In this rapidly evolving connected world of ours, being able to connect things properly is very important — and rest assured, RJ45 is one of those things. If you are building a home office network, setting up an enterprise IT infrastructure, or doing anything else that requires reliable high-speed data transfer between different devices, then you must know how to crimp Ethernet cables well. This guide covers everything about RJ45 connectors in detail: it provides step-by-step instructions on making custom ethernet cables from scratch. The author explains each part involved, starting with what tools are needed, which materials work best, how tight joints should be, etcetera. By the end of it all, not only will readers have learned where they went wrong during previous attempts, but they will also feel confident enough when dealing with future ones because here we tell them why some things didn’t work while others did based on good practices followed throughout this process.
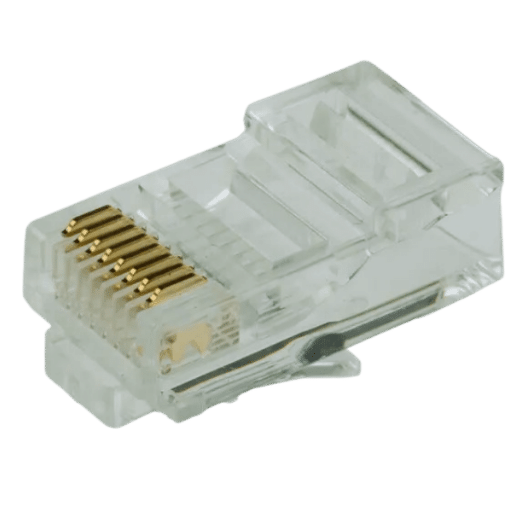
Ethernet networking often makes use of an 8P8C (8 positions, eight contacts) RJ45 connector that is designed to terminate twisted pair cables. The connector itself consists of a plastic housing that holds eight metal contacts in a precise arrangement; these contacts then pierce through the insulation surrounding each wire inside the cable so as to create electrical connections with all eight wires. Most connectors also have a small tab for locking them securely into Ethernet ports – this locks them into place and ensures reliable data transfer over networks. Crimps must be done correctly if one wants good network performance because crimping involves modifying the shape or size of something by flattening it down or squeezing it together firmly until its surface area becomes smaller or its thickness decreases.
To connect Ethernet cables to RJ45 plugs, there are some specific steps that must be followed. First, the outer jacket of a twisted pair of cables is removed to reveal the internal wires. These wires are then straightened out and organized in accordance with either the T568A or T568B wiring standard. After lining them up, they should be cut so that all are the same length before being gently inserted into an RJ45 connector, where each wire must reach its corresponding slot right up until it goes through the other side completely. Last but not least comes crimping; this is done by using special pliers designed specifically for crimping RJ45 connectors, which push contacts down onto conductors, thereby creating secure electrical contact between the two sides of the connection – the male end and the female end (plug). The main aim of performing these procedures is to facilitate speedy data transfer over an ethernet cable by ensuring good physical contact between the metal parts of an RJ45 connector and the wires inside that cable.
Because they are reliable and efficient in transmitting data, RJ45 connectors have gained wide application in residential as well as commercial environments. The major use of these connectors is in Ethernet networking for faster internet connections and local area networks (LANs). In offices, data centers, and homes, such devices are critical as they connect computers, routers, and switches, thereby forming a network backbone. Telecommunication systems employ RJ45 connectors for voice over IP (VoIP) phone systems, among other communication devices. In industrial settings, RJ45 connectors are used with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) together with other control systems to ensure smooth communication and operation.
Knowing the differences and capabilities between Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a cables is essential when choosing an RJ45 connector.
Cat5: The Cat5 (Category 5) is a previous version that can support up to 100 Mbps speeds with frequencies reaching 100 MHz. This standard is used less frequently nowadays due to its poorer performance compared to modern standards.
Cat5e: The Cat5e (Category 5 enhanced) is an upgraded version of Cat5, which allows for higher data transfer rates up to 1 Gbps at frequencies of 100 MHz. It was designed specifically for use with Gigabit Ethernet networks, where it reduces crosstalk.
Cat6: The maximum speed of the Cat6 (Category 6) cable is 10 Gbps over short distances (up to 55 meters). Its frequency range extends up to 250 MHz while having more stringent requirements regarding crosstalk among others making them perfect for high-speed networks.
Cat6a: Designed as an extension beyond what’s possible even after upgrading from a regular cat6, cat6a cables offer support for speeds up to 10 Gbps over longer runs of cable(up to a maximum distance of 100 meters), and also feature cross-talk-reducing shielding, thus enabling operation at frequencies as high as500 MHz which makes them suitable when building data centers or enterprise networks that require top performance
To choose the right RJ45 connector, you should consider your network speed needs, how far apart devices are within proximity limits set by each cable type, and future-proofing considerations, among other factors.
When it comes to choosing between shielded and unshielded RJ45 connectors, the environment and specific application of your network should be taken into account.
Shielded RJ45 Connectors (STP): These connectors have extra shielding around their inner wiring, which protects them from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radiofrequency interference (RFI). They are perfect for places with lots of interference, such as industrial areas with heavy electrical equipment and data centers, among other fast data transfer points, because they offer better protection against external noise.
Unshielded RJ45 Connectors (UTP): These ones do not come with any additional shielding and, hence, can easily be affected by EMI or RFI. However, they are easier to install than the shielded types, more flexible in terms of where they can be used, and generally suitable for most standard office or residential applications where there is minimal interference—typically utilized in situations where cabling will not be exposed to significant external noise sources.
In a nutshell, shielded RJ45 connectors work best when there is high interference or a need for maximum data integrity, while Unshielded ones are good enough for lower-interference, cost-sensitive installations.
When deciding on solid wire versus stranded cable for RJ45 connectors, there are a few things you should know about them.
Solid Wire: Solid wire has a single conductor, which can be used over long distances. This is because it suffers less attenuation than braided cables do. It also tends to be more rigid and stable than other types of wires, so it often finds use in permanent installations such as those within walls or ceilings. Moreover, when terminated with punch-down blocks or insulation displacement connections (IDC), solid wire provides the most reliable connection possible.
Stranded Cable: A stranded cable contains many smaller wires twisted together into one conductor. The benefit of this design is that it makes the cable much more flexible and easy to work with wherever frequent movement or bending might be expected—e.g., patch cables in racks or workstations. However, though stranded cables may exhibit slightly higher attenuation over longer lengths and cost slightly more money, people like them because they are durable enough to withstand being moved all the time while still simple enough for anyone who needs one in an ever-changing environment to find a use for them easily.
In conclusion, if you want something that sees little to no movement over great lengths, then stick with solid wire, but if what you need calls for short-length applications involving lots of flexing and pulling around, then go ahead and get yourself some stranded cable!

If you want to crimp an RJ45 connector effectively, you should have these tools:
These three necessary instruments ensure reliable RJ45 terminations every time whether setting up professional or home networks.
To follow these brief instructions for using a modular crimp tool in RJ45 termination:
These steps give rise to consistent and dependable terminations of RJ-45s that can work well in different networking environments.
To speed up and make more precise your RJ45 terminations, there are some other tools that you can use.
If used together with modular crimping tool these equipments will enable one achieve professional looking network cable terminations which can be deployed at small scale networks or large scale enterprise environments.

Following these steps should help you properly terminate an ethernet cable which in turn makes it work reliably within network setup.
So stick rigidly to these steps and you should be able to crimp rj45 plugs on ethernet cables with confidence that they will work well in your network connections.
It is important to test a crimped RJ45 connection to ensure that your network setup is working properly. Here’s how you can do it:
These procedures confirm both the correctness of assembly as well as full functionality of an RJ45 plug thereby preventing potential networking problems.
In the event of an RJ45 crimping failure, it is crucial to detect and tackle conventional problems in a methodical manner. Here’s what to do when troubleshooting such issues:
These steps will help you solve most issues associated with bad RJ45 crimps, thereby ensuring strong network links that are dependable in nature.
According to some experts, shielding problems in RJ45 connectors can drastically affect network performance, especially in places with high electromagnetic interference (EMI). Here’s what you can do about it:
Toward lessening electromagnetic disturbances’ impact on signal quality stability while traversing LANs, use only genuine high-performance shielded plugs together with correct grounding techniques coupled maintained physical barrier integrity throughout implementation process.
There are several reasons for signal loss in Ethernet cables which can affect your network’s reliability and performance. Here are some of the most common causes and steps to rectify them:
By following these guidelines step-by-step you will be able to recognize as well as fix the problems associated with signal loss over ethernet cables hence making it more reliable for networking purposes.
A: An ethernet rj45, also known as an RJ45 connector, is a jack that connects the ends of cables used for computer networking such as cat6 cables; it is widely used in network cabling to join devices with a router or network switch.
A: In contrast to cat5e and Cat6 cables, which have more stringent performance criteria than their predecessor (cat 5 cable), older versions of this type of cable have lower standards for performance. They offer better signal quality due to reduced crosstalk between wires. Besides having stricter requirements for system noise and crosstalk than its predecessors do (cat 5 and cat5e), cat6 cable can transmit data at rates up to ten gigabits per second over short distances.
A: To crimp an ethernet rj45 cable together, follow these steps; strip the cable jacket, untwist the wire pairs, align the wires in the correct order inside a cat6 connector then use crimping tool to secure them but make sure you read the product description since there might be different types of connectors with their specific instructions on usage.
A: Yes, many RJ45 connectors like CableCreation’s Cat6 RJ45 ends support solid wire as well as stranded cable, though one should always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications to confirm compatibility.
A: Gold plating the contacts within an RJ-45 connector provides greater conductivity while resisting corrosion, thus enhancing reliability/longevity, especially where ether-net connections may oxidize or exposed moisture is relatively high.
A: Yes, you can use Cat6 RJ45 connectors with Cat5e cables and they usually provide stronger and more reliable connections. However, to achieve the best performance it is always recommended using connectors made specifically for that type of cable.
A: Electronics supply stores offer bulk packages such as 50 pack, 100 pack or even larger quantities of RJ45 connectors. You can also find online retailers who sell them in bulk for bigger projects or commercial use.
A: The term 8P8C (eight position, eight contact) refers to the actual interface used in the RJ45 standard. Although often used interchangeably with cable connector and port, technically speaking this connector itself is an 8P8C.
A: Yes, without a tool kit designed for crimping ethernet cables terminated by means of an rj-45 plug there would be no way to properly terminate them. These kits usually contain a crimping tool, cable cutter, and sometimes even a cable tester, which will help ensure that all connections are secure and operational at the end of your work.
A: Yes, pass-through connectors, shielded connectors, and standard modular plugs – these are all examples of different types within the category known as “rj45 connector”. Each type serves its own purpose with regard to usage scenarios or supported wires, so before making any choice, make sure it fits your needs.