
Cat6 (Category 6)
Cat6a (Category 6 Augmented)
Summary
It is clear from the information provided that the best cable to use depends on the specifics of your network configuration. For basic configurations, Cat5e offers a good price to performance ratio. Cat6 offers greater flexibility for achieving high speeds with low interference and is still a good all-around cable. If you seek the most future-proof option that also offers the most resistance to interference, then you should use Cat6a.
The network cable’s features depend heavily on their reliability and performance based on the wire image, such as 24AWG, which is located in its description. AWG, as given in the description, signifies American Wire Gauge, which shows the diameter of the copper wire present in the cable. Ethernet cables use 24AWG, which is standardized as it is relatively easy to manage and has good performance. Conductor thickness has a direct influence on the signal strength, resistance, and cable performance.
Better conductors with increased thickness, such as 23AWG, are incorporated in Cat6 and Cat6a cables, which allows for better transmission over longer distances. These cables also perform better when transmitting high-frequency signals in environments prone to electromagnetic interference (EMI). To illustrate, Cat6 cables with 23AWG conductors can accommodate data transmission speeds of up to 10 Gbps within a range of 55 meters. In comparison, Cat6a cables can reach 10 Gbps over 100 meters as long as they are equipped with extra shielding and have their conductors set at 23AWG or lower.
Evaluating the flexibility of the cable in conjunction with the thickness of the conductor can have notable trade-offs. Thicker wires undoubtedly improve performance and decrease signal attenuation, however they are less flexible and more difficult to work with in compact spaces. Assessing the requirements of your particular network setting, such as a data center with extensive cabling needs versus a small office installation, will assist in determining the correct wire gauge and type of cable needed.
Impedance, insertion loss, and crosstalk also have a direct relation to the conductor gauge and the construction of the cable. For those tasked with designing advanced network solutions, it is often the case that using cables with a lower wire gauge number increases overall performance and reliability. This is especially true with demanding network-powered devices like Power over Ethernet (PoE), which greatly benefit from the use of thicker wires that are better suited for high-power applications.
To assist in organization and identification, network cables are readily available in different colors. Color coding greatly simplifies cable management in complex installations. For instance, blue cables are commonly used to denote network connections, and yellow may identify PoE lines. Certain cables also have designed uses, such as outdoor-rated cables with protective jackets designed to withstand environmental factors, and plenum-rated cables for fire safety built into spaces within the building’s walls and ceilings. Using the appropriate color and type of cable ensures easy maintenance and compliance with installation standards.
Flexibility, low cost, and ease of installation make UTP cables one of the most popular cables for networking. The main benefit of using UTP cables lies in their ability to reduce interference and cross-talk due to the twisting of wire pairs into one unit. Each pair of copper wires in the cable is bound, each with its own specific number of twists per inch to achieve optimal performance. This arrangement reduces the electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can arise from external sources while, at the same time, limiting disruption signals between adjacent pairs, commonly known as crosstalk.
The degree of differencing in resistance is measured in performance categories like Cat6, Cat5e, and Cat6a. For example, a Cat5e cable allows frequencies below 125 MHz but with crosstalk. As higher category cables or cables like Cat6 come in, the upper ceiling of supporting frequencies goes up to 250 MHz while also improving crosstalk protection. Advanced manufacturing processes like more accurate twisting and tighter tolerances also aid in crosstalk reduction. The addition of air separation technologies and spline arrangements in higher-category cables improves strong integrity.
Research suggests that high-performing UTP cables are able to preserve uniform data transmission levels even in heavily electromagnetically noisy industrial environments. These cables are verified to meet benchmarks such as ANSI/TIA-568 and ISO/IEC 11801, which guarantees modern network interference-free performance, including high-speed Ethernet and gigabit capabilities. Therefore, the elegant simplicity of UTP cable design renders them indispensable in contemporary network infrastructure.
Transmission line theory studies the propagation of electrical signals on a conductor in terms of impedance, reflection, and attenuation. To summarize, it focuses on how signals are transmitted with maximum efficiency and minimal degradation because this is vital when designing dependable network systems, such as those that use UTP cables.
Correctly designed high-quality twisted pair cables have the ability to considerably minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between wire pairs. Twisting the wires together ensures that any interference affecting one wire is canceled out by the opposite signal present in the paired wire, thus protecting the signal\’s quality. This eliminates the possibility of data loss while in transmission, even when there is considerable external interference, which enhances the efficiency and reliability of twisted pair cables in modern networking.
ROHS compliance is critical for the Ethernet cable industry in terms of modern environmental and safety regulations. This regulation limits the hazardous materials, such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and some brominated flame retardants, present in electronic and electrical equipment. Ethernet cable manufacturers are able to meet ROHS standards, thereby mitigating the risk of dangerous substances seeping into ecosystems through production, usage, or disposal.
From the standpoint of safety, ROHS compliant cables are able to promote better health conditions within the workplace by eliminating exposure to dangerous materials during the manufacturing and installation processes. Recent studies claim materials such as lead and mercury can be detrimental to health in the long run causing neurological and developmental damage if not dealt with properly.
In addition, ROHS compliance contributes positively towards electronic recycling and waste management. As a worrying global concern, the 2022 electronic waste figure of 54 million metric tons highlight the need for e-waste reduction. The ROHS guidelines make the retrieval of economically viable materials in the recycling phase easier which directly contributes to waste reduction. The regulation permits the recycling of used cables and components without polluting the soil or water, thus supporting the initiatives towards a sustainable circular economy.
In summary, meeting ROHS compliance not only maintains the high safety and environmental standards but also helps achieve sustainability objectives, reduces industrial waste, and encourages responsible production. Therefore, Ethernet cables that are compliant with these standards are more suitable for environmentally sensitive and health-sensitive uses.
Protection of the Environment
Improved Recycling and Waste Management
Health and Safety Benefits
Regulatory Compliance and Market Access
Extended Product lifespan
Support of circular economy framework
Brand reputation and consumer trust
Through compliance with ROHS standards, networking equipment manufacturers and suppliers promote a sustainable future aligned with essential international safety and environmental policies. These standards greatly enhance corporate responsibility in waste and resource management.
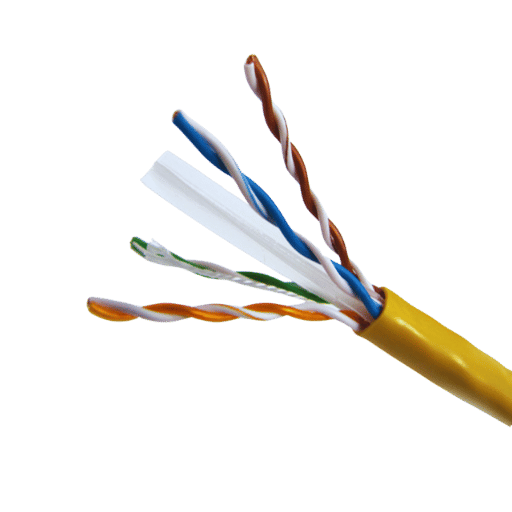
The standards T568A and T568B dictate the arrangement of color-coded wires in a UTP Ethernet cable. Each cable comprises four twisted wire pairs, amounting to eight distinct wires that are named by color.
T568A Standard
T568B Standard
While both are functional, T568B appears to be adopted for business installations. For consistency, use the same standard on both ends when making straight-through cables. For crossover cables, implement T568A on one end and T568B on the opposite end. This guarantees Ethernet network compatibility and performance.
Ensuring the long-term effectiveness, performance, and durability of Ethernet cables requires protective action against damage caused by corrosion, over-strain, and physical stress. Connectors facing extreme temperature conditions, as well as silicone grease gaskets in outdoor or industrial settings, can appreciate moisture seals and help inhibit moisture and water ingress even further. The incorporation of high-grade polyethylene (PE) and polyurethane (PU) as insulation materials is specific to resist weather corrosion, making it even more effective in preventing moisture from entering within.
Another area critical in ensuring the protected usage of Ethernet cables over a longer time period is Stain Relief. Ethernet cables are most likely further damaged by bending, pulling, and stress placed on the connectors. For glue joints, even minor stress may lead to disbanding, while even slight motion may lead to SRS. The SRS also often leads to the destruction of the component subjected to it. Studies show that cover failure with strain-relieving features suffer less than a third of covert damage, thus reducing the overall cost of network infrastructure by increasing total life cost. When utilized in concert with Ethernet cables, these simple techniques can protect them from factors related to abrasion and excessive use, further assuring protection to maintain and enhance expected operating performance over prolonged durations.
Appropriate use of patch cables within a data center enables seamless network functionalities. First, choose cables of appropriate lengths to prevent unnecessary slack which can lead to obstructions in airflow. Identify and troubleshoot interactions with ease by labeling each cable at both ends. To prevent tangling and accidental disconnection, secure loose cables with appropriate management tools such as organizers and racks. Ensure exceptional cable performance by choosing shielded cables to reduce interference. Cables that show signs of wear or damage should be replaced in a timely manner, along with monthly inspections. These measures reduce the risk of downtime while enhancing organization within the data center.
A: UTP Ethernet cable also known as Unshielded Twisted Pair is a type of copper cable and is a common UTP cable in network connections. It is made of twist-paired wires of high quality to decrease alien crosstalk and improve performance. Because of its low cost, ease of installation and maintenance, UTP cables are popular in Ethernet networks.
A: A snagless boot or snagless mold on the connector defines Snagless UTP Ethernet Cables. This feature prevents the locking tab from getting caught or broken off during movement in tight areas. Such design improves cable protection and enhances its utility, especially in dense patching areas within crowded network rooms.
A: Cat6 snagless unshielded cables is one type of high performance UTP cables capable of supporting a data transfer rate of ten Gbps over a limited distance. It uses UmWAVE R b which is purer than what is used in Cat5e cables which results in lesser crosstalk and system noise, thus yielding better bandwidth performance. Adding durability is the snagless feature and reducing costs in comparison to shielded cables is the unshielded design.
A: Organizing Network connections becomes easier with the use of color-coded Ethernet cables as they assist in distinguishing the various categories of a network. These particular system features enhance automation, cable organization, and stratified network designs, which aids in maintenance as well as reduction in the time needed for alterations.
A: UTP Ethernet Cables have a maximum plausible length of one hundred meters, as beyond that, they will lose signal and have connection difficulties. Reducing connectivity issues such as these can be achieved by making use of Ethernet extenders, switches, or other similar devices for longer distances.
A: Whether hand-assembled/interchanged or factory-created, ethernet cables serve the same purpose. They endure minor variations in construction and materials of parts, but hand assembled ones are more susceptible to default errors impacting connection, whereas factory created cables ensures minimal mistakes, resulting in greater reliability, uniform performance, and enhanced speed.
A: The bandwidth capability varies across categories of UTP Ethernet cables. For instance, Cat5e can support speeds of up to 1 Gbps, Cat6 can offer up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances, while Cat6a maintains 10 Gbps up to 100 meters. Further categories like Cat7 and Cat8 can offer even more at up to 40 Gbps and 25 or 40 Gbps, respectively, but at shorter distances.
A: That really depends on the network environment. Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) can be considered for most home and office networks. On the other hand, if your network is in an environment with a lot of electromagnetic interference, you may want to look at shielded cable options. While shielded cables provide better defense against outside noise, they tend to be more expensive and difficult to install.
A: One Ethernet cable is used to make individual connections, like connecting a computer to a router. A pack of cables is beneficial for networks that require multiple configurations or when numerous connections need to be made. Packs of cables are generally cheaper and provide additional cables that can be used later for other projects or for replacements.
A: It does matter because the quality of cables used directly affects the structure’s performance. Quality twist-paired cables reduce alien crosstalk and signal degradation and provide trustworthy data throughput with greater efficiency. Although cheaper cables may suffice for basic connections, in high-speed, high-demand environments, expensive cables are essential, especially for bandwidth-heavy tasks in places prone to interference.