Fiber optic technology is imperative for the success of any modern telecommunications system because of its unparalleled efficiency and reliability with the speed of data communication. SC Duplex fiber optic connector is one of the systems within these that are responsible for maintaining high-quality connectivity and excellent functionality. This guide covers the SC Duplex connector, construction, working, and salient features. From network engineers and IT personnel to those who want to know more about the technology enabling the world’s telecommunication, this article intends to help understand why the SC Duplex connector is favored in fiber optic networks. Get ready to explore the technical specifics and practical relevance that typify this connector and position it as a crucial component in telecommunications.

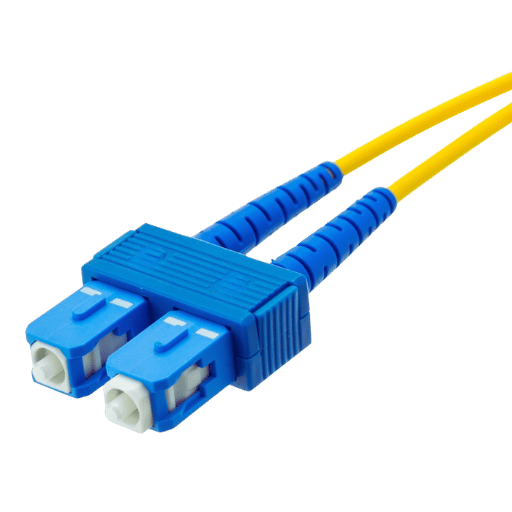
The SC fiber optic connector, referred to as Subscriber Connector, is one of the most common types of fiber optic connectors and frequently used with OM1 cables. It is distinguished by its square shape and snap-in push-pull mechanism, which provides a simple and effective way to fasten and detach the connector. A 2.5mm ferrule is used in the SC connection to achieve precise alignment with the fiber core, allowing light signals to be transmitted with minimal losses. SC connectors are needed in single-mode and multi-mode fiber optics for telecommunications and data networks, and their popularity comes from their simplicity and ease of use.
Fiber optic connectors are required for optical fiber interconnection as they aid in efficient light transmission with minimal loss. The most common connector types include;
Given the requirements for density versus performance and application environment, each option, such as SC or MPO connector type, is chosen.
With minimal signal degradation, the SC connector is vital in fiber networks by providing reliable and consistent connections. The SC connector is distinguished by its push-pull coupling mechanism, which makes it easier to install or remove the connector. These connectors are ideal for large-scale deployments and plenum-rated spaces. They are also popular in telecommunication, enterprise networks, and data centers because of their performance and durability, along with being compatible with single and multimode fibers. Such characteristics ensure effective data transmission, which is key to sustaining the integrity and performance of the network.
The distinctions between SC and LC fiber connectors are evident in their sizes and designs. SC connectors are more prominent than LC and employ a push-pull locking mechanism, which enhances their durability and makes them suitable for scenarios where space is not an issue. In contrast, LC connectors employ a latch mechanism, making them ideal for high-density installations.
Regarding insertion loss, SC and LC connectors are made with low insertion loss in mind, usually between 0.1 and 0.3 dB in favorable conditions. However, most do not achieve this level of performance due to other factors, such as the quality of the connectors, the accuracy of the alignment, and how the installation is done. LC connectors often perform better in dense environments than MPO connectors because of their smaller size and better alignment ferrules.
In traditional contexts regarding SC connectors, these connectors tend to be used in scenarios where the need for durability comes at the cost of available space. This includes their application in enterprise networks, data centers, and telecommunication rooms. SC connectors are also ideal for more extraordinary lengths of single-mode cables due to their robust design and consistent performance.
Alternatively, LC connectors have become the go-to option for areas requiring higher port dentition in a specific area. They are frequently incorporated in modern data centers and other high-speed networks that support transmission speeds of Gigabit Ethernet, 10G, 40G, and even 100G. Their smaller size than SC connectors allows for more efficient rack space utilization, benefiting high-capacity environments. Recently, it has been estimated that an LC panel can support twice the connection density that an SC panel offers, which increases optimization in terms of infrastructure scalability.
Moreover, there has also been an increase in the use of LC connectors in FTTH installations to address the need for faster broadband services without significantly limiting installation flexibility. Meanwhile, depending on the network’s requirements, SC and LC connectors remain important in reliable and efficient optical connectivity.

Experts can seamlessly connect hardware using SC couplers and connectors to eliminate signal loss or costly damage to the equipment. Long-term, regular maintenance, including adequate inspections and checkups, will guarantee that the hardware will function as intended.
Implementing these tips will help maximize the performance and lifetime of multimode fiber cables.
Due to their specific characteristics, singlemode fiber optic cables exhibit the best performance in data transmission over long distances and large volumes of data. The design of these cables contains a smaller core for a single light path, which reduces signal attenuation and distortion over distances. For instance, singlemode fibers can transmit data beyond 40 kilometers without signal boosting, which makes it optimal for telecom lines, metropolitan area networks, and long-distance backbone infrastructure.
Also, the ever-increasing demand for the 5G network and high-speed internet in remote areas can be satisfied by singlemode systems that offer incredibly high bandwidth at vast distances. Improvements in technology have also brought the development of Singlemode transceivers, allowing them to reach data rates higher than 400 Gbps for use in hyperscale data centers and global enterprise networks. These capabilities allow organizations to broaden network infrastructure and adapt singlemode systems for emerging network technologies.
Although the components and cables for singlemode solutions come at a higher upfront cost, the efficiency in the long run and meeting demanding workloads often overcomes the initial investment. For businesses seeking increased dependability, future growth, and broad coverage for communications infrastructure, singlemode systems offer greater reliability than multimode systems.
The performance and efficiency of optical fibers are defined by various characteristics that influence how well the fiber functions under certain conditions. The major parameters are:
Picking the right specifications is highly recommended as they can determine the optimal performance and efficiency of the cables.

There are different fiber optic connectors, and each one is designed for a particular application. Some of the most common connectors are the SC (Subscriber Connector), known for its reliable performance and push-pull design; the LC (Lucent Connector), known for its compact size and its use in high-density applications; and the ST (Straight Tip) connector, popular for robust connections in Industrial applications. Multi-fiber Termination Push on/Pull off (MPO/MTP) and FC (Ferrule Connector) are used in specific cases, including for multi-fiber terminations or more precise applications. The system’s requirements will determine the connector, i.e., compatibility, strength, and size.
As I resolve Duplex connector challenges, I first evaluate the cleanliness and alignment of the connectors because dirt and misalignment could lead to signal loss. I also check the fiber optic cable and adapter for damage. After these preliminary checks, if the difficulties persist, I confirm that the transmitter and receiver are not too far apart and that the combination of bends in the cable does not exceed the maximum for adequate signal transfer. Last, I systematically assess each segment of the link using an optical power meter to diagnose the location of the problem.
SC fiber connectors are incompatible with FC adapters because of dissimilar external features and locking styles. SC employs a pull-push type, while FC makes use of the locking screw type. A unique hybrid adapter that interfaces SC with FC is needed to mate these two types. This guarantees adequate control and firm connection.
A: An SC Duplex Fiber Optic Connector allows for the joining and terminating of fiber optic cables. This device is especially favored in networking and telecommunications due to its coupler mechanism and well-nurtured low insertion loss.
A: The SC Duplex Fiber Optic Connector bears a 2.5mm ferrule diameter and possesses both low insertion loss and a ferrule. It is designed for precise single-mode and multimode fiber applications in dense configurations.
A: The SC is, however, more appropriate for LC single fiber optic connectors, while ST connectors use a wider twist lock, unlike the pull-push mechanism of the SC type. All fiber connectors are chosen where the application’s specific need implies space and performance needs.
A: The duplex clip secures both SC connectors, allowing them to be permanently installed or uninstalled together. This is beneficial when continuous connectivity for receiving and transmitting fibers is needed.
A: Sure, SC Duplex Connectors can be used with other types of fiber optic patch cables. OM1 and OM3 are classified as multimode cables, whereas OS2 is a single-mode cable. It depends on the required data transmission speed and range.
A: Of course, SC connectors come in different forms, such as APC (Angled Physical Contact), which is meant for low-back reflection, or as part of connector kits with other types, like SC to ST or LC to SC. The form will depend on the application parameters.
A: SC Duplex Connectors are used in many areas that require dependable, low-loss SC Duplex Connectors, such as data centers, telecommunications, and networks. These connectors are also found in fiber optic patch cords, fiber jumpers, and transceivers.
A: SC Duplex Connectors minimize signal loss with their high-quality ceramic ferrule and precise alignment. This assures the proper data flow with minimal loss, maximizing the network application’s performance.
A: Sure, SC Connectors that are plenum-rated or OFNP-certified can easily be identified because they have such markings. These markings denote that the plenum connectors adhere to fire safety regulations for air-handling spaces, qualifying for various building codes and safety requirements.
1. The Contact Connection Method Between the SC Connector and the Raw Cleaved SM-Fiber End Is Done Physically
2. SC Connector’s Outside Plant Installation SC 20-Year Test Results
3. SC-FDE Based Fullduplex Relay Communication System Resilient to Residual Loop Interference