Discussions around the balancing act of performance, scalability, and space efficiency in modern IT infrastructure often highlight 1U rack servers. These powerful servers are compact machines that play an essential role in data centers: they allow businesses to meet strenuous workload demands while minimizing physical footprint and energy use. This guide intends to equip IT specialists, systems admins, and decision-makers with a comprehensive understanding of 1U rack servers and their impact on power consumption. From their practical application and tactical advantages to critical focus areas of implementation and future scalability foreseeability, we will demonstrate why they form the core of robust IT ecosystems. Whether you need to refine your existing systems or are considering investments in new hardware, this article aims to fully illustrate the advantages that 1U rack servers offer in terms of their efficient power consumption.
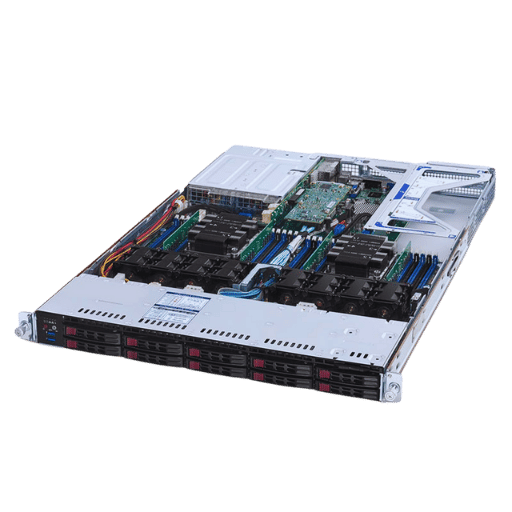
A 1U server is a computer system with processing power that can be contained in one or more chassis. It includes a 19-inch server rack and is 1.75 inches tall. This kind of server offers powerful processing while occupying less space. Typically, these servers are used in corporate IT data centers and cloud computing, where they can harness 1U’s scalability, performance, and a great deal of optimization with space usage. 1U servers are built in a way that includes the CPU, memory, storage devices, and network cards into one sessile case. This serves as a significant boost to performance. 1U servers have a universal size that allows easy construction and servicing of systems mounted on racks and blade servers.
The 1U rack server is a small form-factor server that fits into a single rack unit that is 1.75 inches tall, making it suitable for small server racks. The 1U rack server’s small form factor greatly benefits data centers and IT facilities. It can be used in many applications with varying levels of complexity, from web hosting to virtualization, as it offers high processing performance, adequate storage, and extensive networking faculty. Organizations that emphasize increasing computing resources while controlling costs find the 1U rack server’s modular design efficient due to ease of installation and maintenance.
A small firm can take advantage of server technologies to an outstanding level. Undertaking these systems can enhance data security, allowing companies to safeguard crucial information, including customer and operational data. Improved business performance empowers faster data processing and highly efficient task execution. Moreover, enhancing the ease of management features simplifies IT functions, thus lowering administrative expenses and downtime. Small enterprises can also reduce operational costs by utilizing energy-efficient designs, mainly by dismantling Intel Xeon’s scalable processors. The advantages help a tiny firm remain competitive, especially in a highly competitive digital world.
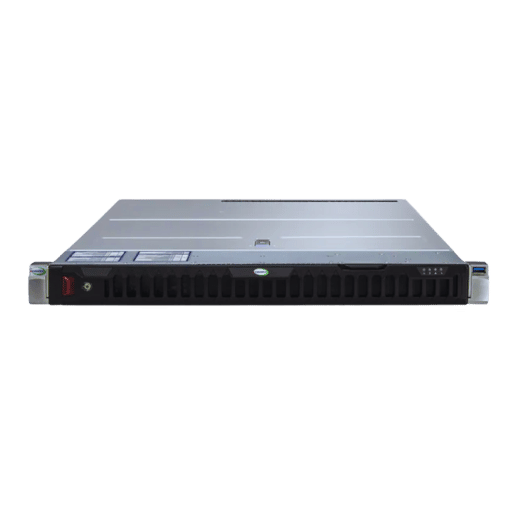

When comparing Dell PowerEdge 1U servers and Supermicro alternatives, considerations like Performance, Reliability, Scalability, and Cost must be analyzed in depth. Dell PowerEdge servers remain unparalleled in advanced support features, built-in monitoring tools, and warranty options. These are particularly useful for mid-range and large enterprises focused on operational ease and dependable customer service. Conversely, Supermicro servers are more popular for their custom configurability. They mainly serve small, flexible organizations with specialized workloads that must be hosted in compact server racks.
Both brands provide hardware of optimal quality, but within Dell’s ecosystem, there is a greater emphasis on user-friendly integration and energy-saving features. At the same time, Supermicro products enable greater Supermicro’s focus on multi-purpose use and lower up-front costs. The decision concerns specific business requirements like the importance of managed complexity versus bespoke tailored hardware solutions.
When evaluating AMD EPYC versus Intel Xeon processors, the following fundamental factors ought to be considered:
Each choice is optimal depending on the workload’s energy efficiency requirements, budget constraints, and overall energy consumption targets. Both processors provide dependable performance for enterprise applications, but these criteria are critical to ensure optimal decisions.
Drive bays are designated locations on servers or computers that can accommodate HDDs and SSDs. They are designed for simple access to facilitate installation or replacement.
M.2 is a new small standard size for SSDs that plugs directly into the motherboard rather than using cables. It flexibly supports SATA and NVMe and is faster because it interfaces through the PCIe bus.
Non-volatile memory Express (NVMe) is a storage protocol for modern SSDs. Compared to hard disk drives (HDDs) using SATA interfaces, which IT administrators are tasked with monitoring, NVMe offers drastically improved performance and lower latency. This protocol is best suited for applications that demand fast data transfer, such as virtualization and databases.

1U servers efficiently enhance virtualization capabilities by hosting multiple virtual machines (VMs). Their size allows more servers to be deployed within a given rack space, which optimizes the utilization of physical resources within data centers. 1U servers have powerful processors, high memory capacity, and fast storage options to handle the demanding workloads of virtualized environments. Other features include hardware-assisted virtualization, which enhances the performance and stability of VMs. 1U servers are designed to be like light within a black hole, delivering dependable results while saving space, which is critical for the growing requirements of modern virtualization applications.
DDR4 ECC (Error-Correcting Code) memory has advanced computing capabilities while ensuring performance and reliability in today’s balancing computing environments. This modern memory standard is indispensable for high-performance computing, data-intensive applications, and mission-critical systems due to faster data rates, lower power consumption, and improved error-correction performance.
DDR4 ECC memory has improved energy efficiency by lowering operating voltages relative to its predecessors, alongside providing increased bandwidth with transfer speeds of up to 3200 MT/s. Furthermore, its correcting measures ensure the detection of single-bit memory errors in real time, greatly reducing the risks of system crashes or corrupted files. Because of this, DDR4 ECC memory holds greater importance in servers, cloud computing, and enterprise workloads where seamless performance is crucial.
Research indicates that systems with ECC memory suffer from significantly higher memory error rates. This type of memory drastically reduces downtime and increases hardware reliability. It also provides better scaling for multi-core processors and heavy parallel workloads, enabling more sophisticated computational processes such as AI training, big data analytics, and 3D rendering. Despite increasing infrastructure demands, DDR4 ECC memory remains crucial for engineers and IT professionals who need dependability in modern computing environments.
1U servers can provide high-performance computing in a restricted space, making them suitable for businesses and enterprises that require both processing power and space efficacy. These servers are typically used in data centers, cloud environments, and enterprise networks that prioritize power, scalability, efficiency, and reliability. The addition of advanced multi-core processors and high-speed memory options such as DDR4 ECC and flexible storage makes 1U servers ideal for demanding workloads such as virtualization, AI applications, and database management. Their slim profile allows maximum rack space utilization, enabling organizations to expand their infrastructure without incurring additional costs or destabilizing operations.
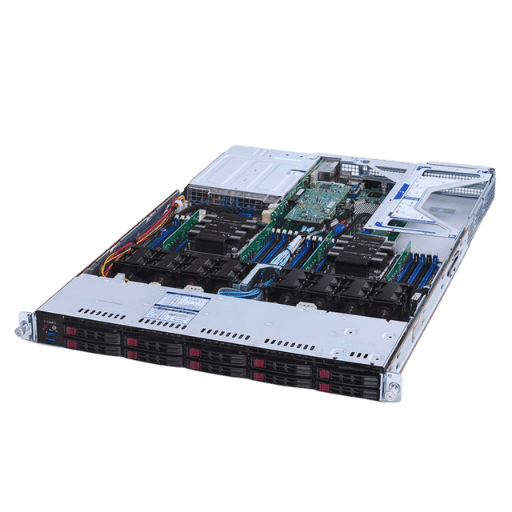
Redundant power supplies are essential for preventing downtime during power interruptions and equipment malfunctions in conjunction with Intel® Xeon® scalable processors. They automatically switch to a backup power supply when the primary one fails, which minimizes system downtime and prevents data loss. This feature is significant in business-class environments and data centers that rely on high system availability. Moreover, redundant power supplies are also hot-swappable, allowing for the replacement of non-functional units without powering down the server, thus maintaining uninterrupted operations.
While assessing energy efficiency and dependability of power supplies for 1U rackmount servers, two choices emerge:
These two options allow server users to sustain uninterrupted performance while lowering energy spending and disruption risks.
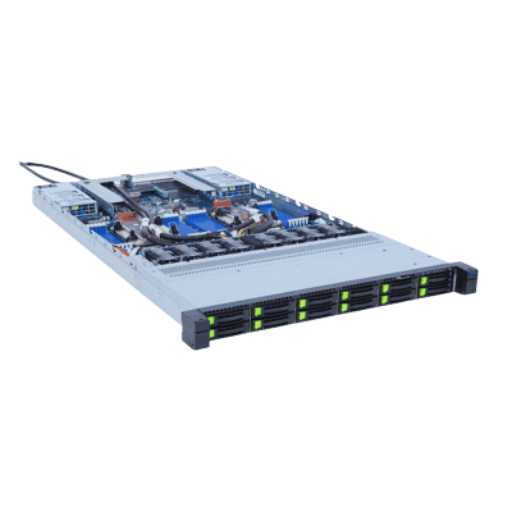
In settings like data centers where space is at a premium, a short-depth chassis is essential for maximizing rack space utilization. These chassis facilitate space installation by decreasing the depth needed, increasing equipment density within a standard rack, or allowing the use of smaller racks. Furthermore, this is advantageous in edge computing and remote monitoring data centers where physical space is more limited. Moreover, short-depth designs also augment cooling airflow management, improving cooling efficiency and overall server performance. Short-depth chassis prove valuable within modern IT infrastructures, especially in small server racks, by providing an optimal solution where performance and space constraints require precise balancing.
Using a 1U or 2U server is a decision shaped by your specific operational needs and limitations. If space efficiency is paramount, a 1U server is best suited because of its high maximum rack density. This is especially useful for data centers that lack physical space. Nevertheless, the 1U server’s slim figure does come with several limitations regarding internal components, including, but not limited to, storage and cooling systems.
In contrast, 2U servers offer more versatility and storage space, making them more suitable for tasks requiring a higher performance level, additional GPUs, or even more advanced cooling systems. Although 2U servers use more rack space, the enhanced configuration options could mitigate the cost incurred for resource-exhaustive workloads when using the server.
In conclusion, choosing between a 1U server and a 2U server depends on the IT environment’s space availability, workload requirements, and long-term growth potential.
A: A 1U rack server is a compact model because it only requires one rack unit (1.75 inches) in height on a server rack. They are highly effective while being efficient with available space.
A: Dell Technologies is the best option for 1U rack servers as they offer a vast catalog of servers, such as Dell PowerEdge servers, noted for their unsurpassed performance, high scalability, and efficient resource operation.
A: Adding PCIe slots on 1U rack servers allows for installing additional GPUs, storage controllers, and network cards. This upgrade increases the versatile performance and configuration options for the whole server.
A: 1U servers are among the most desirable for small businesses due to their low cost, efficient functionality, and scalable capabilities. They are also highly accommodating to brand-new users.
A: 1U rack-mount servers are compact and cost-effective, allowing for cheaper hosting services. Their exceptional dependability and performance are essential for any web hosting service.
A: A 1U storage server is highly relevant in data center management due to its incredible memory capacity, storage solutions, and form factor. These aid in resource maximization and efficient allocation.
A: The “2x 3.5” configuration benefits 1U servers. It permits them to accommodate two 3.5-inch drives, significantly improving the storage capability’s performance-to-size ratio within a single server unit.
A: Supermicro 1U servers are meticulously configured to deliver processing benefits while consuming the least energy possible. They increase efficiency through accelerator-optimized servers aimed at completing high-performance computing tasks.
A: Yes, 1U rack servers maintain an uncomplicated approach to deployment and management because of their global rack mount standard form factor and easy integration with many external management interfaces.
1. Online Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) with High Power Density Achieved in a Low Profile (1U) Server
2. Study on Performance Comparison Between Air and Liquid Close Loop Heatsink in 1U Server