In the realm of network technology, efficiency is paramount. One innovative solution that substantially enhances this efficiency is the IEEE 802.3bt High Power PoE (Power over Ethernet). This standard offers a robust and reliable method for data transmission and power delivery, significantly optimizing network performance. This article delves into the intricacies of IEEE 802.3bt, its applications, and how it can be leveraged to maximize network efficiency.
——
The IEEE 802.3bt standard, commonly referred to as High Power Power over Ethernet (PoE), is an expansion of the original power over Ethernet concept, designed to accommodate a higher power output over Ethernet cabling. This enhanced standard allows for up to 90 Watts of power to be delivered through a single Ethernet cable, enabling support for a more comprehensive array of devices, including those with substantial power demands, such as pan-tilt-zoom cameras and advanced IP telephones.

Power over Ethernet, or PoE, is a networking feature defined by various IEEE standards, allowing Ethernet cables to carry both data and electrical power to connected devices. This alleviates the need for additional power supplies or outlets, streamlining the installation of networked devices, especially in challenging locations. PoE is a foundational technology that has been widely implemented in numerous networking environments due to its simplicity and efficiency.
The IEEE 802.3bt standard introduces enhanced capabilities to the PoE family by doubling the available power per port while simultaneously making it possible for multiple powered devices (PDs) to be supported via a single PSE (Power Sourcing Equipment). This standard is backward compatible with its predecessors, ensuring interoperability with existing infrastructures while providing a future-proof solution for emerging high-powered devices.
The IEEE 802.3bt, or high power PoE (Power over Ethernet), offers numerous advantages that can significantly enhance the efficiency and convenience of network installations.
While IEEE 802.3bt delivers these considerable benefits, it’s important to understand that appropriate network design and cable management strategies are essential to handle the higher power levels and prevent issues such as overheating. Thus, careful planning and consideration should accompany the adoption of this high-power PoE standard.
——
The IEEE 802.3bt standard functions by employing all four pairs of wires within a standard Ethernet cable, as opposed to older standards that only used two pairs. This allows for increased power to be transmitted alongside data through a single cable. It employs advanced techniques such as negotiation between the power sourcing equipment and the powered device, ensuring a safe and efficient delivery of higher levels of electrical power.
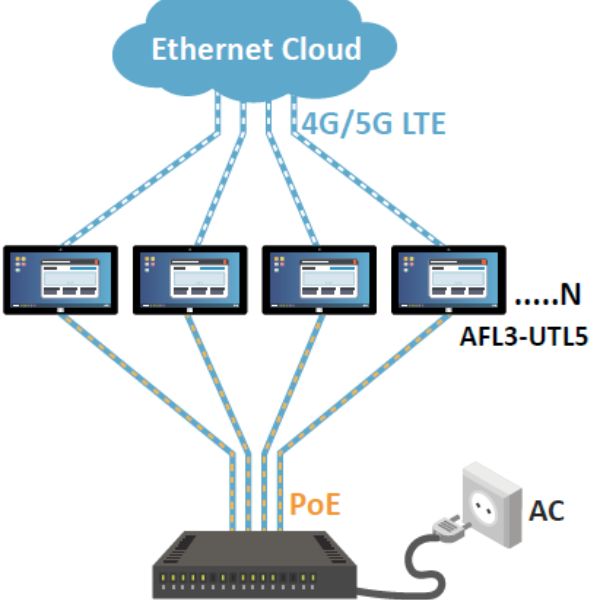
PoE switches play a critical role in an IEEE 802.3bt high-power PoE setup by performing the dual functions of managing data connectivity and providing power. They actively negotiate with connected devices to determine the exact power requirements, manage power allocation, and prioritize system power resources to maintain optimal operation within network infrastructures.
Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology has revolutionized the field of networking by offering a convenient method to transmit both data and electrical power simultaneously over an Ethernet cable. The latest advancement in this field is Type 4 PoE, also known as 4PPoE (Four-Pair Power over Ethernet).
Type 4 PoE is defined by the IEEE 802.3bt standard, which expands the capabilities of power delivery up to a maximum of 90 Watts. This is a significant increase compared to its predecessor, Type 3 PoE, which delivers up to 60 Watts.
This enhanced power delivery capability of Type 4 PoE can effectively support a broader range of devices, including high-performance wireless access points, advanced surveillance cameras, and even certain types of lighting systems.
However, it’s important to note that the increased power delivery comes with specific considerations. For instance, heat dissipation could be a concern due to the higher currents carried by the Ethernet cables. Therefore, proper cable management and cooling mechanisms should be implemented to prevent overheating and ensure reliable operation.
In conclusion, Type 4 PoE presents a powerful solution for businesses and individuals seeking to streamline their network infrastructure and support power-hungry devices. However, understanding its power delivery capabilities and potential challenges is crucial in maximizing its benefits.
PoE injectors serve as an intermediary device that adds power to a data cable, enabling the deployment of high-power PoE to devices without requiring upgrades to existing PoE switches. They are essential for expanding network capabilities by facilitating the integration of high-power devices into a network’s power infrastructure without necessitating a complete system overhaul.
The concept of a power budget in IEEE 802.3bt high power PoE is crucial for network administrators to comprehend. It represents the total amount of power available for distribution among connected devices. It is vital to ensure that the power-sourcing equipment is capable of supplying adequate power to operate all powered devices efficiently without overloading the system.
IEEE 802.3bt is designed to integrate seamlessly with existing PoE infrastructures, including earlier IEEE standards like 802.3af and 802.3at. By providing backward compatibility, it ensures that upgraded high-power PSE can still power legacy devices while delivering the enhanced power capabilities necessary for new high-power devices—ensuring a smooth transition and investment protection for organizations upgrading their networks.
——
When contemplating the implementation of IEEE 802.3bt High Power PoE, decision-makers must evaluate several technical factors to ensure a robust and efficient network. These considerations include assessing the power requirements of current and future PoE devices, guaranteeing compatibility with existing network infrastructure, evaluating the quality and capacity of Ethernet cabling, and planning for potential scalability and power management strategies. Additionally, understanding the impact on network architecture and deployment costs is crucial for an effective implementation.

The endeavor to power high-power PoE devices using IEEE 802.3bt involves determining the power levels necessary to sustain device operation and facilitate peak performance. Devices such as PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom) cameras, digital signage, and thin clients could require power levels exceeding legacy PoE standards. Integrating IEEE 802.3bt-enabled PSE (Power Sourcing Equipment) and PDs (Powered Devices) necessitates a detailed power consumption analysis to ensure adequate power allocation without jeopardizing network integrity.
The efficient design of PoE networks is a foundational component for maximum power utilization. Strategic planning must account for the power loss in cabling and the distribution of power across the network to minimize waste. By optimizing the layout and deployment of network switches and considering the use of power-efficient PoE devices, organizations can achieve an eco-friendly and cost-effective infrastructure that aligns with IEEE 802.3bt capabilities.
Adopting high-wattage power over Ethernet presents its unique set of challenges, including heat dissipation, voltage drops, and potential safety concerns due to increased power transmission. Solutions encompass selecting appropriate cable types and gauges, implementing active cooling mechanisms, and deploying intelligent PSE that can monitor and manage power delivery dynamically to maintain system reliability and safety standards according to IEEE 802.3bt specifications.
Understanding the compatibility of high-power PoE with different Ethernet cables is indispensable. Not all cable types offer the same level of conductivity or heat resistance, which are critical factors under the increased power load of 802.3bt. Network designers must verify that the cable infrastructure, including the category and shielding specifications, is suitable to handle the higher power levels without degradation over time, adhering to TIA/EIA industry standards.
The administration of power delivery and management in IEEE 802.3bt networks necessitates a sophisticated level of planning and technology. Implementing intelligent network management solutions allows for real-time monitoring and control of power resources, ensuring optimal distribution and energy savings. Balancing the power supply across multiple high-power devices without impacting performance is pivotal, as is considering redundancy and failover capabilities to bolster network resilience.
——
The evolution of IEEE 802.3bt High Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology has catalyzed a significant shift in the capabilities of network-powered devices, introducing advanced methodologies for delivering power over Ethernet cables. These advancements have been geared towards increasing the maximum power levels, enhancing efficiency, and expanding the range of applications. The integration of more robust power management features and the development of sophisticated PoE chips and systems reflect the ongoing innovation within this domain.
As Ethernet technologies advance towards 10 Gigabit and beyond, the adaptation of high-power PoE to support Gigabit speeds is a critical development. The combination of high-speed data transfer and elevated power delivery through a single cable streamlines the infrastructure for high-bandwidth applications, including advanced surveillance systems and data centers, thereby driving the adoption of Gigabit PoE in sectors demanding both high-power output and rapid data transmission.
The realm of Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) for high-power PoE is experiencing an influx of innovation. Present trends indicate a shift towards more intelligent power management systems capable of delivering enhanced efficiency through sophisticated techniques such as per-port power prioritization and real-time power level adjustments. Additionally, the miniaturization of PSEs facilitates their integration into a more comprehensive array of devices and reduces their overall energy footprint.
With the ratification of IEEE 802.3bt, a significant impact on power and data transmission requirements has been observed. The augmented power capabilities necessitate reexamining safety protocols and refortifying infrastructure specifications. This standard prompts network administrators to reassess traditional power and data transmission systems, ensuring compatibility and optimizing for a future where increased power delivery is an operational standard.
In network equipment, high-power PoE switches and injectors have undergone substantial technological enhancements. These innovations are characterized by improved power efficiency, increased port counts with high-power output, and the ability to manage expanded power budgets. Manufacturers are also emphasizing creating more resilient network equipment that can maintain high-power output amidst varied environmental conditions.
The trajectory for high-power PoE technology promises continued innovation and an expanding scope of application. Future developments are likely to focus on increasing power efficiency, enhancing the adaptability of power delivery mechanisms, and enriching the management features to accommodate the growing demand for Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Further advancements in semiconductor technologies may also pave the way for novel PoE applications, redefining the limits of power delivery through network cables.
——
Selecting the suitable IEEE 802.3bt High Power over Ethernet (PoE) solution requires careful consideration of various technical specifications and network requirements. This decision can significantly influence your network’s capability to deliver power efficiently to devices such as wireless access points, IP cameras, and VoIP phones. It is essential to ensure that the selected PoE solution meets current needs while also allowing for future scalability and technological growth.
——
When selecting high-power PoE (Power over Ethernet) devices, there are several important considerations to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
In conclusion, a thorough evaluation based on these factors will assist in selecting high-power PoE devices that meet your specific requirements, ensuring a robust, efficient, and scalable network infrastructure.
High-power PoE solutions on the market diverge significantly in terms of port count, power budget, and additional functionalities such as layer three switching or support for legacy devices. Comparing these solutions involves evaluating not only the upfront costs but also the operational efficiency and potential cost savings due to reduced energy consumption or minimized need for electrical cabling.
A scalable and flexible IEEE 802.3bt infrastructure is critical to adapt to evolving technological demands. This requires a forward-looking approach in selecting equipment that not only accommodates the current density of PoE devices but also the anticipated growth and the integration of emerging technologies. Acknowledging the importance of network architecture that can nimbly adjust to changing needs is crucial for a successful long-term deployment.
Case studies offer valuable insights into the practical aspects of implementing high-power PoE networks across diverse environments. Best practices culled from these real-world applications typically highlight the importance of thorough planning, careful assessment of power requirements, and consistent adherence to industry best practices to foresee and mitigate potential obstacles.
To optimize power delivery and efficiency in IEEE 802.3bt networks, it is imperative to employ a holistic view of the entire network design. Guidelines emphasize the significance of meticulous power management, quality of service (quality of service) configurations, and proper load balancing. Efficient power delivery is also facilitated by the deployment of advanced PoE management tools that can provide detailed insights and control over the power being used by each connected device.
——
A: It is an enhanced PoE standard enabling up to 95 watts of power per port for a range of energy-intensive devices.
A: High power PoE simplifies infrastructure by merging power/data delivery and offers cost-effective, scalable deployment flexibility.
A: High-power PoE switches deliver up to 95 watts per port, exceeding standard switches, which typically offer up to 30 watts.
A: Devices such as advanced wireless access points, high-end IP cameras, and other devices requiring substantial power are compatible.
A: PoE type 3 offers up to 30 watts, while type 4 provides up to 95 watts, accommodating devices with higher power needs.
A: It consolidates power supply needs, driving high-performance devices while streamlining installation and maintenance.
A: A splitter divides power and data for non-PoE devices, extending PoE benefits to a broader range of equipment.
A: Power demands and consumption rates of devices should align with network power budgets to prevent exceeding limits.
A: Besides increased power output, these switches support newer standards and higher power budgets and often include redundancy features.
A: They decrease the need for supplementary power sources while facilitating cable management for various PoE-enabled devices.
——
Here are ten reliable sources that provide valuable information about maximizing network efficiency with IEEE 802.3bt High Power PoE Solutions:
These sources provide a comprehensive view of the applications and benefits of IEEE 802.3bt High Power PoE Solutions in maximizing network efficiency.