Considering how frantic the pace of development in the world of technology is, making a choice regarding the appropriate cabling for your network backbone should be taken very seriously. Distinctive offerings of this kind made it possible to achieve a broader set of features and superior operating characteristics than ever before. In this guide, the authors address the technical characteristics, methods of working with, and the use of the Cat6a UTP cables. The Home Office for Residential Usage, Design and Deployment of Enterprise Level IT Infrastructure and all other kinds of IT Networks that require future-proofed connectivity solutions that this article deals with allow comprehension in much more detail the processes underlying these levels of networks. It is critical to note the features and advantages of Cat6a so that when designing, administrators can have a firm network infrastructure that can fully support the digital requirements that would be solicited anytime.
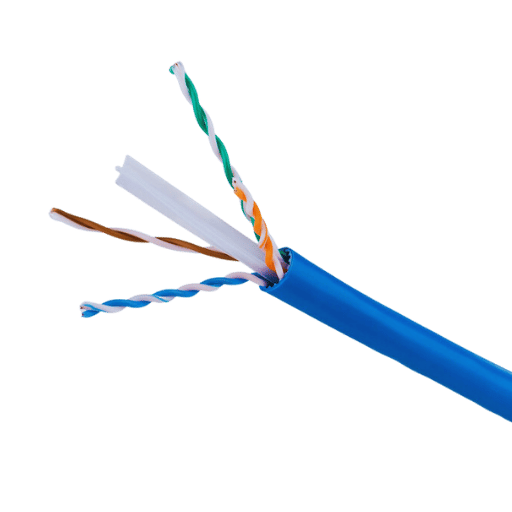
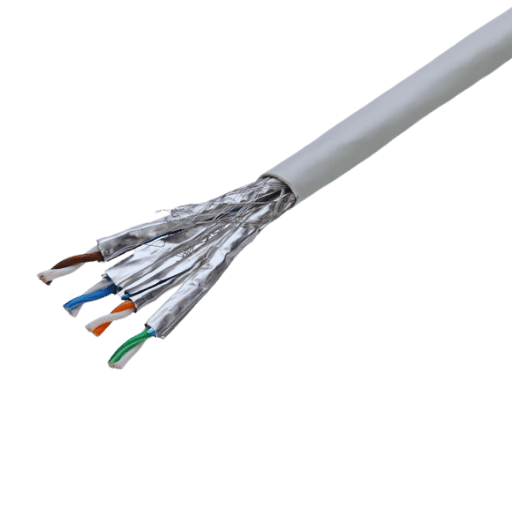
A Cat6a UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cable is a form of category 6 augmented network cable that allows data transmission at maximum speeds of 10 GB per second and includes a bandwidth frequency of 500 MHz over a distance of 100 meters. This cable conforms to the specifications of Cat6 and provides better cross talk and EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) absorption, making it most suited to locations that require high-density and robust networks. It has a physical structure of 4 copper wire twisted pairs, which are used in constructions where shielding is not necessary as the wire twisting reduces unwanted signal distortion and allows signal flow with sufficient data. Such cables are now the most popular in data centers, office networks, and other high-speed workstations; hence, they are expected to be relevant in the years to come with the upcoming Ethernet standards.
The invention of Unshielded Twisted Pair technology, which is very popular today, certainly gets a considerable amount of attention due to the characteristics it offers for data transmission over a network cable. Design is a cornerstone of commercial applications. UTP cables consist of pairs of wires twisted together to improve signal quality and reduce electromagnetic interference. For example, in a Cat6a UTP, four pairs of copper wires are contained, and each pair is twisted at different lengths, which is necessary to minimize crosstalk, which is defined as interference between wires. This treaty, although it does not have another shield, depends on the differential signaling and the native twist to the end negative signals in control.
UTP can also be connected to a broad range of communication network devices, such as Operation Systems switches and routers. From a technical point of view, cable performance is characterized by the twist rate or by the number of twists per meter. For Cat6a, twisting of cables was made in order to enable them to perform better over long distances and over a broad range of frequencies. The drawbacks of a lack of outer shielding materials are more than compensated by simplified construction of the cable, decreased price, better flexibility, and easier installation. The solitary innovation of the Cat 6a UTP was that it was able to compete with shielded cabling systems for the most secure and effective data networks and architectures, which, as a result, made it suitable to be used in advanced digital environments.
When comparing Cat-6 and Cat-6a cables, the main distinguishing factor is their construction and performance capabilities. Although both types of cables are able to support gigabit ethernet, the Cat-6a cable, on the other hand, is capable of supporting gigabit ethernet at greater distances of up to 100 meters. This is a significant improvement in the performance of an ethernet cable. This is an improvement on the Cat-6 cable, which has a capacity of between 37 and 55 meters at the same speed. The Cat-6a achieves this improved performance through a rougher and more intense winding of the wire pairs which increases insulation and ultimately reduces crosstalk in high frequency settings. Cat-6a cables also have a large diameter due to the improved insulation, which makes the cables stiffer but more effective in preventing interference and disruptions. Therefore, improvements in the Cat-6a standards make it ideal for settings and applications that need high-speed data transfers over a long distance.
American Wire Gauge (AWG) is important in network cables as it indicates the electrical and performance parameters. AWG is a standard measure of wire diameters within the cables, indicating that lower numbers of the gauge correspond to thicker wire conductors. Take, for example, the Cat6a cables, which have conductors of 23 AWG. These conductors have a lower resistance, and consequently, the transmission performance offered over longer distances is better than that of cables with higher figures. Such a thickness reduces attenuation, allowing the signal to pass through without losing its quality over long cables. Recent studies have shown that using 23 AWG in Cat6a cables allows 10 Gbps Ethernet connectivity for up to 100 meters. In network professional settings, this specification preserves the quality of data transmission, ensuring that the system is able to send data without delays and system interruptions, which is crucial for the Cat6a high-performance systems factor.
When deciding to use a patch cable rather than a network patch cable, several parameters and conditions need to be taken into account to ensure optimal network performance. These are:
Choosing the right type of cable for your network will involve considering these factors together with environmental factors, the network’s topology, and performance requirements. Patch cables and network patch cables are essential for traversing long distances and retaining a high-performance level when connecting network devices.
There are several factors to weigh when making a comparison between 24AWG and 23AWG solid cables. The other is the American Wire Gauge (AWG) size, which is the measurement that determines the dimensions of the wire. For example, cables with a gauge rating of 23AWG are plotted to be thicker than those with a rating of 24AWG. In general, the greater the thickness, the better because it usually means higher performance in relation to the integrity of the signal and attenuation over long distances. It is also likely that wires with a thicker diameter, such as 23AWG, have stronger mechanical performance characteristics, which, for example, may be useful in installations where the wire is heavily bent or manipulated. Although, one has to consider these advantages with respect to ease of use as flexibility is lost, that is, 24 AWG cables are easier to use in complicated or small spaces. Also of note, 23 AWG cables are more commonly used in high speed environments as this size wire can handle higher data rates, however they do tend to be heavier and more expensive. In conclusion, I would say that the choice of using either 24AWG or 23AWG depends on your particular network performance requirements, the manner in which installation would be performed and the budget that you have.
In a globalized world where telecommunication interconnections and links form the vital foundational framework of continued differentiated sophistication, snagless connectors are essential precisely to this end as they serve to facilitate maximum system output with minimum effort. In this regard, these connectors are specifically constructed with a boot that helps the locking tab during sight or an excessive force application to get caught or broken, which is very helpful for large networked sites when used. Having said that, there is a reduction in harshness caused by interconnectivity issues and an improvement in the system’s integrative reliability and overall efficiency.
According to recent statistics, there is a reduction of up to 30% in maintenance calls regarding repaired connectors and cables in networks that employ snagless connectors. In addition, snagless connectors allow for better routing of cables since the cables cannot get tangled and make it easier to pass through small openings and around or through cable management. In addition, these cables have been tested and found likely to accelerate connectivity unless the network is invaded by mechanical networks that counter this impact. For high-speed transmission purposes, slotless connectors are also becoming increasingly pertinent, as the standard may soon become 10G Ethernet standards. Therefore, in both the modification of existing cable infrastructure and the development of new cable connectivity networks, ensuring all the cables come with Snagless connectors is a wise thing to do. With this strategic decision in place, current existing gaps in network performance can be addressed while any future barriers or likely changes in regulatory policies are mitigated.
Outline the Network Configuration
Pick the Right Cable
Make the Cables Ready
Add Connectors
Squeeze the Connectors
Ready to Install the Cables
Confirm the Construction
Optimize Cable Management
In conclusion, the completion of the efficient installation process of Cat6a UTP cables entails proper planning, accuracy, and cable management to maintain and improve the network’s performance and reliability.
Patch panels are essential for the storage and structuring of network wires by serving as a collection point for several network devices without creating a mess in the office. They make it possible to implement configuration changes with no interruption in the rest of the network, as only components of one part are moved or changed. Many patch panels have several ports on the front, which are wired to punch down connectors at the rear section where the ends of Cat6a UTP cables are attached. This approach allows easy patching and repatching of network connections, which is important in high-density network environments that change on short notice. Through the use of a patch panel, managers are bound to achieve better organization of wires, such as avoiding accumulation, getting tangled up, and having difficulty identifying individual wires, which would consequently make troubleshooting and reducing inactivity easier.
It is important that Best Practices for Network Performance & Sustainability be observed when deploying Cat6a UTP cables in residential and commercial settings. The aim is to achieve optimal network performance and sustain the purpose for the long term. Thoroughly planning routes and cable lengths have been shown to decrease signal deterioration, according to recent studies. A rule of thumb in the industry also states that cable lengths should never exceed one hundred meters to ensure integrity, something vital for high-speed services.
Residential installations have to be babyproof in a way that minimizes the impact of electrical devices on the installation, and the installation socializes power points. Innovative solutions have come up with suggestions of using shielded cables in cases where the EMI is too much so as to not be able to connect. Even more, the utilization of structured cabling using patch panels could make it easier to handle the network, making provision for expansion and maintenance in the future as well.
Given the density of the networking environment, one of the most vital features that the installation should include is advanced heat management features. There are data that point out the need for strategic cabinet cooling to prevent thermal stresses that would otherwise introduce other problems to the cable. Finally, Integrating an automated cable management system, for instance, would be helpful in ensuring that the functioning and aggregate load of networks is accurately managed and controlled using big data technology without compromising on efficiency.
In conclusion, the application of these best practices, together with the use of modern technologies, will considerably enhance the performance and longevity of network installations, whether for domestic use or that of business premises.
In order to achieve maximum speeds of 10 Gbps, the use or Cat6a Ethernet cables is paramount since they are designed to support high bandwidths of up to 500 MHz. In particular, the new Cat6a cables boost the amount of shielding around the wires and add more twists in an effort to reduce the amount of crosstalk and improve the signal much further, which is necessary to maintain good performance at greater lengths. Industry analysis argued that Cat6a cables could perform optimally over 10GBase-T distances of up to 100 meters, which is favorable in large commercial deployments, unlike Cat6 cables, which need amplifiers for less than 55 meters of coverage.
Also, advanced transceivers and switches designed for 10 Gigabit Ethernet speed are also helpful in achieving top speeds as well as maintaining the integrity of the network. Studies in the past have shown that systems that use Cat6a cables within their frame can reduce latency by as much as 50%, allowing data to be transferred faster and reducing causes of congestion. Additionally, using these cables in structured cabling systems allows for easy improvement to faster speeds when there is a need to do so, addressing a future challenge. By following these practices, the network will be able to operate successfully in high-speed data transmission, ideal for current applications that are data-centered.
Cat6a boasts significant advantages over Ethernet cables such as cat 6 which explains its popularity among network cabling standards for high-performance networks. To begin with, Cat6a has designs that integrate the use of additional shielding which reduces interference in the form of AXT and also increases bandwidth making them perfect for cabling. This translates to a stable transmission of data even in places where electrical interference could potentially harm the network.
In addition, it eliminates the need to compromise on distance as it allows for longer runs at 10 gigabit speeds, making it ideal for large commercial spaces. But while Cat6 can in theory run to 100 meters, in practicality it can only be used for about 55 meters before signal quality becomes an issue, cat 6a is able to run an otherwise 10 gigabit cable to 100 meters without needing booster cables to improve signal. This increase in efficiency leads to lower infrastructure costs and expands the capabilities of the network.
Moreover, the implications of investing in Cat6a for the future cannot be neglected. In the near future, this will allow the networks to expand to meet the endless demand for faster cables as CAT 6A has the ability to meet the cable rate of 25 G and 40 G. In general, it can be observed that for businesses that want to be ahead, last longer, and perform, Cat6a is better than the not so appealing cat 6 or the average Ethernet cables.
To improve AXT or cross-talk alien in ethernet cabling, it is essential to add appropriate features and materials that minimize interference as it advances design measures. The latest Cat6 cables physically separate pairs of wires using a shielded twisted pair STP construction or unshielded twisted pair UTP, but this is with increased twisting frequency where axt is reduced due to electrical noise brought about by other cables placed next to the cables. Recent statistics show that the use of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) as a separator in a cable is advanced as a means of further enhancing performance as it keeps pairs apart to reduce the risk of interference from external forces.
Further, compliance with quality management systems such as TIA-568.2-D allows Cat6a cables to meet certain Axt performance standards, which enhances its ability to transmit data even if many devices are linked together. New methods for cable design, such as increased shielding tools and better jacketing materials, help eliminate the chances of cable crosstalk interference, extremely boosting the reliability of a network. By applying such solutions within the environment, the AXT performance is at its best, and thus, installing the Cat6a is very desirable in situations where the data communication relays are high and of high quality.
Yes, UTP cables are suitable for Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications. Recent developments have made it possible for Cat6a UTP cabling systems to carry PoE up to 100 watts, thus dealing efficiently with low and high power PoE standards. They have the required performance level for power and data transmission over a single cable without significant signal degradation, as recent standards and manufacturer’s requirements have confirmed.
PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride) and CMR (Communications Multipurpose Cable, Riser) ratings are essential when making a judgment about the classification of the cables in relation to their installation environment. PVC is one of the most popular synthetic covering for cables because of its favourable electrical, thermal and mechanical properties. As far as PVC cables are concerned, they provide reasonable dielectric strength and moisture and corrosion resistance to the conductors for effective reliability.
However, cables with a CMR rating are appropriate for the vertical spaces between two floors such as in the risers, and these must meet the fire safety requirements. In order to ensure safety and better evacuation of the building and its essential areas, CMR cables are able to restrict the spread of the flames and reduce the smoke generation in the event of a fire.
The National Electric Code describes the requirement that cables with no relevant riser ratings create a higher chance of fire moving between floors. This, in turn, suggests that appropriate cables should be selected with the correct PVC and CMR ratings, taking into consideration not only flame safety but also the strengthening of the system’s reliability and durability in harsh building conditions Although, selecting proper CMR and PVC ratings are useful, it also assists in the effective and safe network installation, limiting the risks and allows for high-quality data transmission.
In general, info and modern best practices suggested by the industry data can help the network installers to avoid these common traps and enhance the quality and the safe of their installations immensely.
A: Unshielded twisted pairs ethernet cables are referred to as Cat6a UTP cables and fall under the category of high-performance data transmission cables. They have much greater features than their forerunners, Cat6. They have a rated maximum data transfer speed of ten gigabits per second and are suitable for ten-gigabit data transmission for distances of one hundred meters.
A: The maximum data transmission rate of Cat6a cables is 10gbps and it has tighter twist in the wires shielding hence they shield the cable from much alien cross talk, that is the reason why their performance is better than Cat6 cables which only carry a data transmission rate of 250mhz. That’s why Cat6a cables are suitable for more demanding applications thanks to its frequent allowances of up to 750mhz.
A: Yes, Cat6a UTP cables are suitable to all common routers and modems, hence there is no need to swap out the current devices in order to enhance your LAN infrastructure. They are beneficial in situations where high speed connections are used since they lessen the risk of network issues.
A: Yes, a variety of color options are available for Cat6a cables. This functionality allows users to color-code network installations for better management and easy recognition of connections.
A: Alien cross talk is the interference of electromagnetic signals transmitted between wires of a single cable or externally placed bundles of cables. Cat6a cables are engineered to reduce this interference, which is imperative as the data transfer rates and reliable transmissions at a distance are prioritized at high to low-density cable placements.
A: A wide range of lengths in Cat6a cables are prevalent which include already made patch cords as well as a solid bulk of 1000ft bulk cables. These are ideal for different wiring requirements whether there is a need for short cable patching or lengthy wire cabling usages.
A: The remarkable touch of the snagless design is the inclusion of a special carrier during the wiring, which helps shield the RJ45 connector from getting snagged. Therefore, they are preferred in areas with frequent plugging and unplugging of cables to minimize wear and tear on the cable nas connectors while maximizing the cables’ life span.
A: Owing to the performance capability of Cat6a cables, which can reach 10g speeds, provide plenty of interference protection, and have a raw power construction of up to 750mhz of frequency, they have been established as the most appropriate cable for high-performance networking. These characteristics allow them to be utilized in today’s networks, which rely on speed and efficiency in the transmission of data.