Over the years, fiber optic cables have become a significant aspect of communication systems, particularly in external environments where performance and toughness matter the most. This guide is aimed at providing the most helpful material regarding the best outdoor fiber optic cables, focusing on the considerations, features, and technologies used. Since such external areas have adverse conditions such as varying temperatures, humidity and even physical pressure, it is very important to appreciate these elements in order to maximize the performance and durability of fiber optics. In this article, we shall ascertain the types of fiber optic cables available, their specifications, where they can be used, and other information that one would require to decide the current market trends so it enables them to satisfy their application requirements well.
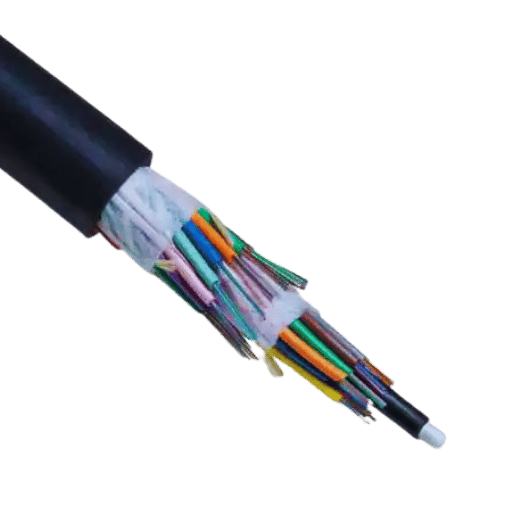
An outdoor fiber optic cable is a kind of cable that is aimed at working in an outer ambient to pass data through light signals. Unlike internal cables, where several factors are neglected, external cables are designed with the understanding that they will be subjected to environmental extremes. Usually, they comprise structural elements such as a strong external casing and water-blocking elements that enhance performance and reliability even in extreme climate conditions. These are the design components that sustain signals over long distances and form part of even day-to-day communication systems like telephone cables, internet cables, and computer networking centers.
There are numerous advantages that contribute to the use of outdoor fiber optic cables in communication with external networks. Cables, first and foremost, are characterized by the provision of high broadband speeds as well as more substantial data-carrying capabilities, which are vital in the contexts of contemporary techno-telecommunications. They are less prone to electromagnetic interference, thus guaranteeing stable and reliable connections even in noisy electrical environments. Moreover, the design of outdoor fiber optic cables is such that they are resistant to damages caused by both the physical and ambient environment, such as extreme weather and attack from rats, leading to lower costs for repair and maintenance and increased durability. In addition, the cables’ lightweight and bending properties allow them to be installed more easily in places with difficult terrains. Therefore, they act as a very crucial link in ensuring that high quality data connections are operational even geographically outside the building.
A number of installation aspects have to be factored in order to avoid problems that may plague the fiber optic cables installed outdoors. One of the factors is that one has to deal with adequate topography, which can affect the routing and placement of cables. This takes adequate time and often appropriate tools are needed to deal with high rises, thick forests, or cities with tall buildings. Also, in extremely cold or hot climates, moisture, as well as exposure to UV rays, can affect moisture stress and cable performance. Therefore, the right materials and housing should be chosen in order to mitigate these challenges. The other major issue is the need to ensure that the installation causes the least interruption possible in areas occupied by people, which calls for engaging with the municipalities and following the provisions. Last but not least, it takes trained manpower to splice or terminate fiber cables with precision since even a slight misalignment of the core in the two mating fibers leads to a loss of signals and connectivity problems. Hence, such lateral issues of overcoming these installation challenges require extensive careful thoughts and actions.

Achieving the expected parameters on outdoor fiber optic cables entails selecting the right cable diameter. The following are the key factors to consider:
Such factors should be handled in order for the diameter definer to be adequate for technical and operational purposes without sacrifice of one for the other.
There are core differences to note when identifying singlemode and multimode fiber optic cables. The singlemode fibers exhibit a single cylindrical cross-sectional area with a core diameter of approximately 9 micrometers, restricting the transmission of only one mode of light along the length of the fiber. This characteristic reduces modal dispersion, allowing the transmission of high bandwidth data over greater distances, thus making single mode favorable for long-haul telecommunication applications. On the other hand, multimode fibers have much larger core diameters of about 50 or 62.5 micrometers, permitting the passage of several light modes at the same time. This structure allows the fiber after connection to be sealed off for easier and cheap termination, unfortunately, makes the transmission distances shorter because of increased dispersion. For this reason, multimode fiber is preferable in these scenarios due to lower cost connections, especially when working with short distances such as in data centers, wide area networks, and local area networks. Factors related to signal integrity, distance, and economics in deployment scenarios play a fundamental role in influencing the choice between singlemode and multimode fibers.
Outdoor-managed, as far as this matter is concerned, has UV and weather-resistant features which are known to assist in long-term use and effectiveness of the fo cable system. The treated or untreated staff under the UV rays will, after some time, become more brittle and may be prone to cracking or failing completely. This is the primary reason why all outdoor cables, for instance, will mostly have UV-cut coating or UV-resistant materials. Moreover, it is also very important to withstand weather factors such as rain, snow, and temperature changes, which will be necessary for the internal components and protecting the quality of signals. It is a fact that these UV and weather-resistant cables help in reducing the maintenance needs for the installation and enhancing the functional lifespan of the installation, thus reducing the rate of replacements and repairs, making it a cost-effective solution.
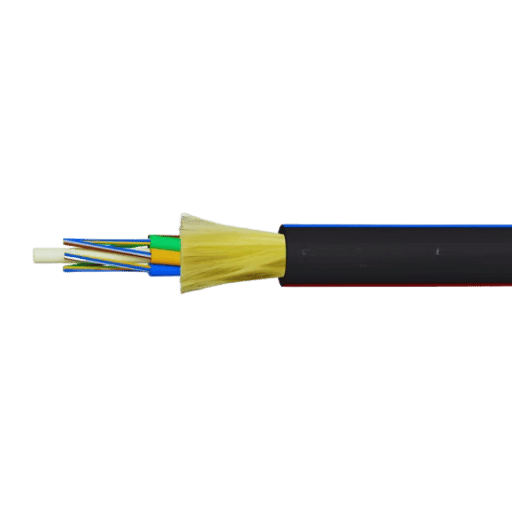
The data transmission capacity of the optical fiber is severely hampered in situations wherein the inflexible tube is to be used in hostile environments or in areas where it can be subject to mechanical abuse or rigorous handling. Here are the key advantages of using armored fiber optic cables:
The use of armored fiber optic cables in specific installations guarantees effectiveness and durability even in extreme environments.
Non-armored cables are used in areas where there is little or no external mechanical stress, thus enhancing the overall flexibility and lightness of the cables compared to the armored ones. These cables are very effective when it comes to interior home wiring or interior wiring of a data center, where the building itself is sufficient to protect against damages. Also, non-armored cables are appropriate for short-range data as these are easy and less expensive to install. They are also favorable in suspended or aerial installations, which require low weight and flexible cables for efficient installation with no extra mechanical protection.
While comparing the cost and lifespan of armored cables and non-armored cables with the help of some top-notch websites, a few insights stand out. The price of Arcred cables is always higher compared to the other cables due to their enhanced features and Bikalvaodiya construction, which is always justified by the right application of these cables in extreme conditions and lesser maintenance. Usually, the bulk is safe and nondestructive, and as a result, they are expensive, notwithstanding the stringent requirements for the nerve for tensile due to the fair operational costs. On the other hand, non-armored types of cables are less costly and are more soft, so they are used for simple installation environments. They bring about a reasonable amount of cost-effectiveness for places that do not require extreme mechanical protection.
Now, the following factors can help clear up the certain technical parameters more thoroughly:
Each type has its specific strengths depending on the parameters of the installation and external factors, the two constituents which define the total cost of ownership and the field of application.

LC Connectors: This type of connector a great fit in a high-density networking environment as it is small in size and space-saving especially in data centers.
SC Connectors: Simple Connector (SC) is known for having a push-pull component and offers low insertion loss and high repetitiveness thus making it suitable in the network.
ST Connectors: ST connectors come with a bayonet locking mechanism which allows for the locking of the plugs to ensure secure connections and tend to be predominantly used in multimode networks in structured cabling.
It is essential to evaluate certain factors in order to choose the proper connector depending on the networking requirements. Firstly, when deciding on the number, the type of network setup should be taken into account, as LC connectors will be useful in high-density areas. Then take into consideration the adaptability, for example ST connectors may be more appropriate for quick and secure installations due to their bayonet-style locking mechanism. On the other hand, if an organization is concerned about the maintenance of such kinds of high-performance networks over a distance, then SC connectors, which are easier to use and have push-pull capabilities, may be an advantage. In the end, however, all these factors have to be managed with budget constraints and the objectives of the overall structural design.

Designed specifically for harsh environmental conditions, outdoor fiber patch cables are solely intended for outdoor applications. These cables are made to endure sun and moisture for long periods of time since they come with a tough protective jacket that is UV resistant. Furthermore, they will very often feature a water-blocking gel or a tape that acts as a barrier to water entering the cable assembly. Under low ambient temperatures, do outdoor fiber patch cables work effectively through the range of? 40 °F -158 °F ( ?40 °C -70 °C) without any out-of-equilibrium response to extreme heat & cold conditions. To provide added strength, the structure may contain an additional enclosure of the fibers with steel wire armor or corrugated steel tape to protect them from chew cables of rodents or physical strikes. All these characteristics together help in supplanting high signal attenuation and loss of signal over long distances, even in highly outdoor environments.
Following these recommendations will allow increasing the service life and operational reliability of outdoor fiber patch cable installation to ensure optimal functioning over long periods of time.
Deploying outdoor fiber patch cables can lead to a multitude of problems that can impact both performance and durability. The following are some of the common problems encountered and a practical resolution:
Signal Loss as a Consequence of the Environment:
Physical Damage:
Installation Missteps:
Resolving such issues systematically reduces the concerns about the stability and performance of outdoor fiber installations.

When installing outdoor fiber optic cables, there are certain things that need to be taken into account while making the installation route. Carry out a detailed site survey to assess accessibility and possible hindrances in order to find the best line. Restrict lines so as to avoid excess signal attenuation and cost of the facility where possible. Also, consider the humidity and temperature during operations and select the best protection suited for the conditions. Maintain safe distances from power lines, heavy machines and, other obstacles to prevent operational hazards. The last routing should consider the relative optimal utility, economy, and impact on the environment.
Requisites include the correct tools to ensure accuracy and protection over the fiber optic cables when putting up outdoor fiber optic cables. Some of the most important tools include:
Thus, providing the installation personnel with these tools oriented to this or that operation will enable the construction of an effective geometric optical network.
Fiber optic networks must be properly maintained on a regular basis. Fiber optic networks are complex, and certain procedures and inspections shall be regularly implemented. Routines that involve physical damage and assuring the lock of any connection, in addition to connector cleaning so as to enhance proper signal strength, are some of the important activities. An optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR) can help in locating and identifying every flaw, such as microlending or a break; thus, repairs can be done accurately and speedily. Carrying out a scheduled preventive maintenance approach is also a good way of avoiding problems. A good set of corrective action might be employed in addressing the more serious situation of symptoms, hence resolving panics that might arise from the moments of loss of the fiber optic facilities.
A: OM3 and OM4 are both multimode optical fibers, however, they have varied bandwidth as well as distance potentialities. For instance, while OM3 has bandwidth limitations with 2500 MHz.km of distance, the OM4 fibre cables are better optimised at this bandwidth with up to 4700MHz.km which is more suitable for longer distance runs that require faster data rates especially at 10GB Ethernet applications.
A: OM1 fiber optic cables are generally limited to use in indoor applications because of the backward specific bandwidth and minimum distance performance. What is more, for outside use it is recommended that a more durable outdoor fiber optic cable such as OM3, OM4 or other non standard fiber optic cable, such as outdoor- armored-fiber-optic-cable is utilized.
A: Single mode fibre cables are recommended for long distances because of their low attenuation & higher bandwidth fibres. Such cables are most appropriate for outside use where there is a requirement for higher data rates and longer distances, as is the case of telecom and data centres.
A: Two fibers go into a duplex fiber optic cable that facilitates the establishment of two-way communication with the provision of sending and receiving information. However, within a simplex fiber optic cable, there is only one fiber, which operates in one direction only and does not allow the receiving of data at the same time. Such duplex cable connection is frequently applied to connect two components for bidirectional data transfer. This connection, for instance, LC to LC, requires a two-way transmission.
A: The direct burial fiber optic cables do not require any extra conduit since they are ready to be buried under the cicumstances of soils and therefore do not require cumbersome channeling. Cables are constructed of durable materials that help resist unfavorable weather conditions such as the heat, moisture, movement and wear of the fiber for long distances in the open.
A: The outdoor armored fiber optic cables have an added efficient level of protection from the mechanical harm by pressure or by rodents because of the presence of an armored layer around the cable. They serve well in outdoor installations that are sophisticated such as those that require stable curvature.
A: The LC connection is adopted for high-density mass fusion splicing setups. LC connectors are beneficial in securely and efficiently joining single mode or multimode fiber optic cable patches. Especially in the High rate data transmission applications such as 10GB ethernet.
A: Such cables are made from plenum rated materials that offer low flammability and low smoke production in the event of a fire allowing the safe use of the cables in air spaces such as ducts and drop ceilings. These are critical in indoor use applications which have to adhere to fire safety codes.
A: A 10gb multimode fiber optic patch is a short cable used to link the network equipment that is capable of supporting 10-Gigabit Ethernet but only for a short distance mainly within the data facilities or between the data switch and servers. It is mostly used as a fiber jumper for transmission high data rates in applications.