Ethernet cable wiring is integral for any networking solution, offering the right foundations to set up reliable and high-speed data transfer. Bulk ethernet cables, especially those that come in 1000ft sizes, are useful for large-sized networking as they allow for a more significant number of configurations for installation. This article goes into detail on the different types, specifications, and applications of 1000ft ethernet cables, as well as the bulk purchasing option. We’ll also cover the benefits of purchasing bulk Ethernet cables, such as cost savings and less wastage. Last but not least, whether you are constructing a corporate office, data center or commercial enterprise, knowing the advantages and adequate technical details for bulk ethernet cabling is essential in order for you to best utilize your network infrastructure.
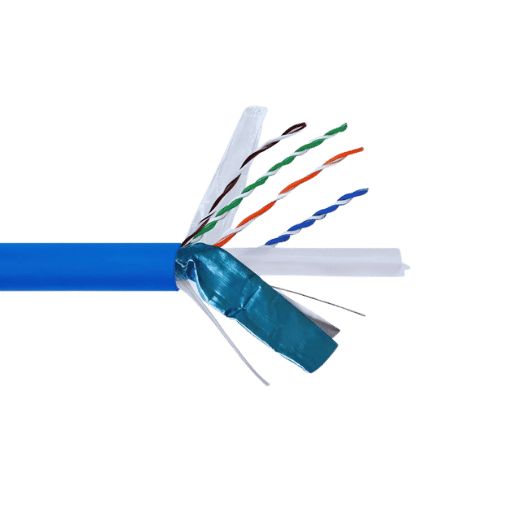
Using long Ethernet cables, particularly a 1000 ft Ethernet cable, has its share of benefits, especially for sizeable network deployments. One of them is affordability because being cost-effective for massive projects is having a great deal. Furthermore, the use of long cables also means fewer connectors need to be used, which helps in reducing the amount of connectors as potential points of failures on systems. In addition to this, bulk purchases of ethernet cables lead to less wastage as neat installations with accurate cuts can be made. For this reason, the cuts aid in bulk purchases, leading to eco-friendliness in installations. All of these factors, coupled with the increase in material development and technology in the networking world, means network engineers are now able to make robust networks that enable fast speed and high data transmission with the help of thick 1000 ft intentional cables.
Bulk Ethernet cables offer the utmost functionality and are the most economical for large networking jobs. The great length makes it easy to connect over long distances while reducing the chances of using more connectors, which ultimately lowers the chances of failure. Being cost-effective still remains a major advantage; bulk buying Ethernet cables lowers the cost per unit and assists when budgeting for large installations. Moreover, bulk buying also helps in better inventory management and less wastage as the cables can be trimmed to the lengths required, which means they will fit the specific needs of the installations and encourage environmentally friendly practices. These features make sure that the bulk Ethernet cables are a superior option to ensure continuous compliance with the network performance requirements in current facility designs.
Understanding the differences between Cat5e and Cat6 cables is essential in identifying the best one that fits particular networking requirements. A comprehensive data comparison of these two cable types can be found below:
Bandwidth:
Data Rate:
Cable Composition:
Length For Best Operation:
Crosstalk Level:
These differences highlight the need to choose between cost and performance, prompting network designers to consider their particular requirements in data throughput, performance, and cost against one another in selecting Cat 5e and Cat 6 cable.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cables are widely deployed in telecommunications and data networking because they are low-cost and easy to install. UTP cables do not use extra shielding which decreases EM interference, they transmit signals through a twisted pair of copper wires. They are highly used in Ethernet networks based on the Cat5e and Cat6 cabling standards. These types of cables are good for transmission over short to medium distances, which usually have adequate transmission ranges in homes and offices. UTP cables, although not the most expensive, can be adequate for many ordinary operations, including voice calls, video calls, and data transmission. Wireless Networking has developed in recent years, hasn’t overtaken UTP cables in the market, UTP cables are dependable and are cost-effective, they are able to provide the user with a good connection without much signal loss over certain distances. Data from the industry shows that networking systems using UTP cable, along with other modern technologies, remain the foundation of network coverage in many areas.

Plenum-rated cables are intended to be placed in the spaces that are used for the circulation of air, which includes the ductwork of a building. Such cables are coated with flame-retardants that are crucial in improving fire safety standards, as they emit less smoke and other poisonous gases when they burn. On the other hand, riser-rated cables are dedicated for use in the vertical spaces between the floors of parallel buildings. Those cables have low flame retardants but are not appropriate for plenum spaces because of their less stringent fire standards. Therefore, whether plenum or riser-rated cables will be used depends on the environment of installation, maintaining building and safety standards.
During the network project, it is important to note CCA and bare copper conductors, especially bare copper cables. Bare copper cables are very good at performing because they have excellent conductivity, low resistance, and durability properties, which ensure that the signal will have minimum loss over long distances, which enables heavy data transmission and high-performance applications. However, bare copper wires are the least expensive so as to ensure that aluminum is used to cover a thin layer of copper instead of entirely covering the wire, while aluminum wires are not left without some coating. Using a thin layer of copper to make aluminum wires easier and more affordable makes an aluminum wire stronger than woven bare copper wire, but woven copper offers greater performance and details.
Industry studies indicate that CCA is able to operate in a particular range of temperatures more efficiently than copper cables, although, from the strength of the wire, the copper tensile strength allows for it to endure low temperatures without putting a strain on it, which reduces the risk of having wires that are damaged. This is imperative to note as the difference can be quite shocking since copper is, on most occasions, 30%-50% cheaper than CCA cables. Materials that are used for projects should be tailored to meet all goals that have been set when conducting the project. Once goals and the costs of the project are determined, top-performance materials such as copper wires can be added.
The relationship between wire gauge, resistance, and gigabit performance must be maintained while selecting the network cables’ appropriate American Wire Gauge (AWG). To begin with, it is worth mentioning that the absolute “thickest” wires are the best since they have the highest gauge number. For example, 23 AWG solid copper wires should be used for gigabit Ethernet applications because of their attenuated loss and better bandwidth than 24 AWG cables. Also, some of the latest technologies have shown that it is more economical to use thicker noses for lengths that need to reach gigabit speeds. The latest information indicates that Cat6 and Cat6a cables used about 23 AWG wires and could transmit signals of 10Gbps across distances of 55m and 100m, respectively. Usability of such great distances has put a lot of emphasis on the wire thickness and expected transmission rate. In summary, with the parameters of the gigabit potential being so significant, the required AWG range must be low for the network to be functional.
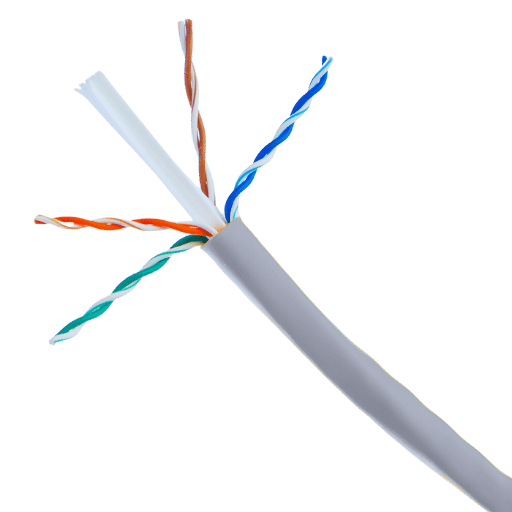
Moving the networks’ bulk cables can be challenging, especially ensuring proper practices while pulling the cable from pull boxes, as it helps protect the cable’s integrity while at the same time making the installation easier. First and foremost, always check whether the pull box has any structural issues that may affect the cable. Also, make sure that the pull box is properly secured on the ground to eliminate the chances of tipping it over, thus causing stress on the cable.
In the case of pulling the cable, ensure that unnecessary pressure is not exerted that might manipulate the positioning of the conductors. Also, be sure to refrain from a twisting approach while removing the cable from the box, but rather simply pull it out straight from the box, as that would ensure that the structure of the cable does not get compromised. In terms of long pulls, getting hold of a reel can help facilitate the unwinding while applying a uniform force to ensure there is no tangling. Additionally, a lubricant for the cable may help reduce the friction, especially in some tight spaces or conduit runs.
Tensile forces shouldn’t, however, be more than 110 N (25 lbs), according to empirical data, in order to not disrupt the cable’s performance characteristics. In addition, It is recommended that the route the cable will follow be planned in advance with consideration for the obstacles to ensure that the path employs a push pull force trajectory that is minimal. Following the practices specified not only enhances the durability of the cable but also conforms to networking requirements, which helps enhance the network’s performance after the cable has been installed.
To maintain signal quality over a distance of up to 1,000 feet, it is necessary to follow standard practices and technical recommendations precisely. To preserve optimal cable performance, here are a few recommendations to minimize losses:
If these recommendations are practiced, network administrators will noticeably improve the quality and efficiency when deploying long network cables, thus avoiding expensive downtime and data loss during transmission.
To maintain the quality of RJ45 connections it is important to adhere to procedures as well as employ some tools. A decent way to start is by acquiring good RJ45 connectors that meet T568A or T568B wiring requirements for a standard pinout. The crimping tools should also be designed to suit the appropriate type of connector for a quality and secure link. Additionally, periodic inspections should be conducted to detect any loose connectors or defective jackets that pose risky threats to the network. King, in his recent study, reported that poor connection of RJ45 ports is responsible for about forty percent of the connectivity problems experienced in an IT infrastructure. Thus, frequent servicing in conjunction with good installation practices guarantees the best performance and durability of the network.
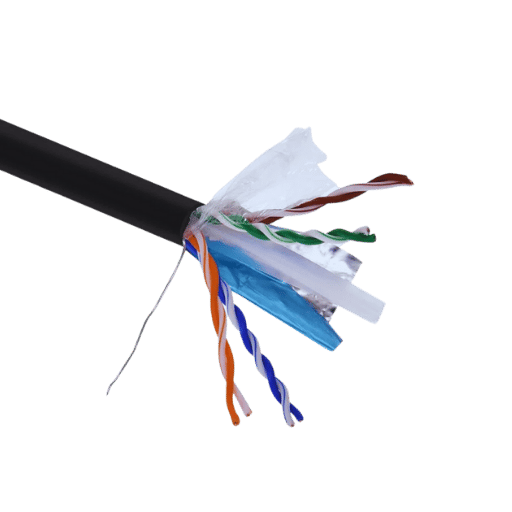

When comparing the Cat6 and Cat5e ethernet cables, one of the key technical specifications to consider is bandwidth capacity. Most Cat-6 cabling offers support up to 550 MHz bandwidth, which means higher data transfer rates with reduced latency, making it more suitable for a wide array of networking activities. Otherwise, the bandwidth of Cat5e cables reaches as high as 350 MHz, which is acceptable for a commonplace networking environment where super-fast speeds are not essential for the tasks being performed. The latest data shows that the performance of both types of cables is satisfactory for networks, but the selection of one or the other would depend on the current infrastructure as well as the future development goals of the network.
The Ethernet cables should be evaluated carefully for the qualities of the conductor materials that are known to enhance the signal transmission and enhance the life span of the cables. For most conductors, copper remains the very best because it is both a good and a flexible conductor of electricity, which augments the data and eases the installation of cables. When using wires made of high-purity copper, signal degradation is minimized, and electromagnetic interference is lessened, helping to increase the general performance of the network. It is necessary to make the distinction between solid copper wire and stranded wire; solid copper is usually employed for permanent wiring and performs best for longer distances, whereas stranded wire is more flexible and, hence, ideally suited for patch cords. Research reviews in the industry indicate that cables with less copper or replaced by other materials tend to underperform, which has been shown to increase attenuation by more than percent20. Follow these reviews to ensure that any unfavorable networking environment sees only the deployment of cables with the best conductor materials.
CAT6 UTP solid cables are further designed for high performance data transmission, for it targets areas in network architecture, with the requirement of reducing interference and increasing data transfer rates. Ethersource’s observations using CAT6 UTP solid cables claim accurate support frequencies up to 250 MHz with an ethernet speed of 1 Gbps over 55 meters and 10 Gbps over 37 meters due to tightly twisted pairs which minimize crosstalk. A solid cable, as claimed, consists of a central conductor made of a single sturdy copper wire, which is characterized by a number of terminals at the ends and is thus the best option when structured cabling is required to be extended for greater distances since it maintains the integrity of signals better. This construction also allows it to be more physically solid with reduced vulnerability to damage as compared to stranded cable; hence, CAT6 UTP solid cables are suitable to be in walls or in perpendicular installations. Most recently, data shows a 30% signal-to-noise ratio when using CAT6 UTP solid cables as compared to lower category cables, thus helping beneficiaries ensure stable high-speed network performance. With the information in front, it is clear that a properly structured cabling installation needs time, hence making IT investments promising.

Buying bulk network cabling on the internet can be very sensitive, and thus, it is important to consider whether the websites are reputable. Other websites that are reliable are Amazon, Newegg, and Monoprice, and they are trustworthy since they have a lot of products and their prices are reasonable. As per the current statistics provided, these sites provide user reviews and ratings, which promote transparency in the quality of the product and supplier reliability. If you want fast shipping, look for vendors that offer quick delivery options, such as Amazon Prime. Finally, check the return and after-sale service policies of the retailer so as to have an easy and pleasant purchasing process.
For companies looking for high-quality, compliant network cabling solutions, ETL and TAA certifications are of paramount importance. An ETL certification means that the product has undergone stress tests by a recognized third-party testing laboratory, Intertek. This certification protects against substandard manufacturing by ensuring that the materials used in the construction of cables conform to approved standards in manufacturing processes making the cable a good choice for residential use as well as commercial installations.
In contrast, TAA compliance is crucial with respect to contracts that are sectioned off for government projects. As stipulated in the Trade Agreements Act (TAA), the products must be produced or substantially transformed in a country that is designated. This clause makes sure that the cables utilized by the contractors for the government don’t just meet the expectations but also the requirements for federal use. Recent data with regard to procurement shows a tendency toward TAA-compliant cables for public sector projects, which had an increase of 25% throughout the year. This high demand for TAA cables indicates their necessity in securing contracts that are aimed at both state and federal levels. While waiting for these cables, companies should confirm certificates of compliance commonly provided by the manufacturer or supplier to avert legal and operational problems.
When looking out for 1000ft Cat5e UTP Solid and Cat6 cables, one needs to keep in mind some technical characteristics and the tendencies of the market. Cat5e cables are mostly sought for residential and small business networks due to their low budget and data rate of about 1Gbps with 100 MHz bandwidth. Stipulating such parameters, Cat5e still remains acceptable for the majority of uses, specifically if they don’t require a high data transfer rate nor a high degree of electromagnetic interference. In contrast, Cat6 does present a superior performance with maximum speeds reaching 10Gbps and a maximum bandwidth of 250 Megahertz. This enables a very efficient usage within large networks where the distance of data transmission is lower.
According to a recent report published, there is a notable spike in the number of Cat6 installations primarily due to the room for growth it offers particularly a 15% rise in preference for Cat6 cables over Cat5e installations per year; this is due to an increased demand for better infrastructure that can keep up with new advancements in technology. Depending on the quality of the material, prices vary with Cat6 being marginally costlier but worth more in the long run thanks to its compatibility with future technologies. Apart from ETL, TAA, and other certifications, companies need to consider the cable details about the shielding, the gauge, and the jacket type in order to adhere to applicable conditions.
A: A 1000ft Ethernet cable, such as cat6 1000ft, is a type of bulk cable that is able to be deployed in large networks where long runs of cables are needed. It is perfect for creating vast network connections in offices, school or other places.
A: The key differences between cat5e and cat6 bulk cable sits in their performance and the materials used. Cat6 cable in comparison can support higher frequencies of up to 250MHz and provide better speeds of around 1Gbps across a larger span of distances as opposed to the cat5e which supports 100Mhz and 1gbps of speed but in limited distances.
A: It is often recommended that ethernet cables should be composed of solid bare copper wire as opposed to CCA (Copper Clad Aluminium) as the former is able to provide better conductivity and be more reliable especially n Power over Ethernet (PoE) systems.
A: Riser rated Ethernet LAN cables (CMR) are designed for use in vertical spaces in buildings such as between the floors of a stand-alone building or classrooms in a multi-storey structure. Although these cables run within the walls and ceilings of a building, they still effectively resist fire propagation across floors.
A: With PoE it is possible to transmit IP data and power over cat6 cables to IP enabled devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless devices like access points without a dedicated power supply.
A: It is true that not all bulk cat6 cables are TAA compliant. One of the aspects of TAA certification is that the products are exclusive to members who meet appropriate production and quality threshold limits which are usually requested for US government and other commercial contracts.
A: The backward support is there with cat 6 cables, and thus, they are supportable for cat5e and cat5 network setups. These cables can be plugged into systems that use the RJ45 network connector ports; however, the network will be working at the lowest category cable speed.
A: The significance of 23AWG is that it refers to the thickness of the copper wire used in cat6 cables. It is bigger than 24AWG that is applied in cat5e cables which in turn improves performance and allows more distance for data transmission.
A: The advantage of having a network Ethernet LAN cable bulk package, such as the cat6 1000ft package, is that it is cost-effective when deploying the cables on large scales. It is very useful for projects that require a lot of cabling as it is easy to use because of its easy-to-use pull box features.
A: Yes, CMP (Plenum-rated) cables are suitable for installation in plenum spaces, which can include air ducts, and they use fire-protective materials. On the other hand, CMR (Riser-rated) cables have a more vertical orientation and fewer fire-protective materials compared to the CMP, which leads to differences in containment areas.