Today’s world is characterized by connectivity on an individual and as well as on organizations levels. One such need of creating consistent network connections is fulfilled by using an Ethernet cable and the most popular type in this category is the Cat6 Ethernet cable used due to its better performance characteristics. This paper will use a 3ft Cat6 Ethernet cable as a case study to examine the Effective range as well as its Structural features and possible applications for this type of cable. Developed within a new generation of cable technologies, the Cat6 Ethernet cable supports high-speed data transmission, crosstalk reduction, and improved signal integrity. This can be used in a wide variety of contexts, including office configuration and a home network. Such an understanding of the abilities and specific advantages of such cables can enhance their use in different networks on various levels and improve efficiency. Through this exploration of the above materials and existing conditions, the reader will understand why a 3ft Cat6 Ethernet cable is versatile and is preferred by many for different network solutions.
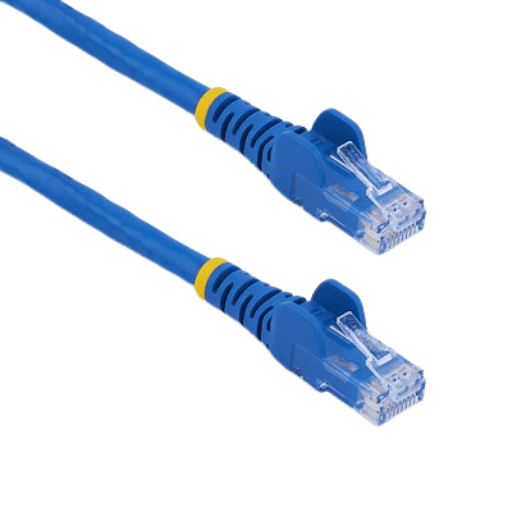

A Cat6 ethernet patch cable refers to the industry-standardized twisted or braided cable that is used for network connectivity and offers up to 1 gigabit per second data transfer rates and a frequency of up to 250 megahertz. It has copper wires that are twisted in 4 pairs to minimize interference and crosstalk, hence improving the quality of the signal. This cable transmits data using electrical signals that are sent between the two connected devices so as to allow the devices access to fast internet and network communication.
In order to appreciate the meaning of the Cat6 standards, it is necessary to investigate the parameters and the technical characteristics that determine such standards. The Category 6 cable, also referred to as Cat6 cable meets the requirements of TIA/EIA and ISO/IEC standards that are specific to the structure of cable networks. It is noteworthy that Cat6 cables are produced with better insulation and control over crosstalk and noise within a system than the previous Ethernet standards, such as Cat5e, allowing a higher level of speed and bandwidth.
A Cat6 cable has a bandwidth of about 250 megahertz and data rates of up to 1 gigabit per second for lengths of around 100 meters. However, for distances greater than 55 meters, attenuation could happen, which is less effective for Gigabit Ethernet applications compared to a shorter 3ft cable that operates at peak rates with minimal signal loss. The characteristic impedance of the cable is usually from 100 to 110 ohms, which makes signal loss low. Based on its construction, a Cat6 cable possesses tightly wound twisted pairs of conductors in a thick gauge, which improves the ability of the cable to withstand electromagnetic interference (EMI), therefore providing more stabilization of signal integrity in data-driven applications. These specifications guarantee the strong network performance of the Cat6 cable, qualified for high-speed and high-bandwidth data systems of the modern age.
A 3ft ethernet cabling has a number of benefits in network configuration, especially in situations when devices are adjacent to one another- for example, in offices or home network cords. The first concerns the lower length of 3 ft, which increases the cable’s efficiency by limiting the signal loss and the time lag, which allows for faster and more reliable transfers. This is vital for high-speed applications where both speed and reliability must be maintained. Finally, the compact size of the cable further decreases the amount of unnecessary materials, increases the cable’s appearance, and enhances the airflow around the network devices leading to better cooling and improved lifespan of the devices. Therefore, considering these beneficial factors, a 3ft ethernet cable can be used in instances where the management of the network is desired.
The Ethernet cables ensure a physical connection for network devices, including computers, routers, switches, etc., enabling data transfer. It consists of multiple twisted pairs of copper wires that are used to transmit electrical signals, allowing the connected devices to communicate with one another. Both ends of the cable have RJ-45 connectors that are inserted in devices’ Ethernet ports, thus enabling secure connections for data transmission. This arrangement is suitable for the movement of data packets with the aid of TCP/IP and such protocols specifically designed to control the flow of data. The Ethernet protocol governs this operation, enabling different devices with Ethernet cat5e, cat6, or cat6a types to work together with consistent performance.
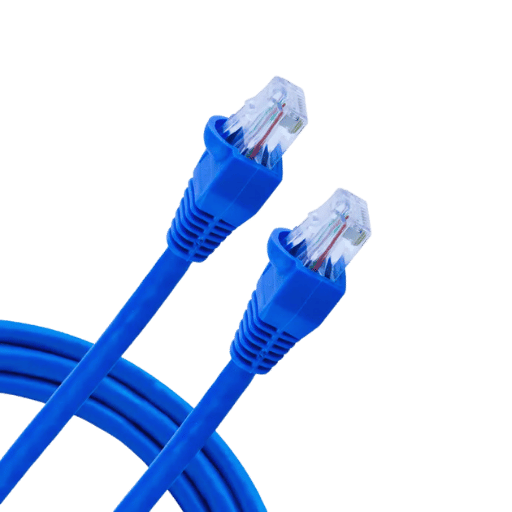

The Cat6 Ethernet cable employs a Snagless construction, which has many benefits that are of great significance in supporting the stability and efficiency of the network. It has a boot that encases the locking tab, thus protecting it from physical forces and keeping the connector in the port. This is an improvement in the durability of the cable, especially in situations where jacks have to be connected and disconnected in quick succession. Also, the Snagless construction reduces the wear of connectors, so their replacements and maintenance are minimized, which aids in achieving constant data flow and high network efficiency.
There are the following parameters and features that set Cat6 and Cat5e cables apart:
Bandwidth capacity:
Data transfer rate:
Crosstalk reduction:
Physical construction:
Backward compatibility:
Cost Consideration:
This detailed comparison serves to delineate the situations when each type of cable is optimal and therefore assists users in selecting the best ethernet cable suitable to their network requirements.
When it comes to power over Ethernet (PoE) networks, both Cat5e and Cat6 cables are workable options, although some differences are foreseen in performance and capabilities. Indeed, Cat5e cables can accommodate the standards for PoE and PoE+ power delivery solutions, which are sufficient for many cases, including VoIP phones, IP cameras, and wireless access points. However, Cat6 cables, having higher specifications, have a definite advantage over powering these devices using higher levels of power, which are needed for PoE++ or IEEE 802.3bt standards. This is very important when powering devices with higher energy, such as LED lighting systems or more sophisticated network devices. Furthermore, the use of Cat6 cables also results in excellent data transmission with minimal interference, which is important in high electrical noise and/or heavy networking environments. With the development of PoE systems, the focus of this study remains on the appropriate cable that will allow improvement of performance and reliability of network facilities as per future projections.
As you consider the different Ethernet cables to use in your network installation, ensure that the cables will meet the required bandwidth and shielding requirements. In the case of bandwidth, standard Cat5e cables are able to follow frequencies of up to 100 MHz, while on the other hand, Cat6 cables extend this bandwidth by reaching up to 250 MHz. This high bandwidth makes it possible for a Cat6 cable to carry out several data transmissions at increased speeds, and this is able to decrease latencies and improve network efficiency performance, especially in high data traffic situations.
On the subject of shielding, Ethernet cables also come in other diverse forms such as UTP or unshielded twisted pair, and STP or shielded twisted pair. Depending on the application of the network and the expected EMI around the area where the cables will be installed, one will choose one of these cables. On the other hand, STP cables are, however, much more effective since they have foils shielding twisted pairs or whole cables in a single entity. Therefore, STP helps to reduce EMI interference and hence ensures that much cleaner data is sent over. Such features are very critical in industrial areas or areas with many electronic devices where signal integrity is very important. By carefully reviewing and following these features, network administrators are able to select the most appropriate cable that meets the performance expectations and industrial set standards.
When terminating Cat6 Ethernet cables, the T568B wiring standard ranks as one of the most commonly used globally, promoting interworking across network systems. In applying one of these wiring schemes, it is imperative to observe the exact sequence of color code arrangement so as to preserve the quality of data transfer. The order for the T568B configuration is first pin 1, which has the white/orange wire; pin 2, which has an orange wire; pin 3, which has a white/green wire, pin 4, which has a blue wire; pin 5 which has a white blue wire, pin 6 which has a green wire, pin 7 which has a white brown wire and last is pin 8 wire which is brown. Adherence to the T568B standard ensures that the Cat6 cables can handle gigabit speed as well as reduce the chances of cross-talk and signal disruptions, which are quite important in today’s networking environment.
When choosing a patch cable, there are criteria that the application must meet:
More information on Ethernet standards can be done through the following features to support the above:
Through evaluating these specifications one can be able to choose and order Ethernet cables that are in accordance with the given requirements as well as operational environment.
The reason for the inclusion of pure copper conductors in the Ethernet cables is because they have very good conductivity and thus ensure that data transmission is effectively done with the least losses. Copper is naturally especially helpful in the sense that it does not get rusty and can provide efficient connectivity for many years. Very importantly, pure copper conductors also provide extra strength for the cables, as well as allowing fairly long distances without loss of transmission quality. Over time, these pure copper wires will be more cost-effective than copper-clad alternatives as they provide stronger possible speeds and improve network efficiency.
In order to appreciate the technical specifications of the 3ft Cat6 Ethernet cable it is important to look at two parameters, AWG (American Wire Gauge) and twisted pair design.
AWG Specifications:
The ability of the Ethernet cable’s individual conductors is observed in the AWG rating. Most Cat6 cables have a 23 AWG conductor which is quite strong and flexible enough to carry signal. It is possible to achieve lower resistance through thicker conductors (lower AWG numbers); this, guarantees high signal strength and hence great data transfer capacities over a longer range. This is very important because, it aids in the reduction of signal attenuation, which is the decrease of strength of signal during transference.
Twisted Pair Design:
Because each Cat6 comprises four twisted pairs of copper wires it is classified as twisted pair cables, this feature helps to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and the crosstalk between them. In terms of noise filtering, tight twists in Cat6 offer better protection, thereby enabling higher transmission speeds. Each pair can also have a spline or cross separator that provides uniform spacing and distances between pairs that would otherwise interfere with each other, thus allowing the cable to reach bandwidths of 250 MHz and data transfer speeds of 1 Gbps over 100 meters when properly terminated.
Identifying these technical characteristics is fundamental in ensuring that the type of Ethernet cable used is appropriate in terms of performance and the durability of the network under different conditions.
In the case of Ethernet cables Ethernet cables such as Cat6, it’s very important to know the bend radius to ascertain that the cable has a signal in its highest integrity over a long period of time. The bend radius is the smallest, and no cable can be bent without the risk of getting kinks or other forms of damage that can affect its usability. Based on suggestions from the best authoritative sources, the maximum bend radius of a Cat6 cable is four times the diameter of the cable. If this limit is present, the internal wire breaks up into several cross points, which diminishes the quality of the data that the transmission brings back. How these are placed, that is, how their trays are used, and how much sharpness or bath curves are incorporated when designing a cable all help maintain the standards. These considerations are useful because the cable is not going to perform electrically in the manner that is sought because the physical properties of the cable impose a limitation on it.
A: CAT-6 cables are designed for transferring images or audio with the speed of 10 Bosch networks layer to keep voice and data flowing. The use of a CAT-6 is recommended for greater transference rates other than those available on CAT-5 s.
A: A three-foot CAT-6 ethernet cable is composed of non-biased CAT-6 components as being exactly 3 feet in length. Perfect for intermediate range applications like connecting computers with remotely placed routers or a patch panel.
A: CAT 6 UTP cables are supposed to be operating at 250 MHz, and therefore offer greater performance levels than CAT 5 cables making them most appropriate for eethernet networking which needs multi directional data rates.
A: The CAT 6 industry grade unshielded ethernet cables are designed to retain their shape and can terminate strength which will lead to fewer chances of cable snag, the connectors are high performance grade which will enable the termination process to provide better signal transference level.
A: There is a bend radius with this cable that is manageable, allowing it to be comfortably maneuvered around cable management systems and does not impact any cable abilities making it versatile in networks requiring intricate configurations.
A: The purpose of the snagless boot of an ethernet cable is to prevent the rj45 connector from being snatched or pulled during installation or removing of the cable. In a way, it helps in preventing the cord from being damaged which increases the life of the cable.
A: The ethernet cable Cat6 is designed for efficient plug-and-play integration within the network. However, in fast ethernet networks, quick data transmission is a requirement that the cable is well suited to. Its configuration allows easy engagement with a wide variety of devices.
A: A 3 ft Cat6 patch cable is best suited for patch panel setups since it enhances short distances connectivity in network cabinets or server rooms and makes it reliable.
A: A Cat6 network cable is most suited for fast ethernet networks where voice and data applications that require high bandwidth will be used due to its high data transfer and performance levels.