——
InfiniBand and Ethernet are two pivotal technologies facilitating data transmission in network environments. They each have unique features, functionalities, and applications, making them suitable for different networking needs. This article provides an in-depth look at both InfiniBand and Ethernet, comparing their data transmission capabilities, latency differences, and the advantages of using InfiniBand over Ethernet.
InfiniBand is a high-performance, low-latency networking technology primarily used in data centers and high-performance computing (HPC) environments. It enables fast, reliable, and efficient data transmission between servers, storage systems, and other devices within a network. Key features of InfiniBand include its high bandwidth, low latency, quality of service (QoS), and scalability.
Ethernet is a widely adopted networking technology used for connecting devices within a local area network (LAN), metropolitan area network (MAN), or wide area network (WAN). It supports both wired and wireless connections and is known for its versatility, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness. Ethernet’s primary functionalities include data transmission, network traffic management, and error detection and correction.
When it comes to data transmission, both InfiniBand and Ethernet offer distinct capabilities. InfiniBand, with its high-speed data transfer rates and low latency, is often preferred for demanding applications that require rapid, uninterrupted data flow. On the other hand, Ethernet, while typically offering lower data transfer rates than InfiniBand, is widely used due to its compatibility with a vast range of devices and applications.
Latency, or the time it takes for a packet of data to travel from one point to another, is a crucial factor in network performance. InfiniBand generally offers lower latency than Ethernet, making it an optimal choice for applications where immediate data delivery is critical, such as in high-frequency trading or real-time analytics.
There are several advantages to using InfiniBand over Ethernet:
——
High-Performance Computing (HPC) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) networking have specific requirements, notably in terms of bandwidth, latency, and data transmission capabilities. In this context, two technologies dominate the conversation: InfiniBand and Ethernet. Each comes with its unique advantages, and their suitability depends on the specific network environment and application. This article delves into an in-depth comparison of InfiniBand and Ethernet in HPC and AI networking environments.
InfiniBand stands out in HPC environments due to its superior performance attributes. It offers high bandwidth and low latency, which are critical in HPC, where rapid, uninterrupted data flow is required. Additionally, InfiniBand supports Quality of Service (QoS), ensuring predictable network performance. It also offloads some of the data processing tasks from CPUs, thus freeing up system resources and improving overall performance. Furthermore, InfiniBand networks are highly scalable, making them ideal for HPC environments that may require expansion over time.
While InfiniBand excels in HPC, Ethernet has its strengths in supporting AI networking. Ethernet’s versatility and compatibility with a wide range of devices make it a suitable choice for AI networking. It provides reliable data transmission, traffic management, and error detection and correction features. Its lesser cost compared to InfiniBand also makes it an attractive option in situations where budget considerations are paramount.
InfiniBand’s flow control mechanisms ensure efficient data transmission, especially critical in AI workloads where large volumes of data need to be processed rapidly. By managing the rate of data transmission and preventing network congestion, InfiniBand maintains high network performance and reliability. Its ability to offload data processing tasks from CPUs also enhances system performance, making it highly suitable for AI workloads.
While both InfiniBand and Ethernet can be utilized for AI networking, their application depends on the specific needs of the network. InfiniBand, with its high-speed data transfer rates, low latency, and excellent flow control mechanisms, is ideally suited for AI workloads that require rapid data processing. On the other hand, Ethernet, with its versatility, compatibility, and cost-effectiveness, makes it an attractive option for AI networking where these factors are of primary importance.
——
The choice between InfiniBand and Ethernet for data center networking can significantly impact performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Both technologies have their strengths and are tailored to meet different network requirements. This article provides a detailed comparison of InfiniBand and Ethernet in the context of data center environments, discussing their impact on network bandwidth, utilization, port configurations, and interconnect options.
InfiniBand and Ethernet can significantly influence the bandwidth available in a data center network. InfiniBand typically offers higher bandwidth than Ethernet, making it suitable for high-performance computing environments where rapid data transmission is crucial. On the other hand, Ethernet, while generally providing lower bandwidth than InfiniBand, offers sufficient performance for many standard data center applications and is compatible with a wide range of devices.
When comparing InfiniBand and Ethernet’s utilization in a data center, several factors come into play. InfiniBand’s high performance, low latency, and Quality of Service (QoS) features make it ideal for demanding applications that require robust and reliable data transmission. Conversely, Ethernet’s versatility, ease of use, and widespread compatibility make it a practical choice for general data center networking needs.
Port configurations for InfiniBand and Ethernet in data centers depend on the specific network requirements. InfiniBand uses a switched fabric topology, which allows for flexible and scalable network design. Ethernet, on the other hand, supports both star and mesh topologies, offering flexibility in network design but may require more cabling and infrastructure compared to InfiniBand.
Interconnects link different parts of a network and play a crucial role in determining network performance. InfiniBand interconnects offer high-speed, low-latency connections ideal for high-performance computing applications. Ethernet interconnects, while typically offering lower speed and higher latency than InfiniBand, are widely used due to their compatibility with many devices and network types. The choice between InfiniBand and Ethernet interconnects should be based on the specific performance requirements of the data center network.

——
Choosing the right network technology is crucial to achieving optimal performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness in any network environment. InfiniBand and Ethernet are two key technologies that have dominated the networking landscape, each with its unique features, benefits, and applications. This article provides a detailed technical comparison between InfiniBand and Ethernet, exploring their characteristics, differences in protocol and data transmission, network adapter requirements, and strategies for optimizing network performance and reliability.
InfiniBand is a high-performance, low-latency network technology primarily used in data centers and high-performance computing environments. It offers features such as high bandwidth, Quality of Service (QoS), and scalability. On the other hand, Ethernet is a versatile and widely adopted network technology used in various network environments, from local area networks (LANs) to wide area networks (WANs). It supports both wired and wireless connections and provides reliable data transmission, network traffic management, and error detection and correction functionalities.
Nvidia’s InfiniBand offers several advantages over traditional Ethernet. It provides higher bandwidth and lower latency, making it suitable for data-intensive applications that require rapid data transmission. Nvidia’s InfiniBand also supports advanced features like QoS and offloads some of the data processing tasks from the CPU, thereby improving overall system performance. Furthermore, Nvidia’s InfiniBand networks are highly scalable, making them ideal for growing network environments.
Network adapters, or network interface cards (NICs), play a crucial role in connecting devices to a network. For InfiniBand, Host Channel Adapters (HCAs) are used. HCAs support the InfiniBand architecture, providing high-speed, low-latency connections. For Ethernet, Ethernet Network Interface Cards (NICs) are used. These adapters are widely available and compatible with a vast range of devices, making them a practical choice for most network environments.
InfiniBand and Ethernet use different protocols for data transmission. InfiniBand uses a switched fabric topology and supports Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA), which allows for direct memory transfers between devices without involving the CPU. This leads to lower latency and higher data transfer rates. On the other hand, Ethernet uses the Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) protocol, which is simpler but can lead to higher latency and lower data transfer rates compared to InfiniBand.
Optimizing network performance and reliability involves several strategies. With InfiniBand, this could include leveraging its QoS features to prioritize critical data traffic, using RDMA for efficient data transfers, and scaling the network as needed. With Ethernet, optimization strategies could include proper network design to minimize traffic congestion, using error detection and correction features to maintain data integrity, and choosing the proper Ethernet standard to meet bandwidth requirements. Ultimately, the choice between InfiniBand and Ethernet should be based on the specific needs and requirements of the network environment.

——
In the realm of network technology, InfiniBand and Ethernet are two dominant names, each offering unique advantages and having its own set of drawbacks. While InfiniBand is known for its high performance and scalability, Ethernet stands out for its widespread use and compatibility. However, choosing the right one can be a challenging task as it depends on the specific needs and requirements of the network applications. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of InfiniBand and Ethernet in network applications, focusing on their scalability, performance, reliability, robustness, and their role in ensuring low latency and high bandwidth.
InfiniBand networks offer significant scalability and performance advantages. They provide high-speed data transfer rates and low latency, making them ideal for data-intensive applications. Additionally, InfiniBand networks support Quality of Service (QoS), which allows for prioritizing critical data traffic, thereby enhancing overall network performance. Furthermore, InfiniBand networks are highly scalable, meaning they can be easily expanded to accommodate growing network demands.
Ethernet plays a crucial role in a wide range of network applications due to its versatility and compatibility. It supports both wired and wireless connections and is compatible with a vast array of devices. Furthermore, Ethernet provides reliable data transmission, efficient traffic management, and robust error detection and correction functionalities. Its widespread adoption makes it a practical choice for most network applications.
When it comes to reliability and robustness, both InfiniBand and Ethernet have their strengths. InfiniBand’s high-speed data transfer rates and low latency contribute to its reliability, while its support for QoS ensures predictable network performance. On the other hand, Ethernet’s robust error detection and correction features help maintain data integrity, contributing to its reliability. However, the robustness of both technologies depends on the network design and the specific requirements of the network applications.
Low latency and high bandwidth are critical requirements in many network applications, especially those involving real-time data processing. InfiniBand, with its high-speed data transfer rates and low latency, is well-suited to meet these requirements. Ethernet, while typically offering lower speed and higher latency than InfiniBand, provides adequate performance for many standard network applications.
Both InfiniBand and Ethernet can be leveraged to ensure a highly reliable network protocol. InfiniBand’s high-speed data transfer rates, low latency, and QoS features contribute to its reliability. On the other hand, Ethernet’s error detection and correction features, along with its traffic management capabilities, enhance its reliability. The choice between InfiniBand and Ethernet should be made based on the specific reliability requirements of the network protocol.
——
InfiniBand, a high-speed interconnect technology, is designed specifically for data center devices. It excels in low-latency and high-bandwidth applications, ideal for HPC and AI. Ethernet, however, is a widely adopted networking technology suited for various use-cases, including cloud computing and internet connectivity. Despite its evolution, Ethernet trails behind InfiniBand in latency and bandwidth capabilities.
Ethernet is optimal for general-purpose networking and is supported by numerous devices and applications. It’s also ideal for long-distance networking and internet connectivity. For traditional data center workloads with less rigorous latency and bandwidth needs, Ethernet may be more cost-effective.
InfiniBand outperforms Ethernet in data center networking due to its lower latency, higher bandwidth capabilities, and efficient protocol for high-performance computing and AI workloads. It provides a reliable, scalable network protocol suitable for high-speed, low-latency clusters and specialized computing resources.
Yes, integrating both Ethernet and InfiniBand technologies in a data center provides the advantages of each technology for different workloads and connectivity needs. For instance, Ethernet can handle general networking and internet connectivity, while InfiniBand is ideal for high-performance computing clusters and AI infrastructure.
Consider application workloads, latency and bandwidth needs, scalability, cost, and infrastructure compatibility when deciding between Ethernet and InfiniBand. Understanding your data center workloads and balancing them with each networking technology’s capabilities is vital for an informed decision.
InfiniBand architecture, designed for high-speed, low-latency, and reliable interconnects in clustered computing environments, uses a switched fabric topology and high-speed communication protocol. Traditional Ethernet networking, on the other hand, generally employs a blend of switches and routers, offering lower bandwidth and potentially higher latency.
InfiniBand is crucial for high-performance computing (HPC) and artificial intelligence (AI) workloads, providing the necessary low-latency, high-bandwidth interconnect for complex computational tasks. It excels in building high-speed, low-latency communication pathways, enhancing performance and efficiency for HPC and AI applications.
Yes, InfiniBand is prevalent in data center environments, particularly in sectors reliant on high-performance computing, like scientific research, financial modeling, and AI. Its capabilities make it essential for expanding data center infrastructures that cater to advanced computational and data-intensive tasks.
An InfiniBand network typically includes HCA (Host Channel Adapters), switches, cables, and management software. These components create a high-speed, low-latency interconnect fabric. The InfiniBand architecture also includes a subnet manager responsible for managing and configuring the network.
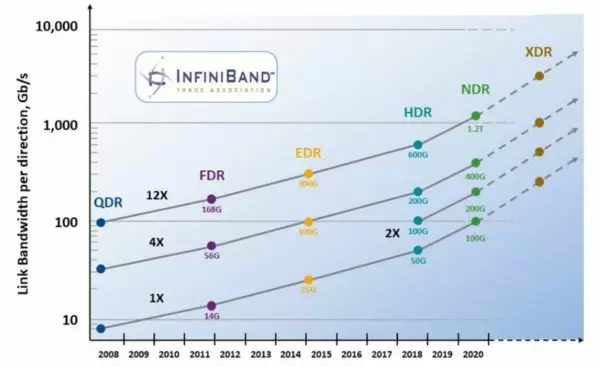
The InfiniBand Trade Association (IBTA) is an industry consortium that drives the development, standardization, and promotion of InfiniBand technology. It facilitates industry leadership collaboration, promotes interoperability, and pushes the advancement and adoption of InfiniBand in data center networking and high-performance computing environments.
——