Nowadays, it is the efficiency and reliability of your network infrastructure that matter most in this information-oriented world. Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) Network Card Adapter Network Interface Cards (NIC) are at the cutting edge of networking technology, with flexible and high-performance solutions for bandwidth and network reliability growth. This article seeks to explain the baselines, benefits, and application techniques of SFP Network Card Adapters in modern-day networking systems. By optimizing your network using an SFP NIC, you will not only be increasing data transmission rates but also ensuring scalability and flexibility within your network architecture. To unleash the potentiality of a company’s network infrastructure, it is important to understand how SFP Network Card Adapters function, whether they are intended for small-scale business enterprises or large data centers whose networks depend on them.
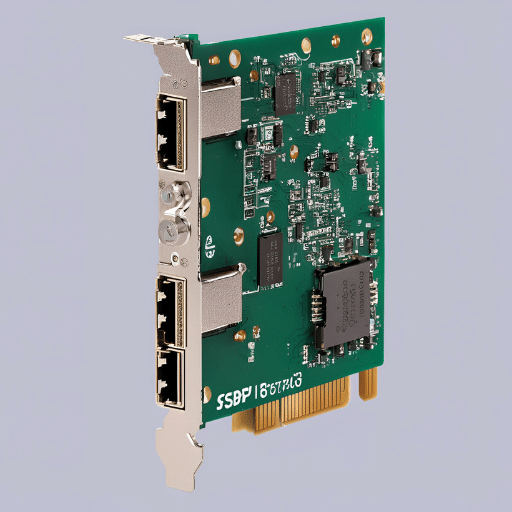
The SFP Network Card, a Small Factor, is a very small and hot-pluggable network device used in telecommunications and data communications. It connects the motherboard of a network device (such as a switch, router or similar) to fiber optic or copper networking cables. With SFP technology, users can access different telecommunications and data networking standards like SONET, Gigabit Ethernet, and Fibre Channel. In addition to making network configurations more flexible, this adaptability also improves the general performance of networks in use. This enables system administrators to easily upgrade their systems to meet growing bandwidth requirements without replacing entire infrastructure units. Additionally, SFP modules are inherently versatile, enabling them to be integrated easily into existing network infrastructures, thus boosting scalability and ensuring future-proofing of networks.
The inception and widespread deployment of high-speed Ethernet and Fiber Optic connectivity have transformed how data is transmitted across networks, representing a huge departure from conventional networking methods. In this regard, the High-speed Ethernet offers cheapness as well as effectiveness that accommodates modern businesses’ increasing demand for information. It achieves an uninterrupted flow of data, ensuring it remains efficient, thus reducing latency and maximizing throughput rates. Conversely, Fiber Optic connectivity can greatly enhance network reliability and performance by transmitting data over longer distances without any signal degradation. These two combined technologies facilitate business processes around big volumes of transactions linked to info; they cause an upsurge in cloud computing and support bandwidth-consuming applications to work with zero problems at all. Therefore, integrating high-speed Ethernet and Fiber Optic connectivity into network infrastructures is crucial for any organization that wants to maintain its competitive edge in the digital era.
As far as connecting computers to networks is concerned, the Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) network cards and traditional adapters serve the same essential function. However they differ greatly in terms of scalability, flexibility and performance.
Traditional network adapters are usually integrated into the motherboard or implemented through separate cards that are designed for specific types of network connections and have fixed capabilities. This means completely replacing them when they become obsolete or fail to meet network demands.
On the other hand, SFP network cards possess a competitive advantage with regard to their modular design. As a result, it is possible for example to change or upgrade optical or copper transceivers so that fiber optic or Ethernet media can be used with different bandwidth requirements without replacing the whole card. SFP modules have been designed in such a way that they support a wide range of data rates and protocols hence making SFP network cards very useful for evolving enterprise networks as well as being cost-effective.
For this reason, compared with traditional counterparts, SFP devices are more adaptable and future-proofed against rapidly changing trends in modern data communication networks.
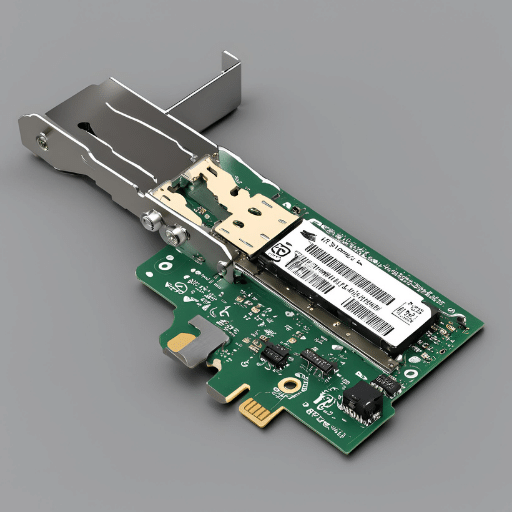
SFP network cards can be attached to different motherboards through PCI Express (PCIe) slots, thus rendering them more connectible and productive. The number of data transmission lanes in these slots is differentiated by their sizes: x1, x4, x8, x16. Therefore, when placing SFP network cards on a server or high-performance computer, one must consider the compatibility and performance implications of the choice of these PCIe slot sizes. A card designed for an x4 slot can fit into an x8 or x16 slot, but using it in a smaller slot than intended could bottleneck its performance due to the reduced number of lanes. It is necessary to have knowledge of the motherboard’s PCIe slot specifications and the needs of the SFP adapter if you want your network performance to be optimal and compatible. With this arrangement, network infrastructures are able to fully exploit the advantages that come with SFP network cards, including speed and flexibility, while avoiding cases where hardware restrictions impair overall efficiency.
Considering the existing and expected network needs of your environment, you should choose between Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet for your SFP network card. With speeds of up to 1 gigabit per second, Gigabit Ethernet is best suited to general office networks, small servers, and home use where high-speed data transfer is not essential. On the other hand, 10Gbe supports bandwidths that can go up to 10 Gbps, implying its suitability for applications in data centers, enterprise-class servers, and networks with high-speed data transfers necessary for tasks such as big database retrieval over networks, virtualization as well as High Definition content streaming. The decision between whether to use a 1Gbe or a 10Gbe should be guided by factors such as the amount of data traffic flowing through the network, how future-proofing might be done on this infrastructure or even budgetary constraints. Choosing 1Gbe over 10Gbe will entail a low initial cost but lower bandwidth, thus making it an expensive option when the size of a business grows fast, and there are expectations that network demands will surge.
To have a network that performs well, it is necessary to have Intel controllers because they are critical in determining the performance of different networks, especially those where speed and efficiency matter most. In order for the data packets transmitted through a given network to flow smoothly and reliably, these controllers are fabricated to help them optimize data flow across the network. By integrating advanced features like Intelligent Offloads and Direct Data I/O Technology, Intel controllers decrease CPU overhead so as to enhance the overall working of a network. In high-demand situations such as those experienced in data centers or enterprise environments, this kind of efficiency is particularly important due to the large volume of data traffic combined with the fast processing speeds involved. Moreover, Intel continuously innovates by incorporating support for new networking standards and protocols into its products, which ensures that its Network Adapters equipped with Intel Controllers always remain compatible with emerging technology, thereby ensuring scalability and future-proofing investments made in network infrastructure.
Look up instructions specific to model you are working on as well as safety recommendations since they vary across brands and models.
Addressing these common issues can lead to the successful integration of an SFP NIC into your network infrastructure. For chronic problems, consult with the manufacturer’s support team for assistance.
If one is using Windows Server, there are some necessary steps to follow. This will ensure that your networking hardware works effectively and efficiently.
These steps should help you configure your Windows Server for use with SFP adapters, resulting in better serviceability, overall superior network performance, reliability, and stability.
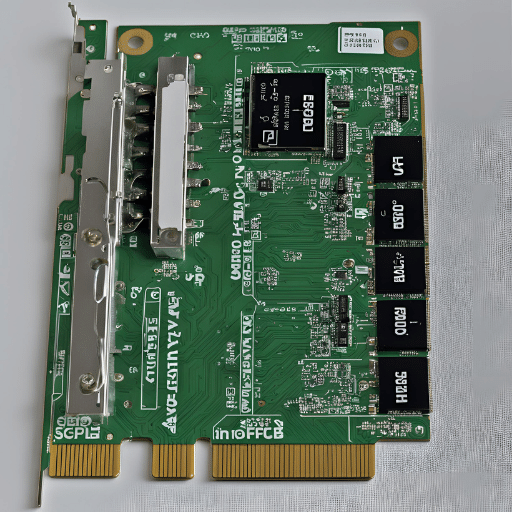
The server adapter cards and consumer-grade network adapters are fundamentally different in terms of their target environments and performance demands. The main differences lie in their quality of construction, dependability, performance capacities, and features, among others. Server adapter cards are specifically designed to withstand the harsh operational requirements of data centers and business environments around the clock. They often come with advanced features that include ECC memory for data corruption prevention, higher bandwidths, and throughputs for handling larger data loads, support for specialized protocols, and redundancy features such as failover or load balancing. Additionally, these server adapters have more support from virtualization technology and can handle traffic from many virtual machines quite efficiently. Conversely, consumer-based network adapters are tailor-made for home use or small offices where cost is a priority rather than high performance or additional capabilities. Thus server adapter cards provide a fundamentally more solid choice for professional and enterprise settings in comparison with other options.
When choosing SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) server adapters for enterprise use, it is essential to consider several factors that would help meet the needs of a corporate environment. First, compatibility with existing network infrastructure and the ability to accommodate current as well as future bandwidth requirements are critical. Moreover, these highly efficient server adapters should have superior performance by supporting high data rates so that they can be able to provide higher speed as well as more volume of data transmission within the office networks where their demand is expanding at an alarming rate. Furthermore, high-quality adapter cards should guarantee dependable service; therefore, one should select the ones that have minimum instances of failures in order not to suffer from frequent outages in connection with internet access. In addition to this criterion for selection of server adapter devices, other factors such as hardware acceleration capability virtualization support and advanced security options are needed because they could improve network efficiency and safeguard against leakages of sensitive information. It is better to buy from reputable brands that offer comprehensive customer care services and warranties so that one gets value for their money plus prepares his or her organization for any upcoming changes in networking expectations.
The networking efficiency, reliability, and security of a Local Area Network (LAN) can be improved by integrating advanced Network Interface Cards (NICs). They are equipped with such features as higher bandwidth capacities to support sophisticated network functionalities like Quality of Service (QoS), which prioritizes critical network traffic, specialized processors chips that offload processing tasks from the main CPU. In addition, they offer solutions for fast and secure data transfer through heightened encryption capabilities and accelerated data processing speeds. Hence, including such NICs in your enterprise networks would minimize data overload, facilitate the handling of voluminous traffic, and improve overall network performance, therefore making them indispensable to growing businesses that have high standards for security as well as performance.
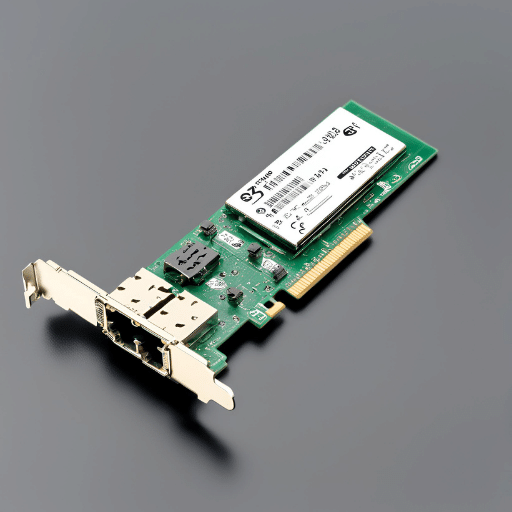
Choosing just the right Ethernet controller for Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) Ethernet adapters is very important in order to maximize network performance and reliability. These ethernet cards serve as a means of directing data traffic between the computing environment and the network infrastructure, making their efficiency and compatibility very crucial. A high-quality controller will diminish the latency period, raise throughput, and guarantee steady attachment between multiple devices in the most demanding conditions like data centers or intensive computational tasks. In addition, its compatibility with modern as well as future designs would mean that one has made an investment that can endure over time, thus avoiding early replacement needs. Businesses have to carefully balance these things out when selecting an appropriate kind of ethernet card because it should also take into account plans for further development of their networks for the long haul.
When Intel controllers of Network Interface Cards (NICs) are compared to those of other manufacturers, it can be observed that Intel often scores the highest in terms of integration, reliability, and support for advanced network standards. The strength of Intel’s controllers lies in their robust performance, i.e., efficient network traffic management, reduced latency, and improved data throughput. This feature makes them perfect for environments where high levels of data integrity and speed are required, such as server farms, cloud computing platforms, or enterprise data centres. Nevertheless, its rivals, such as Qualcomm and Broadcom, also have some competitive features like specialized processing capabilities that make them suitable for specific operational contexts or budgetary considerations in particular. When choosing between Intel and other control units, the choice mainly depends on a given infrastructure’s peculiarities, including compatibility with existing systems, performance needs, and cost implications.
The importance of X8 Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Express slots for high-speed network adapters is their bandwidth capabilities. X8 PCI slots are manufactured to have two times the rate of data transfer that x4 ones do and four times the rate of x1 slots. This is important with respect to high-speed network adapters, as they need substantial bandwidth to ensure optimal performance when transferring large amounts of data across networks. With increased throughput enabled by x8 PCIe slots, the best possible operating conditions can be achieved in cases such as where more than 5000 real-time apps run concurrently on a single server, which usually results in bottlenecks due to limited memory capacity or CPU speed that limit performance in terms of transaction processing rates (TPRs). The decision to use the X8 peripheral component interconnect express (PCIE) slot for network adapter, considering the need for accelerated data requirements by modern firms and continuous progress towards faster network standards, is strategic in nature since it guarantees future-proofing of network infrastructure, allowing the possibility of scaling and ensuring that there will be no interruption and increase flow.
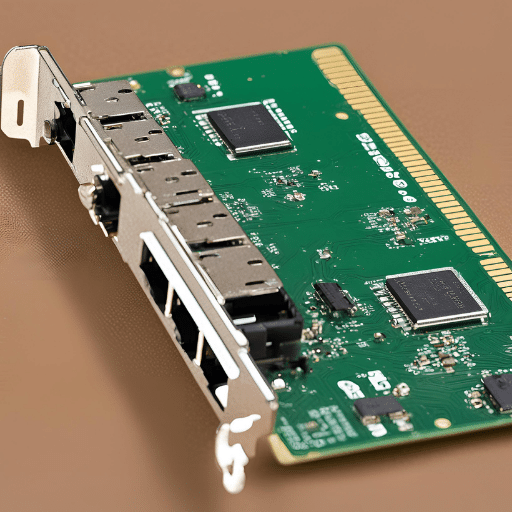
The universality of your network card’s compatibility with Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) transceivers is not guaranteed and depends on a number of crucial factors. To begin with, the Gigabit Ethernet PCI Express Fiber Network Card that you use must have an SFP slot that supports the physical form factor as well as the electrical interface of the specific transceiver. Moreover, there should be mutual compatibility between such transceivers and the firmware in use on the network card, thereby necessitating conformity to specifications set by manufacturers. Lastly, it would be prudent to use only network card manufacturer-approved transceivers for best performance and to maintain the integrity of your network. The use of non-approved transceivers may result in problems from lackluster performance up to outright incompatibility, which significantly affects the reliability and efficiency of your network.
The following guidelines will help you make the most of your fiber optic network with the Gigabit SFP module you select. First, pick out an SFP module which is suitable for the speed and distance requirements of your network that range from 1000BASE-SX over a short distance within a maximum of 550m, up to 1000BASE-LX/LH for longer distances that may exceed 10 km. Ensure that you check manufacturer documentation for compatibility between your network card and devices as well as the SFP module. Quality cabling and connectors are used to maintain signal integrity, especially in areas where there are chances of physical or electromagnetic interference. Regularly monitor network performance and make adjustments as needed, using diagnostics and management features in your network hardware to identify and resolve problems quickly. Lastly, employ multiple SFP ports with appropriate net configuration to provide redundancy and failover capabilities while ensuring continuous operation, minimizing downtime, and efficient data flow throughout the network infrastructure.
To begin with, the Intel manufacturing website explains why SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) network card adapters are advantageous and furthermore, what they actually entail. For example, how SFP adapters can speed up a network, expand its bandwidth capabilities, and promote more flexible communication options mainly in the corporate context. Those who deal with IT and want to optimize their networking infrastructure would find it useful since it provides technical information on how SFP network card adapters work.
This manufacturer website from Intel provides a detailed overview of the advantages and features of SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) network card adapters. The resource explains how SFP adapters can optimize network performance, increase bandwidth capacity, and enable flexible connectivity options in enterprise environments. It offers technical insights into the functionality of SFP network card adapters, making it a valuable reference for IT professionals seeking to unlock the full potential of their network infrastructure.
This scholarly work titled “A Comparative Analysis of SFP Network Card Adapter Technologies Specifically Tailored for Data Center Applications” was published in the Journal of Optical Communications. This research paper also investigates various performance metrics, compatibility with optical networks, and scalability features associated with the SFP adapters, hence offering knowledge on selecting the aptest solution for improving your network efficiency. Moreover, this academic article is good for those who are looking forward to increasing their computer networking capabilities.
A: An SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) Network Card Adapter NIC (Network Interface Card) allows computers to be connected to a network such as the internet or a private network through fiber optic cables rather than traditional copper ethernet cables. This can significantly improve your network’s speed, reliability, and security, especially in environments where high data bandwidth, low latency, and strong communication integrity are required. Such adapters usually support high-speed data rates like 10g ethernet, which makes them ideal for use in applications that involve the transmission of very large volumes of data.
A: For example, the SFP network card adapters are compatible with personal computer models that have PCIe (PCI Express) slots. For instance, PCI Express x1, PCI express x8, and other versions of PCI Express slots are found in most modern computers. To avoid compatibility issues, look up adapter details such as form factor (PCIe sfp, PCIe x8, etc.) and speed(10g ethernet, gigabit fiber, etc.) from your PC specs.
A: Indeed, many types of these cards support different varieties of sfp modules, including 10gb sfp and gbe sfp modules. Thus, depending upon the specific type of an sfp module being used, it gives you the ability to connect directly to various speeds on fiber optic networks. Nevertheless, one must confirm the gigabit sfp modules used by the adapter based on its specifications.
A: Some factors to consider prior to upgrading include the kinds of networks you will link up with; what apps will require faster speeds (high-end applications may necessitate using 10-gigabit ethernet PCI express); the type of fiber optic cables in place; and compatibility with your current system e.g., PCI express gigabit ethernet or PCI-E network support. Moreover, can your system handle a specific expansion slot needed, such as PCI express x8, and does the SFP adapter support the sfp modules you intend to use?
A: Before anything else, turn off your computer and uncover its casing. Identify an open PCI Express slot which corresponds to the form factor of your card (PCI Express x1, x8, etc.). Then gently push the card into that slot, fasten it there and close the case of your computer. After turning on your machine again, you may have to install the necessary drivers from places like the manufacturer’s website such as startech.com pci express gigabit ethernet or for specific chips such as intel 82599en controller.
A: Yes. You can use several SFP network card adapters in one PC if you have available PCI Express slots and enough system resources. This will greatly enhance your network’s bandwidth and ensure that it has redundancy, too. For example, by employing dual 10gb dual PCIe sfp adapters, you double what is available to your network, hence suitable for high-performance computing environments or where high-speed data transfer is required like server applications are involved. Note that this kind of configuration might not work well unless both the motherboard and software support these settings.
A: Even though there are many good brands with various models to choose from, some notable ones encompass 10gtek 10gb pci-e nic network adapter for PCI express x8 slots, which is famous for its high performance and compatibility with standard gigabit sfp modules. Another highly recommended option is the intel 82599en controller-based converged network adapter, which is meant specifically for networks requiring speed and reliability. Finally make sure that the brand fulfills all your requirements for connectivity as well as being supported by your system hardware in terms of compatibility issues.
A: PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet is defined as a high-speed ethernet server connection provided over a PCI express slot using gigabit fiber technology for network connectivity. In the case of SFP network card adapters, this means that these cards can handle gigabit speeds by way of fiber optics, and so are far better than conventional ethernet cards. This feature is particularly critical for data centers or enterprise environments, or any other application where there is a demand for extremely fast and reliable network links.