In today’s very fast-changing digital world, high-speed and dependable networking is a must-have for any business or home. More so, there is a need for quicker data transfer rates, efficient network management, and continuous connectivity, which has resulted in the popularity of SFP+ routers that offer 10 gigabit Ethernet (10G). This article looks at SFP+ routers from various manufacturers, such as MikroTik and Ubiquiti, with an emphasis on their unique features. Whether you want to upgrade your organization’s network infrastructure as an IT expert or looking for the best equipment for high-performance home networks as an enthusiast in the field of technology, this complete overview will give you all the necessary information needed while making choices. We shall be considering the top available SFP+ routers by exploring their features, benefits, and technical specifications, hence enabling one to get the best solution for his/her fast networking needs.
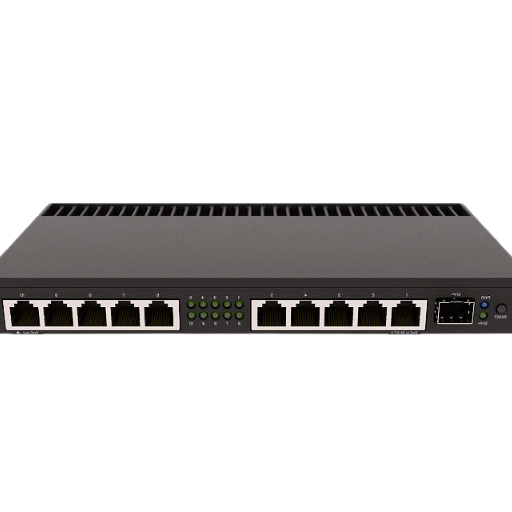

The increasing demand for tasks that require a lot of bandwidth, such as watching videos online, doing research with big datasets in the cloud, and so on, have made 10-gigabyte-per-second speeds necessary in contemporary applications. Faster access to critical resources is why we need higher data transfer rates: this ensures minimal latency, which is useful for real-time data analytics, among other things; larger file transfers become more feasible, too — not to mention seamless video conferencing. Furthermore, organizations could experience scalability issues without them, given their ability to accommodate many users or devices over time within an enterprise network; this helps provide future-proofing while improving security features & network efficiency throughout – both aspects are key components required for robustness when talking about networks capable of achieving these kinds of speeds.
To be able to make a good decision, several key factors should be considered when comparing 10G SFP+ routers from top brands like MikroTik and Ubiquiti. MikroTik routers are popularly known for being affordable while having many features, making them suitable for people on tight budgets who still need high-performance equipment. They offer configuration flexibility that suits complex network setups well. On the other hand, Ubiquiti routers are very easy to use because they have user-friendly interfaces and also perform reliably, which makes them great even for beginners in IT or those who do not want any downtime. However, their unifi series has been commended greatly because it integrates seamlessly with other network components, thus simplifying management as well as scalability.
Apart from these two giants, there are many other 10G SFP+ router manufacturers that can compete favorably, too. For instance, Cisco provides enterprise-grade solutions with massive support teams behind them, plus advanced security features meant specifically for large organizations that require the highest levels of performance and reliability. Similarly, Netgear caters to different needs through various models, which are characterized by being tough enough even if used in harsh environments such as those found at home offices or small businesses.
To summarize this article; MikroTik is cost effective yet powerful; Ubiquiti emphasizes ease-of-use alongside reliability; however both Cisco Systems Incorporated (Cisco) Inc., NETGEAR International Inc., among others also provide competitive options depending on enterprise & SMB networks – ultimately your decision will depend on what you need most i.e., low budget vs best performance or simple management against maximum uptime!
Ethernet’s development has seen many breakthroughs, moving up from one gigabit per second (1Gbps) to ten gigabits per second (10Gbps) Ethernet. In the late 1990s, Gigabit Ethernet was introduced as a copper cable standard in IEEE 802.3ab, and it significantly increased previous rates of data transmission. Due to its ability to cater to more extensive bandwidth requirements necessary for video conferencing and large-file-transfer systems, among others, this technology was widely accepted in offices and data centers.
The need for greater speeds prompted the invention of 10Gbps Ethernet under IEEE 802.3ae, which utilized fiber optic cables and then later on twisted-pair copper cables through IEEE 802.3an so as to cope with higher capacities brought about by data-intensive applications advancement alongside virtualization together with cloud computing. More rapid processing of information can be achieved when deploying this type of internet connection, thus reducing latency periods besides enhancing overall performance within networks, hence making them crucial parts of modern network infrastructures that allow for easy connectivity while at the same time preparing them against future demands posed by growing amounts of data traffic.
Ethernet is still evolving as a technology since it serves as the foundation upon which various enterprises establish their networks in relation to speed and efficiency needs demanded by current consumer environments.
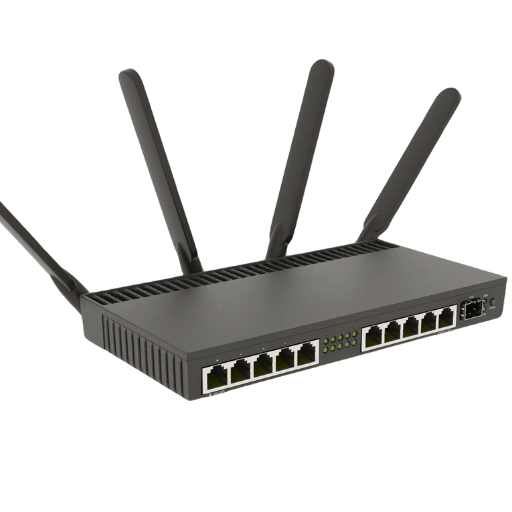

Various unique features make MikroTik cloud router switches (CRS) outstanding in the market for networking hardware. These gadgets combine a router with a switch, which brings about flexibility and cost-effectiveness in different network scenarios. Besides this, MikroTik CRS models have advanced layer three (3) switching capabilities that enable effective routing, firewalling, and traffic management. The RouterOS operating system also contributes to its versatility, widely known for being packed with many features such as dynamic routing support, hotspot management support, VPN support, and QoS support.
Moreover, MikroTik CRS devices come with a simple interface that is easy to understand during setup and management and thus can be used by beginners as well as experts in the field of networking administration. With high throughput plus low latency, they provide robust performance levels capable of meeting modern high-speed networks’ requirements, also supporting them greatly. What makes these switches so attractive for businesses looking towards reliability along with scalability while seeking network solutions is their powerful hardware coupled with extensive software features at affordable prices.
Designed for high-demand networking environments, the MikroTik CCR2004-16G-2S+PC boasts superior performance and advanced features. With a 1.7GHz quad-core Annapurna Labs Alpine v2 CPU and 4GB DDR4 RAM, it offers powerful processing capabilities necessary for managing intricate networking tasks. It has 16 gigabit Ethernet ports and 2 SFP+ ports which provides modern network infrastructures with high-speed connectivity options.
Hardware-accelerated IPsec encryption is one of the most impressive features that the CCR2004-16G-2S+PC possesses; this alone can enhance security measures while not compromising its speed. This is very useful if a company needs secure VPNs or wants their data to be sent encrypted. Moreover, this device supports two power supplies in case of failure – this ensures continuous service operation and reduces downtime risks dramatically.
Moreover, the CCR2004-16G-2S+PC utilizes all the capabilities of MikroTik’s RouterOS software fully thereby offering an extensive range of network functions. Among them are such advanced routing protocols as BGP and OSPF, multi-level firewall filtering, bandwidth management tools, and hotspot gateway functionality, among others professional level network monitoring tools too are supported by this device, therefore providing full visibility into network traffic patterns at any given point in time. It combines robust hardware components together with flexible software features, making it a reliable option for professional or enterprise networks where versatility matters most.
A powerful and flexible operating system for routing is the RouterOS by MikroTik. RouterOS supports among other things dynamic routing, firewalling with VPNs and bandwidth management as advertised by some leading tech sources. This includes protocols like BGP, OSPF or RIP which can create networks that are efficient in terms of scaling and resilience too.
On the security front line – IPsec VPN support together with advanced firewall features have been integrated into RouterOS to allow secure communication over the network between different segments. Bandwidth management tools within this operating system enable fine-grained traffic control so that resources are optimally distributed across a network even when it is loaded heavily thus maintaining high performance levels always.
In addition to all these, RouterOS comes bundled with various monitoring as well as diagnostic toolkits needed for keeping an eye on traffic graphs reflecting real-time interfaces plus logs, among others, used mainly for health maintenance within networks besides rapid problem identification or isolation should they occur. Regular updates combined with modular architecture make this software always adaptable while still being secure enough against emerging threats targeting enterprise environments where large-scale deployments often take place professionally, too. The fact that the CCR2004-16G-2S+PC router relies heavily on them means none other than Mikrotik’s Router OS could be behind its stellar performance records!
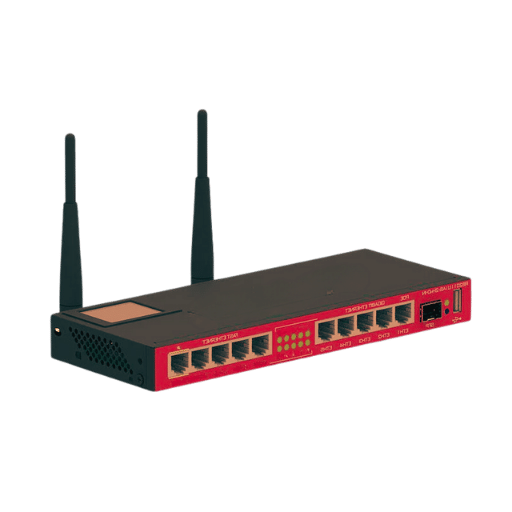

When it comes to comparing the Edgerouter with the MikroTik Cloud Router Switch (CRS), different reviews by most reputable tech sources have identified a number of similarities and differences.
Performance and Hardware: The Edgerouter has gained popularity for its strong performance with the help of flexible EdgeOS firmware, which is great for high speed gigabit routing. Conversely, MikroTik’s CRS devices have been commended due to their advanced layer 2 & 3 switching capabilities that make them versatile enough to serve as both switches and routers.
Feature Set: VPN support, VLAN capabilities and QoS features are available on either device. Nonetheless, what sets apart Edgerouter from the rest is its CLI customization coupled with community support said to be best suited for network engineers looking for extensive customization at a deeper level.MikroTik’s CRS boasts a RouterOS that works well with switching capacity which ensures seamless integration between these two functionalities.
Usability and Configuration: The user interface of Ubiquiti’s Edgerouter has been hailed as being relatively easy to use while also coming equipped with abundant online resources that simplify setup for non-networking professionals. On the other hand, It may take longer than expected for one to get familiar with how MikroTiks’ CRS devices function since RouterOS offers many features — however, this should not worry anyone since it enables users to configure almost everything about their network connections.
Cost Effectiveness: Both products are priced competitively based on what they offer in terms of functionality, but sometimes, people may find themselves needing combined switching/routing capability. In such cases, Mikrotiks’ CRS can be more cost-effective.
In conclusion, therefore, whether you choose an edge router or Mikrotik crs will depend largely on your specific networking needs; if you want high routing performance along with ease of use, then go for an edge router otherwise, if enhanced switch features plus deep configuration options within less space consumed is what you’re looking for in a device then mikrotik crs should work best for you.
In modern network architecture, aggregation and redundancy are very important for high availability and the best performance. These two elements can be used together by Ubiquiti Networks in its solutions aimed at improving efficiency and reliability of the networks.
Aggregation: Ubiquiti has UniFi Switches which support LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol). This makes it possible to combine many network connections into one logical link. This process aggregates more traffic through several physical links thereby increasing bandwidth that is available for mission-critical applications.
Redundancy: EdgeSwitches with EdgeRouters from Ubiquity come with strong redundancy features such as VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol). HA or High Availability configurations allow a device to fail over smoothly between active and standby devices. With this protocol, failure of one device means another takes up immediately hence continuous network service provision.
With these in place on any given structure of the ubiquity network, not only does it achieve maximum performance, but it also ensures no downtime occurs, thus making the network seamless even during failures.
Ubiquiti’s control software takes care of network management and deployment with ease. UniFi Controller, UISP (Ubiquiti ISP), and AmpliFi app are included in this dedicated controller.
UniFi Controller: This software lets you manage all of your UniFi devices centrally, giving you a powerful tool for configuring and monitoring networks. It comes with detailed analytics, real-time metrics as well as the ability to manage multiple locations from one interface. Also zero-touch provisioning, firmware updates and detailed network maps that simplify complex deployments are centralized too.
UISP (Ubiquiti ISP): UISP was designed for Internet Service Providers (ISPs). It allows them to have complete visibility into their network infrastructure and customer devices. The platform supports monitoring, maintenance, and configuration tasks, thus ensuring high service reliability and performance levels.
AmpliFi App: The AmpliFi app is for home network users who want an easy way of managing their Wi-Fi networks through a smartphone. It simplifies things like setup, guest access management or even parental controls.
By implementing these tools together with others Ubiquiti ensures that its deployments are done flexibly, precisely & easily which improves both operational efficiency and user experiences alike.
When looking for the correct SFP+ router for your network, it is important to understand what sets RJ45, SFP, and SFP+ ports apart from each other.
RJ45 Ports: These are Ethernet ports that are most commonly used. They were created to connect twisted-pair copper cables. One standard configuration supports up to 1 Gbps but they can also work with several speeds. These ports can be used easily and flexibly, so they are often employed in connecting computers or switches within a network.
SFP Ports: AKA small form-factor pluggable ports, these have modules that allow different transceivers to be plugged in depending on the desired link. This means they can handle both copper and fiber optic connections supporting speeds up to 1Gbps typically. In terms of network design flexibility, there is more possibility regarding this kind since it can cater to longer distances and various media types, including but not limited to fiber optics.
SFP+ Ports: With data rates normally ranging between 10Gbps – ten times higher than their predecessors’- these advanced versions offer much faster speed options as compared with regular SFPS. They should, therefore, not miss out on any high-performance networks where fast, reliable data transmission is necessary. Data centers are known heavy users of bandwidth, thus making them perfect candidates for employment of such ports in addition to enterprise networks.
Knowing all these types will enable you to choose the right router for your network by considering performance requirements against infrastructure capabilities.
CPU Specifications: The CPU, also known as the Central Processing Unit, carries out data packet processing and routing functions. In a high-performance SFP+ router, it is recommended that one uses a multi-core processor preferably Intel or ARM brands. Higher numbers of cores together with quicker clock speeds allow for concurrent management of multiple data streams hence lowering latency in resource hungry network environments.
RAM Specifications: Random Access Memory (RAM) acts as an operational memory for routers where they store routing tables among other things like ARP caches needed for real time processing. For this reason modern SFP plus routers should have no less than 8 gigabytes of RAM installed but higher capacity modules are better since they enable the device to handle lots concurrent connections and heavy traffic loads without slowing down.
Power Supply Specifications: The power supply unit (PSU) is responsible for providing stable power to all parts of a router, such as its CPU, RAM chips and transceivers, etcetera; therefore, total energy consumption by these components should be taken into account while selecting PSU type. Redundant power supplies are necessary, especially when dealing with enterprise-class equipment so that there can be uninterrupted operation even during failures on one side or another. Where reliable PSUs come in handy because not only do they boost router performance but also save electricity, which leads to overall system stability.
Redundant Power Supplies: It is necessary to have redundant power supply units for network routers as they operate continuously in environments that require high availability. They create a backup system where another power supply unit takes over when the first one fails without any downtime. This additional feature is important since it keeps the network up and running all the time and prevents loss of data or delays that can affect business transactions. Redundant power configurations can greatly minimize the chances of experiencing a shutdown, which makes networks more reliable and stable.
Layer 3 Characteristics: Layer three characteristics are inclusive of IP routing functionalities; these are basic requirements for an effective scalable network design. Such features enable routers to handle traffic between different subnets as well as VLANs, hence allowing the use of advanced routing protocols like OSPF, BGP & EIGRP. When used together with Layer 3, security becomes better through advanced ACLs. This also enhances load balancing for an optimized flow of information. The adoption of layer three aspects not only guarantees enhanced performance but also redundancy while giving us control over our traffic, thereby increasing overall efficiency within the entire network, thus making it more reliable too.

VLAN Configurations: To set up VLANs on SFP+ routers, you need to split up one physical network into different broadcast domains. This is done to boost the performance and security of the network through traffic separation. You can configure this by accessing the router’s web interface and then going to VLAN settings, where you will define VLAN IDs together with their interfaces. After that, assign ports accordingly to each VLAN and configure the 802.1Q tagging on the router. Such isolation enables better traffic management as well as troubleshooting which confines all broadcast traffic within specific VLANs.
VPN Configurations: Creating a VPN (Virtual Private Network) using SFP+ routers allows for safe remote access into the network. First, set VPN parameters via the web interface of your router, followed by choosing what type of VPN to use depending on how secure you want it to be; SSL, IPsec, or L2TP are some examples. Create user accounts that can log in through this connection and then ensure correct routing over the VPN by implementing appropriate rules. All these steps guarantee private channels between different locations, thus protecting data sent across public networks from being intercepted while in transit.
Command Line Interface (CLI): The CLI is used by network administrators for specific and detailed network configurations. Ensure you are familiar with the most commonly used commands, as this will help a great deal in increasing proficiency, which comes through practice. Repetitive tasks should be automated using scripting tools to ensure that configurations remain consistent throughout. In case of troubleshooting or future references, it is good practice to have comprehensive documentation when configuring via CLI; this should include command logs and configuration steps. Moreover, tab completion, command history, and contextual help, among others, can be used so as to work smarter, not harder, with the advanced features of CLI.
Graphical User Interface (GUI): This option presents itself as an easy-to-use platform for setting up networks where beginners can equally benefit just like their experienced counterparts would do. When working on complex configuration tasks using GUIs, more often than not, there are visual elements provided that act as shortcuts or guides, thus making everything appear less difficult. Firmware must be updated regularly so that one can have access to the latest patches besides other security features, but sometimes people tend to ignore such things until they realize it’s too late, i.e., backup configurations should also be done regularly through the graphic user interface, hence enabling fast recovery from any problem that may arise.
In order to manage networks comprehensively and consistently, managers ought to adopt both CLI and GUI methods.
To mix cordless and wired networks with SFP+ routers, follow these steps for an uninterrupted and efficient network setup:
Through following these procedures, one can successfully blend a cordless together with a connected set-up using routers that support SFP+, thus establishing a secure, scalable and high-performing infrastructure.

MikroTik:
Affordable yet feature-packed networking equipment is the hallmark of MikroTik. These routers range in price from $50 to $500 and come in many different models suitable for various network sizes or types. They have advanced routing functionalities, full support for IPv6, and a strong security feature set, among other things. Additionally, these devices support different protocols used for managing networks while running on an extensible operating system called RouterOS, which provides firewalling and VPN capabilities alongside routing functions.
Ubiquiti:
Ubiquiti products are known for their simplicity combined with powerful performance targeted mainly towards enterprises; thus, it is no surprise that they are priced higher than most consumer-grade brands. A typical Ubiquiti router might cost between $100-$1000 depending on its specific model number and the features being offered by the manufacturer at any given time. One thing that sets ubiquity apart from other manufacturers is its user-friendly UniFi Controller software, which greatly simplifies network configuration, monitoring, etc. Other key highlights include advanced security protocols, seamless scalability, high throughput, etc, making them a perfect fit even when deploying large-scale networks.
Others:
Other companies’ SFP+ routers are also in the market, such as Cisco, Juniper, and Netgear. For example, Cisco is known for its dependability and wide range of features, but they do cost more, with a price tag that can be anywhere between 300 dollars all the way up to as much as 3000 dollars. These routers perform exceptionally well when it comes to speed, safety features, and enterprise-level support for business applications. In comparison with Cisco, which has higher prices, juniper and Netgear provide mid-range options balancing price and performance. This can be achieved by charging their clients anything from 150 dollars going upto 1200 dollars. Such devices are good choices for small or medium size enterprises because they come fitted with strong security measures as well as easy management tools that use fewer resources while delivering reliable performance throughout.
While deciding between SFP+ and RJ45 connectivity, many things should be taken into account like network speed demand, distance limitation as well as infrastructure cost. For high-speed network environments, SFP+ (Small Form-factor Pluggable) ports are beneficial because they can support data rates of 10Gbps or higher. They work best where fiber optic cables are preferred or necessary since they allow for longer distances, up to several kilometers, without significant signal degradation.
On the other hand, RJ45 ports use traditional copper cables which are usually cheaper and easier to install in existing setups. Normally, RJ45 is good enough for shorter distances that range from 100 meters downwards while supporting speeds of up to 10Gbps. However, it is more vulnerable to electromagnetic interference than its fiber optic counterparts.
In terms of performance and scalability, SFP+ is better suited for enterprises with large amounts of traffic across campuses or throughout a data center. Meanwhile, RJ45 would still be considered affordable and efficient within small-medium businesses or environments where cable runs are relatively short. Ultimately, what should guide this decision-making process is what exactly this network needs. These are some of the factors that you may want to consider when balancing between speed vs distance vs budget constraints.
To get the best deals on network equipment, combine reputable online retailers with networking specialty stores.
You will find right network products matching your exact requirements and ensuring that every dollar spent is worth it by considering these leading stores.
Ascent Optics
WISP.net.au
A: The number of gigabit ethernet and 10g sfp+ ports must be considered. This can include configurations with 8x or 2x ethernet ports. You should also check if it supports 10 GB connections, has a console port for management, advanced security features for VPN and firewall applications, as well as compatibility with high-speed standards like ten Gbps full-duplex line and 2.5g ethernet to optimize office network performance.
A: It is small in size but big on performance thanks to one (1) 1g Ethernet port coupled with four (4) 10G SFP+ ports which allow high-speed connectivity. The device utilizes the Marvell Amethyst family switch-chip which helps with data processing efficiency while supporting static routing that enables better traffic management within your network environment. Additionally, this model offers a console port designed specifically for easy configuration through the command line interface option. With DDR4 RAM and NAND storage included among its features, Mikrotik CRS305-1G-4S+IN represents powerful yet affordable devices suitable even when there is a limited budget available for purchase intended use being office networks.
A: Yes, they are! In order to ensure simplicity during the setup process, Ubiquiti made their software rich in intuitive features so anyone, regardless of whether he/she has prior experience working on such projects, will be able to understand what needs to be done next without much struggle. From simplified installation steps all the way down to guided configuration procedures, everything about these routers was supposed to make life easier. Both technical and non-technical personnel were tasked with configuring and managing networks. An Omada SDN platform for centralized control over the entire network is also added.
A: While some 10GBase-T modules are compatible with Cat6 cabling for up to 55 meters, the majority of 10G SFP+ routers use either optical or direct attach cables (DACs) to connect other network devices. However, if you have an office that is wired with Cat6 and need to make ethernet connections over longer distances but still want to take advantage of the benefits provided by using a 10GSFP+router, there are certain models available on the market that come fitted module slots capable housing compatibility modules allowing connectivity via already pre-installed infrastructure in form cat six cable assemblies.
A: When you buy your MikroTik or Ubiquiti 10G SFP+ router, think about buying compatible modules for each 10g sfp+ cage – optical or DAC, depending on the requirements of your network. Ethernet ports may need gigabit ethernet switches or 2.5g ethernet switches to expand the network. For uninterrupted power supply and secure mounting, you can add UPS and rack mount kits to your cart. If it is not included with the router, then you might also require a console cable for initial setup and configuration.
A: The addition of gigabit and 10 Gbps full-duplex capabilities can greatly improve performance on an office network by allowing higher data rates as well as simultaneous transmission in both directions, thus reducing bottlenecks while maximizing per port bandwidth which ensures smooth handling of high-volume, low-latency applications like video conferencing, large file transfers among others; this also allows connection of multiple high-speed devices without compromising performance.
A: In case you need assistance configuring your high-speed networking router, most manufacturers, such as MikroTik and Ubiquiti, have extensive support resources, including user manuals, forums, customer support hotlines, etc. Furthermore, there are many community forums where people share knowledge through videos or step-by-step guides that can be very helpful too; therefore, if it’s complex, it may be worth considering hiring someone who specializes in networks so they can configure it right from the start to end ensuring best performance & safety features possible.
A: To find out if your existing wireless networking products are compatible with a 10G SFP+ router, check the product detail pages or datasheets for both devices and see whether they support the same standards such as gigabit ethernet, 2.5G/5G/10G speeds, optical or wired port types, etc. Also, ensure that the router supports the same network layers & protocols as those used by your wireless devices so that integration can be seamless; should you need help on this matter, most manufacturers’ customer service teams will guide you accordingly.