In the digital era, data centers are the main storage points, processing units and distribution channels for information. Among the many categories available, Tier 3 data centers are known for being the most reliable while still remaining fairly cheap with good performance. The intention behind this guide is to explain what Tier 3 data centers are all about; this will involve looking at design features as well as operational requirements and benefits among others. Once these areas have been covered it should be clear why more businesses opt for Tier III facilities over any other type when they need strong but affordable data management solutions. For those who work in IT or manage data centres or lead companies — no matter your position or job title within an organization — this article provides everything necessary not just to understand but also succeed in dealing with complex issues related to tier three datasites effectively.
The level ranking model itself was created by Uptime Institute to reflect on a data centers redundancy level, fault tolerance as well as sustainability during operation. There are four categories in this model; from tier one up until tier four where each represents different standards for performance and redundancy.
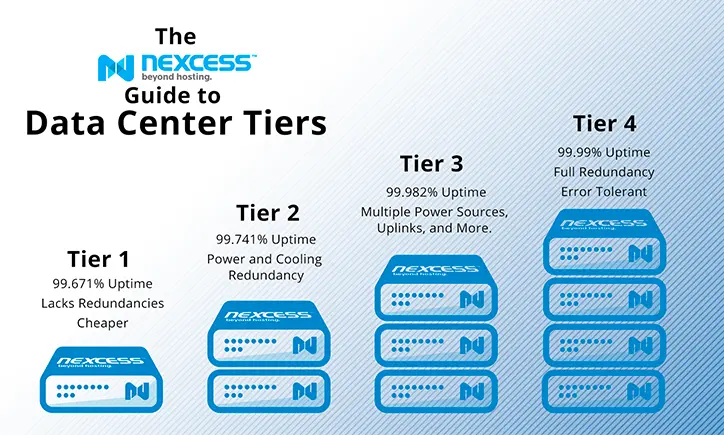
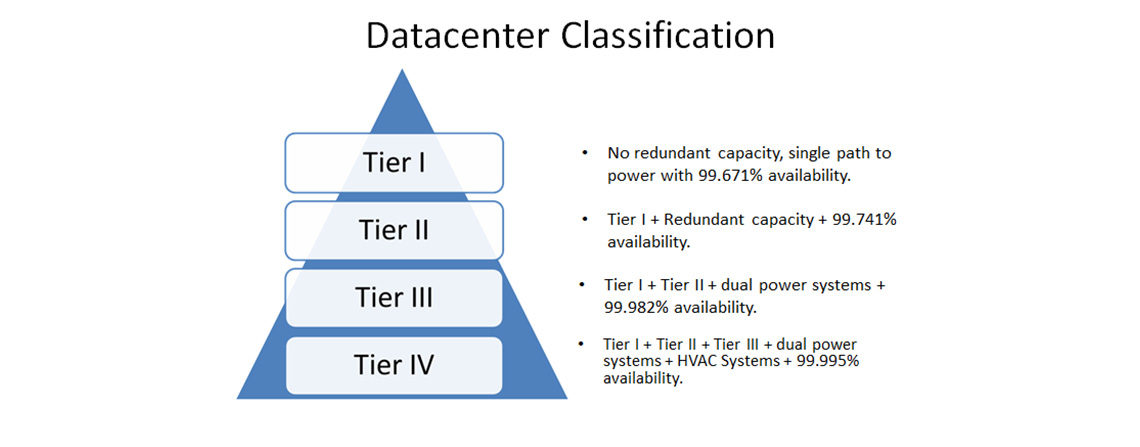
Data centres belonging to Tier 1 provide basic capacity without any duplication suitable for small businesses and non-critical applications which have an availability rating of 99.671%.
Tier 2 facilities introduce some redundancy into power and cooling systems thereby supporting even more robust operations that boast of 99.741% availability.
Commonly called “concurrently maintainable,” Tier 3 were designed with multiple power and cooling distribution paths so that no component could be taken out or replaced without shutting down the whole system. Its availability stands at 99.982%.
Data centres in Tier 4 have the highest fault tolerances and redundancies among all other categories, meaning one single failure within their components cannot affect operations at large scale while providing an uptime assurance of 99.995%.
Being placed midway through hierarchy cost wise while still maintaining reliability makes tier three very attractive option for most businesses requiring high uptimes but not ready yet or willing enough to invest heavily into achieving them as would be necessary were they aiming at securing themselves within fourth tiers walls.
A few key characteristics make certain datacenters superior over others in terms of efficiency or dependability. Such attributes are designed carefully so that they may balance cost effectiveness and reliability while supporting robust infrastructure.
These technical standards not only demonstrate how robust tier three data centers can be but also show their versatility as cost effective solutions suitable for various business needs where reliability matters most.
Comparing Tier 3
data centers with other tier levels requires understanding the uniquenesses and requirements of each level. Below is a simplified comparison between tier 1, tier 2, tier 3 and tier 4 data centers:
From a detailed analysis of these factors, it becomes clear that tier three data centers are the best option as they offer both reliability and affordability. They provide much higher availability and redundancy than tier one or two but do not require huge investments like in the case of tier four.
Tier certification is important in establishing the efficiency, reliability and general capability of a data center. The certification level, which is set by Uptime Institute directly impacts operational protocols as well as preparedness for different scenarios.
In conclusion, different levels of tier certifications have various effects on service reliability, infrastructure investment, operational resilience and customer confidence in data centers. Therefore organizations need to consider their specific needs vis-a-vis industry requirements while selecting a particular level of a data centre tier which aligns with their corporate objectives.
Uptime Institute is an organisation that plays a critical role in the tier certification process for DCs (data centers). Established in 1993, it is an internationally recognized body tasked with evaluating the performance and reliability standards of these facilities. They created ‘Tier Standard: Topology,’ which categorizes them into four tiers based on redundancy fault tolerance, among other things.
The Uptime Institute’s certification procedure consists of strict evaluation and confirmation processes done by external specialists. These assessments consider the sustainability of a data center’s design, construction, and operation with reference to its tier level, which must be met. If an establishment passes these tests successfully, it is awarded a tier certificate that recognizes its efficiency and dependability.
Apart from increasing the credibility and market value of data centers, Uptime Institute’s tier certification program sets a basis for better design practices as well as operational improvements continually. This system helps operators identify areas which need strengthening thereby making it more reliable while at the same time enhancing performance; this in return will increase customer confidence.
There are numerous advantages associated with getting tiers certified for data centres since they greatly contribute towards boosting their operational excellence, credibility and market share. The most important benefit is that there will be high levels of reliability where by such facilities should never fail to provide necessary services hence ensuring business continuity plan is not interrupted. In addition to this, it saves on power consumption because resources are utilized efficiently according to strict standards set during design phase so energy not wasted unnecessarily leading also reduced operational cost.
Moreover, another advantage brought about by having tiers certification is that clients who require stable systems can easily identify them through looking for those marks indicating various levels like one star or two stars among others; thus attracting top notch customers becomes easy too since people know where best quality services can be found always.Furthermore,a certified facility serves as an assurance factor especially when dealing with critical information processing activities involving large volumes of sensitive data likely targeted by cyber criminals; therefore businesses feel safe knowing that their valuable records protected well against all odds even hackers.In addition,the whole exercise creates awareness among employees about continuous improvement culture coupled with proactive maintenance planning thus enabling them detect early signs danger before it escalate into major crisis situation beyond management control measures taken were insufficient last time round.Besides,it makes sense compete effectively against other market participants whose products lack this type of endorsement.
In conclusion, what the tier certification does is to add robustness in terms of technicalities involved while ensuring sustainable operations within data centers beside positioning them appropriately vis-à-vis their customers’ requirements so that long term success achieved even during demanding times in business.
What distinguishes a tier 3 data center from other types is its sophisticated infrastructure which consists of multiple components designed to ensure maximum uptime and reliability. Here are some key points about this level:
In summary, these elements make up a data center environment that ensures service delivery is not only reliable but also efficient in terms of operational effectiveness while keeping services available maximum uptime.
Redundancy is the main priority when it comes to designing power and cooling distribution paths in Tier 3 data centers. These facilities boast of concurrently maintainable infrastructure which means that any single component (such as a UPS, generator or cooling unit) can be taken offline without affecting the overall operation of the center.
In general, power redundancy coupled with cooling redundancy in Tier 3 facilities ensures that there is no compromise on operational integrity of a data center even during maintenance activities or when failures occur hence providing an ideal setting for critical IT services.
One of the most important things about tier three data centers is that they are built for reliability. This means that there should be very little downtime or failure in any system within the structure. The best way to guarantee higher uptime is by using multiple systems where one acts as a backup for another; this applies power and cooling infrastructure as well. Typically, these facilities have several power feeds so that if one fails, another can take its place. Generators are used in an N+1 configuration which denotes having more than what is necessary thus covering for any failures while UPS (uninterruptible power supplies) act as buffers during blackouts.
It should be noted that redundancy also matters when it comes to heat dissipation. Therefore, advanced cooling units in tier three data centers are designed such that some can be taken offline without affecting others around them. For instance, cold water circuits may fail leading to overheating but it won’t affect overall performance since there still will remain other chillers working properly.
Furthermore, such a facility should monitor every aspect of its environment closely at all times if maximum uptime has to be achieved. This means having various sensors scattered throughout measuring things like airflow rate, humidity levels among other variables so as not miss anything vital necessary for quick response in case of any change from normal conditions detected which might lead into potential failure prevention being done before it’s too late (proactive measure). It should also have automatic power transfer switches between mains and generators which comes into play during outage events thereby reducing downtime period experienced during such situations.
In addition to this physical security measures must be put in place within these data centers since they are highly vulnerable targets for malicious attacks due their significance critical services supported by them offer Various control systems like biometrics access controls combined with surveillance cameras help prevent unauthorized entry thus keeping both operationally safe and available environment
To achieve consistent availability and reliability, data centers belonging to tier three category must also be duplicated. This is done through designing the structures with many backup systems that can continue running even if one fails. In case of power failure these redundant power systems ensure continuity by providing an alternative source of electricity which is generated by uninterruptible power supplies commonly known as UPS coupled with backup generators.
Moreover, another thing that helps in redundancy creation within these facilities is cooling. For a data center to function properly it needs low temperatures hence there should always be more than one cooling system just incase one fails or becomes faulty. These cooling units are made up of multiple chillers, air handling units and towers among others so they can work continuously without stopping thus preventing IT equipment from heating up.
Another important aspect about tier three data centers deals with networking. Network redundancy means setting up more than one connection between two points to avoid single point of failure which may cause communication breakdown hence leading to loss of important information. These centers ensure this by having several network links and diverse paths through which packets can travel from their origin to destination thus making sure that there is always an alternative route in case one link goes down thus reducing chances for data transfer interruptions.
Furthermore, duplication of data has been achieved using mirroring and replication techniques. In order not to lose any content during hardware crash or other catastrophes, storage devices must contain two or more copies of every file required by applications running on them; this ensures quick recovery when disaster strikes since it will only take few minutes restoring from secondary sites rather hours waiting for new drives arrive at the site.
In conclusion we can say that redundant features built into these types of centers create strong environments where everything works well most time without failure thereby enhancing reliability levels and operational uptime capabilities. Such kind planning helps such like facilities support critical IT operations with less disruptions taking place.
Physical and cyber security are necessary to maintain uptime. Redundancy is built into the design and protocols of Tier 3 data centers so that they can achieve 99.982% availability as promised. These security measures include multiple levels of protection against unauthorized access, such as surveillance cameras, biometric access controls and mantraps; and defenses against cyber threats like firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS) or regular security audits.
Environmental Control: Continuous monitoring of environmental conditions within the data center – temperature, humidity, airflow etc., ensures equipment operates under optimal conditions for performance. Should any of these variables fall out of range automated system will make adjustments in real-time so as to prevent any possible failures.
Reducing downtime in a data center requires strict adherence to operational standards and best practices. The following strategies are based on industry-leading resources which have proven effective at mitigating hours of downtime:
Compliance and Audits: Regularly conduct audits compliance checks against set industry standards regulations so as to identify rectify weaknesses within both physical logical aspects long term reliability performance improvement can be achieved through this approach

Several main trends are driving the growth of tier 3 data centers:
It is important for Tier 3 data centres to keep up with these changes so as to meet the needs of modern enterprise IT environments while ensuring reliability, efficiency and security.
Emerging technologies have greatly impacted tier three facilities. Some of the areas that have been affected by this include advancements within these centers and capabilities that they possess. They are driven by various key emerging technologies such as AI (artificial intelligence) which is being integrated together with ML (machine learning) to optimize operations in data centers, enhance energy conservation as well as predict maintenance requirements. Another important technology is Edge Computing; it enables tier III establishments process data nearer to source thereby minimizing delay & improving performance.
Moreover new cooling techniques like liquid immersion or even block chain based security systems need to be adopted within such facilities since they help cut down on energy consumption levels alongside operational costs too. Also growth of 5G networks has extended functionality scope for third tier establishments because faster connectivity along side higher data transfer speeds can now be realized through them.
Therefore integration of these technologies creates more flexible scalable efficient third level centres which are better placed in meeting changing business demands and regulations; besides their ability to withstand various threats over time will continue increasing due development brought about by mentioned technological advancements hence making them greener while at same ensuring higher performance standards at all times.
Among the most significant challenges faced by tier-three data centers today involves a demand for energy efficiency amidst growing operational needs. As demand for space continues growing, there’s a need to adopt innovative cooling methods coupled with proper management strategies aimed towards sustainability; also, observing environmental regulations may require shifting towards the use of renewable sources of power supply so that carbon footprint can be minimized accordingly.
Security is the primary concern today as we see more complex cyber threats and for this reason security measures must advance and be forward-looking. Although it enhances transparency and data integrity, it requires a strong encryption and verification process.
Scalability is also difficult because growing enterprises need more data centers that can handle increased capacity while still performing well. This may involve modular solutions or edge computing options which provide a way forward by allowing for step-by-step growths coupled with localized processing of information to cut down on delays as well as enhance efficiency in general.
Moreover, seamless operation between legacy systems and new technologies calls for interoperability. The use of open standards alongside flexible architectures could help in integrating different systems thereby creating a conducive environment that fosters unity within infrastructure even when faced with diverse challenges.
In conclusion, what will happen to Tier 3 data centers in the future depends on their ability to adapt with changing technology, environmental conditions and security needs. These problems can only be solved through adoption of modern discoveries characterized by high levels of efficiency together with stringent safety requirements.
To know if your company should move to a tier 3 data center, consider some factors against what these facilities offer:
In conclusion, if your organization needs high dependability levels together with strong backup power systems, robust physical access measures supported by top-level digital surveillance capabilities, and future growth prospectiveness, then you should probably choose a tier three data center. However, always remember that cost implications should be aligned with financial objectives and operational plans for success realization.
When considering the move to a tier 3 data center, it is important to conduct a thorough cost benefit analysis. Below is an outline based on what most businesses in this industry are currently doing:
In summary, though choosing a tier three data center involves huge starting and running expenses, its reliability, security features, compliance requirements, and flexibility can prove far higher than these costs. Organizations must assess their specific needs vis-a-vis financial capability so that they can ensure strategic positioning through such a move while also achieving favorable return on investment (ROI).
1. Online Retail Giant
Background: This e-commerce company was growing rapidly but still required a strong IT infrastructure to keep up with its expanded operations.
Problems: The business experienced frequent outages as well as slow speeds when processing information, thereby making operational efficiency and customer satisfaction poor.
Solution: They moved into a tier 3 data center that has 99.982% uptime guarantee and improved data processing capabilities.
Technical Parameters:
– 99.982% Uptime or better which means there would be less than an hour and a half of downtime in any year.
– Concurrent maintainability allowed them to perform maintenance without interrupting service provision.
Outcomes: The business attained smooth running even during peak traffic periods leading to higher client satisfaction rates too.
2. Financial Institution
Background: To protect sensitive customer data while meeting strict regulatory standards was the main goal for this major bank.
Issues: Cybersecurity and compliance with PCI-DSS among other regulations such as GDPR were some challenges faced by the organization.
Solution: Stringent security measures were put in place through implementation of tier three data centers designed specifically for financial institutions like banks so they can also meet all these requirements easily.
Technical Parameters:
– Enhanced security protocols included multi-tiered protection against different types of cyber threats.
– Regulatory compliance involved following industry norms like PCI-DSS or GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
Results: Strengthening privacy protection levels provided by law thus enhancing trust from customers who know their information is safe guarded well enough always.
3. Medical Center Network
Background: A reliable storage facility was necessary within this hospital network where patient records could be kept securely alongside supporting integrated healthcare systems.
Challenges: The need to work with highly sensitive health related information that cannot afford any amount time being down for maintenance purposes etcetera – zero tolerance for downtime scenario analysis
Solution: For high availability and strong data safety, the best thing to do was transferring them into a tier III datacenter.
Technical Parameters:
– High Availability implies 99.982% uptime or better which guarantees that there will always be continuous operation almost throughout the year.
– Data security measures included encryption as well access control lists (ACLs) among others so as to protect these records from unauthorized persons gaining entry.
Results: Better management of patient data files plus reduced chances of experiencing problems caused by intrusions into computerized systems containing personal medical histories therefore enhancing risk management against breaches.
4. Worldwide Telecommunications Company
Background: A telecoms operator needs an infrastructure capable of supporting its global operations securely and at scale
Challenges: Ensuring stable connections; managing vast volumes
Solution: The company opted for utilizing tier-3 data centers due to scalability requirement and security concerns.
Technical Parameters:
Scalability made possible through building many smaller sections which can then be combined when needed thus enabling growth without too much interruption.
For better safeguarding of information assets advanced protection mechanisms were put in place such as firewalls as well physical perimeter defenses like biometric locks etcetera
Outcomes: It helped streamline international business activities while allowing smooth expansion into other territories seamlessly.
These examples show how different sectors can utilize highly reliable, secure and scalable Tier 3 Data Centers. It is important to evaluate technical parameters appropriately for strategic alignment with business requirements hence significant ROI realization.
These sources collectively provide a well-rounded view of Tier 3 data centers, from theoretical foundations and standards to practical implementation and performance analysis.

A: A tier classification system has been created by the Uptime Institute as a way to measure uptime and performance for data centers. It is a process that groups data centers into one of four tiers based on their infrastructure’s fault tolerance, reliability and operational sustainability. They are ranked from Tier I being the least complex with minimal redundancy and uptime capabilities to Tier IV which offers maximum levels of fault tolerance and operational uptime.
A: The difference between these three types can be seen in their infrastructures. For example, while there is only one path for power and cooling in Tier I centers with no redundant components resulting in them having an uptime of 99.671%; Tier III ones have multiple routes for both power as well as cooling plus systems allowing maintenance without shutting down whole centres leading to them offering an uptime rate equaling 99.982%. On the other hand; A typical Tier IV facility incorporates multiple active power distribution paths, multiple cooling distribution paths with at least one path being concurrently maintainable, fault-tolerant site infrastructure including electrical supply, storage area network(SAN), servers etc guaranteed by SDB standard where applicable in order provide continuous service availability throughout all operations hence ensuring upto 99.995% uptime.
A: This step verifies that architectural plans comply with necessary criteria so that they can be awarded an appropriate level under Tiers Classification System(TCS). The Uptime Institute or any other authorized body carries out this certification exercise which serves to show whether or not given designs meet expected standards on resilience; redundancy among others when it comes to building such facilities designed accordingly depending on what level each falls into according its expected performance during operation stage also known as rating phase if we may say so.
A: Yes, a data center can upgrade its tier rating. This can be done by modifying the infrastructure so that it meets higher standards of redundancy, fault tolerance and uptime required for the next level in the classification system. This may involve significant investment in terms of infrastructure upgrades such as adding more power paths with cooling capabilities; ensuring equipments are powered through different sources like electricity or generator among others; improving on reliability features like having backup systems incase one fails among many others which contribute towards achieving greater levels of resilience necessary at each stage according to this scheme. Normally people do this because they want their centers perform better but also there could be operational need which have become stringent overtime where owner’s desire is not just meeting them but exceeding expectations as well when possible.
A: Data center performance is directly affected by the tier classification system, mainly in terms of uptime, fault tolerance and dependability. Higher-level centers such as Tier III or Tier IV are designed to provide more redundant systems with better performance so that they have backup capabilities that greatly reduce risks associated with downtime or even breaches. The stepwise approach followed in this system ensures compliance to international standards for design; operation and risk management which greatly affects efficiency and performance of such facilities in general.
A: Based on specific operational requirements as well as cost considerations, an enterprise may prefer selecting among different types like Tier II, Tier IV etcetera; however some businesses may opt for higher levels like Tiers Three instead of Two because they offer much higher availability i.e., 99.982% uptime compared to 99.741% offered by lower tiers like Two. Another thing that differentiates between them is maintainability; while it is possible to do maintenance without any disruptions with Three but not Two which requires shutting down everything during maintenance period thereby causing downtime thus affecting services being delivered through such centres negatively especially those whose operations run throughout twenty four hours daily.. Besides its lack fault tolerance when compared Four still provides good reliability mixed up with affordable prices making these kinds suitable for organizations seeking high availability without spending too much money required achieving certification at Four level.
A: In order to guarantee an uptime rating equaling 99.995%, multiple steps must be taken into consideration within the framework of tier four classifications for data centers. This involves having all IT equipments being dual-powered alongside full compatibility with topology adopted by infrastructure comprising each facility; use fully redundant subsystems also known as active-passive mode where one acts as backup while other serves primary purpose; implementation fault tolerant site infrastructure having different independent distribution paths serving information technology equipment among many others. Moreover, such centers are designed with ability to concurrently maintain every single function without affecting operations during any failure (concurrently maintainable). In addition sufficient protection against physical disasters is provided here thus ensuring highest level operational continuity required at this category.
A: Although aimed mainly at improving infrastructure redundancy, fault tolerance and uptime, data centre tier standards indirectly contribute towards preventing security breaches. More secure physical and operational environments are built in higher level facilities through stringent security measures which includes but not limited to advanced monitoring systems, strict access controls or even comprehensive disaster recovery protocols among others. By minimizing service disruptions caused by down times during which attacks may take place continuously forever, these safeguarding levels ensure continuous operation so that no windows exist for potential breaches to occur within secured areas thus reducing risk periods associated with hacking into sensitive networks or systems.