In the realm of optical communication, Single-Mode Fiber (SMF) cables, specifically OS1 and OS2, play a pivotal role. These cables, while similar in many aspects, have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. This article presents a comprehensive comparison of OS1 and OS2 cables, discussing their specifications, performance, and suitable usage scenarios, providing an objective guide for professionals in the field.
Fiber optic technology has revolutionized the telecommunications industry by offering high-speed data transmission over long distances. At the heart of this technology are fiber optic cables, which use light to transmit data. This results in less signal loss, reduced interference, and faster data transmission compared to traditional copper cables. Among the different types of fiber optic cables, single-mode fiber (SMF) cables, such as OS1 and OS2, are particularly noteworthy due to their potential for long-distance data transmission.
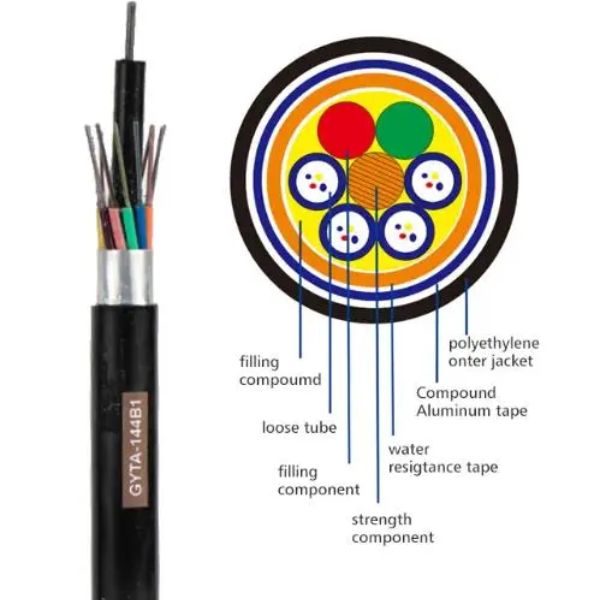
Fiber optic technology uses pulses of light to transmit information from one point to another. This light travels through a fiber optic cable, which is made up of a core, cladding, and protective jacket. The core carries the light signals, while the cladding keeps the light within the core using a principle called total internal reflection. The protective jacket shields the inner components from damage.
OS1 and OS2 cables are both types of single-mode fiber cables, but they have several key differences. OS1 cables are predominantly used for indoor applications and have a maximum distance of 10km. They have a higher attenuation (loss of signal), which is typically around 1dB/km. On the other hand, OS2 cables are designed for outdoor applications and can transmit data over distances up to 200km with an attenuation of 0.4dB/km.
Single-mode fiber cables, including OS1 and OS2, offer several benefits. They can transmit data over longer distances than multi-mode fibers due to lower attenuation rates. Additionally, they have a higher bandwidth capacity, which means they can carry more data at once. This makes them ideal for applications that require high data transmission rates over long distances, such as telecommunications and internet service providers.
| Feature | OS1 Cable | OS2 Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Distance | 10km | 200km |
| Typical Attenuation | 1dB/km | 0.4dB/km |
| Application | Indoor | Outdoor |
When choosing between OS1 and OS2 cables, consider your specific needs. If you need a cable for indoor applications and shorter distances, OS1 could be a suitable choice. However, if you need a cable for outdoor applications and longer distances, OS2 would be more appropriate. Also, consider the cost – OS2 cables are typically more expensive than OS1 cables due to their superior performance.
In the realm of fiber optic technology, single-mode fiber cables, specifically OS1 and OS2, are widely recognized for their ability to transmit data over long distances. The maximum transmission distance is a critical factor in defining their utility and effectiveness in different applications. This article seeks to provide a technical and professional insight into the maximum transmission distances of OS1 and OS2 cables, factors affecting these distances, their optimal applications, and considerations for selecting cables based on transmission distance.
OS1 cables, primarily designed for indoor use, can effectively transmit data up to a distance of about 10 kilometers. This makes them suitable for applications within buildings or campuses where the required transmission distance is relatively short.
Contrastingly, OS2 cables, engineered for outdoor applications, exhibit superior performance in terms of transmission distances. They can efficiently deliver data over an impressive distance of up to 200 kilometers. This makes them the preferred choice for long-haul networks and metropolitan area networks (MANs).
Several factors can affect the transmission distances of fiber optic cables:
The transmission distances of OS1 and OS2 cables make them ideal for different applications:
When selecting cables based on transmission distance, consider the following:
Optical fiber cables are the backbone of modern communication networks, enabling high-speed data transmission over long distances. Single-mode fiber (SMF) cables, specifically OS1 and OS2, are particularly noteworthy due to their potential for long-distance data transmission and minimal signal loss. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the core size and performance of OS1 and OS2 fiber cables, compares their specifications, discusses mode conditioning, offers tips on maximizing performance, and outlines the standards governing these cables.
The core size of a fiber optic cable is crucial to its performance. Both OS1 and OS2 cables have a core size of 9 micrometers, which allows for minimal signal dispersion and maximum transmission distance. This small core size enables single-mode transmission, where only one light path (mode) travels through the fiber, minimizing signal loss and increasing bandwidth.
| Specification | OS1 Cable | OS2 Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Core/Cladding Diameter | 9/125 µm | 9/125 µm |
| Maximum Distance | 10 km | 200 km |
| Attenuation | 1 dB/km | 0.4 dB/km |
| Application | Indoor | Outdoor |
Mode conditioning is a technique used in single-mode fiber cables to improve signal quality. It involves launching a laser into a multi-mode section of the cable before it enters the single-mode section. This process reduces differential mode delay, a phenomenon that can cause signal distortion in long-distance transmissions.
Maximizing the performance of OS1 and OS2 fiber cables involves several considerations:
Several standards govern the specifications and performance of OS1 and OS2 fiber cables:
With their high-speed data transmission capabilities, single-mode fiber cables like OS1 and OS2 are critical components of modern communication infrastructures. Their unique properties make them suitable for a variety of applications across different industries and environments. This article provides an overview of the practical applications of these cables, discussing industries suited for OS1 cables, advantages of OS2 cables in specific applications, key considerations for integrating these cables in networks, performance, and reliability analysis, and real-world case studies of OS1 and OS2 implementations.
OS1 cables, with their design optimized for indoor applications and shorter distances, are ideal for industries where the network infrastructure is confined within a single building or campus. These include:
OS2 cables, designed for outdoor and long-distance applications, offer significant advantages in specific scenarios:
When integrating OS1 and OS2 cables into networks, consider the following:
Both OS1 and OS2 cables offer high performance and reliability. OS1 cables, while limited to shorter distances, provide reliable data transmission within buildings. OS2 cables, despite being more expensive, deliver superior performance over long distances and harsh outdoor conditions, making them a worthy investment for specific applications.
The selection of the right fiber cable is a critical decision in designing and implementing an efficient network infrastructure. This decision hinges on a variety of factors, including the specific requirements of your network, the intended application, and future expansion plans. This article provides a comprehensive guide to selecting between OS1 and OS2 cables, offering guidelines for determining the most suitable fiber cable type, providing a comparative analysis for various network configurations, discussing how to future-proof your network infrastructure, and presenting expert recommendations.
Choosing between OS1 and OS2 cables requires careful consideration of several factors:
Here are some general guidelines to help you choose the right fiber cable:
| Network Configuration | OS1 Suitability | OS2 Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Short-distance indoor networks | High | Low |
| Long-distance outdoor networks | Low | High |
| Future network expansion | Medium | High |
| Cost-sensitive projects | High | Low |
Future-proofing your network involves choosing cables that not only meet your current needs but also accommodate potential future developments. While OS1 cables are excellent for current short-distance needs, OS2 cables, with their long-distance capabilities, provide a more future-proof solution for networks expected to expand.
Experts generally recommend the following:
——
A: OS1 and OS2 denote two distinct types of single-mode fiber (SMF) cables, with differences rooted in their composition and performance characteristics. OS1 is purposed for indoor use and offers a reach limit of 2 kilometers. Contrarily, OS2 is intended for outdoor applications, providing a reach capacity of up to 10 kilometers.
A: OS1 fiber is not recommended for outdoor utilization due to its inability to withstand typical outdoor environmental conditions. It finds its optimal use in indoor scenarios like data centers and office infrastructure.
A: The fiber core, the central segment of the fiber where light propagates, is engineered for single-mode transmission in OS1 and OS2 SMF cables. This design allows for transmitting a singular light mode, resulting in lower signal attenuation and greater reach.
A: OS1 and OS2 cables, while both designed for single-mode transmission, are not interchangeable due to variances in their composition and performance. Cable selection should consider the specific application and environment.
A: Key distinctions include reach, jacket type, and outdoor applicability. OS1 cables, designed for indoor use, offer a maximum reach of 2 kilometers and feature a standard tight-buffered build. OS2 cables, suitable for outdoor use, support up to 10 kilometers of reach with a loose-tube construction.
A: OS2 SMF cable features a robust construction, rendering it suited for outdoor installations and exposure to harsh weather conditions. The superior durability and extended reach of OS2 make it an ideal choice for outdoor long-haul deployments.
A: OS1 and OS2 SMF cables are classified based on performance specifications, including maximum reach, environmental suitability, and build type. This categorization aids users in selecting the most suitable fiber cable for their networking needs.
A: OS2 SMF cables can be employed for indoor use, particularly in scenarios demanding longer reach and robust build. However, OS2 cables typically incur higher costs than OS1 cables. Therefore, the decision to use OS2 indoors should take into account network requirements and budget constraints.
A: The comparison between OS1 and OS2 SMF cables informs network design decisions, offering insights into reach capabilities, suitability for diverse environments, and cost considerations. This allows network designers to make well-informed choices, ensuring optimal network performance and reliability.
A: Both OS1 and OS2 SMF cables can withstand bending within specified limits without significant impact on performance. However, compliance with the recommended bending radius is crucial to prevent fiber stretching and ensure signal integrity during installation and operation.
——