This blog will thoroughly explain the advancements in the techniques utilized for performance and efficiency in optical networks and the newly created devices suitable for telecommunication splits based on fiber optics. On a fundamental level, telecommunications, data centers, and network infrastructures are entirely based on modern technology, enabling commands to be executed within nanoseconds.
Data centers are defined by their ability to bring a cross of deregulated dimensions to various places. Electricity and wireless networks transmit data and build the modern technological world, benefiting humanity. The Fiber Optic Splitter Diary entails just such devices that those interested in contemporary technology and telecommunications should begin learning about immediately.
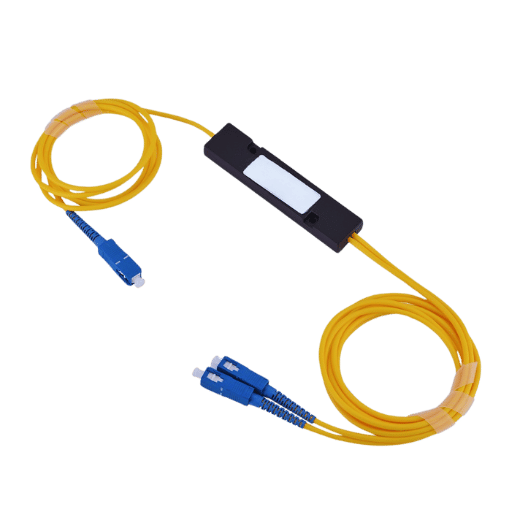

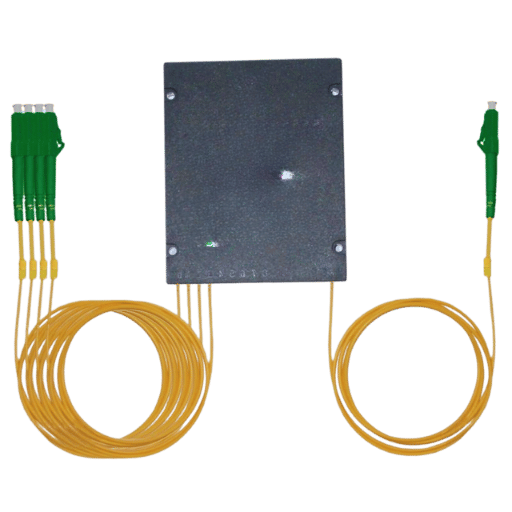
An optical splitter is a passive device that operates in fiber optic networks to split a single optical signal into multiple outputs or merge several signals into a single output. It principally aids in distributing optical signals across different endpoints, for example, in Passive Optical Networks (PON).
Optical splitters are key in modern telecommunications infrastructure. They ensure light signals are divided evenly or proportionally without external power.
A fiber optic splitter divides the incoming optical signal into two or more outputs or merges multiple signals into one output. These devices are passive, meaning they do not need any external power source. Factors such as split ratio, insertion loss, and uniformity, which dictate how efficiently the signal is distributed among the outputs, determine performance. To achieve multiple destinations from a single point, PONs use fiber optic splitters for the economical and efficient transmission of optical signals.
An optical splitter works by taking in a signal during the optical communication process and splitting it into different output signals. This process can be done using high-quality optical parts that maintain the wavelength and quality of light while breaking it. The performance of the splitter depends on two factors: the split ratio, which measures how the output signal is distributed among the various outputs, and insertion loss, which is the measure of loss of the signal during the process of splitting. These devices are configured to ensure that they are uniform in distribution, which is ideal for applications in Passive Optical Networks (PON), which require single signals for numerous end users.
The two main types of splitters used in contemporary networks are Fused Biconic Taper (FBT) and Planar Lightwave Circuit (PLC) Splitters.
The most advanced of the two choices, PLC splitters tailored to dense modern networks offer superior performance and scalability. This proves yet again the mass adoption of modernization in network technology.
While picking a fiber optic splitter, pay special attention to the factors given below:
By clearly outlining these pointers, an appropriate splitter can be selected that best augments the network’s structure and performance.
The most vital metrics or parameters to consider in assessing optical splitter models are their splitting, design configuration, and insertion loss ratio.
Adhering to these parameters maximizes your chances of selecting a model that guarantees optimal performance and reliability while remaining integrated into your network infrastructure.
The functionality and compatibility of an optical splitter in any given network will rely on how its input and output ports are arranged and their respective quantities. The input ports define the number of signals a splitter will accept, whereas the output ports outline how many resulting paths will be created from the split signal. A splitter with a port ratio corresponding to your network’s distribution requirements is best for performance. Configurations like 1×4, 1×8, or 1×16 are mainly for advanced growth and signal management. Striving for correct port configuration ensures minimal signal loss while maximizing network efficiency.

Every time the optical splitter is used, each optical signal is weakened. This weakening is called insertion loss, a fundamental aspect of splitter operations that needs to be considered during network design. Good-quality splitters are designed to reduce insertion loss and provide uniform signal distribution at all ports, achieving uniform performance across all output ports. Regarding splitter type, network architecture, and range restrictions, appropriate calibration can reduce the expected harm to signal quality.
Attention to detail in selecting and installing components is critical to reducing signal loss in fiber optic networks. To reduce attenuation, use low-attenuation optical fibers and trim all connectors, splices, and splitters to industry standards. Connection contamination and misalignment can yield degraded signals, so ensure connections are clean and properly aligned. The network’s design scheme should incorporate suitable power budgets, employing optical amplifiers as needed for prolonged transmission distances. Network signal integrity can be maintained through constant testing and maintenance.

In contemporary audio systems, digital optical audio splitters are of prime importance due to their ability to effortlessly distribute digital audio signals from one source to several outputs. These devices capture and use TOSLINK (Toshiba Link) technology, an industry-standard optical fiber interface that conveys digital audio signals using light. This ensures minimal interference and high-quality sound reproduction.
As far as these splitters are concerned, linking television or gaming consoles to multiple devices such as soundbars, audio receivers, or home theater systems share a single audio source. Every two-way or four-way optical splitter can effectively preserve the bass frequencies alongside the original audio quality. Dolby Digital and DTS audio-compatible peripherals are also included in newer models, permitting use with advanced surround sound systems dedicated to immersive theater experiences.
Research suggests the optimal performance for telephone-grade optical fibers lies within the 10-meter range. Beyond this range, splitters experience output signal degradation due to increased distance. In parallel, lower-end 4 K-compatible televisions are being released, which provides more uses for these devices. This illustrates the relevance of digital optical audio splitters for high-definition entertainment systems.
When picking an optical splitter, users should prioritize models made with sturdy materials like metal and high-grade PVC to reduce the signal loss caused by mechanical wear. Some devices now integrate low latency technologies that enhance gaming or real-time audio streaming synchronization. Digital optical audio splitters, when pursued with an emphasis on their quality and compatibility, can streamline operational versatility within the audio framework.
Important guidelines must be followed when integrating optical audio splitters into soundbar systems. Modern audio devices such as soundbars support multiple input and output standards (formats), such as Dolby Atmos, DTS:X, and PCM. Hence, selecting a splitter that can help these audio standards is crucial. High-quality audio content splitters that boast 192kHz/24-bit audio support should be ideal due to their sound fidelity.
Equally important is the number of devices you plan to connect. Splitters with one or multiple ports are practical for a soundbar and home theater setup with gaming consoles and streaming players. They are available as 1×2, 1×3, 1×4, and more, which allows multiple outputs to be connected to a single source. Using splitter models with gold-plated connectors and advanced shielding can minimize the number of devices with audio devices.
All TOSLINK Cables can be universally supported, and signal quality with high-grade fibers is retained over distances of up to 10 meters. Users must also check that the splitter and soundbar support the same audio protocols to avert unsynchronized issues, particularly with formats like ARC (Audio Return Channel) or eARC. Observing these points ensures that splitters can boost audio performance in various home entertainment systems.
Employing a Toslink digital optical audio splitter comes with many advantages, including:
With increased efficiency and excellent sound quality, a digital toslink fiber optical splitter can significantly improve audio setups.

By following the steps above, users can optimally use the fiber optic splitters without interruptions.
Following the guidelines provided will help ensure the reliable performance of your network equipment.
A: Fiber optic splitters are elements in an optical fiber network that divide single optical signals into multiple signals for further processing. It splits the light beam by using a PLC splitter, which is a passive zone element, or it can be referred to as a power splitter, that redistributes the optical signals into different paths without external power.
A: Passive sc fiber splitters do not require an external power source to work and use natural properties of light to split the signal. In contrast, an active splitter employs command signals using an external power source, enabling greater control and amplification.
A: Splitter 1 in 2 configuration splits a single optical signal into two signals. It improves the network by permitting better signal routing to several endpoints, which improves data accessibility and allows several instruments to share similar data simultaneously.
A: A Toslink splitter or a digital optical audio splitter adapter can be used with other equipment, such as sound bars. These devices help connect multiple audio outputs, enhancing the overall audio experience.
A: An HDMI converter connects an HDMI cable to different devices. While not directly considered a splitter fiber optic cable, it can be used with them to ensure that all digital signals passed through different cabling systems are sent correctly.
A: A digital optical audio splitter adapter is essential for a home theater. It enables the audio signal to split and route to several devices, such as an amplifier or many speakers, ensuring that all channels produce high-quality sound.
A: Fiber optic splitters support Dolby Digital and DTS 5.1 audio formats. They help distribute high-grade digital audio signals to different devices without compromising the sound quality of the formats.
A: Dual port toslink digital optical adapter helps connect two devices to receive the same audio signal. This is useful for system design flexibility.
A: A 1×3 spdif toslink optical splitter enhances the capability of simultaneously distributing a single digital audio signal into three audio devices, enabling seamless audio distribution through a Toslink fiber optical splitter 1, which is crucial in complex audio setups.
A: “LC compatible” describes the connector style used in an optical fiber system. LC connectors are small, reliable, and favored in high-density network situations. LC-compatible fiber optic splitters ensure these devices can be integrated seamlessly into circuitry by employing LC connectors.
1. Ultra-low Loss Multiport Optical Splitters
2. Testing the Silica-based PLC Optical Splitters with an ‘In Situ Uniaxial Tensile Test’ Experiment Design
3. Design and analysis of 1 × 2N Y-branch optical splitters for telecommunication applications.