Choosing the right hardware is important in network connectivity to ensure that it performs well and remains reliable. RJ45 and SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) connectors are two common ways of connecting network devices among many options available. This article intends to point out what sets RJ45 apart from SFP by looking at its distinctive technical features, capabilities, and practical applications. Such critical points will help network professionals make informed decisions for improving their network infrastructure as well as meeting specific connectivity needs. It is essential to understand the difference between RJ45 and SFP connectors because this knowledge can greatly contribute to achieving high levels of efficiency and strong performance in any system, whether upgrading an existing one or building a new network.

Compact transceivers that are hot-swappable, called Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) modules, are typically used in data communications and telecommunication networks. SFPs permit equipment to connect with copper or fiber optic networking cables. These modules support ethernet, fiber channels, SONET, and many more communication standards.
Versatility is a key feature of SFPs because they can be programmed to work over different types of optical fibers, such as single-mode or multi-mode, as well as copper cables for both short-range and long-range links. Depending on network needs, data rates supported by these devices range from 100 Mbps up to 10 Gbps which makes them suitable for various applications. It is commonly used in enterprise networks, data centers, and telecom infrastructure where switches need to be connected with routers or any other networking equipment.
Consequently, the ability to quickly transmit at high speeds combined with flexibility and scalability has made small form factor pluggables one critical element within contemporary architectures of computer networks today.
Comparing RJ45 Ethernet cables to fiber optic SFP connections involves many things, such as speed of transmission, distance, interference, and cost.
In summary, therefore either, choosing RJ45 ethernet cords versus fiber-optic sfp connections will depend on what specific network requirements exist at any given time. Ultimately speaking, rj45 represents affordability connectedness over short distances while moderate-speed needs are ideal, whereas interference resistance is critical, especially where high speed long haul applications come into play.
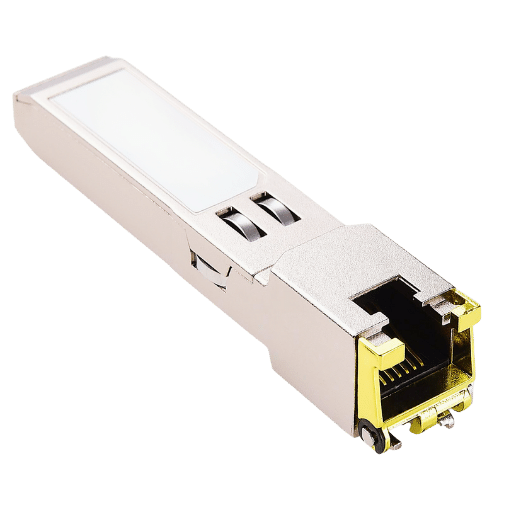
Physical and operational differences between RJ45 and SFP ports are necessary for determining their fit for different networking applications.
Therefore, it can be said that the ideal time to use an SFP is when you need versatility while a RJ45 will come in handy for short range applications.
RJ45 ports and SFP ports are back separate media types to provide for different networking needs. Copper cables are used by RJ45 ports, which are known as Ethernet networks and can work well within short distances of up to 100 meters. Such copper cables are cost-effective in combination with RJ45 ports and deliver enough performance for most home or office network setups.
On the contrary, SFP ports have a lot more flexibility when it comes to connectivity options. Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) modules allow for both copper and fiber optic cables to be used interchangeably. Fiber optic cables used in conjunction with SFP modules support higher data transfer rates than their copper counterparts while also being able to transmit signals over significantly longer distances – multi-mode fiber can reach up to 550 meters, whereas single-mode fibers span up to 100 kilometers.
Which one should be adopted RJ45 or SFP is largely determined by specific network requirements. In cases where there is a need for short-distance coverage on a tight budget, then usually people go with RJ45, which uses copper wires, but if you want high performance, scalability as well as long haul connectivity, then it would be better if one opts for SFP ports using fiber optics instead.
To appropriately compare the speed and distance capabilities of RJ45 and SFP, performance measures have to be accurately assessed. They are usually used along with Cat5e and Cat6 copper cables, which can transfer data up to a maximum of 1 Gbps over distances of 100 meters. For higher rates, Cat6a or Cat7 copper cables may be employed, supporting speeds of up to 10 Gbps but still limited by 100 meter distance.
On the other hand, SFP brings more flexibility and performance into play than any other type does. Copper, as well as fiber optic connections, are supported by SFP modules. Speeds and distances are similar when using copper just like what is obtained with RJ45; however when combined with fiber optic cables these same modules achieve much higher speeds at much longer distances. Multi-mode fiber can enable one to transfer data at rates close to or even equaling 10 gigabits per second for spans not exceeding 550 meters, while single-mode fibers support between 1Gbps up to 100Gbps with transmission distances reaching as far as 100 kilometers.
In general terms, therefore, it can be said that if your need is short-haul connectivity where there will be moderate speed requirements, then go for an RJ45 connection, but if you want high speed over long-range networking capability, use SFP connected through fibre optics instead. The decision on which one to choose should take into account such factors as specific network demands in terms of speed needed; how far apart network devices are from each other (distance); budget etcetera.

RJ45 ports are most commonly used in situations that require low cost and simplicity. They work well in typical office environments, small to medium-sized businesses, and homes where the length of the network connection is not more than 100 meters. Such connections are good for basic Ethernet uses, including linking workstations, printers, and access points to local area networks (LANs), as well as PoE (Power over Ethernet) applications, which enable electrical power transmission together with data on a single cable, thereby making installations easier for devices like IP cameras and VoIP phones. Their user-friendliness, wide compatibility range, and cheapness have made them become the preferred choice for many traditional networking needs.
Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) modules have a lot to offer when it comes to long-distance and high-speed networking. To start with, these modules are highly adaptable and can support both single-mode and multi-mode fiber optics, which can cover up to 100 kilometers in distance and operate at speeds between 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps) – 100 Gbps. This flexibility means that SFPs will work well within any type of network environment, from campus networks all the way up through data centers or even enterprise backbones. Secondly, compared to traditional copper connections, SFPs provide better performance in terms of data integrity over longer distances because they generate less signal interference and have lower latency. Another advantage is their hot-swappability – this feature allows for convenient upgrades or maintenance without causing too much network downtime. Finally, it’s worth mentioning the scalability aspect which is inherent in every Small Form-factor Pluggable such as SFPs, thus making them an ideal choice, especially for those organizations that would want easy expansion ability without necessarily incurring additional costs, hence being able to add only required number of appropriate SFP modules whenever there is need for more network connectivity points.
In terms of distance, speed requirements, scalability and budget a few important things should be kept in mind when choosing between RJ45 Ethernet and Fiber Optic SFP for your network. In general, RJ45 Ethernet is good for shorter distances, which are usually up to 100 meters, and is great for most standard office environments where speeds can go up to around 10 Gbps. They are cheaper than fiber optics and easier to install; hence, they are commonly used in small or medium-sized networks.
On the other hand, fiber optic SFP modules are designed for high-speed needs as well as long-distance transmissions, which sometimes exceed even 100 kilometers. These modules can support faster data rates ranging between 1 Gbps all the way up to 100 Gbps while offering more flexibility plus scalability, thus making them perfect for large businesses such as enterprises, data centers, or campus networks. Signal interference is less with fiber optics, therefore reducing latency and leading to better data integrity over longer distances.
Ultimately it comes down to what exactly does your company need from its network? If you need high-speeds over long distances with ability of scaling upwards then fibre optic SFP modules would provide robust solutions for you but if most of your connections will be within short ranges and cost is a concern, the practical choice would be RJ45 ethernet cables.
Combo ports are also called multi-purpose dual ports. They are network interfaces that can support both RJ45 Ethernet and fiber optic SFP connections on a single physical port, although only one can work at a time. This double capability gives them great flexibility which enables network managers to switch from copper to fiber connections depending on what the current network requires without having to acquire new hardware. Combo ports simplify network design and implementation, especially in environments with different or changing connectivity needs. They help leverage existing investments into infrastructure, prepare for future growth, and maximize network performance by choosing an appropriate connection type dynamically.
In order to maximize the capabilities of a network switch, it is important to recognize the benefits unique to each type of port. Most often, RJ45 Ethernet ports are used because they are cheap and easy to deploy, especially over short to medium ranges up to 100 meters. On the other hand, Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) ports can be more versatile as they support both fiber optic and copper connections, which in turn enables them to cater to increased bandwidths over longer distances, thus making these ports essential in high-performance networks like those found in data centers or enterprise infrastructures.
A strategic approach involves analyzing current and future network needs, such as bandwidth requirements, distance limitations, and specific environments involved. A combination of RJ45 and SFP ports can save costs now while providing scalability later. For example, using RJ45s for regular office setups allows cheap yet efficient networking, whereas SFPs on backbone links or inter-building connections guarantee strong signal strength coupled with high-speed data transfer rates; hence, minimal latency is realized within the system. Administrators should choose different port types appropriately so that they may enhance switch performance, enable scalability support, and maintain network reliability continuously, keeping it up all through the years when necessary.
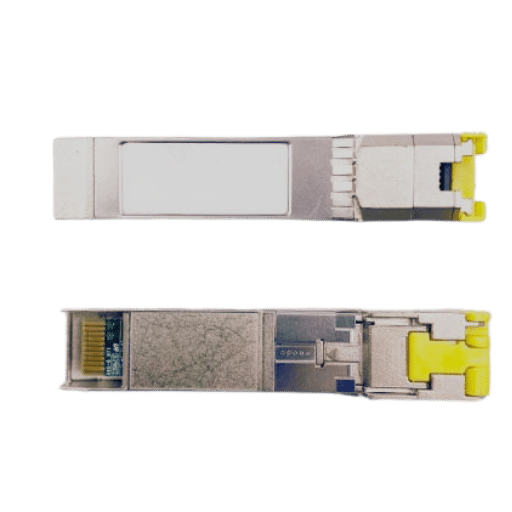
To ensure a smooth transition while changing from copper to fiber connections, one needs to carefully prepare and take into account several factors. First off, assess the current network infrastructure in terms of what it can do now and where it falls short. Consider areas that require increased bandwidth or longer distance transmission and upgrade them with fiber optics. Do a cost analysis by comparing investments such as new fibers cables, SFP modules, etc., against anticipated advantages like better performance or reduced maintenance costs in the long run.
Moreover, appraise whether the existing network devices are compatible with this type of technology; some may need upgrades or replacements so as to work well with fiber optic cables. Additionally, environmental conditions should not be ignored since these wires are known to be more robust than their copper counterparts and less vulnerable towards electromagnetic interference.
Finally, train your networking staff adequately on how to deal with fiber connections during installation as well its maintenance practices afterwards. This will enable them address any hiccups that might occur during roll out phase due lack of knowledge. It is also important to test all new links thoroughly before fully integrating them into systems lest they cause disruptions across networks, thereby leading to downtime situations that could have been avoided altogether had proper checks been done early enough. All these considerations, if well taken care of, will make it possible for system administrators to migrate from copper-based networks towards those using optic fibres, thus making them more ready for future demands on the network.
Step 1: Review Network Needs
Evaluate what you need for your network and find places that require more bandwidth and a broader range which can only be provided by SFP ports. This should involve checking the current usage, anticipated growth as well as specific applications needing the upgrade.
Step 2: Take Stock Of The Hardware
Do an inventory of all networking equipment in use. Identify devices currently using RJ45 ports and see if they would work with SFP modules or not. Also identify any equipment that needs replacement or upgrades to support SFPs.
Step 3: Choose Appropriate SFP Modules
Select the right SFP modules for your requirements. Consider distance, data rate and fiber type (single-mode vs multi-mode) among other things while making this decision. Ensure they can work with both old and new network gear.
Step 4: Get Ready For Installing Them
Buy the needed transceivers, cables and fibre optic related stuffs before hand. Plan how you will install them so that it happens smoothly without interrupting everything else on your network.
Step 5: Physically Install The Modules
Start installing by inserting respective SFP module(s) into designated switch port(s). Use optical cables to connect between different locations where necessary ensuring they fit tightly enough not to lose signals or disconnect often.
Step 6: Configure The Network Devices
Configure various network devices so that they can understand or make use of these new connections after plugging them in. You may have to update firmware, change settings and ensure correct communication over new ports by devices involved.
Step 7: Test Connectivity Across Links
Test each created connection thoroughly; use relevant monitoring tools if possible while doing so just to be sure links are all up & running well enough then check for signal degradation/lagging/packet loss among other things which may affect performance negatively too.
Step 8: Monitor And Fine Tune Accordingly
Keep monitoring how good or bad the network performs even after finishing up installing everything needed. Look out for areas needing optimization and make necessary adjustments aimed at achieving peak efficiency where possible. Also, ensure continuous improvement.
RJ45 to SFP port migration can be successful if administrators follow these steps which will enable them take advantage of fiber optics capabilities in meeting current and future needs of networks.
Transition to SFP modules are considered considering the requirement of equipment and its costs. To begin with, you have to purchase compatible SFP modules, which vary on the basis of speed (1G, 10G, 40G, 100G) and reachability. Among the most popular Enterprises for these components include Cisco, Juniper, and HP, where a single unit cost ranges between $20 to over several hundred dollars depending on specification levels. Also, it is important to note that for better performance, one will need high-quality fiber optic cables whose prices are affected by type(single mode vs multi-mode)and length as well.
Also switching into using SFPs may require some upgrades in existing network hardware so as they can work together but this can be quite costly. Sometimes, you might have to buy new network switches that support interface with SFPs; hence, they may cost thousands, especially if they are high-end models.
It should also be noted that during installation or maintenance there must be skilled personnel who know how these things operate therefore their wages might increase labor costs too .This means people working in IT departments should get trained about fiber optics because it will require special skills which could demand more money through certifications among other related programs.
Briefly put despite high initial investments on sfp modules plus their related equipments; improved scalability in terms of networks’ performance over time as well reduced delay times justifies for such expenditure. You must do a thorough analysis of benefits Vs costs before moving from one current situation to another based on financial ability and future needs according to the organization’s budgetary limitations combined with required features for networking at large.

Example 1: Small Office Network for Business
For its office network, a small marketing company with 20 employees uses RJ45 ethernet cables to connect desktop computers, laptops, printers and VoIP phones. They attain fast gigabit speeds that are reliable thanks to Cat6 Ethernet cables thus ensuring smooth data transfer, video conferencing and collaborative work without perceivable delay. The cost-effectiveness and ease of installation of these types cables make it perfect for this environment.
Example 2: Educational Institution Network
RJ45 cabling has been employed by a mid-sized school with multiple buildings on campus in order to create an extensive network infrastructure. Classrooms, computer labs administrative offices as well as other areas are linked together using Cat5e cable while interactive whiteboards are among some devices connected through this system too besides security cameras which also use it. Online learning platforms are supported by stable, cost-effective networks; such systems enable student information systems (SIS) access while minimizing interruptions during administrative communication channels, which require frequent updates.
Example 3: Healthcare Clinic Network
A healthcare clinic specializing in outpatient care has implemented RJ45 cabling across its facilities to connect different medical devices, diagnostic equipment and workstations. To facilitate quick but secure sharing of electronic health records (EHR), patient appointment scheduling, and telemedicine support services provision high speed transmissions necessary for managing these functions must be possible at all times, hence the need for Cat6a Ethernet cables within this setup . The integrity of private patient information is kept intact through strong performance reliability exhibited by RJ-45 connections, even as they enhance operational efficiencies within clinics.
These examples demonstrate how small-to-medium-sized networks can effectively utilize RJ-45 cabling for connectivity needs while considering performance trade-offs between costs and scaling capabilities.
For high-capacity networking, integrating small form-factor pluggable (SFP) modules provides many benefits to enterprises. The network can be made more flexible with SFP modules since they allow for hot swapping, which means that hardware upgrades or changes can be done without any downtime. Such data rates are supported by these modules that usually range from 1 gigabit per second up to 10 gigabits per second thereby catering for various network needs. Additionally, this type of module is compatible with different standards and protocols, making it possible to integrate them seamlessly into an existing network infrastructure. Being smaller in size permits the use of more ports within networking equipment, leading to increased connection capabilities. Furthermore, copper or fiber optic connections are supported by SFPs thus enhancing their applicability across different types of networks. These modules also provide better signal quality while reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI), which ensures reliable transmission over long distances even at high speeds.
Compared to conventional fixed ports, SFP modules are a great way to boost network performance. Most notably, this is achieved through improved data rates, lower latency and better bandwidth control. It is worth noting that some traditional network ports cannot support such high data rates as 1Gbps let alone 10Gbps which can be enabled by SFP modules thus facilitating faster transfer of information. Moreover, being hot-swappable allows these devices to be changed without causing downtime thereby increasing their reliability and uptime.
In tests where things were compared side by side, it was found that networks that used SFP transceivers recorded lower levels of latencies thanks to better processing of signals as well as their efficient transmission. As such, low latencies are essential for systems dealing with real-time data processing like VoIP or video conferencing. Additionally, another advantage is seen in terms of scalability with regards to bandwidth whereby higher speeds can be achieved without necessarily replacing the entire infrastructure hence cost cost-effective measures are taken into account. Furthermore, due to its small size factor, SFF (small form factor) pluggable optic fiber module enhances port density, allowing more connections within limited spaces, making them ideal for large-scale environments such as those found in data centers.
Finally, the ability of these devices to work with copper cables or fiber optics makes them suitable for different networking needs; hence, they can operate at peak performance over extended distances with minimum electromagnetic interference, thus improving the overall efficiency and dependability of networks.
A: In network connectivity, RJ45 as well as SFP differ in terms of their form and usage. Copper ethernet cables are used with an RJ45 connector for standard gigabit ethernet applications which usually use Cat5e or Cat6 cables. On the other hand, SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) transceivers work with fibre optic cables or copper cables enabling higher speeds and longer distances than what can be achieved by means of RJ45 ports. Therefore, this makes SFP more versatile and adaptable for different types of networks.
A: Yes, provided that one device supports an SFP connection; you can use an SFP port on your Ethernet switch instead of an RJ45 port to link them together. This is because compared to RJ45 –– if we employ fiber optic cables –– using an SFP port allows for higher speed connections over longer distances. However, this necessitates appropriate SFP transceiver(s) as well as cable(s) which should be compatible with both devices.
A: Definitely! There are several benefits offered by using sfp ports rather than rj 45ethernet ones on a switch. Firstly, they provide greater flexibility by supporting wider range of media types including fiber optics cables for long distance higher speed connections , also copper cables can be used too . Additionally typical rj 45ports cannot support high speeds but sfp portscan thus making them suitable for applications where large amounts of data need to be transmitted at high bandwidths.
Introduction to small-form-factor pluggables (SFPs) refers to their being compact, hot-pluggable transceivers used in data communication and telecommunication networks. SFP modules support various communication standards like gigabit Ethernet and fiber channel among others. They make it possible for network equipment interfaces to be easily upgraded so as to accommodate different types of network cables such as fibre optic or copper thereby greatly enhancing flexibility and scalability of network infrastructures.
A: Yes, gigabit ethernet connections can use SFP. The SFP transceiver is designed for data rates specific to gigabit ethernet that commonly run at 1 Gbps. These modules allow gigabit speeds over both fiber optic and high-quality copper cables. Depending on network devices and connection distance, an appropriate type of SFP module – whether it be for fiber or copper – has to be selected.
A: If you want to connect two devices using an SFP port and an RJ45 port, make sure you have a compatible SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) module as well as the right network cable. Start by inserting the SFP module into one device’s SFP port. For fiber connections, link a fiber optic cable with the second device’s corresponding port through the SFP module. In case of a copper connection (if supported), employ a copper ethernet cable fitted with an RJ45 connector. Verify whether your cable type and SFP module meet the speed and distance requirements for this connection.
A: There are several reasons why someone might choose SFP ports instead of RJ45 for network connectivity; these include being able to go beyond copper ethernet cable limitations in terms of distance, higher speeds required on networks plus different types (copper vs fiber optic) being used where flexibility is desired among others like easy upgrades without replacing switch thus providing cost-effective scalable solutions for any size business.
A: The main reason why sfp is preferred over rj45 in some cases lies within its ability to support both fiber optics as well as copper cables, which can cover longer distances while achieving higher speeds than what an Ethernet port with rj45 interface could normally do. Additionally, these sfp modules allow for flexibility when switching between various network cable types and speeds, which is very useful in dynamic networking environments where needs change over time.