Regarding dependable, efficient network connectivity, the RJ45 connector is undeniably central to Ethernet technology. Understanding RJ45 connectors is vital for optimal performance, whether you are setting up a home network, maintaining a commercial IT infrastructure, or fixing connections. This guide looks into details on the best practices for working with RJ45 connectors and Ethernet cables. From understanding specific pinout configurations to exploring common use scenarios, this article comprehensively overviews networking projects that will benefit all user levels, from beginner to expert. Stay tuned for more details about this tiny but powerful connector.
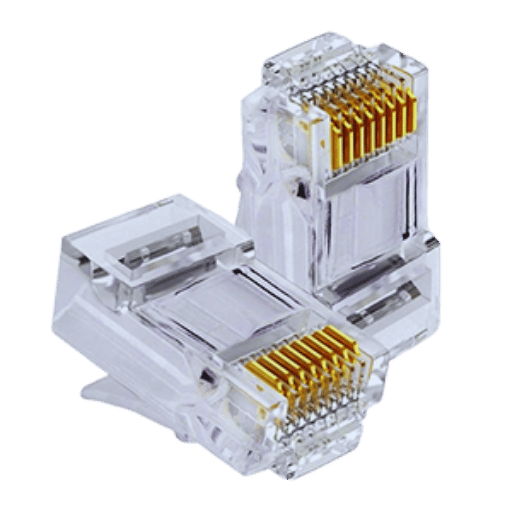
An RJ45 connector is one of the most recognized connectors in the networking world since it connects Ethernet cables. It has eight split pins, which correspond to the eight wires in a twisted-pair Ethernet cable allowing devices to transmit data. RJ45 connectors function by guaranteeing that each wire is placed in the correct socket according to the T568A or T568B pinout standard to achieve reliable communication. These connectors are very important in wired networks since they optimize data transfer rate and reliability, thereby increasing performance level in contemporary networking systems.
RJ45 connectors are used to link Ethernet cables in a wired network. They comprise eight metallic connectors corresponding to the eight wires found in a twisted-pair cable, thus guaranteeing the alignment requisite for data transmission. These connectors are manufactured according to T568A or T568B standards, which specify the order of the wires for the best possible communication. Built for strength and compatibility, RJ45 connectors are essential for dependable and effective network connection.
RJ45 connectors have an important function in modern Ethernet networks since they permit high-speed data transmission. These connectors support data rates from 10 Mbps to 10 Gbps or above. They are used in Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and 10-gigabit Ethernet. They are found on Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a cables, which are the most used in enterprise and home networks.
In Ethernet RJ45 connectors, the eight metal pins represent the eight wires within a twisted pair cable, which are allocated specific roles for signaling and data sending. Cross-talk and signal weakening or attenuation due to interference or absence of alignment is very crucial; hence, to follow vertical standards, the T568A or T568B can be used. As an example, properly terminated RJ45s will limit latency and packet loss, both factors that affect VoIP and video conferencing.
The development of RJ45 connectors has been oriented towards performance and durability, which have resulted in improved designs. Widely available shielded versions of these connectors ease electromagnetic interference (EMI) in electrically noisy environments, which can affect performance. For this reason, RJ45 connectors are ideal for high-performance networking in medical, industrial, and corporate settings.
To cater to different networking requirements, several RJ45 connectors with varying construction, shielding, and compatibility have been developed. Some of the most common types are listed below:
Shielded RJ45 Connectors (STP)
Shielded connectors come with enhanced protection to guard against electromagnetic interference (EMI) due to the presence of an extra metal layer. They are best suited for areas with heavy electrical noise, like industrial factories, medical units, or places near large machinery where patch cables are utilized. Research indicates that shielded connectors have improved signal integrity when used with shielded cables. Moreover, these connectors maintain required transmission speeds of 10 Gbps over 100 meters.
Unshielded RJ45 Connectors (UTP)
This type of RJ45 connector comes with no additional shielding. As these RJ45 connectors do not come with shielding, their weight and cost are lower. Common in residences and low interference settings, unshielded connectors are typically sufficient for smaller-scale applications, such as home networks or small offices where EMI is minimal.
RJ45 Connectors with Cat5e
These connectors are tailored for Cat5e cables and maintain Ethernet capabilities of 1 Gbps with a frequency of 100 MHz. They are widely available in households and business facilities and are a smart selection for basic networking use because of their low cost.
Cat6 RJ45 Connectors
Cat6 connectors are built to cater to high-performance computers with supported data transmission speeds of 10 Gbps at 250 MHz, making them suitable for high-speed networks. Enhanced performance is achieved with better building materials, such as gold-plated contacts, which help prevent signal loss.
Cat6a RJ45 Connectors
Much like CAT 6, Cat6a RJ45 Connectors are used in augmented category 6 systems and boast data rates of 10 Gbps with frequencies up to 500 MHz. Enhanced reliability and robustness mean these are favored in most data centers, corporate frameworks, and other demanding and high-end tasks.
Pass-Through RJ45 Connectors
These connectors simplify the crimping step, which allows inspection of the wires prior to crimping. The errors that may come as a result of misaligning to the positions marked on the connectors for the wires are removed. This makes them ideal with network engineers as accuracy allows without sacrificing on speed.
Industrial Ruggedized RJ45 Connectors
They have strong enclosures designed to withstand dust, water, and shock to survive in harsh environments. These are used more frequently in manufacturing, transportation, or outdoor telecommunications fields that might fail with standard connectors.
Professionals familiar with the different types of RJ45 connectors available can choose the most suitable one for their needs in terms of environmental conditions, performance, and budget constraints.

To make the right choice between Cat5e and Cat6 Ethernet cables, it is critical to consider the factors of performance, structure, and use cases tailored to your specific needs.
1. Bandwidth and Speed:
Enhanced Cat5e, as the name suggests, has inherited features from its predecessor, Cat5, and supports Gigabit Ethernet at a maximum distance of 100 meters at 100 MHz. Cat6 cables, on the other hand, have the potential to handle 10 Gbps but only up to 55 meters at 250 MHz. There is a positive connotation for Cat6 businesses, as the higher frequency translates to better data throughput and reduced latency.
2. Crosstalk Reduction:
Crosstalk pertains to the unwanted interference arising from adjacent signal transmission simultaneous to the signal of interest. Tougher interference is more effectively reduced in Cat6 cables than in Cat5e cables. Like all Cat5e cables, Cat6 cables have tighter twists of their internal wire pairs, but many versions also have a central spline that allows better signal isolation and interference reduction, leading to better data transmission.
3. Evaluation of Durability Versus Cost:
The performance enhancements of the Cat6 cables provide them with stricter shielding, electromagnetic compatibility and buffering standards or features compared to Cat5, which increases their durability in various environments. Cat6 cables further add to modern applications, particularly in high-performance networks or places where electromagnetic interference is dominant. Moreover, Cat6 cables are better suited for upgrades, considering the advancements in network technology.
4. Use Case Scenarios:
Basic home networks or small-scale offices would benefit greatly from the use of Cat5e cables, given the low demands of browsing or streaming video content. Large business networks, data centers, or other setups that require advanced streaming and gaming along with heavy data transfer prefer to make use of Cat6 cables due to their increased performance.
5. Financial Implications:
Since Cat6 cables offer better performance as well as construction quality, they are, on average, more expensive than Cat5e cables. However, the price difference for more complex engineering tasks like data centers and business networks is offset given the increased value in performance, responsiveness, and stability in the long run.
Picking the best option:
Cat5e is still a viable option for many applications within a budget, but purchasing Cat6 cables can enhance network performance and facilitate future development. The superior cable, Cat6, offers faster speeds with lower latency, making it the ideal solution for professional or demanding use cases.
Choosing network cabling requires one to understand the difference between shielded and unshielded cables since each one has its advantages, as well as drawbacks, in terms of performance and interference. Shielded cables, or STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) and FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair), have additional protective shields covering the twisted pairs of wires in the cable. This shielding also minimizes external electromagnetic interference (EMI) as well as reduces crosstalk between adjacent cables. Because of these features, shielded cables are best suited for high EMI environments such as industrial, data center, or any other electronic devices rich facility. On the other side, shielded cables do need to be properly grounded, which adds to the cost and increases the complexity of installation.
On the other hand, UTP does not have added shielding, which does make it more affordable and flexible. Lower EMI workplaces such as homes, small offices, and residential setups regions widely rely on UTP wires. Though basic in design, modern evolution of UTP cables like Cat6 or Cat6a do offer strict designs and standards, making them capable of handling daily networking duties.
A consideration of these cables includes their distance range, transmission speed, and other relevant features. In the presence of considerable interference, shielded cables tend to have longer maximum lengths, or runs, without loss in signal quality. In this case, for example, Cat6 FTP cables can sustain optimal performance over 55 meters at 10 Gbps within high EMI environments, while UTP cables may lose significant portions of their signal. UTP cables, on the other hand, remain unparalleled in cost as their terminations and installation do not require specialized tools and grounding features.
The choice between a shielded and unshielded cable should be defined by operational needs and conditions as well as financial limits within a particular project. The shielded option provides adequate protection for high-demand applications as well as more advanced circuitry, while unshielded options are economical and fairly dependable, providing a cutting-edge solution for a standard network.
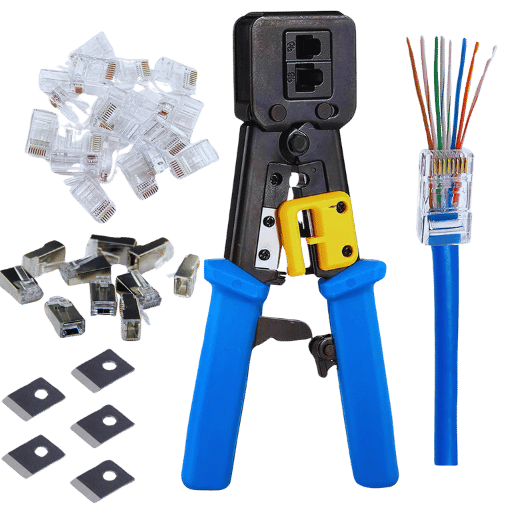

To properly crimp an RJ45 connector, you must have the following tools, which all play an equally important part in the proper termination of the cable:
Crimping Tool
In securing the connector to the cable, having an RJ45 crimping tool is mandatory. It is usually manufactured with some blade compartments for cutting and stripping Ethernet cables. Modern tools are built to accept various types of connectors like CAT5e, CAT6, or CAT6a cables and different ethernet cable connectors.
Cable Stripper
A cable stripper is used to expose the internals of the outer jacket of the Ethernet cable. Care must be exercised at this stage to prevent cutting through vital components of the cables.
Cutting Tool
With a sharp cutting tool, you are guaranteed clean cuts of the individual twisted pair wires. This avoids having rough, ragged edges that would make it difficult to fit into the connector.
RJ45 Connectors
You also need RJ45 connectors that are compatible with the type of shielded or unshielded cables you have. Shielded connectors are often used in areas where cables would be subjected to EMI, while unshielded connectors suffice for normal use.
Cable Tester for Network Cables
A network cable tester assists in checking the continuity and configuration of a cable after crimping it. This ensures that the pairs of the cable are terminated according to T568A or T568B wiring standards, which helps in preventing issues with the type of cable used.
Accessories for Managing Cables
During the crimping process, organizing tools such as zip ties and cable combs can help eliminate loose cables. This step reduces the number of errors and increases the network installation efficiency.
Eye Protection and Gloves
Some tools may be sharp, or the cables may have exposed strands, which can be dangerous. To avoid injury, safety equipment such as gloves and eye protection should be used.
When installed and maintained properly, Ethernet cabling systems reinforce the overall network reliability while reducing the chances of network downtime. This is achieved by ensuring that there is minimal potential downtime caused by incorrect terminations or unreliable Ethernet cabling systems.
Strip the Outer Jacket
The first step involves me using a cable stripper to carefully strip 1 to 2 inches of the outer jacket whilst ensuring that the inner wires are not damaged. This step reveals the twisted pairs contained inside.
Untwist and Arrange Wires
For the next step, I deal with the pairs by untwisting them and straightening each wire individually, preparing them according to the T568B standard. The correct sequence of the wires is very important for proper data transmission.
Trim Wires to Length
The next step involves me trimming the wires to the correct length. In this case, I leave approximately half an inch of wire from the outer jacket, which makes it easier for the wires to fit properly into the connector.
Insert Wires into the Connector
With the clip facing in a downward position, I proceed to insert the wires into the RJ45 connector, ensuring that all of them are fully seated and in the right order.
Crimp the Connector
The last step consists of placing the connector into the crimping tool and applying some force to tighten the wires and the connector, which ensures a reliable connection. After crimping, I inspect the connector to confirm proper termination.
It’s Incorrect Wiring Order
Not following the correct wire order may result in a connection that does not work. As a best practice, reconfirm the wiring order with the standard used in your project, whether T568A or T568B.
Not Insert the Wires Completely
Partial seating of the wires may result in flaky or nonexistent connections. Verify that all wires are flush with the mouth of the connector before crimping.
Not Trim the Cable to The Recommended Specification
Lack of trimming may result in untidy and sometimes troublesome connections during crimping. For proper cable placement, a specific trimmed level should be maintained.
Not Applying Enough Force While Crimping
Over crimping may cause the cables to loosen from their slots. Make sure there are good connections by using a reliable crimping tool and evenly distributing the required pressure.
Using Low Quality Connectors
Aesthetically displeasing connectors may disrupt the junction’s reliability. Make sure connections are made properly by checking for common faults on the cable connectors used before mounting them.
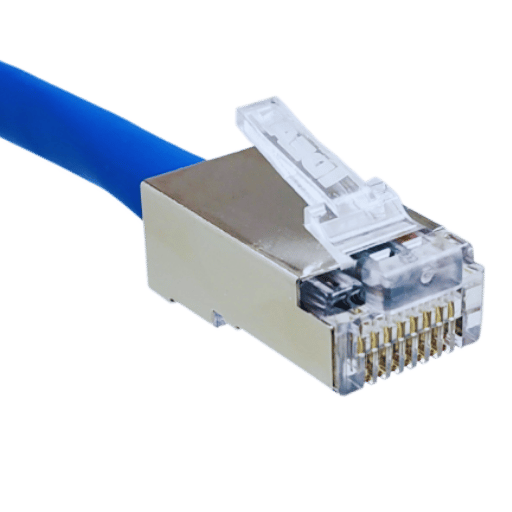
Shielded RJ45 connectors are essential in keeping telecommunication networks up to the industry’s standards of dependability and various standards of quality, especially in areas with a high risk of electrical interference or it being abundant. Shielding functions optimally in reducing electromagnetic distractions (EMI) and radioactivity distractions (RFI) that affect how information and signals indeed flow in ethernet cable connectors. Such a function is highly relevant in industrial industries, IT units, or areas that have a conglomerate of electronic equipment.
The benefits of shielded connectors go as far as improving the signal-to-noise ratio, giving them more enhanced data processing abilities. According to recent industry insights, shielded connectors used in high-speed networks, supporting gigabit ethernet and ten-gigabit ethernet, have been known to cut off around 90 percent packet loss and transmission error compared to unshielded counterparts in an interference-ridden area. With barriers, shielded protect crosstalk whereby the signals that are next to each other clash with each other to guarantee that they are solid and dependable in huge bundle of cables.
Through comprehensive steps and not simply one of them, shielded connectors guarantee the elimination of external barriers and interference. They also ensure a uniform quality shielded cable that goes with the ground to avert disturbance in shielded wires, which aids in attaining precise results. Using the shielded RJ45 helps dodge chronic network failure, trigger reduced disturbance of work functionality at its peak, and optimise shielded accords greater faith in the overall performance output of the apparatus provided.
Factories, data centers, or places with heavy machinery require shielded connectors owing to electromagnetic interference (EMI) on a higher level. These connectors function perfectly for applications needing high reliability and data performance in areas with interference.
For standard offices and residential settings, shielded connectors offer very little protection against EMI, thus making unshielded connectors a more economical choice. Their lack of EMI protection makes them suitable for environments where interference is not a concern.
Both options are interchangeable depending on the environment and the particular form of interference one is most likely to encounter.
By reducing or eliminating electromagnetic and radio frequency interference (EMI), Shielded connectors increase network performance and context of communication. The foil or braided metal shielding that surrounds the conductors is capable of reflecting and absorbing damaging EMI before it contacts the inner conductors. This ensures stable and reliable data transmission even in high interference environments.
For high-speed networks such as Ethernet systems operating at 10 Gbps or more, crosstalk and signal attenuation is greatly reduced with the use of shielded connectors, which increase overall throughput. Studies indicate cased shielded systems emit up to 800% lower EMI emissions when compared to unshielded systems, further increasing network security by mitigating the risk for external signals leaking through. For new and emerging technologies, shielded connectors help industry performers standards of Category 6A and beyond, which enables support for bandwidth-intensive applications like video conferencing, cloud computing, and large-scale data transfers. Shielded connectors aid in enhancing the reliability and stability provided to the demanding environments in which the network provides infrastructure through signal integrity and noise immunity.
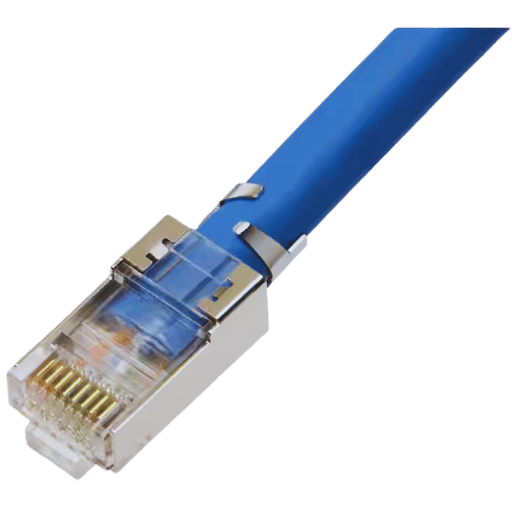

1. Tools and Materials Needed
The tools that ought to be prepared are Ethernet cables, RJ45 connectors, a cable crimper, a wire stripper, and scissors or a cutting tool.
Stripping the Jacket of the Cable
Twist the wires around for purposes of unmaking the twisted pairs. Now make use of a wire stripper to carefully take away 1-2 inches of the outer jacket of the Ethernet cable.
Arrange and Untwist the Wires
Now that the pairs have been conveniently unmade, ensure that all the wires have been straightened. This has to be done as per the T568A or T568B heading standards, depending on your network arrangements.
Wires Cut to Desired Length
Ensure that the wires are cut in such a manner that they all align and are even. Also, remember that the RJ45 connector can only be so big.
Insert the Wires Into the RJ45 Connector
Ensure the wires slide properly into the RJ45 connector. Each wire must be placed into the right slots that reach metal contacts.
Crimp the Connector
Put the connector in the crimping tool and firmly stamp the coupler to secure the wires and solder it in.
Wires should always be pushed into the crimping tool to create the best connection.
Cabling
With a cable tester, you should now be able to check the connectivity issue and see that there are no wiring issues before deployment.
Taking these steps will guarantee the correct installation and the best performance of RJ45 connectors in your networking system.
For extended retention of RJ45 connectors and to ensure network integrity is preserved, the following practices should be considered:
These practices not only prolong the life of RJ45 connectors but also improve the quality of network services provided.
A: An RJ45 connector is a terminus receptacle used for connecting and interfacing Ethernet networks. It is the primary connector for twisted pair cables like Cat 5, Cat 6, and Cat 6a, which are used in ethernet cable connections. RJ45 connectors receive peripherals used for local area networks (LANs) and the internet.
A: There exists a difference in the categories of Ethernet cables in the case of RJ45 connectors Cat 5 and 6. Cat 6 additionally supports higher frequencies and faster data transmission than provided by cat 5. Although the appearance is the same, the Cat 6 connectors have a separator spline, which reduces crosstalk and is in fact, a Cat6 connector, which provides better performance for gigabyte Ethernet.
A: Yes, shielded RJ45 connectors are specifically designed to be used with shielded Ethernet cables and provide better protection against electromagnetic interferences (EMI) and radio frequency interferences (RFI). Such RJ45 connectors are common in the industrial field or for any work that needs additional protection for a signal.
A: Cat6 RJ45 shielded pass-thru modular connectors are designed for easier termination of Cat 6 shielded cables. These connectors are a type of RJ45 plug that can shield cables and have easier installation features. The pass-through design allows wire verification to be done pre-crimping, enabling wires to be inserted through the connector.
A: A Cat6 plug or connector is used in affixing an RJ45 plug on the cable, while a Cat6 coupler is used to link together two separate Cat6 cables. Choose the Cat6 connector if you have a cable that needs a plug at its end. Use a Cat6 coupler when the network cable you are using needs an extension but does not want the signal quality to reduce. Both are important in creating and expanding CAT 6 cable networks.
A. RJ45 jack, also known as a female connector or port, is an RJ45 plug socket. Jacks can be found on network devices, wall plates, and patch panels. RJ45 plug is a male connector at the end of the network cable. The jack and plug together complete the connection and allow Ethernet data transmission.
A: Yes, several concerns should be addressed when using RJ45 connectors for longer cable runs. Firstly, make sure that you are using the correct category of cable and connector for the desired speed and distance. For longer lengths, higher category cables such as Cat 6 or Cat 6a might be necessary. Also, use shielded cables and connectors to minimize interference. Moreover, make sure to stay within the maximum length requirements for Ethernet cables which is generally 100 meters for most categories.
1. Title: Gripper Engineering for an Autonomous Maintenance System of Radios Base Station
Summary:
2. Article: Suppression of mode conversion using the improvement shielding effect of an Ethernet cable connector based on imbalance factor matching.
Overview:
3. Title: The Thermal Properties of an Ethernet Connector in Power System Applications Using an Engineering Mechanics Approach
Abstract: