Regarding the ever-evolving telecommunications sphere, fiber optic technology has become essential in transmitting data with high speed. Among the different types of fiber optic cables are the ST fiber patch cables, also known as straight tip cables, which are mainly used for device-to-device connectivity in modern networks. This article presents general information on ST fiber patch cords, particularly their shape, purpose, and areas of use. This article offers the most important principles regarding the advantages of ST connectors, how optimal maintenance techniques can be performed, and how to choose the right type of fiber patch cable for different network applications. Suppose you are an IT-related practitioner, a network engineer, or simply interested in technologies. In that case, you can cope with the overwhelming knowledge provided on the ST fiber patch cables.
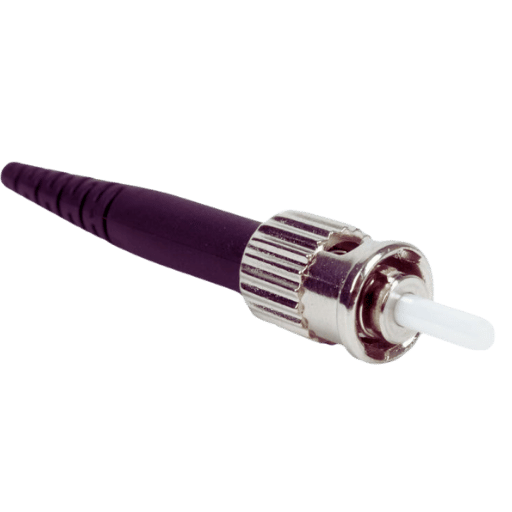

After all, ST fiber patch cables are a specific type of optical fiber that incorporates a straight tip connector with a bayonet latch type of coupler. This is beneficial since it facilitates the latter’s functionality, making ST connectors appropriate for many different networking and telecommunications fields. The primary benefit of ST cables is their high capacity for data transmission over a considerable distance which meets the demands in places such as data centers, telecom networks, and enterprise infrastructures where fast and reliable network connections are needed. Also, the design of the cables enhances the performance of self-extinguishing plenum optical assemblies in service since they contribute to the reduction of signal loss and interference.
ST fiber patch cables include several dimensions that provide added benefits and increase their use in various networking situations. First, the bayonet-style coupling of the cables facilitates a firm hold on the wires, making it difficult for the cables to give way unintentionally, which is essential for duplex fiber optic patch applications. Second, the ST connectors have been created such that less signal is lost with lesser back reflection, which is helpful when sending information over great distances. Moreover, standard patch cords with ST connectors support single-mode and multimode fiber types, providing versatility in applications. In addition, the rugged design characteristics of ST fiber patch cables protect against climatic conditions and, hence, can be effectively used indoors and outdoors. Finally, using network elements supporting the types of equipment provides further enhancements to nested structures.
Networking professionals greatly favor ST fiber patch cables as they possess several advantages. First, the reliable bayonet-style connection reduces the chances of it being accidentally disconnected, which is very useful in high-class environments, for instance, when using multimode duplex fiber optic cable. Second, the construction of ST connectors means there is very little signal and back reflection, so signal transmission over long distances is effective. Furthermore, the ability to handle single-mode and multimode fibers brings versatility for use in different situations, whether in an enterprise or telecom mode. Furthermore, the practical mass of cables offers protection against harmful settings, making it useful in both exterior and internal applications. Finally, using standard telecommunications devices makes it easier to complete the integration, allowing device refreshes and additions without disruption to the network.
While choosing ST fiber patch cables, it’s also necessary to know the difference between the single mode and multimode fiber optic cables, as this will affect the cables’ performance, range, and cost, respectively. The light rays in a single-mode fiber optic are transmitted through a single glass fiber blank. This makes it suitable for long-distance transmissions as there are fewer data losses, obtained over long lengths, making single-mode applications perform better in telecommunications and data centers, which need transmission over a large bandwidth to be accessed over wide networks.
On the other hand, Multiple-mode fiber Optics uses two or more glass strands and uses light at more than two densities. This arrangement is made for distances much shorter than achievable with the previous design, that is, inside a building or on a campus. Multimode fibers accommodate high initial bandwidth and distance. Nonetheless, these fibers have short distances but considerable problems with modal dispersion, causing a drop in efficiency as the length expands. For that reason, the selection between single mode and multimode fibers ought to fit the necessity of the network, length, and installation costs simultaneously. With the right type of fiber selected, the fiber optic systems will be efficient and stable.
In the case of ST fiber patch cables, the end type on both sides has the highest degree of compatibility and fiber optic system performance. This quick-connect bayonet-type closure is practical in use from the operator’s standpoint, which explains why this type of ST connector is usually found in multimode fibers. Still, there is a need to check the compatibility of the connectors with the systems they will fit onto, as the LC, SC, or MTP could be dissimilar types associated with losses in signals or disconnection opportunities.
Such parameters also determine the data transmission efficiency of the electrical connectors. For example, low-loss fiber optic connectors that limit the optical signal loss to less than 0.3dB (i.e., 0.2dB) are handy. High return loss fiber optic connectors (preferably above 20dB) lower the reflection of light, which can create communication challenges. Furthermore, the construction materials in the connector housing, e.g., plastic or metal, affect the strength and possible application. Thomas M, Engineering Standard D, Conductors cable compatibility with external Vending Machines. Specific factors such as these determine the quality and reliability of the performance of the fiber optic connections that the users wish to have.
In the case of fiber optic cables, the outer diameter is one of the most important parameters influencing their performance and range of applications. It should be noted that the standard outer diameter specification is 3.0mm for robust patch cords, providing better resistance to moisture and mechanical stress. This thicker jacket provides increased protection where necessary and improves the handling properties of the cables, allowing them to be more easily routed and organized in rackmount and data center environments.
Moreover, an outer diameter also influences the cable’s bend radius, which should be considered to prevent signal loss. An excessive bend on a fiber optic cable can lead to excess attenuation and loss of the cable’s intended performance. It, therefore, follows that a cable with an outer diameter specific to 3.0mm will guarantee no or limited wastage of valuable spaces but rather effective installations with no data loss. In addition, there is a high likelihood of uniformity in performance because of the conformity with internal cable parameters, which include the outer diameter, to the established industrial benchmarks.
OM1 and OS2 ST patch cords are tailored to particular types of network architectures and applications owing to their different features specific to other fiber optic network systems.
To conclude, selecting the ST patch cables, otherwise known as OM1 or OS2, depends on the specific networking needs, which comprise distance, bandwidth, and transmission speeds that will ensure good connectivity at all costs.
OM4 ST Patch Cords are utilized to advance data communications within high-speed networks. Working with a core cable 50 microns in diameter and transmitting at an 850nm wavelength, OM4 cables can support much greater bandwidth. OM4 cables can carry up to 40 Gbps data over a distance of 150 meters and up to 100 Gbps over 100 meters. This especially makes them useful in data processing centers and corporate networks where fast information handling and movement is a prerequisite. The improved design enhances the modal bandwidth and minimizes modal dispersion. The most common defects occur in modern-based applications such as cloud computing and high-definition TV, where high-speed connectivity is important, making OM4 a very useful component.
OM1 and OM2 ST duplex fiber patch cables have been developed, and applications in multimode optical fiber have also been opted for. However, they have essential variations in performance and capability. The actual orange jackets on OM1 cables contain a core with a diameter of 62.5 microns and are considered low band efficiency—it can handle (1Gbps) over 275 meters. However, OM2 cables with yellow jackets have a core of 50 microns rather, have better bandwidth performance, and perform better data rates of up to 10Gbps over a distance of 82 meters and 2.5 Gbps over 150 meters. OM2 enhanced this capacity to enhance the applicable performance of the present day, whereby higher data rate efficiency is a must. The type of cables can be seen in local area networks (LAN), data centers, and the rest. However, selecting either of them should, on the other hand, look into bandwidth requirements and distance coverage to achieve the most needed performance.
These recommendations will ensure the successful installation of ST fiber patch cables and the optimal quality of transmission within the networks.
To preserve the connections and avoid malfunctioning their ST fiber optic cable connectors for a long time, one must perform several maintenance tasks regularly. As a first step, connectors should be examined periodically for elements such as dirt, dust, or moisture that could obstruct the signal further. Before reconnecting the cables, cleaning with specialized mechanical solutions, such as lint-free wipes soaked in cleaning fluid at the connectors’ ends, is recommended. A haywire connection will avoid loss. Similarly, ensure that protective caps are utilized when the knowledgeable control connectors are not attached to avoid accumulating dirt. Finally, record any maintenance actions carried out, noting down the dates of the cleaving, including observing the activities performed and how these relate to the cleaning and other issues. As such, constant maintenance is critical in maintaining the quality of the connections and the ultimate durability of the fiber optic system.
When it comes to ST fiber optic cables, there are several issues that might be encountered regularly, affecting performance and reliability. Here are some common trouble spots and ways to solve them:
However, regular examination, adequate cleansing, and observing necessary procedures during installation can avoid most of these common issues, enabling optimal utilization of ST fiber optic systems.
Plenum duplex fiber patch cables have many benefits, especially regarding fire hazards or air quality. Below are the major advantages:
Therefore, Plenum duplex fiber patch cables are important in enhancing safety and performance in critical installation zones, meeting customers’ quality standards and regulations at the same time.
Specific installations require the use of armored cables to prevent external injuries. Armored cables are used appropriately in those situations as follows :
Considering the aforementioned uses, these scenarios justify the use of armored cables to enhance the installation’s safety and reliability, as well as the use of compliant cables with appropriate installation requirements with respect to the relevant regulations.
Adherence to best practices is required for the performance and longevity of the stainless steel ferrule ST connectors’ installation. First, appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) should be used to neutralize sharp edges and metal debris while inserting the connector. A compressor should be used to dry the area to avoid contamination of the connector and fiber.
Before connecting, ensure the fiber optic cables have been stripped and cleaved correctly because, in most cases, improper handling leads to a lack of signal or connection in some instances. Care must be taken to prevent scratching and busting the precise surfaces of the stainless steel ferrules. When tension is applied to the mating connector, use the support only to ensure that the connector linearly goes into the adapter. It is also necessary to insert the connector into the mating surface in such a manner that the connector fully engages and does not lead to an increase in losses. Whenever feasible, the connectors should also be inspected; these will include, as appropriate, lint-free wipes and cleaning solutions against microfibers to ensure quality transmission.
A: An ST Fiber Patch Cable is a form of optical fiber patch cord with ST connectors at both ends. In networking, this kind of cable is used to interconnect different optical devices. It has a reputation for having very strong connectors made of stainless steel ST that do not need frequent disconnection.
A: The main variation between an ST Fiber Patch Cable and an LC Fiber Patch Cable is the configuration of the connectors. The ST type is characterized by a 2.5 mm stainless steel ferrule, which is normally seen in lamp installations. On the other hand, the LC type is compact, with a 1.25 mm ferrule, which is mostly used in fast-growing compact network systems.
A: A multimode duplex fiber optic patch cord is indicated for short—to medium-range high-speed data communications. This fiber optic cable’s positive attributes are its increased bandwidth capacity and low optical signal loss, which allow good data transmission and, thus, appropriate use in data centers and LANs.
A: OFNP means Optical Fiber Nonconductive Plenum Cables. Cables offered by OFNP are installed in areas such as the plenum ceilings (used in structural air distribution) because they have fire hazard properties and produce very low smoke and no harmful gases when ignited.
A: A jacket fiber jumper with a zip cord is a patch cord. In this case, such a variation of the patch cord includes constructing a zip-cord type where the two individual fibers can be easily pulled apart, even if housed in a flexible and tight buffer. The invention simplifies the management and routing of cables on the sites of network installations.
A: Strong stainless steel ST optical fiber connectors fasten any optical fiber cable in a reliable and safe manner. They allow many connections and reconnections, which is necessary in spaces where connections need to be reliable and long-lasting.
A: As the name suggests, an ST plenum duplex fiber patch cable has a standard plenum rating and is a form of duplex fiber optic patch cable. It has ST-type duplex fiber connectors and was developed according to the code requirements for the area where the materials should be fire-rated.
A: A multimode cable with high bandwidth is chosen mainly because it can transmit large volumes of data over short distances with minimal signal attenuation. It is helpful in high-bandwidth-demanding networks requiring fast data transfers, such as data centers and telecommunications systems.
A: Duplex ST fiber connectors are a special type of fiber optic connector used in duplex fiber optic patch cables designed to terminate and hold two optical fibers simultaneously. This helps send and receive data, allowing data transmission in both directions, which is necessary for different types of networking.
A: A patch cord terminated with duplex connectors means that both ends of the fiber patch cord are provided with duplex connectors, which means that data can be sent and received at the same time. This is important for efficient and quick data transmission over the network.