What are Simplex and Duplex Fiber?
In the realm of fiber optics, two fundamental forms are predominantly used – Simplex and Duplex fibers.
- Simplex Fiber: A Simplex fiber cable consists of a single strand of glass or plastic fiber. It is designed for a single transmission direction, commonly used in applications that only require one-way data transfer. For example, an interstate trucker using a GPS tracker inherently uses a simplex fiber cable.
- Duplex Fiber: Unlike Simplex fibers, Duplex fiber cables have two threads – one for transmitting data and the other for receiving data. This cable type is suitable for communication systems that require simultaneous, bidirectional data transfer. Ethernet networks are a prime example of systems that utilize Duplex fibers.
Definition of Simplex and Duplex Fiber
Simplex Fiber – A type of fiber optic cable that contains only one fiber. Simplex fiber is most often used for applications that only require one-way data transfer. It is a single-threaded communication, allowing data to flow in only one direction at a time. Due to its unidirectional nature, it’s commonly utilized in systems such as radio and television networks.
Duplex Fiber – In contrast, Duplex fiber optic cable has two fibers: one for transmitting data and the other for receiving it. This allows for simultaneous, bidirectional data transfer. Duplex fiber optics are the standard for most computer networks as they enable a fast and reliable connection for sending and receiving data. It is perfect for systems that warrant a two-way data stream, promising an efficient means of communication.
Characteristics of Simplex and Duplex Fiber
Simplex Fiber Characteristics
- Unidirectional Data Transfer: Simplex fiber allows data transmission in one direction only. It’s a single-threaded communication, ideal for systems that don’t necessitate two-way communication.
- Cost-Effective: As it consists of a single fiber strand, the production costs for Simplex fibers are relatively lower, making them a more economical choice for one-way data transfer applications.
- Limited Bandwidth: Due to its inherent one-way communication, Simplex fibers offer limited bandwidth compared to Duplex fibers.
Duplex Fiber Characteristics
- Bidirectional Data Transfer: Duplex fibers support simultaneous data transfer in both directions, making them suitable for systems requiring two-way communication.
- Greater Bandwidth: Duplex fibers provide a higher bandwidth capacity due to their bidirectional nature, facilitating faster data communication.
- More Expensive: Owing to the two-fiber construction, Duplex fibers are typically more expensive to produce than Simplex fibers. However, the performance benefits often justify the added cost.
Applications of Simplex and Duplex Fiber
Simplex Fiber Applications
- Television Broadcasting: Simplex fibers are primarily used in television broadcasting, where the information is required to be sent in one direction only, from the broadcaster to the television sets.
- Radio Broadcasting: Similar to television, radio broadcasting also utilizes Simplex fiber for efficient one-way communication.
- Meter reading: Various industries employ Simplex fibers for remote meter reading systems, where data needs to be transmitted from the meter to the central system.
Duplex Fiber Applications
- Telecommunication Networks: Duplex fibers are extensively used in telecommunication networks for simultaneous two-way communication.
- Computer Networks: Modern computer networks rely heavily on Duplex fibers due to the need for rapid and concurrent data transmission and reception.
- Data Centers: Data centers, which require high-speed data transfer and real-time data processing, make substantial use of Duplex fibers.
Advantages of Simplex and Duplex Fiber
Advantages of Simplex Fiber
- Cost-Effective: Since simplex fiber utilizes a single thread, it is generally more affordable in terms of production and implementation costs.
- Ideal for Single-Direction Transmission: Simplex fiber is optimal for applications that require one-way data transmission, making it an excellent choice for broadcasting services.
Advantages of Duplex Fiber
- Two-Way Communication: Duplex fiber’s capacity for simultaneous transmission and reception of data makes it ideal for telecommunication and computer networks.
- Higher Bandwidth: Due to its bidirectional nature, duplex fiber provides a higher bandwidth capacity, allowing for faster data communication.
- Greater Efficiency in Data Centers: The ability of duplex fibers to handle rapid, concurrent data transmission makes them incredibly efficient in data center applications.
Disadvantages of Simplex and Duplex Fiber
Disadvantages of Simplex Fiber
- Limited Directionality: The primary disadvantage of simplex fiber is its unidirectional nature. This limitation makes it unsuitable for applications requiring bidirectional data transfer.
- Bandwidth Limitation: Simplex fiber also has a lower bandwidth capacity compared to duplex thread, limiting its data transmission speed.
Disadvantages of Duplex Fiber
- Cost: Duplex fiber involves two fiber strands, making it more expensive to produce and implement than simplex fiber.
- Complexity: The bidirectional nature of duplex fiber also contributes to its complexity, requiring more rigorous maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal performance.
Critical Differences Between Simplex and Duplex Fiber

Transmission Method
The primary difference between simplex and duplex fiber lies in their transmission methods. Simplex fiber offers one-way data transmission, meaning that data can only be sent in one direction – from the transmitter at the source end to the receiver at the destination end. This makes simplex fiber ideal for applications that only require data to be sent in one direction, such as broadcasting services.
On the other hand, duplex fiber offers two-way data transmission. It uses two fiber strands, one for transmitting data and the other for receiving it, enabling simultaneous bidirectional communication. This equips duplex fiber to handle applications that require data to be sent and received concurrently, such as telecommunications and computer networks.
Usage in Communication Systems
In communication systems, the choice between simplex and duplex fiber depends on specific requirements. Simplex fiber is used for unidirectional data flow, making it economical for applications like digital signage and surveillance. Duplex fiber enables bidirectional data flow, making it ideal for complex systems like telecommunication and computer networks.
Installation and Requirements
When it comes to installation and requirements, both simplex and duplex fibers have their unique considerations:
- Installation: Duplex fiber, due to its bidirectional nature, generally necessitates a more complex installation process compared to simplex thread. This is due to the requirement of aligning two separate strands for data transmission and reception. Simplex line, with its unidirectional data flow, has a relatively straightforward and less labor-intensive installation process.
- Hardware: Hardware requirements differ for simplex and duplex fibers. For simplex thread, a single set of transmitters and receivers is sufficient. However, a duplex cable requires two groups of transmitters and receivers due to its bidirectional data flow.
- Cabling: Duplex fiber requires a larger space for cable management due to the use of two fiber strands. A simplex thread, using a single strand, requires less space and thus is easier to manage in constrained environments.
- Maintenance: Duplex fiber requires more rigorous maintenance due to its complexity. Regular monitoring of both transmission and reception lines is necessary to maintain optimal performance. Simplex thread, on the other hand, has comparatively lower maintenance requirements.
Remember, choosing between simplex and duplex fiber is dependent on the specific needs and capabilities of the system in question. It’s essential to carefully consider each aspect, from installation to maintenance, to make an informed and efficient choice.
Performance in Data Transmission
Simplex and duplex fibers offer distinct capabilities in data transmission. Simplex yarn is ideal for one-way information, providing uninterrupted data streams for applications like broadcasting. It ensures high-performance transmission with minimal signal degradation. In contrast, duplex fiber enables robust two-way communication, facilitating simultaneous bi-directional data flow. It is well-suited for complex network systems that require rapid data exchange. However, a duplex thread requires stringent alignment and maintenance. While it offers higher data transmission rates, it comes with increased complexity and maintenance needs.
Cost and Suitability
- Cost: Duplex fiber cable is typically more expensive than simplex due to its increased complexity and capability for bidirectional data transmission. It requires more material resources and advanced technology for its construction, contributing to its higher cost. Simplex fiber, being more straightforward in terms of technology and resource requirements, is more cost-effective and ideal for systems with budget constraints.
- Suitability: Duplex fiber is suitable for complex network systems where high-speed bidirectional data transmission is required. It excels in environments that demand real-time communication, such as telecommunications and data centers. Simplex fiber, with its straightforward one-way message, is suitable for systems that prioritize uninterrupted data streams. It is commonly used in digital signage, monitoring systems, and broadcasting.
Understanding Fiber Optic Cables and Connectors
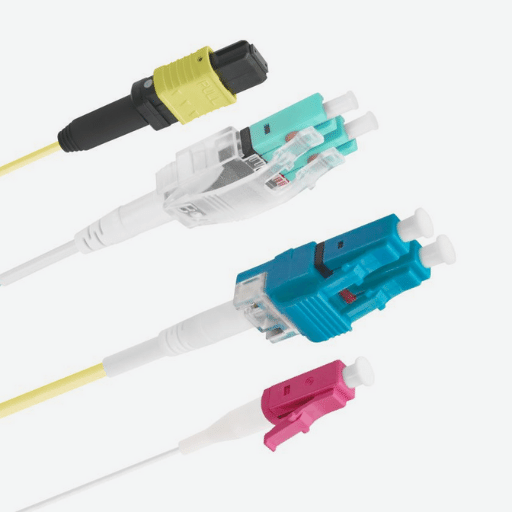
Types of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are mainly categorized into two types: Single-mode fiber (SMF) and Multi-mode fiber (MMF).
Single-mode fiber cables have a small diametric core that allows only one mode of light to propagate. Because of its narrow body, it eliminates distortions and reduces data transmission loss, making it ideal for data transmission over long distances. Applications include telephone and cable TV, long-range data transmission, and high-capacity voice services.
Multi-mode fiber, on the other hand, has a larger core diameter that allows multiple modes of light to propagate simultaneously. This characteristic enables high data transmission rates over short distances, making it suitable for data and audio/visual applications in LANs, SANs, and data centers.
Choosing between SMF and MMF depends on the network’s specific requirements, such as transmission distance, data rate, and cost.
Importance of Connectors in Fiber Optic Systems
In fiber optic systems, connectors play a critical role for several reasons:
- Signal Transmission: Connectors provide the physical contact necessary for signal transmission between devices or network segments.
- Flexibility and Scalability: They allow for system flexibility and scalability by enabling reconfiguration of networks and systems without significant hardware changes.
- Reduced Signal Loss: Quality connectors ensure low signal loss, which is vital for maintaining the overall performance of the optical network.
- Network Integration: Connectors enable the integration of different types of networks, systems, and devices, which use various transmission modes and speeds.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Proper connectors make maintenance and troubleshooting tasks more accessible by allowing quick disconnection and reconnection of fiber optic cables.
Choosing the correct connector type is as important as selecting the appropriate fiber optic cable, as the connector significantly influences the fiber optic system’s efficiency and reliability.
Advantages of Duplex Fiber Optic Cables
Duplex Fiber Optic Cables bring multiple advantages to the table, making them a preferred choice in many networking scenarios:
- Bidirectional Communication: Duplex cables allow simultaneous, bidirectional data transmission. This means data can be sent and received at the same time, which significantly enhances communication speed and efficiency.
- Reduced Interference: Duplex fiber optic cables are constructed in such a way that the two strands are isolated from each other, reducing the chances of signal interference between the send and receive channels.
- Reliability: Owing to their design, duplex cables provide a high level of reliability. If one path fails, the other can still transmit data, ensuring a consistent communication flow.
- Easy Installation and Maintenance: Duplex cables come with two fibers pre-installed in a single jacket, which simplifies the installation process and makes maintenance easier.
- Enhanced Bandwidth: Duplex fiber cables offer enhanced bandwidth as they utilize two fibers, which effectively doubles the cable’s data transmission capacity.
In conclusion, duplex fiber optic cables are a robust solution for applications requiring high-speed bidirectional data transmission with minimal signal interference and high reliability.
Considerations for Simplex vs Duplex Connectors
When deciding between simplex and duplex connectors for fiber optic systems, several vital considerations come into play:
- Application Requirements: Simplex connectors are ideal for applications that require one-way data transfer, while duplex connectors are better suited for applications necessitating simultaneous bidirectional data transfer.
- Cost: Simplex connectors might present a more cost-effective solution for systems with limited budget constraints. However, the enhanced efficiency and reliability of duplex connectors could offset their initial cost over time.
- Maintenance: While simplex cables may require more careful management to avoid tangling, duplex cables, being housed within a single jacket, can be easier to maintain.
- Installation Ease: Installing duplex cables could be more straightforward, given the pre-installed fiber pair, reducing the risk of misconnections.
- Future Proofing: With the ever-increasing demand for higher data speeds and bandwidth, opting for duplex connectors may provide a more future-proof solution.
In conclusion, choosing between simplex and duplex connectors largely depends on the specific needs and constraints of the fiber optic system in question. It is essential to perform a thorough analysis of the application requirements, budget, and long-term goals before making a decision.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Even with meticulous planning and execution, fiber optic systems may encounter diverse issues. These can range from minor inconveniences to significant complications that can disrupt data transmission. Here are some common problems and the recommended troubleshooting steps:
- Poor Transmission Quality: This could be due to dirt or dust on the connector’s end face. Use a fiber optic cleaning kit to carefully clean the end face and inspect it using a fiber inspection microscope.
- Loss of Signal: A complete signal loss might imply a break in the fiber cable. A visual fault locator can help trace the cable path and identify the location of the holiday.
- High Insertion Loss: This might occur when there is a poor connection between the connectors. Ensure the connectors are correctly mated and consider replacing them if the issue persists.
- Physical Damage: Accidental bending or twisting of cables can cause physical damage. Regularly inspect lines for any bends or twists and replace them if they are damaged.
Troubleshooting is an integral part of maintaining an efficient and reliable fiber optic system. It’s crucial to identify issues promptly and apply the appropriate solutions to minimize disruptions.
Applications and Use Cases for Simplex and Duplex Fiber
Simplex Fiber Applications
Simplex fiber optics, with their one-way data transmission capability, find use in various applications where one-way communication is sufficient. Here are a few critical applications:
- Television Networks: Simplex fiber cables are widely used in TV networks for broadcasting signals from control centers to the viewers’ devices.
- Radio Stations: Much like TV networks, radio stations also use simplex fiber cables to broadcast their signals to radios across vast distances.
- Internet Service Providers: ISPs often use simplex fibers for sending data to users, especially in cases where download speed is more critical than upload speed.
- Security Systems: Many security systems, like CCTV cameras, use simplex fibers to transmit data back to a central location.
- Sensor Systems: Simplex fibers are also used in various sensor systems where data needs to be sent from the sensor to a control or monitoring station.
Duplex Fiber Applications
Duplex fiber optics, which allow for simultaneous, two-way data transmission, are often employed in circumstances where data must flow in both directions simultaneously. Below are some prominent applications:
- Telecommunications: Telecom companies leverage duplex fiber for phone and internet services, enabling users to download and upload data simultaneously.
- Data Centers: In data centers, duplex fiber cables are crucial for connecting servers and storage devices, facilitating efficient data exchange.
- Computer Networks: Duplex fibers are widely utilized in computer networks to ensure smooth, uninterrupted bi-directional data flow between various devices.
- Cable Television: Duplex fibers are also used in cable television networks, allowing for two-way communication between the service provider and user devices and enabling services like video-on-demand.
- Industrial Control Systems: Many industrial control systems use duplex fibers to send and receive control signals and feedback simultaneously, ensuring real-time process control and optimization.
The use of duplex fiber may differ based on the requirements of the specific application, but the common thread is the need for reliable, real-time, two-way communication.
Use Cases in Networking and Telecommunication
In the realm of networking and telecommunication, duplex fiber optics prove to be indispensable. An integral use case is Ethernet Connections, where duplex fibers are used to establish high-speed connections between routers, switches, and other networking devices. These connections support high data rates, typically up to 100 Gbps, and ensure smooth, simultaneous two-way communication, which is critical for the functioning of large-scale networks.
Another significant use case is Long-Haul Networks. Telecommunication companies leverage duplex fibers in their long-haul networks to connect different cities and countries. Here, duplex fibers offer the advantage of carrying massive volumes of data over long distances with minimal loss, supporting the high-speed, global connectivity that we rely upon in today’s digital age.
Lastly, duplex fibers play a crucial role in Wireless Communication Networks. They are used extensively in the backhaul of wireless communication networks, where data from thousands of individual users is aggregated for transmission to the core network. The ability of duplex fibers to support significant volumes of two-way data flow makes them an ideal choice for these applications.
In summary, whether it’s connecting networking devices, supporting global communication networks, or enabling wireless connectivity, duplex fibers are foundational to modern networking and telecommunication systems.
Comparison in Industrial and Commercial Environments
Duplex fibers play a crucial role in both industrial and commercial environments. In industrial settings, they enable robust and reliable communication for monitoring and controlling intricate processes. In commercial applications, they facilitate high-speed connections for data centers and office networks, enhancing productivity. While their usage varies based on specific requirements and challenges, duplex fibers are valued for their bidirectional data flow, durability, and capacity to handle high volumes of data traffic.
Scalability and Future-proofing Considerations
Scalability is critical for duplex fibers, allowing networks to adapt and expand as data traffic increases. With the ability to support higher bandwidths through equipment upgrades, duplex fibers extend infrastructure lifespan while reducing costs. They are well-equipped to handle emerging technologies, making them a robust and future-proof solution for data transmission.
Optimizing Performance and Installation of Simplex and Duplex Fiber

Best Practices for Simplex and Duplex Fiber Installation
Here are some best practices to consider when installing Simplex and Duplex fiber:
- Plan your route: Always plan the path for the fiber cables. Avoid sharp bends and try to minimize the distance as much as possible.
- Ensure cleanliness: Simplex and Duplex fibers must be kept clean to maintain their effectiveness. Use fiber cleaning supplies to prevent dust and dirt from affecting the transmission.
- Test your fibers: Before and after installation, it is crucial to test the fibers. This can help to detect any possible defects or performance issues.
- Label your cables: Effective labeling allows for easier troubleshooting and maintenance. It also reduces the risk of accidental disconnections.
- Proper Storage: If the fibers are not immediately used, they should be stored appropriately to prevent any potential damage.
- Observe safety protocols: Installation should always be carried out in compliance with safety protocols. This includes using the right tools and wearing protective equipment.
- Professional Assistance: For complex installations or when in doubt, seek assistance from a professional. They possess the necessary expertise to ensure a successful and safe installation.
Factors Impacting Data Transmission Efficiency
Numerous factors significantly impact the efficiency of data transmission in both Simplex and Duplex fibers. Here are the principal ones:
- Cable Quality: The quality of the fiber optic cable itself plays a crucial role. Higher-quality cables typically ensure better performance.
- Cable Length: Transmission efficiency tends to decrease with an increase in cable length, which can introduce signal loss.
- Connector/Splice Loss: Ineptly performed splices, dirty connectors, or poor-quality components can result in significant data losses.
- Bend Radius: A smaller bend radius can cause light to escape from the fiber, resulting in data loss.
- External Interference: External factors such as temperature, moisture, and pressure changes can affect data transmission efficiency.
- Network Traffic: Higher network traffic can slow down data transmission.
- Installation Errors: Improper installation can cause a host of issues, including physical damage to the fiber, resulting in reduced efficiency.
- Equipment Quality: The quality of the transmitting and receiving equipment can significantly impact data transmission efficiency.
Signal Quality and Interference Management
To ensure optimal signal quality and manage interference in fiber optic communication, several strategies can be employed:
Signal Amplification: Optical amplifiers can be used to boost the strength of the signal, particularly over long distances where signal degradation is a common issue.
Use of High-Quality Cables and Components: Investing in high-quality fiber optic cables and components helps in reducing signal loss and interference. Such wires and parts are typically designed to withstand various external factors that may impact signal quality.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning: Regular maintenance and cleaning of fiber optic cables and components can help prevent dust and dirt accumulation, which can interfere with signal transmission.
Proper Installation and Handling: Ensuring a adequate bend radius during installation, avoiding cable kinks, and limiting the number of splices can contribute significantly to maintaining signal quality and reducing interference.
Temperature Control: Extreme temperature fluctuations can affect signal quality. Therefore, maintaining an optimal temperature and humidity level can help in efficient signal transmission.
Use of EMI Shielding: Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can impact signal quality. Using EMI shielding can help in reducing such interferences, thus maintaining signal quality.
Network Traffic Management: Efficient network traffic management can help in preventing network congestion, thereby ensuring smooth data transmission.
By effectively managing these factors, the consistent quality of data transmission through fiber optics can be assured, thereby leveraging the full potential of this technology.
Integration with Networking Equipment
Successful operation of a fiber optic communication system is mainly dependent on its effective integration with the existing networking equipment. This ensures that the system can function optimally within the more extensive network infrastructure. To achieve this, compatibility of the fiber optic cables and components with networking equipment such as switches, routers, and servers should be ensured. Additionally, system configuration settings might need to be adapted to accommodate the unique attributes of fiber optic technology. Following manufacturer guidelines and seeking assistance from network professionals can guarantee a seamless integration. Optimized integration not only boosts the overall network performance but also extends the lifespan of the fiber optic components.
Maintenance and Upkeep for Long-Term Performance
To ensure the long-term performance of a fiber optic communication system, regular maintenance and upkeep are crucial. Here are a few key recommendations:
- Regular Cleaning: Fiber optic components should be kept free from dust and other contaminants to maintain signal quality. Use recommended cleaning tools and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect your fiber optic system for signs of wear and tear. Any damaged components should be replaced immediately to prevent further damage and maintain system performance.
- Temperature and Humidity Control: Maintaining an appropriate environment is essential for the longevity of fiber optic components. Keep the system in an area with controlled temperature and humidity.
- EMI Monitoring: Continually monitor your system for EMI interferences. Use necessary shielding to reduce such interferences.
- Regular System Updates: Keep your system up to date with the latest software and firmware updates. This can help in optimizing the system’s performance and prevent potential issues.
- Professional Servicing: Engage professional services for periodic comprehensive checks and necessary adjustments. This ensures the system’s optimal functionality and prolongs its lifespan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between simplex and duplex fiber optic cables?
A: Simplex fiber optic cables have a single fiber and are used for applications that only require one-way data transfer, whereas duplex fiber optic cables have two threads and support bi-directional communication.
Q: When would you use simplex fiber optic cables?
A: Simplex fiber optic cables are commonly used in applications where data needs to travel in only one direction, such as in point-to-point communication and in situations where space is limited.
Q: In what scenarios are duplex fiber optic cables used?
A: Duplex fiber optic cables are used in scenarios where bi-directional communication is needed, such as in network switches, servers, and situations where equipment requires simultaneous two-way data transfer.
Q: What are the critical characteristics of simplex fiber optic cables?
A: Simplex fiber optic cables are known for their single fiber design, lightweight, and ability to transmit data over long distances without signal loss.
Q: What are the advantages of using duplex fiber optic cables?
A: Duplex fiber optic cables offer the advantage of simultaneous bi-directional communication, higher data transmission capacities, and the ability to support total duplex communication channels.
Q: Can simplex and duplex fiber optic cables be used interchangeably?
A: No, simplex and duplex fiber optic cables serve different purposes and are not interchangeable. Simplex lines are unidirectional, while duplex cables support bi-directional communication.
Q: How do simplex and duplex fiber optic cables differ in their connectors?
A: Simplex fiber optic cables use a single connector for one-way transmission, while duplex cables use two connectors for bi-directional communication.
Q: What are the typical applications of simplex fiber optic cables?
A: Simplex fiber optic cables are commonly used in communication systems, video transmissions, and in scenarios where only one-way data transfer is required.
Q: What are the common uses of duplex fiber optic cables?
A: Duplex fiber optic cables are commonly used in local area networks (LANs), fiber modems, switches, and in situations where bidirectional communication is essential.
Q: How are simplex and duplex fiber optic cables relevant in the context of network communication?
A: Simplex and duplex fiber optic cables play a crucial role in facilitating efficient and reliable data transmission in network communication by offering tailored solutions for unidirectional and bi-directional communication needs.
References
- FS Community Blog – A detailed comparison of simplex and duplex fiber optic cables, including their construction and applications.
- Fiber Savvy News – An article discussing the design and functionality of simplex and duplex fiber cables, highlighting their transmission capabilities.
- Quora Discussion – A community discussion that uses analogies to explain the concept of simplex and duplex fiber optic cables.
- r/networking Reddit Thread – A technical discussion about when to use simplex and duplex fiber cables, emphasizing their transmission properties.
- L-com FAQ – An FAQ page explaining the differences between simplex and duplex fiber optic cables, focusing on their construction and usage.
- Holight Optic – An article discussing the differences between simplex and duplex fiber optic cables, including their structure and applications.
- Fiber-Mart News – A news piece comparing simplex and duplex fiber optic cables, highlighting their construction and functionality.
- CBT Nuggets Blog – A blog post discussing the differences between simplex and duplex fiber, focusing on their data transmission capabilities.
- VPI Technical Articles – A technical article comparing different types of fiber optic cables, including a section on simplex and duplex fiber cables.
- Fiber Optic Association Guide – A guide from a professional association providing an overview of fiber optic cables, including explanations of simplex and duplex lines.
Post Views: 5,891





