The modernization of telecommunications would not have been possible without the use of LC fiber optic connectors, which offer high-speed data transmission over longer distances with minimal signal loss. This advancement would not be possible without LC Duplex Connectors. Their ability to guarantee proper positioning and link between fibers makes them essential. Of all connector types, the LC Duplex Connector remains in great demand because of its small size and effective results. Such broad use of this connector gives rise to various perspectives, including the design features, application areas, and, most importantly, the advantages of this device. Consequently, the reader will become aware of why such an LC Duplex Connector is commonly used to ensure great connection among the fiber optics in the contemporary world.
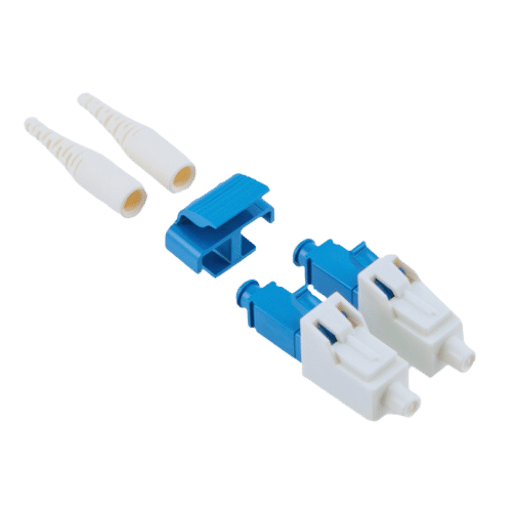
The LC Connector, once known as the Lucent Connector, is a single-fiber optical connector invented by Lucent Technologies and belongs to the small form factor category of connectors. Its application is common for joining optical fibers in places with high-density usage. The LC connector uses a 1.25mm ferrule, half the size of an SC connector ferrule. Hence, more ferrules can be connected in a small area. Its push-pull feature helps in easy connection and disconnection of the cable while protecting optical fibers from moving too much and losing signal. These attributes have aided its widespread use in many modern telecommunication and data communication networks when added to the efficiency, low cost, and usability of the LC connector for both single-mode and multi-mode fibers.
More than a century and a half after the invention of the first telegraph, a device that allowed faster communication over great distances than any previously conceived fiber optic technologies appeared. They allow data to be transmitted at higher speeds over greater distances. These technological advancements are impressive, starting with the optical waveguide, the core, and a cladding layer, rationalized by bending optical glass and encased in the outer protective layer. Additionally, fiber optic communication is distinguished by low losses, exceptional protection, electrical neutrality, and high transmission security, making it suitable for modern telecommunication systems, including high-capacity intercontinental connections. A promising area here is the application of fiber optic materials in communications, which will be helpful both in sizeable multinational telecommunications systems and in small isolated networks.
The LC Duplex’s low profile makes it a fit for cramped spaces within equipment like data centers and telecommunications devices. In most cases, a small form factor of a connector provides developers with critical economies of space that prove beneficial in recent infrastructural networks. In this case, the insertion of a connector features a latch that increases the force holding the connection and keeps it from separating. This assists in situations with high connection and disconnection cycles for the product. Also, the LC Duplex is widely accepted because it works with both single and multimode networks, making it convenient to use different network applications. Precision-manufactured parts provide an optimal level of insertion loss and consistent quality performance, making the LC Duplex suitable for high-performance networking applications.
LC connectors are appreciated for their size and ease of use in tight spaces, as seen in the case of data centers and telecommunication systems. Their small form factor saves precious space over more significant types of connectors, making them an ideal choice for today’s supported networks. The LC connectors also incorporate a push-pull latching mechanism that allows a secure pull and stable lock up to a source while minimizing disconnection, thus improving reliability. Moreover, they are also quite effective with single-mode or multimode fibers and, therefore, can be used in different network infrastructures. This versatility and their robust construction and precise manufacture make LC connectors an attractive candidate for any network’s optimal efficiency and performance.
“Duplex fiber communication” means the transmission or exchanging of data in both directions at the same time over optical fiber. This is usually done by employing two strands of fiber, where one strand sends the signal, and the other one receives the signal, and this allows for the full-duplex communication mode. Each fiber connector, like the LC Duplex connector, is designed to cope with these circumstances where both ways of inserting or extracting a fiber optic cable or connector are indeed used. Such precise segmentation of the double-way communication through special connectors allows for frictionless data flow. With such dual-sided methods, duplex fiber communication systems can provide high-volume transfer of information, which is crucial for up-to-date telecommunication systems. The application of duplex communication is important in areas like the Internet and cloud computing, which require balanced two-way traffic.
The centers of another cross on an LC connector’s axes, that is, the LC’s center of another cross, contain multimode fibers that help to maintain high bandwidth communication within confined spaces, such as data centers, local area networks, and other limited areas. Such fibers enable several modes or light paths to propagate simultaneously, becoming too much modal dispersion. Still, they are quite well controlled in the layout and design of LC multimode connectors. Most of the time, the core diameter of the multimode LC connectors is greater than that of the single mode to accommodate light generated by the ordinary multimode laser emitters, mainly where the area or cost is being considered. Therefore, LC multimode connectors go hand in hand with those areas that require rapid data transmission while maintaining low costs for better network integration.
Due to their compact design, LC connectors are favored in fiber optic applications because they make it easier to install high-density networks, which is essential for the current technological infrastructure and requires saving space. Their push-pull mechanism helps to minimize the risk of fiber damage, thereby reducing maintenance complexity. Moreover, LC connectors can deliver high performance with low insertion loss and high return loss, giving assurance of signal integrity and network reliability. Such attributes would render them suitable for use in data centers and telecom networks where high-volume capacity data transmission is of utmost importance.
In answering the “Standard LC Specifications and Compliance” issue, LC connectors’ parameters adhere to a set of standards that ensure their interoperability and functionality in a wide range of fiber optic networks. Most connectors’ compliance falls under the TIA/EIA-604 FOCIS-10 classification, which outlines their physical and mechanical features. Their structure usually contained a 1.25mm ferrule (made of zirconia ceramic), providing considerable accuracy and durability. In terms of compliance, they satisfy IEC 61754-20, which offers additional parameters for performance and reliability. It is these specifications and standards that guarantee LC connectors provide the required high quality and operational performance in a variety of applications and, at the same time, meet current industrial standards.
The first thing to remember when looking at the OM3 Fibres and Single Mode fiber optic options is that their subsystem applications and performance characteristics differ slightly. According to Western sources, OM3 Fibres are intended explicitly for multimode transmission and have a wide range of applications in communications spanning three hundred meters with data rates of around 10 Gbps. They serve cost optimization in local area networks (LANs) and data centers, as long distances are not used to stretch high bandwidth. However, single-mode fibers have a small core diameter, and therefore, only one mode of light goes through the fiber; therefore, they are capable of long-distance communication. This property leads to low attenuation and distortion, which is ideal for telecommunication and large network backbone applications. Single-mode fiber optic cables are known to be more expensive since they are used for a wider range of applications, but on the other hand, they are guaranteed to provide a consistently high bandwidth over long distances, which has a lot of demand in certain situations.
In fiber optics, cabling is intricately designed to address physical traits and apply color coding to enhance swift detection and installation. According to TIA/EIA-568-C.3, standard OM3 cables are identified as aqua munching color; this aids the technicians in getting appropriate information concerning the type and functioning of the cables. The cable jackets are designed to be durable and resistant to environmental factors, providing protection and ensuring longevity in various installations. Single-mode fibers, identified by their yellow jackets, are also color-coded by the standard requirements to help the organization and upkeep of the network by providing easy visibility. These standardized color codings, as seen in current industry-practicing websites, facilitate the rapid and accurate identification of fiber types, reducing the risk of errors during network configuration and maintenance operations. The overall color and design-related stipulation conform to international standards to ensure maximum efficiency when deployed in different settings.
It is essential to have regular performance ethics; it will begin with inspecting the connectors for dirt, dust, and discoloration at regular intervals. A fiber optic cleaning kit and fiber optic diagnostic testing such as Fiber One-Way Link Testers can be used, which measure in one direction and help identify potential problems at multiple circuitry points. Do not blow compressed air on the contact since it can also throw dust particles into the optical connector. As a precaution, always use the provided caps on all unused connectors to protect their end faces. Through these measures, the chances of transmitting errors through data are minimized, which increases the efficiency of the fiber optic system.
When using LC connectors, it is essential to note that these types offer tools and techniques for creating efficient connections. Some of the most widely employed tools are precise fiber cleavers that provide even cuts on the ends of fibers. Furthermore, a high-end crimping tool ensures that the spindle side of the duplex fiber connector is tightly secured to the fiber optic cable. Visual Fault Locators (VFL) are great for detecting faults using a laser light that illuminates broken or defective cable sections. Other essential cleaning tools include pulled lint-free swabs and cleaning solutions for connectors and different cleaning tools. To assess the fiber optic links for integrity and efficiency, Optical Time-Domain Reflectometers (OTDR) tools are used. These techniques and tools are essential for professionals as long as good fiber optic connectivity is maintained.

Use Cases in Telecommunications
Due to its small dimensions allowing for space-saving arrangements, LC duplex fiber optic Connectors have become indispensable in telecommunications. They are deployed in large volumes in central offices and wiring closets to achieve effective, high-speed, long-distance data transmission. These connectors are compatible with single-mode and multi-mode fibers, allowing use in various telecommunication applications. Their contribution toward reducing the signal loss in telecommunication networks is quite significant, contributing towards enhancing the network reliability with better bandwidth utilization and minimal interference.
Use Cases in Data Centers
LC duplex fiber optic connectors have become crucial in providing interconnects among servers, storage, and networking equipment at very high speeds in data centers. Their small size maximizes space in the data center racks and promotes neat cable management and high port density, which is important for data centers facing unending data challenges. LC connectors in producing these devices also support high-speed communications protocols such as Ethernet and Fibre Channel, which operate at extremely low latencies and high reliability, adding to the already established use of the standard connectors in modern data centers.
LC duplex fiber optic connectors have become one of the most critical components for solutions for contemporary network systems. They make it possible to provide high-performance and dependable interfaces in complex systems. As networks continue to evolve in this era of big data, the compact size of LC connectors permits high-density configurations, an absolute must in enterprise environments. Due to their precision manufacture, LC connectors provide ultra-low signal losses necessary for rapid data transfer over large networks. In addition, LC connectors can work with existing and future devices, thus providing an alternative to upgrading the IT structure. They are easy to install and require little maintenance, making them more suitable for cost-effective, robust network solutions.
The connectivity landscape of fiber optics is undoubtedly dynamic due to rapid technological advancement and the need for faster means of data transfer. Among many, an exciting growth trend for the market is the use of fiber optics with 5 G networks to improve mobile broadband communications and the advancement of IoT networks. Also, interest in the development of bend-insensitive fibers is increasing, which can help cable preserve signals more effectively, and thus, data, even in complicated routing, is more assured. Lastly, passive optical network (PON) usage is increasing, especially in domestic and commercial broadband services, due to their efficiency in bandwidth distribution at lower costs. These trends affect the perspectives of the global connectivity of networks, promising faster networks with improved characteristics because of the requirements associated with contemporary digital communications.
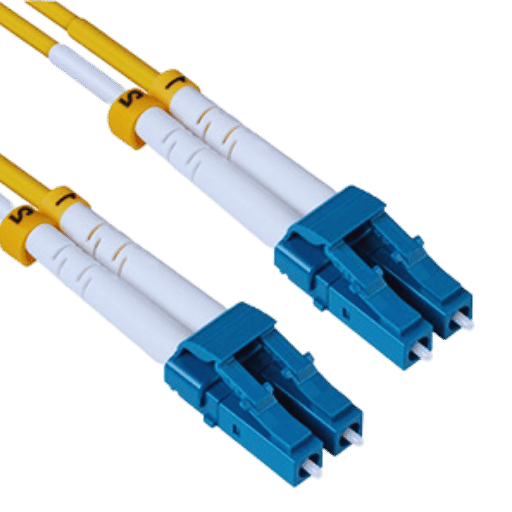
A: An LC Duplex Connector is a small form factor (SFF) fiber optic connector used in high-density situations. It has two fibre connections in a single unit, enabling bidirectional links. Compared with the connectors SC or ST, the LC duplex connectors are smaller, more efficient, and have a lower insertion loss.
A: The components of an LC Duplex Connector include the housing, ferrules, duplex clip, and boot. The housing encloses two ceramic ferrules that fix the fiber in position and alignment. The duplex clip attaches two simplex connectors, while the boot relieves strain on the cable. Further, the connector has a latch that engages with a receptacle on the adaptor or transceiver to establish stable connections.
A: LC connectors are significantly smaller than SC connectors and are best suited for high-density patch cable configurations. Their performance concerning insertion and return loss is similar, if not better, than that of SC connectors. Also, due to the reduced size of LC connectors, greater port density is possible on networking equipment, which is especially useful in data and telecommunication centers.
A: LC Duplex Connectors can be used with singlemode cables and multimode cables. It can be combined with many cable designs that incorporate patch cables of 2mm, 3mm jacketed, and even duplex assemblies of 900µm tight buffered fibers. Top-speed multimode data transmission cabling also has LC connections on OM3 and OM4 products; however, singlemode cabling is also usable for longer connections.
A: Every application has criteria that help it select the type of connection, whether PC or APC. PC connectors are applicable in most applications since they have a flat end face, and their return loss performance is acceptable. But in duplex LC configurations with high power or sensitive applications, the return loss performance is critical, and this is where Gerber APC connectors come into play. In Fiber to the Home (FTTH) networks, the singlemode fibers are usually connected using APC connectors.
A: Optical Loss Values should be included in the pertinent contract clauses in lease agreements. A high-grade, reliable duplex connector for LC is estimated to have an operative insertion loss equal to or less than approximately 0.3 dB. The low loss value of LC connectors makes them very suitable for use in high-performance optical networks. The actual insertion loss, however, can be influenced by factors such as the type of fiber, the polish of the connectors, and the quality of installation, among others.
A: Yes, LC Duplex Connectors are produced in different colors. The most popular colors are beige and blue, where beige color is for multimode fibers while blue is for singmode fibers. The Omni directional Media standard is now reaching for a higher bandwidth. The term Aqua is used for OM3 and the OM4 multimode fibers. These color codes assist technicians in color coding the fibers to make it easier to pinpoint the exact fiber type in mismatches, preventing them from cutting or removing the wrong fiber. Manufacturers also use other colors for their customers with special projects or to support the connections of multiple multimode duplex networks.
A: To care for LC Duplex Connectors, the fiber end face should be wiped and cleaned regularly by using tools specially designed for the task, such as fiber optic cleaning pens or cassettes. It is advisable not to touch the ferrule tip with bare hands. Always replace the dust caps on connectors whenever they are not being used. For more aggressive contamination, cleansing with lint-free wipes and isopropyl alcohol may be recommended. Proper cleaning also reduces the chances of damage being inscribed on the fiber end face, thereby providing low insertion loss.