A DAC (Direct Attach Cable) Cable is a networking cable used to connect different networking devices, such as switches, routers, and servers, to form a network. It is also referred to as Twinax Cable, consisting of two conductive wires twisted together to form a cable. The DAC Cable is a famous data center and high-performance computing application option.
The DAC Cable has emerged as a preferred choice over other networking cables due to its high data transfer rates and low latency. It can transmit data at speeds of 10Gbps, 25Gbps, 40Gbps, 50Gbps, and 100Gbps, depending on the networking equipment it is connected to. Additionally, DAC Cables can be manufactured in various lengths, such as 1m, 3m, 5m, 7m, and 10m, to accommodate different network setups.
A DAC Cable connects networking devices through a direct electrical connection to transmit data. It is a passive copper cable with built-in transceivers on each end, which convert electrical signals to optical signals. The transceivers are connected to the networking equipment’s equipment’s equipment sports, and the copper wire transmits the data between the two devices. This direct connection results in lower latency, providing faster data transfer rates and reducing the chances of signal loss.
The DAC Cable offers several advantages compared to other networking cables, such as:
High speed – DAC Cables can transfer data at high rates, preventing bottlenecks and allowing quick network access.
Low latency – The direct connection between networking devices offered by DAC Cables provides low latency, reducing delays when transmitting data.
Energy efficiency – Since DAC Cables do not use any power supply, they consume substantially less power than other networking cables.
Cost-effective – Compared to Fiber Transceivers, DAC Cables are a more cost-effective solution for networking setups.
When deciding between DAC Cable and Fiber Transceiver, it is essential to consider the specific use case and network requirements. While DAC Cable provides high speeds and low latency, Fiber Transceiver is a better option for long-distance communication and high electromagnetic noise environments. Fiber Transceivers use optical signals to communicate, eliminating the risk of electromagnetic interference and providing better insulation than copper cabling.

Cisco is one of the leading networking equipment manufacturers globally, and compatibility with their devices is a critical consideration when choosing a networking cable. DAC Twinax Cables have been thoroughly tested and approved for use with Cisco equipment, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance. With the advancement of technology, newer Cisco equipment is now designed to use DAC Cables to connect between switches, routers, and servers. Using the appropriate DAC Cable for each device is always advised to ensure maximum compatibility and performance.
DAC cables are an essential tool for interconnecting servers and other network devices, as they provide a reliable, low-latency, cost-effective, and easy-to-use connection.
DAC cable can be used for a wide range of applications, such as:
High-speed data transmission between switches, routers, and servers
Interconnecting data centers
Connecting rack-mounted devices in a data center
Connecting storage devices
Supporting high-bandwidth Ethernet applications
DAC cables are ideal for use in data centers due to their ease of use and reliability. The copper cables provide a high-speed, low-latency connection between server racks and switches, making it easier for network administrators to manage network performance and ensure uptime. DAC cables can also connect switches to routers, providing a high-bandwidth connection ideal for large amounts of data.
DAC cables offer several benefits for high-speed data transmission, including:
High-speed transmission: DAC cables can support speeds of up to 10Gbps, allowing for fast and reliable data transmission.
Low-latency: DAC cables have a low-latency connection, reducing the possibility of data loss or signal degradation.
Cost-effective: DAC cables are a cost-effective solution for network cabling, reducing the cost of traditional fiber optic cabling.
Easy to use: DAC cables are easy to install and use, reducing the time and labor required for cabling.
DAC cables are essential for interconnecting data centers, providing a high-speed, low-latency connection ideal for large amounts of data. DAC cables can be used to connect data centers or to support cross-connects within a single data center. This makes it easier for network administrators to manage network performance across multiple data centers and ensure uptime.
Ethernet networks require high-speed, low-latency connections to support fast data transmission. DAC cables are essential for Ethernet networks, providing a cost-effective, high-speed solution for interconnecting Ethernet devices. DAC cables can connect a wide range of Ethernet devices, including switches, routers, and servers, providing a high-bandwidth connection ideal for large amounts of data.
DAC cables can connect routers to other network devices, providing a high-speed, low-latency connection ideal for large amounts of data. DAC cables can also connect routers to storage devices, providing a high-speed connection suitable for data backup and recovery. Additionally, DAC cables can connect routers to servers, providing a high-bandwidth link ideal for data processing and analysis.
Passive DAC cables, as their name suggests, are passive and require no external power source. These cables only convert the digital-to-analog signal and do not modify or amplify it in any way. Passive DAC cables are commonly used for shorter cable lengths and within limited spaces.
On the other hand, active DAC cables are equipped with dynamic electronics technology that wirelessly transmits data. Active DAC cables do not just convert the signal but amplify it, resulting in a more robust and more precise audio signal. Active DAC cables are ideal for longer cable lengths, as they are less prone to signal loss over distance.
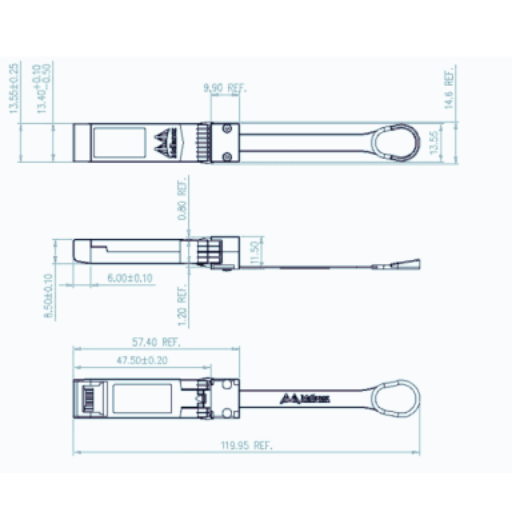
Passive DAC cables are simple cables that convert digital signals into analog signals. These cables do not require external power and are just a ‘’ure pass-through of” of the call. They work by receiving a digital signal from an electronic device, converting it into an analog signal, then transmitting it to an audio output device.
Recommend Reading: 10G DAC High Speed Cable VS 10G AOC Active Optical Cable: Who is better?
One advantage of Passive DAC cables is their affordability, as they are typically less expensive than Active DAC cables. Additionally, Passive DAC cables do not require any external power sources, making them more convenient to use. Their lack of circuitry makes them less prone to signal interference, resulting in better signal quality. However, Passive DAC cables may not always be suitable for longer distances or amplifying weak signals.
Active DAC cables are designed with active electronics, which help to adjust wave signals and promote wireless data transfer. Active DAC cables boost the strength and clarity of movements transmitted over longer distances. By amplifying the call, they provide clear and powerful audio.
One of the significant benefits of using Active DAC cables is their ability to transmit signals over longer distances with minimal signal loss. This makes them ideal for use in large venues or other areas with significant signal interference. Additionally, because Active DAC cables amplify the signal, it can significantly improve signal quality.
However, Active DAC cables require an external power source for their active electronics, which can be challenging to use in specific environments. They are also typically more expensive than Passive DAC cables, which can be a drawback for some users.
The main difference between Passive and Active DAC cables is that Active DAC cables use active electronics technology to amplify signals, resulting in a more robust and more precise audio signal. On the other hand, Passive DAC cables are more affordable, widely available, and do not require external power.
Data center technicians require flexible cabling solutions that quickly adapt to changing situations. Breakout DAC cables provide this flexibility, allowing technicians to easily connect devices without time-consuming setup procedures.
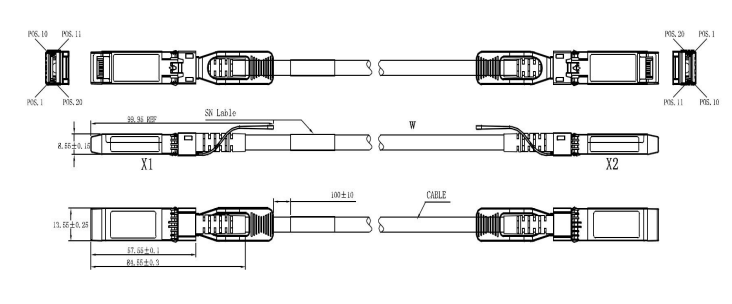
A Breakout DAC (Direct Attach Copper) cable is a copper-based cabling solution that transmits data between two devices. It consists of multiple copper pairs encased within a protective shield and terminated with connectors. Breakout DAC cables typically feature SFP+ (Small Form-factor Pluggable) connectors, allowing a variety of transmission speeds, including 10Gbps and 40Gbps.

Breakout DAC cables are passive cables, meaning they do not require any external power or active components to transmit data. They convert electrical signals into optical signals and vice versa, allowing data to be sent over a copper cable.
Connecting a Breakout DAC cable involves plugging one end into the ddevice’sSFP+ port and the other into the receiving ddevice’sSFP+ port. This straightforward process allows for quick and easy setup of devices within a data center environment.
Breakout DAC cables provide several benefits over other cabling solutions, including flexibility, low latency, and cost-effectiveness. Their flexibility allows for easy installation and quick responses to changing network environments. This makes them ideal for use in data centers and cloud computing applications.
They can transmit data with minimal latency, providing a reliable and stable connection between devices. Breakout DAC cables are also cost-effective compared to fiber-optic cables, making them an attractive option for professional network installations.
Given their versatility, Breakout DAC cables are commonly used in various industries, including telecommunications, cloud computing, and high-performance computing. These cables provide reliable connectivity for servers, switches, and storage devices, making them an essential tool for data center technicians.
Breakout Fiber Cables are an alternative cabling solution to Breakout DAC cables. While both provide reliable data connection, Breakout Fiber Cables use optical fibers to transmit data and are more expensive than Breakout DAC cables. They are also more fragile, requiring more care in installation and operation.
However, Breakout Fiber Cables provide longer transmission distances, making them ideal for use in data centers that span multiple geographic locations. Both types of cables have advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial to choose the right cabling solution for the specific application.
Selecting the correct Breakout DAC cable for your setup requires consideration of several factors, including cable length, device compatibility, and transmission speed requirements. Choosing a line that can handle the necessary data transfer rates and devices is crucial while fitting with the data center’s center’s central architecture.
DAC (Digital to Analog Converter) cables are essential for transmitting digital audio signals from one device to another. Whether used in professional audio settings or for personal entertainment systems, choosing the suitable DAC cable is critical for high-quality sound transmission and compatibility with your device.
The first step in choosing the suitable DAC cable is selecting the correct cable assembly. DAC cable assemblies are available in various lengths, connectors, and configurations. When selecting a DAC cable assembly, you should consider several things, such as the distance between the devices, the number of connectors required, the type of connectors used, and the quality of the cable itself. Different connectors include BNC, SC, ST, LC, and MTP/MPO.
Connector types are a critical factor in the overall performance of a DAC cable. Different connector types have different levels of compatibility with devices, and choosing the correct connector type can significantly impact sound quality. For example, BNC connectors are commonly used in professional audio settings, while LC and SC connectors are most widely used in home audio systems. Choosing a cable that uses the correct connector type for your devices is essential.
Recommended Reading: Fiber Color Codes
Another essential factor to consider when using DAC cables is the power consumption required by the cable itself. High-quality DACs can require a significant amount of power to operate correctly. Some DAC cables do not have the necessary internal filtering and regulation devices to ensure they do not draw too much power. Choosing a DAC cable with appropriate power regulation is critical for ensuring compatibility with your device and avoiding damage to your equipment or data.
DAC cable length is another critical factor in overall performance. Longer cables can introduce signal degradation and interference, reducing sound quality. Ensuring that your DAC cable is not too long or too short is essential to achieve optimal performance. Several factors, including the cable quality and the type of connectors used, determine the maximum cable length.
Finally, ensuring compatibility between your devices and DAC cables is essential. Most devices have specific requirements for the DAC cables they can use, and using the wrong cable can result in poor sound quality or equipment damage. When selecting a DAC cable, ensuring your device’s specifications is critical.

A: DAC cables offer several benefits, including cost-effectiveness, simplicity, and low latency. They are a budget-friendly option compared to optical transceivers and allow for easy installation as they come with connectors on either end, eliminating the need for additional components. DAC cables also provide low latency, making them ideal for high-speed data transmission.
A: The main difference between DAC cables and optical transceivers is the medium used for data transmission. DAC cables use copper wire, while optical transceivers use fiber optic cables. While DAC cables offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness, optical transceivers provide longer reach and higher data rates.
A: Yes, DAC cables can be classified as active or passive. Active DAC cables have built-in electronics that boost the signal strength, allowing for longer cable lengths and higher data rates. Passive DAC cables, on the other hand, do not have any electronic components and are limited to shorter cable lengths.
A: DAC cables can be used with various networking devices, including switches, routers, servers, and storage devices. They are widely used in data centers and other high-performance computing environments.
A: DAC cables can support various data rates, including 10G, 40G, 100G, and even higher. The specific data rate depends on the type of DAC cable and the capabilities of the devices it is connected to.
A: A breakout cable is a type of DAC cable that connects multiple devices using a single line. It has connectors on one end that can be split into various connectors on the other, enabling the devices to communicate.
A: DAC cables are compatible with QSFP (Quad Small Form-Factor Pluggable) and SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) transceivers. They offer a reliable and cost-effective alternative to traditional fiber optic connections.
A: The maximum cable length of DAC cables depends on the specific type and data rate. Generally, copper DAC cables have a fixed height of up to 15m, while active optical DAC cables can reach longer distances, up to several hundred meters.
A: DAC cables can be used as an alternative to AOC (Active Optical Cable) cables. While AOC cables use fiber optic technology for data transmission, DAC cables offer a cost-effective solution for shorter distances and high-speed connections.