Fibre Channel serves a central role within the context of advanced data storage and networking technologies. Its high reliability, low latency, and high data throughput capabilities make it the backbone of enterprise-grade storage area networks (SANs). What makes Fibre Channel an industry-leading protocol for massive storage infrastructure? It is the goal of this article to explains the fundamentals principles, benefits, and use cases of Fibre channel, while clarifying its structure and functioning protocols. This includes anyone working in IT, network infrastructure, or those interested in high speed data transfer mechanisms, students and professionals alike.
The Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) is a protocol for the high speed transfer of data, and is intended for the transport of SCSI commands over Fibre Channel networks. FCP enables communication between different servers, storage arrays, and other devices with very low latency and high efficiency. SCSI commands are converted to FCP frames and transmitted through the network. FCP is common in SANs because of its easily achieved scale, performance, and support for large mission critical environments.
Flexibility and precision is needed in any enterprise, sometimes ports need to be added or removed or certain boundaries set, through the use of even more subdivisions. The same levels of accuracy must be applied to defining network locations as well, as now we can require accuracy on two levels. Ports and their subdivisions must be continually changed, modified, added and/or split; again, such activities play a major role in the general operations of any network.
According to recent developments in Fibre Channel technology, the Gen 7 Fibre Channel integrations might support ports capable of 128 Gbps and will provide value for difficult tasks such as data-heavy workloads, virtualization, and cloud integration. Enhanced reliability alongside lossless data transfer makes Fibre Channel ports the preferred ones for SANs in enterprise environments.
Moreover, these features enable dynamic port mapping and dynamic zoning which improves prevention of unauthorized users from important resources. For example, zoning enables administrators to set boundaries around devices within specified areas of the network, ensuring that communication is only allowed within those boundaries and is compliant with data security protocols.
The other latest information highlights noteworthy decreases in latency as well. Through the advanced port configurations, Fibre Channel ports can achieve latencies of 20 microseconds which is phenomenally lower than other Ethernet solutions. This is a necessity for sectors like financial services which operate in real time and require instant coordination with data.
With increased speed, reliability, and comprehensive management, Fibre Channel ports promote innovation in high-computing environments and with the drop of restriction with reliance, transforms them into vital elements for contemporary networking systems.
These topologies help enable the design and implementations of various networks to be flexible to fulfill the different demands regarding performance and scaling.
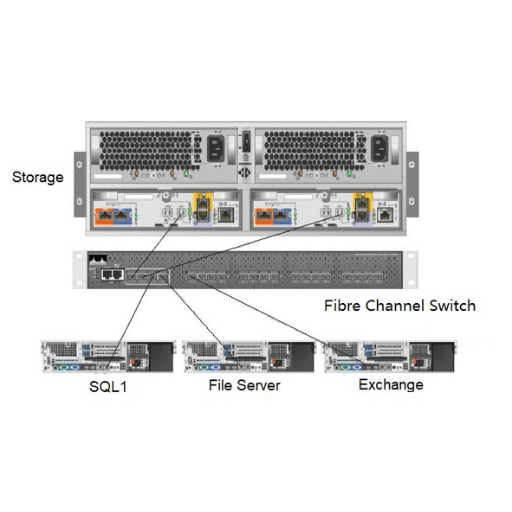
Both technologies provide their own distinct advantages based on the needs of the storage network.
Fibre Channel enables high-speed networking that is dedicated to a single purpose – storage. The technology works on a self-contained infrastructure, thereby assuring optimal performance, low latency, and high dependability, which is ideal for enterprise environments with demanding storage requirements.
FCoE amalgamates Fibre Channel and Ethernet and routes Fibre Channel traffic over conventional Ethernet networks. This lessens the urgency for independent network structures and allows the sharing of Ethernet cables for both data and storage traffic. In contrast, FCoE comes with a potential for more complex networks and relies on superior performance Ethernet networks to achieve the reliability and performance of traditional Fiber Channel.
Fibre Channel is often the preferred option when dealing with performance sensitive workloads, while FCoE is often adopted when there is a need for cost saving measures or ease of infrastructure.
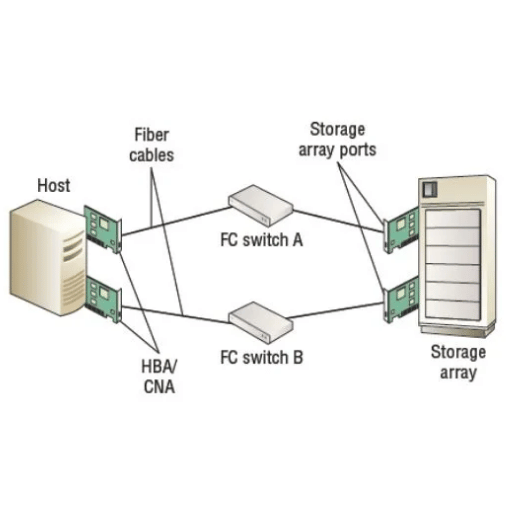
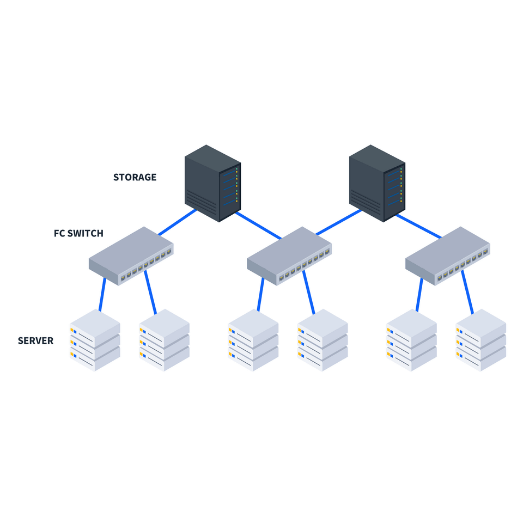
A Fibre Channel Storage Area Network (SAN) is comprised of its operational components which strategically collaborate for maximal energetic efficiency, high-speed connectivity, and storage reliability.
As described, this architecture is flexible, enables efficient, scalable storage solutions that fulfill the requirements of enterprises.
Fibre Chan nes(FC) is a highly efficient and capable networking technology developed for Storage Area Networks (SANs), which operate with very low latency and achieve high data throughput of between 16 Gbps and 128 Gbps. Unfortunately, the technology is limited to dedicated infrastructure alone. The only positive aspect, however, is that it guarantees the mitigation of typical network bottlenecks which leads to its enhanced reliability as data is transmitted without interruption.
One of the primary reasons Fibre Channel excels in high-speed environments is its use of a lossless transport mechanism, which is vital for the preservation of fibre channel physical and signaling integrity. It employs buffer-to-buffer credit flow control which helps in efficient utilization of storage buffer capacity managed at each link by preventing dropped packets. Additionally, Fibre Channel offers support for multi-pathing which is a feature that enhances fault tolerance and increases data throughput by providing alternative data paths in case of link failures.
As stated in an industry analysis, FC has demonstrated sustained performance under challenging conditions, which makes it well-suited for latency-sensitive tasks bed Offshore Services, high-frequency trading, and wide-range databases. As an illustration, modern 64 Gbps Fibre Channel technology possesses almost double the data rate compared to 32 Gbps predecessors, yielding unprecedented levels of storage performance for enterprise-level operations.
The NVMe over Fibre Channel (NVMe/FC) protocol further enhances the functionality of Fibre Channel due to its support for SAN components. These devices are able to interface with next generation storage devices, enabling them to have quicker data transfer rates and lower latency. These advances make Fibre Channel one of the most important sought features to achieve high-speed, scalable, secured SAN infrastructure for data-rich industries.
In a Fiber Channel configuration, a Host Bus Adapter (HBA) is one of the interfaces between servers and the storage network. It interfaces the data transport with the host system as well as the storage devices, ensuring proper relations and efficient data handling. Functions such as data encoding and decoding, error checking, and flow control are performed by the HBAs. They relieve the server CPU from performing these activities, achieving better overall system performance and reduced latency in data operations.
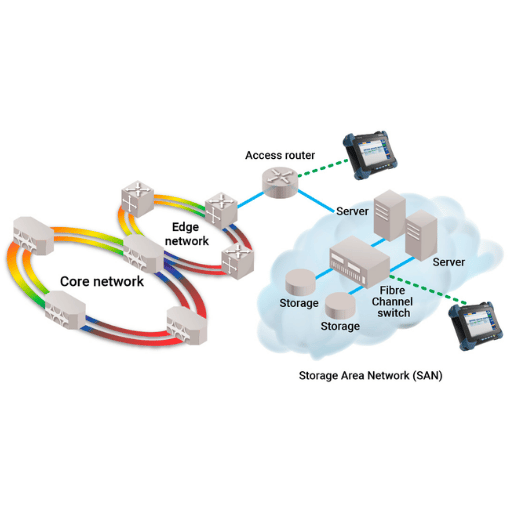
A Fibre Channel switch is an example of a device within a Fibre Channel network whose purpose is to allow communications between the devices in a storage area network (SAN). It connects devices and facilitates the transfer of data. it’s principal activity is to manage data traffic by knowing where each data frame is coming from and where it is going. Fibre Channel switches also allow for zoning, which limits which devices are able to communicate with each other for optimal performance and security. This kind of switch allows the SAN to have high bandwidth and low latency while ensuring reliable data transfer which is essential for performance and scalability.
Fiber optic cables serve an important role in Fibre Channel systems because they enable long distance data transmission with little to no signal degradation. Instead of relying on electrical impulses, these cables make us of light signals, which allows them to reach bandwidth rates needed for contemporary Storage Area Network (SAN) use cases. For example, single-mode fiber cables are rated for distances exceeding 10 km which is ideal for wide area networks, whereas multi-mode fiber cables are best suited for lower distances used in data centers.*
The distinctive attribute of fiber cables in Fiber Channel systems is their exceptional resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI), which guarantees data accuracy in scenarios fraught with intense electric noise. Also, various types of fiber connectors like LC, SC and MPO coupled with advancements like nanostructured OM4 and OM5 fibers improved the durability and efficiency of these systems. With the addition of fiber cables, data rates of Fiber Channel networks is now as high as 128 Gbps, thereby providing faster access to vital information and reducing waiting time.
Along with data storage requirements growing continuously every year, research suggests that fiber cables will be vital towards the scalability and flexibilty of SAN infrastructures. In the ever-changing world of enterprise data storage and transfer, the unrivalled speed, reliability, and durability fiber cables offer makes them an irreplaceable link in the already strained chain.
Fibre Channel remains a crucial standard for expanding organizational capabilities because of its specific and efficient handling of big data. Newer businesses find it difficult to deal with the increasing volume of data due to the need for high reliability and dependability. For example, the high scale virtualization, AI, and machine learning workloads require Fibre Channels’ seamless data handling features. Its Gen 7 technology supports throughput speeds of astonishing 128 Gbps.
Moreover, businesses that are growing and looking to expand their storage infrastructure can do so with minimal disruption due to the technology’s support for scalability. Fibre Channel networks provide a lossless transport mechanism, which is fundamental for industries where data replication and backups is of utmost importance. In addition, research shows that Fibre Channel is consistently more favorable than its competitors such as iSCSI in ultra-low latency situations, leading to better performance for enterprise level applications.
Fibre Channel’s capability is further boosted with modern standards such as NVMe over Fibre Channel which makes data harder to access less efficiently stored. This is critically important for businesses employing advanced high-performance flash storage devices. In a multi-tenant data center, zoning and logical isolation security features also make the environment safer, assuring sensitive data is protected.
Implementing Fibre Channel enables businesses to successfully respond to the demands of digital transformation and economic growth. This integration offers unparalleled advancement reliability and advanced technology, positioning the channel as a scalable and secure solution for business activities.
The efficiency of network architecture design is boosted by Fibre Channel connectivity as this enables high speed, security and reliability of data transfer. Organizations that need low latency and high throughput for mission-critical applications are best suited for this technology. Fibre Channel’s ability to scale seamlessly makes it an ideal candidate of increasing data demands with efficiency to reduce pareto optimal size of resources. Zoning and segmentation as security features assure data protection in complex multi-user environments. These features place Fibre Channel above all others when targeting the optimization of modern IT infrastructures.
A: Fibre Channel is primarily utilized in high-speed networking as an enterprise’s storage networking protocol and focuses on linking servers with storage systems. FC is known for its functionality, low latency, and having the capabilities to operate efficiently. It also differs from Ethernet, which is a general-purpose networking protocol as Fibre Channel is specifically tailored to handle controlled block data transmission specialized in storage area networks SANs.
A: Both Ethernet and FC are hardware networking technologies that serve different purposes. Fibre Channel is primarily dedicated to storage networking that requires preestablished infrastructure with low latency and high-speed data transfers. Ethernet is a more generalizable protocol for communications over the network. In addition to his employment in telecommunications, Ethernet has developed support for storage protocols like iSCSI. Compared to Ethernet, FC is relatively the best for the enterprise level storage networks.
A: An FC switch is a network component that interlinks devices within the Fibre Channel fabric. Its importance to the Fibre Channel network is that it enables a switched fabric topology to be implemented which offers high speed, low latency interconnections between the servers and storage devices. The FC Switches determine the shortest path for the data transmission using Fabric Shortest Path First protocol and thus helps in efficient communication in the SAN.
A: In performance and latency, Fibre Channel has a great advantage over iSCSI SAN which makes it more appropriate to use with mission critical applications. But on the contrary, the infrastructure of Fibre Channel is expensive since it requires specialized hardware. It is easier and cheaper to implement iSCSI SAN which operates on Ethernet networks but it does not perform as well as a Fibre Channel in high demand situations. The selection of either one is dependent on particular business requirements, financial limitations, and prior infrastructure especially for the integration of fibre channel data solutions.
A: The key components of a Fibre Channel network are: 1. Essential Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) or network adapters in the servers utilize the gateway’s native fc interfaces. 2. FC switches aid in the construction of a switched fabric. 3. Storage systems that have native FC interfaces. 4. High speed optical fibre cables. 5. Data transmission is done over Fibre Channel protocol. 6. There is management software for monitoring as well as for configuration.
A: The Fibre Channel Industry Association (FCIA) is a non-profit entity that advocates for the advancement of Fibre Channel technology and standards. FCIA works along the International Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS) to formulate and revise the specifications of Fibre Channel. The FCIA actively participates in the development of the FC technology, promotes the use of Fibre Channel among different suppliers, and provides education to the industry on the advantages and uses of the Fibre Channel.
A: Some recent advancements in the field of Fibre Channel Technology are: 1. Speeds of up to 32 Gbps are supported by Gen 6 Fibre Channel, which is part of the gigabit fibre channel technology. The speed is increased to 64 Gbps in the Gen 7 Fibre Channel. 3. Enhanced reduction in energy consumption and increased latency 4. Enhanced security features 5. Increased cloud and virtualized environment acceptability 6. Improved capacities for monitoring and advanced diagnostic These continuing improvements continues to secure the position of Fibre Channel as a solid solution for enterprise storage networking and disaster recovery applications.
A: Efficient data replication and synchronization between the primary and secondary sites is enabled by low-latency, high-speed Fibre Channel performance, thus supporting disaster recovery and business continuity. The capability of extending FC SANs over long distances through Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP) enables the organization to maintain real time or near real time copies of critical data at remote locations. This feature makes it an excellent candidate for more dynamic and robust disaster recovery solutions along with the reliability and the data integrity features of Fibre Channel.