This exhaustive manual leads us into the complicated world of data center architectures and infrastructures, revealing the layers and parts of technology that form the backbone of the digital era. Our internet cannot work without data centers which process, store and disseminate large amounts of information in various forms including emails and cloud services. The physical and software frameworks that guarantee optimal performance and reliability are also provided herein, alongside with the emerging developments in state-of-the-art data center designs. Irrespective of whether you have been around for a while or just want to get some ideas, this piece is meant at showing how this complex environment keeps spinning on its hinges.
A modern data center adapts to the changing needs of digital transformation and focuses on scalability, reliability, and efficiency. It uses virtualization, automation, and energy-saving technology to meet the high demands of cloud computing and big data analysis. A modern infrastructure also provides businesses with flexible, resilient software-defined networking (SDN), software-defined storage (SDS), and advanced cooling solutions. These components support a wide range of services and applications. It helps improve performance, reduce costs for organizations and harm the environment as little as possible.
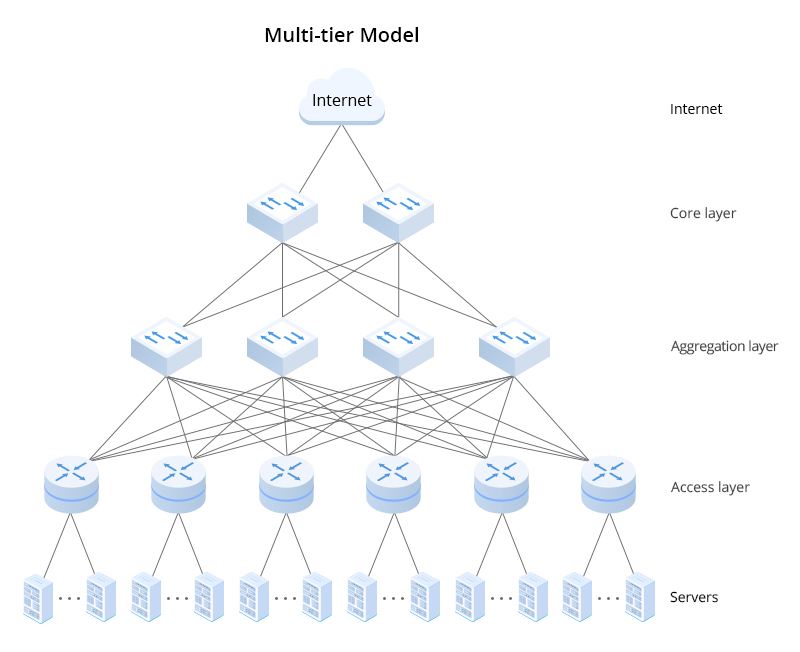
These key components are vital in ensuring that data centers can operate efficiently and reliably when handling huge amounts of information:
By combining these components, data centers build an infrastructure that can support today’s digital environment and keep pace with its future growth.
In an era that has been evolving so rapidly, scalability and flexibility in data center architecture could be considered as the MVPs. Scalability makes sure that a data center can grow with everything else, worry-free. It lets businesses be free of a possible bottle neck or performance degradation when scaling up. Flexibility on the other hand is the adaptability of the infrastructure to incorporate new tech — like cloud computing and AI which keeps things competitive and efficient! When combined these aspects create something resilient enough to roll with any market demand, tech advancement or business goal you may throw at it!
Using redundancy and reliability in data center design is key to maintaining continuous operation. Network paths, cooling systems, power supplies all must be backed up. A failure should never result in the whole thing going down. The point is to keep these facilities running at all times. Of course, reliability can’t be overlooked either. High-quality materials and components are a must for every system here. They need to last as long as possible so that maintenance is needed less frequently. All of these efforts will ultimately reduce downtime and keep customers happy.
Having systems in place which use less energy is important for keeping costs down and the environment clean. Standard methods of cooling take too much power for such big facilities like data centers, especially when you consider how many there are around the world right now! So new ways have been adopted like liquid cooling or using outside air more often instead of air conditioning units (which are basically giant fans). Cutting down on electricity usage also helps when it comes to power supplies and renewable energy sources being used. Overall, these practices not only help with global environmental initiatives but save tons of money long-term.
When considering building a data center two things are crucial: safety measures from break-ins and a solid disaster recovery plan. Security features include things like biometric access controls or surveillance systems that prevent unauthorized access to servers holding sensitive information about businesses or individuals alike – nobody wants their personal details stolen by some hacker! And if everything does go wrong — there’s always a chance something catastrophic could happen — this recovery strategy would kick into gear: regular backups of important files paired with failover systems (backups that automatically activate) would make sure any lost data can be quickly restored without further loss occurring elsewhere due to human error.- It’s an unfortunate fact that disasters happen, but they don’t have to ruin everything you’ve worked so hard on.
After working in the data center industry for many years, I’ve learned that the landscape around data centers has drastically changed. This evolution is most notable when comparing cloud, colocation and enterprise data centers. Each of these serve different purposes and cater to various needs within the IT ecosystem.
Third-party providers run cloud data centers, offering virtual resources over the internet. They’re super flexible when it comes to scaling up or down and are ideal for businesses that need to adjust their resources quickly based on demand without spending money on physical infrastructure upfront. The main perks include being cost-effective, scalable and flexible.
On the other hand, Colocation data centers give businesses a space they can rent to keep their own servers and hardware in-house. This offers things like physical security, power, bandwidth and cooling systems that a company might not be able to afford on its own or even need if they only have a few devices. If you still want control over your physical servers but don’t want to manage an entire facility this could be a great option for you as well. This option is best for organizations that need more security, reliability or bandwidth availability but still want control over their hardware.
Lastly we have enterprise data centers; privately owned and operated by businesses themselves. Normally located on-premises or at a dedicated facility these bad boys offer maximum control over all your data systems! They’re perfect for companies with specific security or regulatory requirements who cant risk sharing any parts of their infrastructure with other companies. While you do get heightened levels of customization and control it does come at a pretty penny; You’ll need some serious capital investment if you’re looking into building one from scratch.
Choosing between these options will ultimately depend on factors such as your budget, how much control you need over everything as well as what your scalability requirements are depending on your goals with business in mind.
Thanks to cloud computing, data center architecture has changed forever. This new technology has pushed the industry to shift their focus more towards scalable and agile solutions. Traditionally speaking, data centers were often built with a focus on optimizing physical space and hardware for peak capacity. But now in today’s day-and-age if you’re not utilizing everything that’s virtualization, redundancy or distributed computing you will fall behind your competition. These principles are what allow us to scale our resources up or down with ease when needed in turn giving us the ability to meet fluctuating demands head on. This migration from one way of thinking to another has given rise to better energy-efficiency within the industry, resilient designs that can withstand whatever comes their way while ultimately saving time and money for business owners.
When designing data center architectures that bolster scalability and can work with cloud services, there are a few things to keep in mind. Flexibility in infrastructure means you can make accommodations for new workload demands and technologies without needing to go through the process of physically changing the center. Automation makes sure resources are managed effectively, with easy scaling up or down when it is needed, and it also helps with reducing human errors. Network architecture has to be built so that it’s capable of handling high volumes of data traffic with minimal latency so that connectivity between on-premises data centers and cloud services never suffers. Of course, security and compliance are incredibly important as well since using cloud services opens up new possible vectors for vulnerabilities. By taking a holistic approach to both physical and cyber defenses, businesses can guarantee data will remain secure no matter what platform it might be on. By keeping these considerations in mind you’ll build a center that is easily scalable while being seamlessly integrated with cloud services – which lets your business prosper in today’s digital landscape.

To create a network in a data center that can reach extremely fast speeds and have almost no delay, it’s important to take into account how both the hardware and software work together. The hardware side of things is made up of High-Performance Computing components. One such component is advanced networking hardware with high-speed switches and routers. These will be able to support bandwidth-intensive applications without slowing down other processes. On the flip side, Software-Defined Networking offers flexibility and control, allowing admins to manage traffic efficiently in real time. Doing this greatly reduces any latency issues. But there’s more you can do beyond that as well! If you implement an edge computing structure, you move data processing closer to your end users, which then cuts down on transit times. Setting up direct connections with internet service providers and cloud platforms will ensure that their data has the fastest route possible as well. So you see, by using all these strategies together, you’ll have a network that works quickly and reliably.
If implemented correctly, redundancy networks can save your servers from disaster! By building multiple pathways in your infrastructure design, you won’t have to worry about one weak link ruining everything else. In terms of actual devices like routers or switches it’s good practice to use dual-powered systems so that if one power source fails there’s still another going strong. You should always look for ways to make your network resilient against failure so that downtime doesn’t become catastrophic if something goes wrong with your device or path.
Modern workloads are getting pretty intense when it comes to processing power needs, so making sure you’ve got the right infrastructure setup is crucial. To start off, consider adopting some Software Defined Networking (SDN) tools into your management suite so administrators can automate changes to the network. Next, think about adding in some Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) software as well. This type of software can virtualize specific network services that would normally have to be ran on a physical device. So overall you end up with something that’s both more scalable and flexible which gives you greater deployment options. Rounding out the list is high-speed Ethernet fabrics. The faster you can move data around your network the better off you’ll be, so it may be worth investing into some new gear if yours is outdated.
Keeping data safe means protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data by implementing comprehensive security measures. This consists of deploying network firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor for and block unauthorized access. It also means making use of strong encryption protocols when transmitting and saving data so that even if someone does get in they can’t do anything with what they find. To maintain accountabilities with industry standards and regulations regular audits must be done as well as vulnerability assessments. Lastly access control policies must be strict to ensure insider threats are minimized.
Optimizing performance while lowering costs is possible through efficient DCIM strategies. By deploying management software that has monitoring tools built in managers will be able to better see how much power a server is using, if cooling systems need adjusted or what the overall environmental conditions inside the data center look like. Having all these insights helps them make well-informed decisions about allocating resources, planning capacity needs or where investments should go for equipment. Another aspect DCIM manages is energy consumption which will help reduce any carbon footprint left behind from operations.
The ways automation benefits management and operation of a data center are endless but it has to be implemented first. Automation tools enable complex processes such as provisioning servers or configuring networks without ever needing human intervention which dramatically reduces human error risk while freeing up other projects staff could work on instead. One great thing about having an automated process chain is its ability to quickly adapt to workload changes whether that’s scaling up or down for more/less resources needed at given times [saving money]. Maintaining available services all day every day can happen through predictive maintenance AI-driven analytics provide which help identify problems before they even occur as well as automatically fixing them should something actually break through scheduled maintenance.

The arrival of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in data center operations has meant that things are about to get much smarter, more efficient, and predictive with how these centers are managed. The goal with AI algorithms is to analyze a mass amount of data from different sources within the data center. This includes server workloads, energy consumption, and cooling system efficiencies. Analyzing all this information will help identify patterns or anomalies that would be practically impossible for a human to see on their own. With this knowledge, data center operators can leverage these insights for predictive maintenance, foreseeing potential failures or inefficiencies before they occur and preemptively addressing them. Automation driven by AI can also adjust resources based on real-time demands; helping out what you need when you need it so you don’t waste energy or time. In simple terms, AI just enhances current operations; it reshapes how infrastructure should work which ultimately saves on money and resources.
Data centers have been evolving their cooling systems for some time now. It’s not a surprise that as technology advances so does its demand for efficiency and sustainability. Classic forms of cooling such as air conditioning have gradually been replaced with more advanced versions.. One huge leap was adopting liquid cooling technologies such as direct liquid cooling and immersion cooling methods which directly remove heat from components more efficiently than any other method we’ve seen previously.. Additionally, people wanted to find ways to reduce energy use while still being effective in cooling down each unit., thus comes free-cooling through outside air and evaporative techniques . These advancements were not only better for our environment but also significantly helped lower operational costs by optimizing how energy was used. As the industry keeps growing developers are looking towards using renewable resources to power data centers entirely reducing carbon emissions.
The future of design will obviously change over the years as technology advances. The design of a data center will be influenced by technological advancements and changing business needs. For example, modularity and scalability will play a big role. Designers want to create spaces that can expand rapidly without disrupting existing operations.
Next in line is sustainability.. Future data centers will aim to be 100% green from adopting advanced cooling technologies to using materials and construction methods that minimize environmental impact.
Automation and AI-driven management are promised for future centers as well. With these techs set in place with minimal human intervention, these techs will save on time, energy used, help you predict when they’ll fail so you can fix it before it happens etc.
Lastly, edge computing will influence how we build our data centers significantly.. In order for IoT devices and real-time data processing to work properly (fast), our data centers need to be closer to users reducing latency and increasing speed.
With all this in mind, the future design of Data Centers revolves around flexibility, sustainability, intelligent operation with AI’s integration, and proximity to end-users all while being able to meet evolving demands from society itself.
In the realm of data center architecture and infrastructure, staying updated with the most reliable and comprehensive sources is crucial for professionals and enthusiasts alike. After careful evaluation, here are three relevant and reliable sources that span a range of media and formats, providing valuable insights into data center architecture and infrastructure:
Each of these sources is chosen for its accuracy, credibility, and relevance to the topic of data center architecture and infrastructure. They cater to a broad audience, from those new to the field to seasoned professionals, and provide essential information that can help guide decision-making processes in the design, construction, and management of data centers.

A: Data center architecture is the way the inside of a data center is set up and designed. It’s good to have because it’ll make sure everything runs smoothly, that you’re able to store plenty of information, and to decrease any risk of problems when you least expect them. The right version of an information system helps with new technology that moves quickly, prevents hardware from overheating, and can easily add on extra storage systems.
A: Cooling systems help drastically with keeping a place at the best temperature possible. If things get too warm in an area, the hardware could malfunction or become useless. But by using great cooling systems they will continuously keep everything running at its best level as well as remove excessive heat so nothing overheats.
A: The four main kinds of information centers are traditional, converged, hyper-converged, and cloud ones. Traditional ones let people manually configure their equipment which works well for enterprises with specific needs that they know about beforehand. Converged infrastructure combines all resources into one package so there isn’t much anyone has to do after that point. Hyper-converged infrastructure makes everything even easier by putting all elements into a software framework which doesn’t need much management once it’s turned on. Cloud centers are used by service providers who offer their resources online or through a dedicated network.
A: Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) can save your data when there’s no other option available to keep your devices on during an outage. With them in use you don’t have to worry about losing anything or having to turn anything back on ever again. Having something like this can lower plenty of risks for a center.
A: Meticulous planning is how they achieve it. Everything from cables to routers and switches has to be considered. Data center managers are responsible for monitoring network performance, ensuring optimal configuration, and updating components all to make sure they can handle increased data flow or integrate new technology.
A: When it comes to building design and infrastructure there is a lot that goes into it. Some of the main things that need to be thought about include scalability, redundancy, security, and energy efficiency. Server racks and storage capabilities need to be able to expand without compromising system performance. Uptime needs redundancy in power supply and data connectivity. Security needs must protect against both physical threats as well as cyber threats. And lastly the design should focus on using energy-efficient materials with cooling systems that reduce operational costs.
A: Cloud-based services are being used more often leading them to become increasingly reliant on low-latency data flow which is increasing the demand of new cloud technologies leading edge computing now being on the rise for this type of technology. The future architecture of data centers will have to be adaptable with these demands in mind. There are also efforts being made to become more sustainable through advanced cooling systems that reduce energy consumption and integrating renewable energy sources like solar power into operations.