Choosing the right cable in the networking field significantly affects your system’s performance and reliability. For instance, considering protective property includes deciding whether to use shielded or unshielded Cat 6 cables. Conventionally found in Ethernet networks, these cables perform differently in protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, critical to signal quality and data transmission. This article is focused on the comparative review of the performances of shielded and unshielded Cat 6 cables for their construction and applied target use. Here is the section where the basics of technical differences with their applications for the network requirements will be introduced to make the right choices for the specified needs.
What is Shielded Cat 6 Cable and How Does it Work?

Understanding the Basics of Cat6 Cable
A Category 6 cable or Cat 6 cable is a standard type of twisted pair cabling utilized in Ethernet and other network physical layers. Like any other Ethernet cable, it too has four twisted pairs which allow data rates of up to 10 Gbit/second for lengths not greater than 55 m. The design of the cable has been able to reduce crosstalk and EMI due to increased twist levels and better shielding than previous standards like that of Cat5e. Placing the pairs in this way leads to better performance and reliability while operating at high speeds in networks.
How Does Shielding Improve Ethernet Cable Performance?
The performance of the Ethernet will improve due to the covering or shielding made from conductive material enclosing the inner cables. This conductive shield helps to protect metallic or/wire carrying signals from magnetic or radio interference. The use of shielded cables including shielded twisted pair and foiled twisted pair cables is particularly useful in areas where there is a lot of electromagnetic interference such as in factories and other places with heavy electrical equipment. Because of the decrease in external interference and crosstalk, the shielded Cat 6 cables can maintain better performing network, with a faster data rate and fewer errors in transmissions.
The Role of Shielding in Reducing Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Shielding is the most effective method in the prevention of Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) in the Ethernet cables. Noise and disturbances produced by interference distort the data transmission to a great extent. In shielded cables internal twisted pair wires are wrapped in either foil or braided metal to provide a shield against electromagnetic radiation. This construction helps in restricting the amount of IM from outside. Moreover, it also reduces crosstalk between the pairs of the cables resulting in better quality of the signals being sent. With the use of shielding Cat 6 cables emit better signal and use even in non cable friendly areas filled with heavy machinery and broadcast use devices.
Why Choose Shielded Cat6 Over Unshielded Cat6?
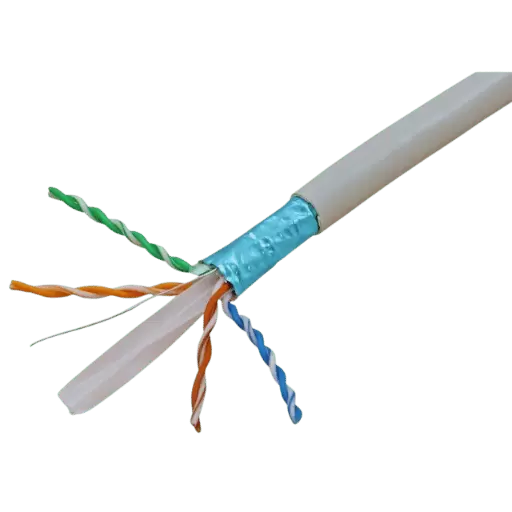
Advantages of Shielded Cat6 Cable
- Improved Signal Quality: Using a shielded Cat6 reduces the chances of signal quality degradation. Their shields do not allow electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio interference (RFI) to affect the data thus allowing use in high external noise environments.
- Enhanced Data Capacity: These cables tend to enhance data speed because of the shielding thus minimizing crosstalk and external interference, which are detrimental. Shielded Cat6 cables are known to transfer data up to 10 Gbps and distances of up to 55m instead of the unshielded Cat6 which is in a noisy area.
- Increased Dependability: The increase in the rather high degree of reliability comes from the fact that these errors in transmission are far removed. Making shielded Cat6 cables enables a stable connection and is paramount in today’s world where data flow is required nonstop because of example use high definition video streaming and real time data use.
- Increased Lifespan of Cable: Generally, shielded cables are much stronger and more robust than unshielded cables. They further help to shield against EMI as well as physical stress, making a cable management and control reasonable for a long term period.
- Best suited for Industrial Use: In locations with high EMI sources, such as manufacturing plants or places with lots of machinery, shielded Cat6 cables still guarantee network performance. The field tests show that these cables perform very well even in industrial areas with minimal data loss and downtimes.
- Adherence to Stricter Standards: Limited edition Cat6 shielded cables do meet greater industry standards for EMI and RFI than the bare ones. These measures are vital for mission-critical applications and are an extra peace of mind to the network administrators.
When used shielded Cat6 cables instead, users are assured of excellent and high quality performance that can withstand rough conditions for commercial as well as industrial Ethernet networking requirements.
Comparing Shielded and Unshielded Cat6 Cables
In looking at specific characteristic differences when Cat6 cables are shielded or unshielded, the following factors come into play:
- Protection from EMI and RFI: Users of shielded Cat6 cables do not have to worry about electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). This is particularly important for high-performance systems that operate in environments that contain many sources of interference, if any at all. On the other hand, the unshielded cables may be working in an EMI and RFI-environment, thus have a less efficient operation of the network.
- Installation Complexity: Shielded cables are more complicated to handle because of the exactness that should be applied to achieve proper bonding of the cable shield and connecting the ends of the shielding layer in appropriate places. On the other hand, unshielded ethernet cables are less complicated in connection thus suitable for use in an average household or office setup.
- Physical Durability: The average life of shielded cables is generally high since more protection covers these as no foreign objects are allowed into the area and replacing those shielded cables is hardly needed, if at all. Unshielded cables, as implied, are used in less heavy-duty application and work, but they are average anyway.
- Cost: You need to have deep pockets before investing in shielded Cat6 cables as this category is predominantly expensive. On the contrary, cost of manufacturing should be cut down since unshielded cables are sufficiently employed in areas that are not exposed to elevated levels of EMI/RFI.
- Application Suitability: In scenarios requiring high reliability and performance, such as data centers or industrial environments, shielded cables are the preferred option. Unshielded cables can be installed in most common commercial and residential applications where EMI and RFI are unlikely to be an issue.
To summarize, the determination of the usage of shielded or unshielded Cat6 cables is dependent on the nature of the environment and its protection against EMI/RFI interference. Shielded cables are more robust and long lasting than unshielded ones, however, this comes with a cost and a more challenging installation process while unshielded cables are easier to use, install and cost less for less challenging installation circumstances.
Common Applications for Shielded Cat6
Ruggedized Cat6 cables are recommended in wet or very noisy electromagnetic environments such as EMI and RFI. These applications include:
- Data Centers: The presence of electronic computers in high concentration requires Cat6 shielded cables to enable transmission of data without compromising the network.
- Industrial Environments: Industries, manufacturing plants, etc. are also filled with heavy machines which deal with heavy EMI/RFI. In such environments, sheath cables work to improve the network as much as possible.
- Broadcasting Facilities: Audio and video signals are quite prone to interference while transmission. Very high frequency shielded Cat6 cables lower the noise making sure high fidelity audio and video transmission is achieved.
- Medical Facilities: Hospitals, clinics use different electronic devices that can produce EMI. During such situations, shielded Cat6 cables guarantee the performance of efficient and stable key network tools in the healthcare industry.
- Military Applications: Due to the requirement during the military operations process, the use of shielded Cat6 cables to offer communication that is less prone to interference makes this system preferable.
How to Install Shielded Cat6 Cable

Steps for Proper Installation of Shielded Ethernet Cable
- Cabling Routing: Mapped the ideal path for the cable so as to restrict the chances of exposure to EMI/RFI with every possible effort towards avoiding physical barriers to installation.
- Collection of Cables and Tools: Assemble all the ancillary items for cable stripper, crimpers, shielded connectors, and grounding kit.
- Measurement and Cutting of Cable: Prepare the measurement of the necessary length of the cable, take into account additional length for future re-works and cut it depending on the tools at hand.
- Jacket Removal: Gently pull off the internal and external jacket of the cable sheath to prevent breaking the inner insulation and the wires.
- Insertion of Shielded Connectors: The shielded connectors are mounted on the becomes of the weighted coaxial shielding the two ends for protection taken for proper insertion.
- Installation of Grounding: With the help of the grounding kit installed at the ends of the cable, connect the cable shielding to ground.
- Cabling Testing: Connect the cable continuity and check the operational capability of the system to its performance in every practical aspect.
- Cable Management: All these activities included the tying of the cable along the route that shall have been determined using cable ties or any other means avoiding bending and/or places of stress.
Do’s and Don’ts of Shielded Cable Installation
Do’s:
- Do ground properly: This requires you to ensure that both ends were grounded with concerns to the shielded cables with concerns to noise.
- Do use proper bend radius: The cable is also expected to withstand certain minimum bend radius as provided by the manufacturer to prevent any damages to the cable and performance.
- Do use proper type of connectors: Remember to use shield connectors and accessories every time you connect shielded cables in installation to the system.
- Do necessary testing: Tests should be qualitative inclusive but not limited to continuity test and performance test for the installed cables.
- Do cable management: Each cable should be tagged for efficient identification in the future.
Don’ts:
- Don’t route the cables in the same direction as power Line access cables: The colocated area should be avoided with shielded cables placed close electrical wiring.
- Don’t pinch the cable and don’t crush the cable: Do not tighten the cable unions on the cables to vandalize the shielding and the conductors.
- Don’t forget to ground: Failure to ground the Cable completely may result to great disturbance in the operation due to EMI/RFI.
- Don’t exceed maximum cable length: Also do not forget about the maximum cable length which is the greatest distance allowed for CAt6 cables use without retiring it.
- Don’t strip too much of the jacket: Remove only enough of the jacket thus exposing the required length of wire which is needed, aimed at ensuring that the internal parts are intact and in place.
Using RJ45 Connectors with Shielded Cat6
With shielded cat6 cables and a RJ45 connector, it is critical to take care of the termination to ensure that the performance of the cable and its shield is not affected.
- Choose the Right Connectors: A metal body supported earthing shrouds upon the connectors supporting shielding brackets protects against EMI. Use Cat6 shielded RJ45 connectors.
- Prepare the Cable: Remove the cable jacket but not too much of it, just enough to expose the inner wires that will fit into the connector. Avoid friction stripping unless bonding everything together otherwise leaves zip jacket out.
- Maintain Shield Continuity: Ensure that the foil shield & drain wire of Cat6 Cable is in contact with the metal shell of the connector. This is very important as it provides independent continuity of the shielding across the cable assembly.
- Terminate Each Pair Correctly: Follow the T568A or the T568B wiring standard to arrange the twisted pairs into a pin head at the connector. This is done to ensure that there is an efficient performance pin configuration.
- Crimping Process: To terminate shielded RJ45 connectors, use a robust crimping tool. Squeeze the connector on the cable evenly while crimping to hold the connecting structure firmly in place without ‘crushing’ the shielding and that everything is in position.
- Testing the systems: After disconnection, all necessary tests should be performed for the verification of the connection and the cable’s performance as well. This includes the efficiency of conductive communication and the quality of cable meet the category six standards.
Applying these logo design procedures makes it hard for engineer managers to claim that the RJ45 terminations consisting of shielded Cat6 cable are not effective in shielding any em interference.
What are the Common Issues with Shielded Cat6 Cables?

Common Mistakes in Shielded Cable Installation
- Improper Shield Termination: Failing to connect properly the foil shield as well as drain wire to the metallic shell of the connector which reduces the electro-magnetic interference control.
- Excessive Jacket Removal: Removing a great portion of the outer jacket of the cable which destroy the mechanical support built inside the cable and expose the inner wires to risk.
- Incorrect Pair Arrangement: Non adherence to either T568A or T568B standards wiring whereby proper and effective pin out configuration is not observed.
- Poor Crimping Technique: Bad habits such as use of bad quality crimpers or applying pressure unevenly which may cause connector rupture and no guarantee of shield continuity.
- Inadequate Testing: Missing comprehensive testing after termination which means there are potential isolated defects and performance issues in the cable assembly.
How to Troubleshoot Shielded Cat6 Cable Problems
- Visual Inspection: Perform the initial visual check for damaged parts on the cable including, cuts, bends, or cut off header cables. Check the status of the outer covering for good installation.
- Continuity Testing: Check every pair for breakage with the cable tester; there must not be inner breakage or short-circuit in the cable. If the continuity test is successful, the two ends of the wire have been successfully soldered together.
- Shield Integrity Check: Use any special tester having a shield continuity test capability and ensure that the continuity of the shield is intact. This provides assurance that the foil shield and drain wire remain properly connected to the metal casing of the connector.
- Certification Testing: Verification of willing cable analyzer for performing certification tests up to Cat 6 cabling standards. This involves parameter measurements on crosstalk, return loss, and attenuation among others.
- Review Wiring Standards: Double check that the ponytail sheath is trimmed off or did not impede wiring terminations making sure the two options wiring T568A or T568B were adhered to. Arranging the pairs wrongly will have negative consequences on performance.
- Replace Faulty Components: In case of problems on the above steps, faulty connectors need to be removed or the faulty cable sections need to be re-terminated. At times, the problem could be with the connectors themselves or even the crimping process which is done wrongly.
These troubleshooting steps should be followed in a systematic manner so that difficulties in the shielded Cat6 cables can be diagnosed and corrected and the network optimally utilized.
Maintenance Tips for Shielded Cat6 Cables
- Visual Inspections: An occasional inspection of the cable should be done for signs of wear. Check for visible issues like cuts, abrasion, kinks in the cable and deformation of connectors too.
- Handling and Installation: Never over-bend a cable because excessive tight bending can create damage the constructive element making the performance worse. Operate within the recommended minimum cable bend radius.
- Cable Management: Avoid strong pull on any cable towards any direction to eliminate bending and other risk. For example, instead of allowing dangling cables, they should be secured to the desks, for instance, using adhesive tape, or Velcro straps.
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Do not expose the cable to sources of EMI like power lines or electrical cables. This guarantees that the shield will be intact and the damage to the desired signal will be minimal.
- Factors such as temperature and humidity: People should make sure that the cable will not be subjected to high or low temperatures as well as moisture or corrosive substances. Also, the area of installation should be within the recommended specifications pertaining to temperature and humidity.
- Regulatory Compliance: Make it routine for testing procedures aimed at cable utilization in the future. In a specified period, remove the communication cable tester to determine line and cable continuity and signal measuring to establish whether the signal shield is damaged or sealed. Where any problems arise during such tests, act fast to correct them so as not to affect network performance.
Having deployed these maintenance methods, it is possible you could prolong the life of your shielded Cat6 cables while guaranteeing dependable network involvement.
How Does Shielded Cat6 Improve Network Performance?
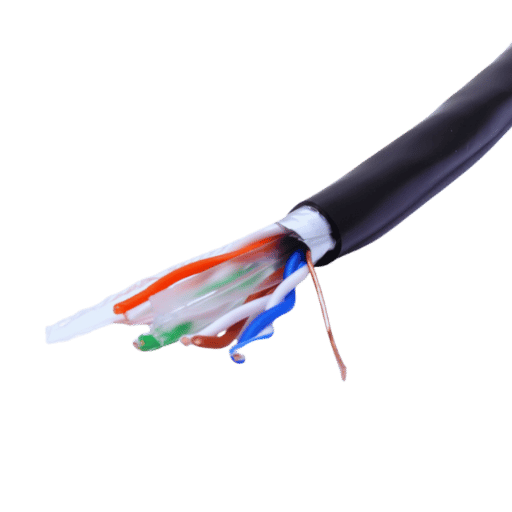
Reducing Crosstalk and Ensuring Data Integrity
Shielded Cat6 cables minimize crosstalk which is the undesirable signal interference from other cables. Cat6 cables with added shielding layers above and around the individual pairs of wires in the cable have even greater efficiency. This reduction in crosstalk means that more accurate data and higher quality signals will be provided over the Cat6 cables thus improving the overall performance of the network.
Maximizing Bandwidth with Shielded Cat6
This provides a wider bandwidth up to 250 MHz for the Shielded Cat6 cables. In comparison to the unshielded ones, the transmission rates are much superior in the case of Shielded Cat6. The shielding decreases external interferences and thus preserving signal quality. Hence this less interference and noise enables the network systems to function effectively, using maximum data throughputs and bandwidth even when there is a presence of hefty electromagnetic noise. This makes Shielded Cat6 perfect for any application which involves high quality and dependable data transmission.
Long-term Benefits of Using Shielded Ethernet Cable
The adoption of shielded Ethernet cables presents various gains in the long run, thus making them a worthy device that one can rely on for a stable network structure. First of all, they are able to prevent the effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) where such external influences might be strong, such as in industrial sectors or heavily electrically active areas. This makes for a more stable and reliable network connection over a period of time. Secondly, shielded cables tend to be more robust than unshielded ones thanks to the additional material protection – thereby contributing to prolonged durable life of the cable and less replacement. Finally, because shielded cables can transmit more data at a decreased error rate, they afford the networks higher bandwidth optimization potential, reducing the chances of the networks becoming obsolete as data increases. The overall impact of these is a decrease in maintenance and an increase in effectiveness regarding the operations of the network.
Reference Sources
Category 6 cable
Ethernet
Modular connector
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What would you say is the contrast between shielded Cat 6 and unshielded Cat 6 cables?
A: The primary factor in the differentiation of shielded Cat 6 (STP) cables and unshielded Cat 6 (UTP) cables is their structure. Shielded Cat 6 cables contain extra layers of metal foil or a mesh of braids around the insulated treatment of twisted pairs to eliminate EMI. On the contrary, UTP cables only use the twisted pair method to control all types of noise. In cases of high interference, shielded cables work well, while UTP cables have less usage, hassle, and installation and are more convenient for the users.
Q: What are some instances where a shielded Cat 6 cable is preferable to an unshielded Cat 6 cable?
A: If you intend to run the Cat 6 cable in highly energetic electromagnetic interference (EMI) environments (for example, in power generation areas), you may also decide to use a shielded Cat 6 cable. Several instances recommend the application of shielded cables, including in an industrial area with many machines operating. 2. Close to electricity cables or electric appliances. 3. Cable installation in data centers with a high number of cables. 4. Outdoor cable fittings. 5. In a situation where cables are in a run along with power cables, supplementary shielding works to help protect the quality of the signal and enhance shielding from external interference.
Q: What are the advantages of using a Cat 6 shielded cable?
A: One of the most common cable types that people use in day-to-day operations are the Cat 6 shielded cables. Some advantages that these cables have include: 1. Improved immunity to EMI and crosstalk 2. Longer Transmission of Signals with a High Fidelity 3. Better Efficiency in High Acoustic Environments 4. Lower alien crosstalk in areas with many cables 5. Good for climates and outside use 6. Higher performance in bandwidth-supporting applications than the unshielded ones 7. Providing an assurance that, willingly or accidentally, the work will not need any additional adjustments.
Q: Are there any drawbacks to these shielded cat 6 cables?
A: Shielded Cat 6 Cables is effective as earlier explained. However, there are some drawbacks of using such cables. 1. These cost more than unshielded cables. 2. They are more difficult to use due to excessive stiffness and weight. 3. These have to be grounded firmly to perform properly 4. Electro-shielded cables are often not required in environments that are not subject to a lot of interference. 5. Large thickness of the cable, which might interrupt the application of cable management 6. It is much more complicated to install and needs advanced connectors.
Q: Is it possible to mix shielded and unshielded CAT 6 cables in a network?
A: Yes, you are allowed to use shielded and unshielded Cat 6 cables within the same network. Nevertheless, as a best practice, use the same cable type for every run along the cable route. For instance, if a shielded cable is used to initiate the cable run, shielded patch cords and shielded jacks should also be used for that run. It will be more efficient and secure to leave off the shield from certain areas than to intermingle shields and non-shields in one cable run.
Q: What is the maximum length of cat 6 shielded cables that is permitted?
A: The maximum distance that is commended for Cat 6 shielded cables is 100 meters (328 feet) of a full horizontal channel, including the associated patch cords at either end. This is synonymous with the distance that is provided for unshielded Cat 6 cables. In most cases, however, shielded cables tend to be more efficient over longer distances than unshelled cables, especially in areas where there is likely to be electrical interference. Beyond 100m distance limitations, one may require a network extender or fiber network cable.
Q: What procedures must be undertaken when completing and earthing a shielded CAT6 cable?
A: The end termination and grounding of a shielded Cat 6 cable are done to enhance its efficiency. Following are the basic steps: 1. While designing connections for STP cables, make sure to use compatible shielded plug/receptacles specifically created for Cat6 design 2. When stripping the cable, be very fussy with the shielding 3. Follow T568A or T568B wiring standards to complete the termination of the individual twisted pairs 4. Solder the shield of the cable to the metal shield of the connector. 5. Make sure that Roger’s tube is shielded and clipped to the ground of the patch panel or apparatus 6. The same shielding is also used on the patch cords, and all long runs on cable 7. Ensure that the grounding system installed in the building is intact It’s advisable that this be done professionally in order to achieve efficient grounding and performance.
Post Views: 5,846




