
Cat 5e is an enhanced type of Ethernet cable designed for high-speed data transmission and networking. It belongs to the twisted pair cable category and can support speeds up to 1 Gbps. Its reliability and cost-effectiveness make it the go-to choice for home and office networks.
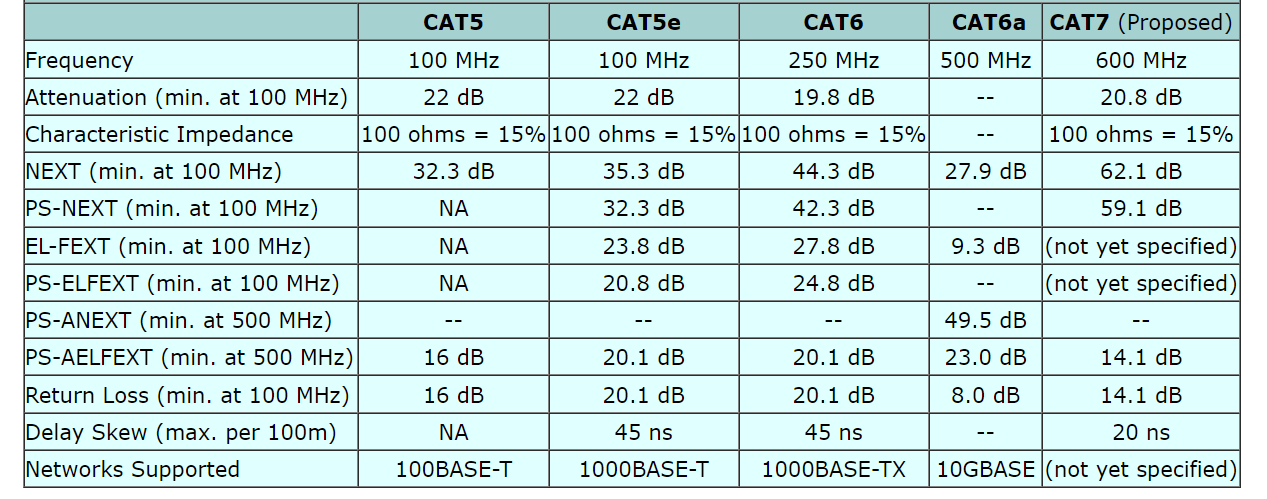
Although they may look alike, Cat 5e and Cat 6 cables differ significantly. Cat 6 lines offer speeds up to 10 Gbps, while Cat 5e cables support up to 1 Gbps. Using a thicker wire gauge and a tighter twist in Cat 6 lines reduces crosstalk for better signal quality. However, Cat 6 lines are pricier and may require special connectors and equipment for installation.
Ethernet cable standards, established by the IEEE, outline performance requirements for different types of cables. Common measures include Cat 5, Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 6a. Each bar has its specifications for bandwidth, crosstalk, and more. Choosing the correct cable standard is crucial based on network requirements and equipment used.
One significant advantage of Cat 5e cable is its cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for small to medium-sized networks. It’s readily available and easy to install, requiring no special connectors or equipment. Plus, it’s backward-compatible with slower Ethernet standards, making it versatile for new and existing networks.
Cat 5e Ethernet cable finds use in various applications, connecting computers, printers, routers, switches, and other network devices. It’s perfect for both home and office networks, as well as industrial use in harsh environments. Cat 5e cable ensures reliable, high-speed connectivity for voice, data, and video applications when paired with networking components like switches and routers. It’s a trusted choice for professionals and consumers due to its affordability and dependability.

Cat 5e cable, a popular Ethernet cable, has been a game-changer since its introduction in 1999. It quickly became the networking industry’s go-to choice, earning the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) recommendation for Gigabit Ethernet in 2001.
Transmission speed, measured in bits per second (bps), determines how quickly data travels across a network connection. To ensure uninterrupted communication within a network, it’s crucial to have a cable that can safely and accurately transmit data at high speeds.
Several factors can impact the transmission speed of the Cat 5e cable. Cable length plays a significant role, as longer lines result in slower speeds. Additionally, external interference from electrical equipment can cause signal degradation and negatively affect overall Speed. Poor cable quality, age, and damage also contribute to speed limitations.
While Cat 5e cable offers a maximum transmission speed of 1 gigabit per second (Gbps) over a maximum distance of 100 meters, Ethernet cables provide higher rates, longer distances, and better noise reduction capabilities. For example, Cat 6 can transmit data at up to 10 Gbps over a maximum length of 55 meters.
Gigabit Ethernet, a standard for high-speed communication, offers impressive data transfer rates of up to 1 Gbps (1000 Mbps). Cat 5e cable specifications support a maximum data transfer rate of 1 Gbps over a maximum distance of 100 meters. Slow speeds are typically attributed to factors such as poor cable quality, age, damage, and other previously mentioned factors.
Cat 5e and Cat 6 are two widely used Ethernet cables. Cat 6 outperforms Cat 5e in transmission speed and noise reduction, but it comes at a higher cost. Cat 5e, on the other hand, is a more affordable option that meets the requirements of many applications. Whether to choose Cat 5e or Cat 6 depends on the network’s specific needs. If Speed is a top priority, Cat 6 is the recommended choice. Otherwise, Cat 5e should suffice as long as the network’s bandwidth requirements are met.
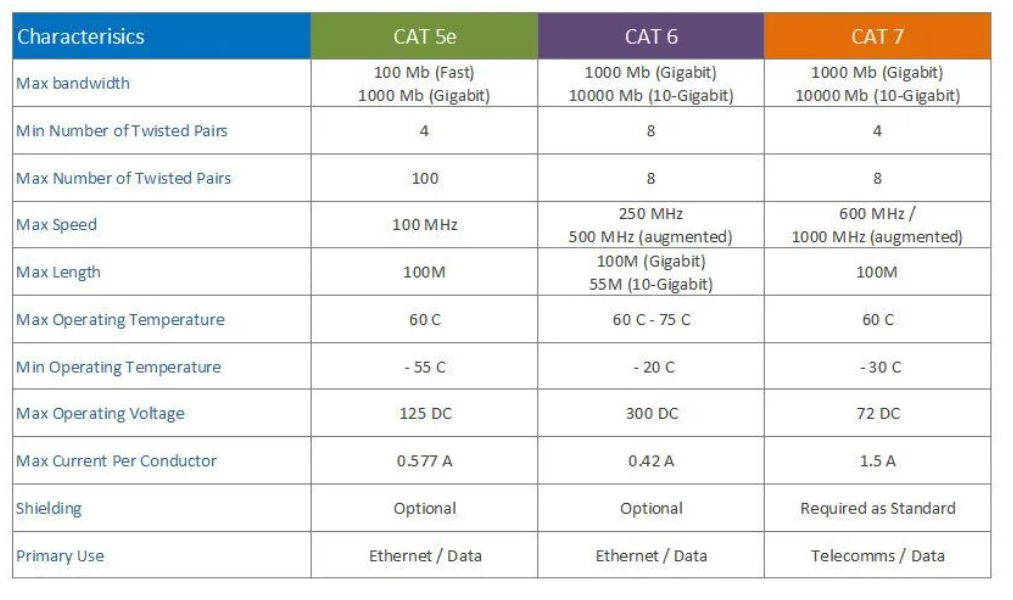
Cat 5e cable is classified into different categories based on its transmission capabilities. Categories 1 to 5 are designed for voice communications, while Category 6 and higher are used for data transmission. Cat 5e, or Cat 5 enhanced, is an upgraded version of Cat 5 cable with higher bandwidth and frequencies for fast data transmission.
When selecting a Cat 5e cable, several essential factors must be considered. The cable’s length, bandwidth, and frequency are critical in determining its suitability for specific applications. The cable’s insulation, durability, and compatibility with other networking devices should also be considered.
The choice between bulk and pre-terminated cables depends on your network’s requirements. Bulk cable is perfect for custom installations, allowing you to cut and configure the line to meet your needs. Pre-terminated line, on the other hand, offers quick and easy installation without requiring specialized tools.
Adhering to industry standards and specifications is crucial when choosing a Cat 5e cable. The Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) have established detailed standards for network cabling, including Cat 5e cables. These standards ensure the wires meet the minimum electrical characteristics, physical parameters, and performance requirements for specific data types.
Choosing the suitable Cat 5e cable for a home network requires considering factors such as the size of the house, the number of devices being used, and the desired speed and data transfer rate. Larger homes may require longer cables, while homes with multiple devices may need lines with higher bandwidths and frequencies.
Recommend Reading: Understanding the Basics of DAC Cable
Cat 5e ethernet cable is famous for fast data transmission in local area networks (LANs). It can achieve up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps) over distances of 328 feet. However, like any network technology, Cat 5e speed can be affected by specific issues that hinder its functionality.
Bandwidth limitations can impact your Cat 5e cable’s Speed. This refers to the data the line can transmit in a given period. If you’re experiencing reduced Speed and performance, it’s crucial to check the cable installation and termination and look for any defects or damages that might affect performance.
Crosstalk occurs when signals from one cable interfere with adjacent wires, causing unwanted noise and reduced performance. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) from other electrical devices can also disrupt signal quality. To combat these issues, opt for high-quality cables with proper shielding to minimize crosstalk and EMI.
To ensure your Cat 5e ethernet cable maintains its Speed and performance, handle it carefully to avoid damage from physical stress. Regular testing and maintenance can help identify and resolve potential issues before they cause significant disruptions. Additionally, practicing proper cable management, such as avoiding sharp bends and correctly routing cables, minimizes the risk of damage.
Although Cat 5e is widely used, newer options like Cat 6a and Cat 7 cables offer higher speeds and better performance. Upgrading to these cables may require additional equipment and installation, but it’s a worthwhile investment for businesses or organizations requiring high-speed, reliable networking capabilities.
It’s crucial to recognize that Cat 5e ethernet cable has limitations and may not be suitable for all applications. High-demand tasks like video streaming or cloud computing may require upgrading to Cat 6a or Cat 7 cables. Before deciding, assess your organization’s needs and consult a network specialist to determine the best action.
Recommend Reading: Why Choose a 200g qsfp56 Optical Transceiver?
Choosing the appropriate CAT 5e cable is essential for achieving optimal network speed and performance. By following a few important tips, you can ensure that your network maintains top-notch performance and Speed.
Selecting the suitable CAT 5e cable is crucial to achieve maximum network speed. Consider factors such as cable length, shielding, and category when choosing. The type of cable you choose, whether shielded or unshielded, should align with your networking goals. Different lines can impact your data transmission rates, particularly over longer distances. Select a bar that offers the necessary Speed and bandwidth for your needs.
To keep up with evolving technology, it’s important to future-proof your network infrastructure. Cat 5e is a reliable, cost-effective option that meets the data transfer speeds required by most organizations today. However, with the expected increase in network demands, investing in more advanced cables like Cat 6 or Cat 6a, which offer higher speeds and bandwidth, may be worthwhile. Remember that these cables may require compatibility with your network equipment, so consult a professional before installation.
If your network speed drops significantly, various potential reasons exist, ranging from device and user load to wiring issues or signal interference. Regularly check for cable damage or wear to maintain optimal speed and keep cable runs as short as possible. Ensure you use the correct termination method and conduct regular certification testing to catch problems before they arise. Additionally, consider using patch panels to minimize interference, avoiding signal loss and delays that can occur with determination.
If you’re experiencing speed and performance issues on your network, upgrading your equipment may be necessary. Start by considering upgrades to your modem, router, or switch, as these devices significantly impact network capabilities. Sometimes, simple steps like clearing browser caches and increasing available memory boost Speed. Approach upgrades cautiously, as they can affect connectivity, power consumption, and performance. Consult a professional before making any changes to your network infrastructure.
Understanding the significance of CAT 5e speed and selecting the suitable cable can position your organization for a fast, reliable, and future-proofed network. Consider the factors mentioned in this article and work with a network engineer to choose and install the suitable CAT 5e cable for your needs. Doing so will enhance your network’s performance, reliability, and user experience.
Recommend product: Optical Transceivers
A: Cat 5e works by transmitting data using twisted pairs of copper wires. The cable is designed to reduce electrical interference and crosstalk, ensuring reliable data transmission. It uses RJ45 connectors to connect devices such as computers, routers, and switches.
A: Cat 5e cables are an improved version of Cat 5 cables. While both can support data transmission up to 1 Gbps, Cat 5e cables have stricter specifications for crosstalk and system noise. This results in better performance and reduced interference compared to Cat 5 cables.
A: Yes, Cat 5e cables can support Gigabit Ethernet. They are designed to handle data transfer speeds of up to 1 Gbps, making them suitable for most home and small office networks.
A: The maximum length of a Cat 5e cable for Ethernet transmission is 328 feet or 100 meters. Beyond this distance, signal degradation may occur, leading to reduced network performance.
A: Cat 6 cables are an enhanced version of Cat 5e cables. They have higher specifications for crosstalk and system noise, allowing them to support higher data transfer speeds and reduced interference. Cat 6 cables are recommended for Gigabit Ethernet and can transmit data up to 10 Gbps over short distances.
A: You can use Cat 5e cables as a substitute for Cat 6 cables in most cases. However, Cat 5e cables may not fully take advantage of the higher performance capabilities of Cat 6 cables, especially for high-speed applications or when transmitting data over long distances.
A: Cat 6a cables are an improved version of Cat 6 cables. They have even stricter specifications for crosstalk and system noise, allowing them to support data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps over longer distances. Cat 6a cables are typically used for demanding applications and can provide better network performance.
A: Cat 8 cable is the latest standard for Ethernet cables. It is designed to support data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps over distances up to 98 feet. Cat 8 cables have even stricter specifications for crosstalk and system noise than previous categories.
A: Cat 8 cables have higher data transfer speed capabilities than Cat 6a and Cat 6 cables. While Cat 6a cables can support data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps and Cat 6 lines up to 1 Gbps, Cat 8 cables can reach speeds up to 40 Gbps. Cat 8 bars are also designed for shorter distances.