Choosing the right Ethernet cable to build a dependable and high-performing network is important if you want your infrastructure to work seamlessly and last long. Out of the myriad of options, Cat6a STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) Ethernet cables are popular because of their greater performance, less interference, and higher durability. But what is the essence of Cat6a STP cables, and how do they benchmark against other options? This article answers all questions regarding this tailored cabling solution while discussing its features, advantages, ideal applications, and technical details. If you are a network engineer or just a casual user aiming to enhance connectivity in your home or office, this guide will provide you the foundational information needed to make the right decision.
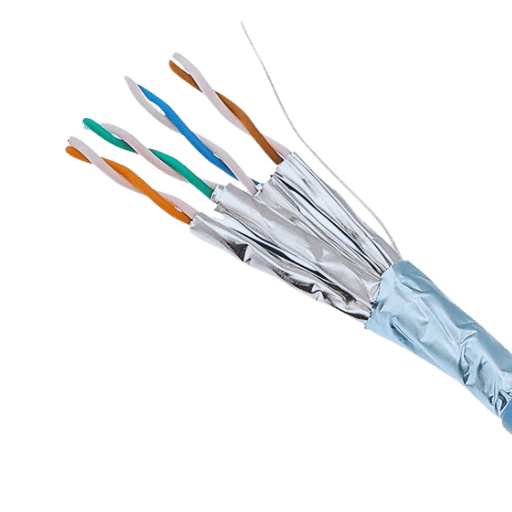

STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) Cat6a cables are Ethernet cables with an improved level of performance, capable of data transmission speeds of 10 Gbps for distances up to 100 meters. The designation ‘STP’ indicates that the cable has additional shielding placed on its twisted wire pairs, which reduces EMI (electromagnetic interference) and crosstalk. Due to the additional shielding, Cat6a STP cables are suited for use in heavy electronic interference environments or places where reliable data transmission is crucial, such as data centers and industrial environments.
In Cat6a, STP refers to a Shielded Twisted Pair. This means that there is extra shielding around the internal pairs of wires in the cable. The shielding enhances the protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and reduces crosstalk between neighboring cables, thereby increasing the stability and reliability of data transmission. These properties make STP cables well-suited for high-performance applications in environments with high electronic interference.
Improved Noise Immunity
Decreased Crosstalk
Transmission of Data at a Higher Speed
Moderate Performance Decline due to Increased Electrical Activity
How to Prepare Your Network for the Future
Improved Lifespan and Strength
Adherence to Standards and Norms
In addition to the expanded capabilities Cat6a STP cables bring to a network, they also enhance overall performance, dependability, and readiness while safeguarding it from obstacles like interference.
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): STP Cat6a cables have an extra shielding layer, which helps protect them from electromagnetic interference (EMI). They are ideal for places like industrial settings or zones with numerous electronics, where there is high interference. Generally, they are more costly, with the caveat that they need to be properly grounded to achieve optimal performance.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): UTP Cat6a cables are devoid of shielding, which makes them rely on twisted pairs for minimizing EMI. For moderate interference, these are effective and less expensive. Most standard office or residential networks can use these, as they are easier to install.
Key Difference: In high-EMI conditions, STP cables offer greater protection than UTP cables, which are low-cost and low-maintenance. Consider the environment of your network to choose which one best meets your requirements.
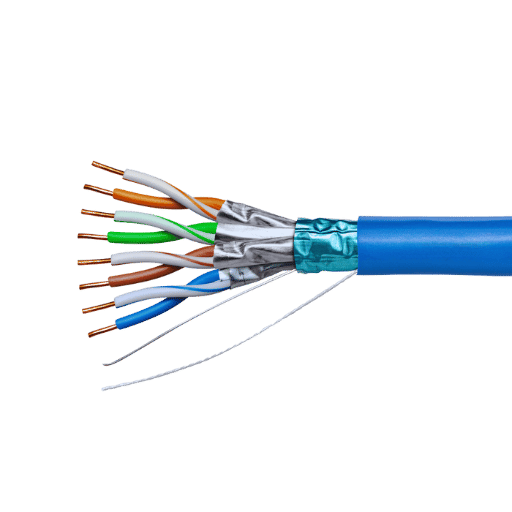
The use of shielded Cat6a cables as compared to unshielded is favorable in the context of electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to the protection shielded versions have against crosstalk and EMI. Such features make shielded variants optimal for industrial areas and any other type of high electronic zones. On the other hand, unshielded Cat6a cables are more applicable in residential or standard office setups where EMI is low. Choosing between shielded and unshielded cables stems from the environment and use case conditions. In most normal cases, unshielded Cat6a is the best option in terms of affordability and reliability.
The Shielded Cat6a Ethernet cables contain individual shielded twisted pairs and an overall shield, which reduces the effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk. Interference that occurs during signal transmission between parallel cables is known as crosstalk. In cross talk, data is either lost or there is a signal degradation. Similarly, EMI interrupts the cable signal during exposure to high-frequency electronic devices, power cables, and many more.
Shields are achieved in many ways, such as wrapping foil around individual wire pairs or using braided shielding around the cable. The above-mentioned methods provide a barrier that absorbs and reflects outside interferences. As a whole such methods yield superior performance for network connections, mainly in case of electrical data centers and industrial noise centers, shielding such wearables also improves electrical sustainability making them longer lasting.
Research states that shielded Cat6a cables have an alien crosstalk of forty percent reduction when compared to unshielded cables. Furthermore, semi-conducting shielded cables over a hundred meters maintain their transmission strength at ten gigabits, making signal preservation easier. Such goals provide achievement to set goals by ANSI/TIA and ISO/IEC for high-speed networking.
In the end, the strong shielding on Cat6a Ethernet cables aids in reliable data transmission, reduced latency, and minimal packet loss. This is useful in applications such as video conferences, transferring large files, and high-frequency trading systems where clarity of signal and network reliability are of utmost importance. It is advisable to use shielded Cat6a cables for emphasizing performance in areas with high electromagnetic interference.
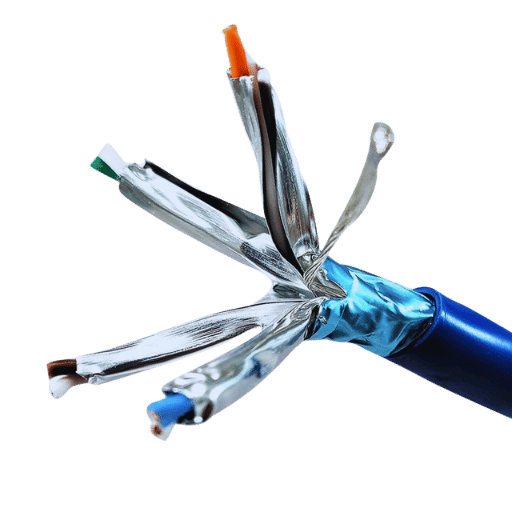

Unlike other connectors, RJ45 stands out as the most compatible connector for Cat6a STP cables because of its ease of use and reliable performance. It helps in high speed data transfer and guarantees secure and stable connections in commercial areas alongside homes. Moreover, RJ45 connectors are standardized which eliminates barriers in device and network interoperability. They are known to withstand high performance Ethernet applications because of the compact configuration that guarantees protection against disconnections. The locking mechanism additionally enhances their durability.
Correct attachment of shielded RJ45 connectors is paramount for upholding performance levels and maintaining the shielding’s effectiveness. Below are considerations one must bear in mind for achieving successful installations:
Preparing the cable
Shield Preservation
Pair Untwisting
Wires Arrangement
Trim Excess Wire Length
Insert Wires into the RJ45 Connector
Test the Connection
Important Aspects
Compliance with Standards
Effect of Shielding on Cable
Transmission Performance
These guidelines and considerations will enable you to improve the reliability, durability, and performance of shielded RJ45 connectors in demanding network environments.
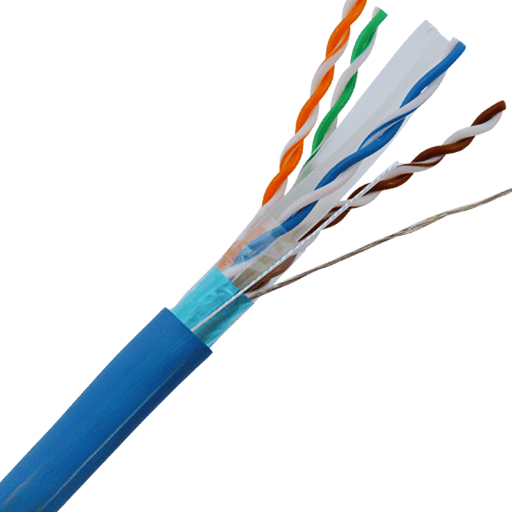

The abbreviation 26 AWG details the thickness of the wire used in Ethernet cables. AWG, or American Wire Gauge, measures the diameter of a wire—in this case, a 26 AWG wire is thinner relative to higher numbers like 24 AWG. For networks, this means that 26 AWG cables are less rigid and simpler to install in strained areas but may have a bit more signal loss over longer distances. While implementing 26 AWG cables in a Category 6a network, particular attention must be paid to the length of the cable to ensure it performs optimally, particularly for high-demand, high-speed data transmission applications. With proper installation and care, 26 AWG cables can provide reliable performance within supported specifications.
The wire gauge of Ethernet cables affects network performance parameters such as signal attenuation, carry current, and structural strength. Cables with higher AWG numbers (26 AWG, for example) have thinner conductors, which can create greater resistance. This higher resistance can result in greater signal attenuation, especially in long distances, thereby potentially hindering data transmission effectiveness in high-speed networks. Industry standards recommend limiting cable length for 26 AWG wires to about 55 meters (180 feet) for 10 Gbps operation in Category 6a specifications while recommending 100 meters (328 feet) for the thicker 23-24 AWG cables.
Cables like 26 AWG are easier to install in tight spaces, but their flexibility and reduced diameter are not without disadvantages: they cumulatively create greater thermal dissipation. Compared to most PoE applications, cables with 23 24 AWG have lower resistance and greater diameters, making them less susceptible to these issues. Testing has shown that thicker cables provide better performance in scenarios with high data throughput due to their superior signal-to-noise ratios.
To reduce some of the potential issues that may arise, it is imperative to select cables that possess high grade shielding and Category 6a compliance. Following guides concerning the design of the network and implementing length suggestions guarantees that even 26 AWG cables can function adequately for contemporary networking requirements, such as 10GBASE-T transmission, operation.

Meeting industry standards and ensuring that Cat 6a Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) cables perform optimally requires their installation with specific tools. The tools listed below are a comprehensive collection of what is needed:
Cable Stripper and Cutter
Shielded RJ45 Connectors
RJ45 Crimping Tool
Cable Tester With PoE Compatibility
After the installation of the device, the numerous veriifiable connections require the use of a network cable tester, Advanced PoE testers are recommended as they support transmitting power to test if power delivery or data streams have faults.
Grounding Bars and Clamp Tools
Punch Down Tool
Measuring Tape and Cable Management Accessories
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Wrist Straps
Adequate tools that meet the technical specifications can guarantee smoother installations of the Cat6a STP cables. Grounding bars and clamps along with the ESD wrist straps can prevent damaging delicate components, enabling the long-term dependability of the networking system. All described tools provided in the document if used and maintained well, can endure prolonged service life, aiding in reducing costs needed for additional installations and succeeding in maximizing the durability and performance of the system.
Finalize the Cable
Expose and Arrange Twisted Pairs
Level the Wires
Put the Wires into theRJ45 Connector
Crimp the Connector
Ensure the Accuracy of the Termination
Through meticulous attention to detail and careful workmanship, a reliable termination of Cat6a STP cables is achieved while ensuring optimal performance and conformity to applicable standards.
The following is a step-by-step approach for testing and troubleshooting Cat6a STP installations:
Carry out Continuity Checks
Confirm Wiring Order
Verify Shielding Protection
Test Signal Quality
If there are errors, revisit the terminations, cable slack, as well as grounding locations. Addressing these issues will system performance and reliability.
A: Cat6a STP Ethernet Cable is high-performance network cable that supports 10 Gigabit Ethernet. It is capable of exceeding 10Gbps over a distance of 328 feet (100 meters) and offers higher protection against electromagnetic Interference.
A: Cat6a STP cables outperform standard Cat6 cables. They are capable of maintaining 10Gbps speeds over longer distances, which is attributed to improved shielding, a higher bandwidth capacity of 500 MHz compared to 250 MHz in Cat6, and lower crosstalk and electromagnetic interference.
A: A snagless shielded Cat6a patch cable is very beneficial due to its snagless RJ45 connectors that enable trouble-free connection during installation. Its shielding reduces electromagnetic Interference while the snagged design protects the connectors making them ideal for demanding network environments.
A: Certainly, Cat6a STP cable is indeed favorable for all PoE applications, especially high-powered PoE++ (802.3bt) that can deliver up to 100W. The construction and shielding of Cat6a STP cables are robust, which is advantageous in carrying data and power over longer distances without deterioration.
A: Affirmative, Cat6a STP cables are completely backward compatible with older Ethernet standards like Cat6, Cat5e, and even Cat5. They are compatible with Fast Ethernet (100Mbps), Gigabit Ethernet (1Gbps), and 10GbE, making them versatile for different networks and future upgrades.
A: Select a length that can comfortably reach from your device to the network port without excess slack. Common lengths include 1 ft, 15 ft, and 25ft. Custom lengths can be tailored within specific measurements. Also, while Cat6a can support up to 328 feet, shorter cables, on average, perform better than longer cables, especially for high-speed connections.
A: Ordinary Cat6a STP cables can’t be used outside. There are, however, outdoor-rated Cat6a cables which have extra shielding from the UV rays, moisture, and extreme temperatures. If you do need to run cable outside, ensure that you buy an outdoor-rated Cat6a STP.
A: Purchase cables from recognized testing laboratories like UL (Underwriters Laboratories). They should at least adhere to, if not surpass, the TIA/EIA-568-C.2 standard for Cat6a performance. Manufacturers like StarTech.com are reputable and, as such, offer specification documents and compliance documents regarding their cables.