FS boxes are a must-have for any residential or commercial electrical system where electric switches, outlets as well as connectors need to be located securely. It is important to know the different types of FS boxes, their purposes, and which additional equipment can help them work best for anyone involved in electrical work. This piece covers everything there is about FS boxes and their covers, including specifications with classifications given, installation procedures, and safe practices that guarantee an effective power connection setup. If you have been doing this job for long or just trying out new things at home, then let this manual serve as your resourceful companion on matters pertaining to FS boxes and covers, too.
What is an FS Box?
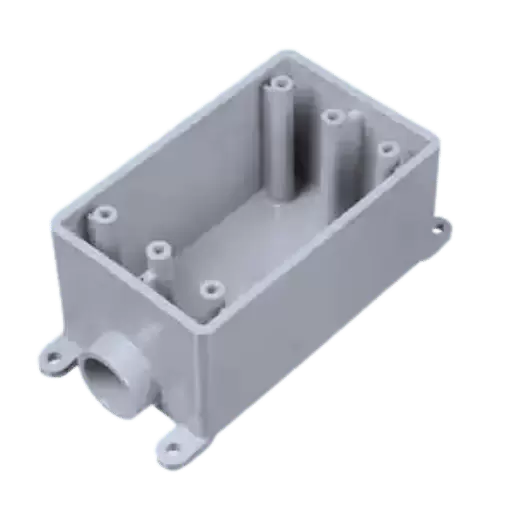
FS Box Definition and Components
An FS Box, called also a device box, is an electrical enclosure used for switches, outlets and other devices. It is typically made of metal or tough plastic material and serves as insulation and structural support for electrical connections. An FS box comprises housing proper; brackets/holes for mounting; pre-cut conduits entries that make wiring easy.
Difference Between FS and FD Boxes
FS boxes and FD boxes are two types of device boxes in electrical installations with slightly different functions and unique characteristics.
In terms of designs and uses, FS is a single-gang box that accommodates one device, such as a switch or outlet. It is shallow and has only one conduit entry point, so it fits well when there is limited space behind the wall.
On the other hand, FD box is deeper than FS. It can hold multiple devices or larger ones that need more wiring room. An FD may be a single-gang, double-gang or bigger configuration which allows for more devices and greater complexity of wiring.
Below are some specific details about FS versus FD boxes:
Dimensions and Size:
- FS Boxes: Typically have a depth of about 1.5 to 2 inches.
- FD Boxes: These are deeper than FS boxes at around 2.5 to 3.5 inches deep (or even deeper) to accommodate extra wires needed for larger devices like motors, etcetera.
Capacity:
- FS Boxes: Smaller size limits them to housing just one device at a time.
- FD Boxes: These can contain numerous appliances simultaneously or big-sized gadgets, thereby providing enough space for intricate wiring systems.
Conduit Entries:
- FS Boxes normally have one or two points where conduits enter; if necessary, these points can be fitted with hubs for better connection security.
- FD Boxes: They come with many conduit entry points on all sides thus allowing versatile methods of connecting wires through them .
Materials:
- FS Boxes: Most commonly made from metal but also available in durable plastic materials suitable for regular applications where they will not be exposed too much moisture etcetera which could cause rusting etc..
- FD Boxes: They are often made using stronger substances that meet stricter regulatory standards, particularly applicable within commercial establishments like malls, offices, hotels, factories, and schools. Such places often require robustness in design, thus malleable iron boxes are used alongside high-quality transceivers, etcetera.
Knowing these variations is essential in selecting the right box for any electrical installation since proper selection ensures safety, compliance with electrical codes and overall system efficiency.
Common Uses of FS Boxes
Because they are small and strong, FS boxes are adaptable and popular in many electrical settings. Below are some examples:
Residential Wiring:
- In houses, FS boxes often hold one switch or receptacle each. This works well because it allows them to be very compact.
Outdoor Installations:
- People put these outside to keep connections safe from the weather. These work for garden lights, outlets on the exterior of buildings, etc., and you can use them anywhere you need electricity outside.
Industrial and Commercial Settings:
- FS boxes can also function as enclosures for control switches and other individual devices in industrial or commercial environments where there may only be one device per box needed; this way nothing gets lost! Companies love their durability too – being tough means able to handle harsh conditions while remaining reliable.
Surface Mounting:
- If you cannot cut into a wall but have to install something on top, then Surface Mounting is what you want. These are designed for either walls or ceilings, so they are a good choice when retrofitting!
Knowing how versatile FS Boxes can be will help anyone choose an enclosure that best suits their needs, enhancing safety and efficiency in any electrical project.
How to Choose the Right Device Box?
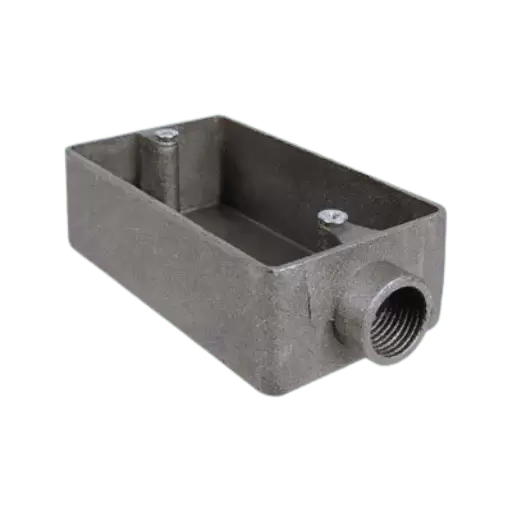

Material: PVC vs. Cast Aluminum
When choosing FS boxes, the choice of material is very important because of its implications on strength, cost and suitability for different environments.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Pros:
- Cheap: Generally speaking, PVC boxes are less expensive than those made from cast aluminum hence commonly used in residential applications.
- Corrosion-Resistant: PVC does not corrode or rust therefore it can be utilized in wet places or regions with a high level of corrosion.
- Lightweight: In comparison to metals, PVC is much lighter thus making it easier to install and putting less strain on mounting surfaces.
- Non-Conductive: Being a nonconductive material means that there is no need for grounding as this provides inherent insulation against electrical faults.
Cons:
- Strength: This type of box lacks strength when compared with metal ones hence may not work well in heavy duty industries where mechanical impact or wear tear is expected to occur frequently.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Extreme cold makes PVC brittle while excessive heat causes deformation so it cannot be used under such conditions.
Cast Aluminum
Pros:
- Strongness: Cast aluminum is extremely durable which enables it withstands huge mechanical impacts thus making them ideal for commercial and industrial applications where robustness required most.
- Heat Resistance: Boxes made out of this material can tolerate higher temperatures than those manufactured using PVC therefore providing reliable performance in areas characterized by frequent temperature variations.
- Shielding: Metal enclosures offer excellent electromagnetic shielding especially if used together with transceivers since they protect sensitive electronic equipments from interference .
- Weight : Although lighter as compared to steel ,cast aluminum maintain considerable amount of strength thereby balancing between durability and ease in handling .
Cons:
- Corrosion: Even though aluminum has better resistance towards rusting than steel ,it still corrodes over time particularly when exposed to acid or salt environments .
- Costs : Usually,costs associated with purchasing cast aluminium boxes are higher than those incurred during acquisition of pvc packages thus might affect budget considerations.
- Conductivity: Due to its conductive nature ,cast aluminum requires proper earthing so as to ensure electrical safety which might necessitate additional installation steps .
To conclude, whether PVC or cast aluminum FS boxes are used depends on where they will be installed. For instance PVC is cheaper, prevents corrosion and easy to install hence applicable in less demanding areas while cast aluminium is more durable, can withstand heat and shield against electromagnetic waves thus suitable for heavy industries and places with strong performance requirements.
Size and Configuration Options
It is fundamental to take into account the size and configuration alternatives while choosing FS boxes for ensuring compatibility with specific installation needs. Both PVC and cast aluminum FS boxes are available in various sizes, which are usually indicated by standard measurements, such as 2×4 or 4×4 inches; these sizes accommodate different numbers of conductors and different levels of electrical load. Similarly, configurations can be single-gang, double-gang, or multi-gang, allowing more than one device or a connection to be integrated within one enclosure. Customizable knockouts and entries that offer flexibility in conduit and cable routing are also common features. It is important to match the size as well as the configuration type of an FS box with what an application requires so that it can be installed securely and efficiently.
Certification and Standards
When choosing and installing FS boxes, it is important to comply with certification and standards. In order for both PVC and cast aluminum FS boxes to be safe and effective, they have to meet specific regulatory requirements. Certifications like UL listing and NEMA ratings are very essential. A product that has gone through UL testing meets high levels of safety, among other things, while NEMA rates an enclosure’s resistance against different environmental factors, including dust, water, or corrosion. Reliability during the installation process can be increased by following these certifications, not forgetting about conformity with local electrical codes and regulations.
What Are the Different Types of Device Boxes and Covers?
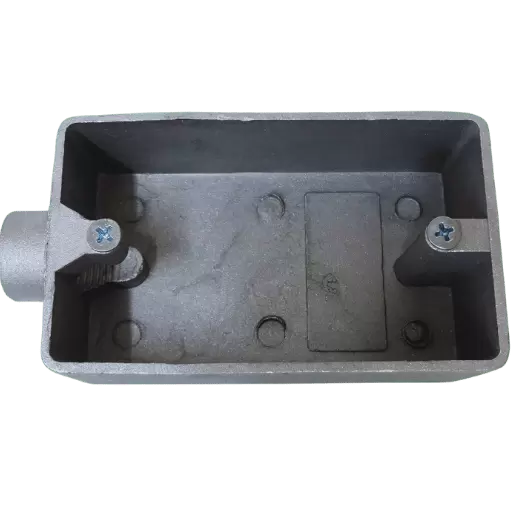

Single Gang vs. Multi-Gang Boxes
The single gang boxes are made to accommodate one electrical device, which could be a switch or an outlet, and they can, therefore, be used in places that have limited space. Conversely, multi-gang boxes position multiple devices side by side to provide a comprehensive solution for intricate wiring specifications. The preference on whether to use single or multi-gang boxes is guided by the amount of appliances the user wants to install and the size of the room available. Multiple-gang boxes are advantageous as they allow several components to be brought together in one housing, thus making installation and maintenance less complex.
Weatherproof and Non-Weatherproof Boxes
Weather-resistant boxes are purposely designed to protect electrical connections and devices from rain, snow, dust, etc. Usually made of strong materials like PVC or metal, they come fitted with seals and gaskets that keep out dampness. They are suitable outdoors or in areas susceptible to moisture and extreme weather.
On the other hand, non-weatherproof boxes are acceptable for indoor use where there is no need to protect them from the surroundings. These ones do not have extra insulating seals and therefore may be applied in homes, offices or factories that are well regulated against climactic extremes. The choice between weatherproof and non-weatherproof boxes largely depends on the place where they will be installed as well as their vulnerability to environmental effects.
Mounting Options for Device Boxes
Device boxes can be installed in a number of different ways depending on the application and the structural environment. Some of the key methods of installation are as follows:
- Surface Mounting: This approach is suitable for situations where it is required to fix the box directly onto the surface of a wall, ceiling or other structure. It is widely adopted in both indoor and outdoor scenarios, often with weatherproof boxes for additional safety.
- Flush Mounting: This method requires the box to be positioned so that it rests flush with the surface of the wall or ceiling, thereby creating a neat and unobtrusive finish. It involves cutting an opening into the wall and securing the box inside the cavity; commonly used in residential and commercial interiors.
- PVC Box Mounting on Surfaces (with hubs for conduit connections typically involved): This is a variation on surface mounting that specifically uses lightweight, non-corrosive PVC boxes—ideal where metal might corrode or non-conductive materials are preferred.
When choosing how to mount your device box, think about what type of structure it will attach to, whether this area is exposed or not, ease-of-accessibility should any maintenance need done thereon, and aesthetic considerations, among others too. Properly installing these units guarantees safety standards are met while adhering to electrical codes governing their use.
How do you install an FS Box in a Conduit System?

Preparation and Tool Requirements for installing transceivers, hubs, and splices effectively.
To install an FS box in a conduit system, it is important that one prepares well and uses the right tools. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to prepare for the installation process and what tools are needed.
Preparation Steps
- Evaluate The Installation Area: Make sure that you choose a place where this device will meet all electric requirements and also be within the local electrical codes. Ensure that there are no barriers around it which may hinder its performance and should also be able to withstand different weather conditions if need be.
- Measure And Mark: Use any measuring instrument so as to determine correctly where the box should be placed then indicate with marks where drilling will take place for accuracy during fixing.
- Switch Off The Power Supply Before Installing Or Modifying Any Hubs Or Transceivers: Always ensure that power is disconnected from an area until work has been completed because failure may lead into dangerous situations caused by electricity.
Tool Requirements
- Drill And Drill Bits For Creating Openings In Malleable Iron Boxes Among Other Surfaces: These are used when making holes through which these structures can get attached. Check whether sizes of bits correspond with screws or wall anchor dimensions.
- Screwdriver Set: Consists of both flathead screwdrivers (slotted) and Phillips head screwdrivers (cross-slotted) designed to tighten or loosen screws, respectively, especially during fastening various components together securely.
- Wire Strippers And Cutters: These help in preparing electrical wires for connection with FS terminal points by stripping off insulation covers then cutting them into required lengths depending on distance between two adjacent terminals.
- Measuring Tape: It is essential in taking accurate measurements of distances so as not make errors while positioning boxes precisely within conduit systems.
- Leveler: This tool is used to confirm whether something being worked on is properly leveled horizontally or vertically before proceeding with other activities like attaching objects to it; leveling ensures stability besides enhancing the aesthetic value achieved after completing construction works, such as mounting cabinets onto walls.
- Conduit Bender: This may be necessary if the bending of conduits is required while installing this device at different angles according to design specifications provided by manufacturers.
- Fish Tape: This tool comes in handy during wire-pulling exercises where one needs to pass cables through pipes easily without much struggle experienced if done manually.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Gloves, safety goggles and insulated tools should always be worn by installers for their own protection against any possible injuries arising from direct contact with live wires or other dangerous parts of electrical systems being worked on.
Having these tools and following the preparation steps will ensure that the installation process of an FS box into a conduit system goes smoothly and is done efficiently.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
- Drill mounting holes: Use the drill and correctly sized drill bits to make mounting holes at the indicated spots. Make certain that they align with FS box’s mountings.
- Install wall anchors: Where necessary, put wall anchors inside the drilled holes for a better grip of screws.
- Mount FS box: Place the FS box over the drilled holes and use screws to hold it in place with a screwdriver. At this step, ensure that the box is level.
- Run conduits to the FS Box using hubs to manage cable entry points efficiently: Shape conduits as required by using conduit bender. Run them to the FS box while making sure they are well secured and aligned.
- Pull wires through conduits: Using fish tape, draw electrical wires through conduits into the FS box.
- Connect wires: Strip wire ends with wire strippers, connect them according to wiring diagram & code requirements within an FS box terminal.
- Secure conduit connections: Check all connections firmly so as not let any movement or wire exposure occur where they attach onto an fs-box.
- Check installation: Go through each connection point, alignment as well as entire setup twice just to be sure everything meets the safety & technical standards of installation.
- Restore power supply: Once everything has been put into place securely and verified, then restore the power supply back on again within such areas where installations were being done earlier.
- Test the system after installing all hubs, splices, transceivers, etc., for proper functionality: Carry out functional tests to confirm whether there is any problem or not on how f.s boxes together with connected systems function.
By doing these installation steps one after another very carefully ensures safe, code compliant and efficient set up of fs-box in a conduit system.
Tips for Ensuring a Secure Installation
- Use Good Materials: Use conduits, connectors and FS boxes that are of high quality. This will ensure that they last for a long time without getting spoilt. Also, it is important to note that low-quality materials may wear out prematurely and even cause safety risks especially in transceivers and hubs.
- Be Consistent With Checking And Maintenance: Always inspect your installation on a regular basis so as to spot any potential problem at an early stage. Pay close attention to the condition of hubs and boxes when carrying out this exercise. Doing consistent checks is one way of maintaining the setup’s integrity, thereby guaranteeing long-term security.
- Adhere To Manufacturer Guidelines: Make sure that you follow instructions given by equipment manufacturers concerning installation and maintenance strictly. These steps are designed with both safety and performance optimization in mind.
- Safety Precautions: Before beginning any installation work, switch off power supply first. This helps prevent accidents like being electrocuted or even death sometimes since electricity can be very dangerous if mishandled. Another thing is to always use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when dealing with such things because they protect one from electrical hazards that might occur during this process.
- Mount malleable iron boxes securely to prevent damage to sensitive electronic equipment: Ensure all parts are firmly fixed together by ensuring that each component gets mounted securely where necessary otherwise, some items might become loose after due to vibrations, among other environmental factors, which can lead to instability in an installation if not well grounded.
- Ensure System Reliability through Proper Wire Management including hubs and splice techniques: Arrange wires properly so that they do not tangle or interfere with each other over time as this may cause wear out leading to failure later on. Proper wire management also makes it easy for one troubleshoot when need be thus enhancing maintenance convenience too.
By following these hints during your wiring exercise, you will greatly increase safety measures while improving the lifetime of electrical systems around you.
What Are Common Problems with Device Boxes?
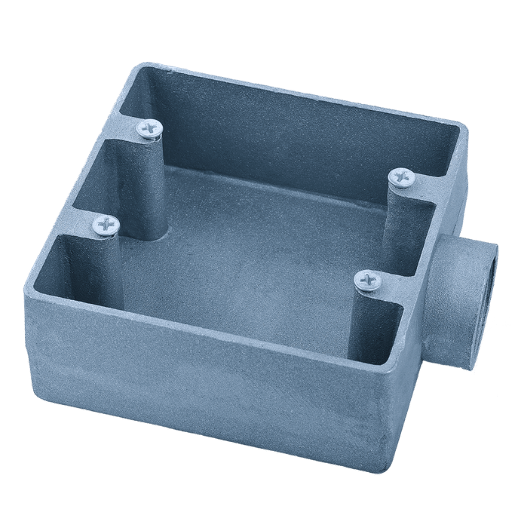
Troubleshooting Connection Issues
- Loose Fittings: Inspect for screws and fittings that are not tight. Fasten any parts that have worked loose to make a firm joint.
- Rust: Check for signs of corrosion or rust, particularly around hubs and transceivers. Clean away affected areas with a suitable product or replace parts as necessary.
- Overloading Circuits: Ascertain whether the circuit is carrying too much power. Either decrease the load on it or fit a device box with higher rating.
- Wire Destruction: Examine wires for fraying or other damage. Substitute any wire which looks like its insulation has been compromised so that it can still work correctly.
- Wrong Wiring: See to it all wires are linked onto rightful terminals according to wiring diagram provided; then do rectifications where necessary.
- Defective Components: Carry out tests on all components found inside device boxes and replace those that are defective in order to bring them back into operation again as required by design.
Maintenance Tips to Extend Longevity
- Frequent Inspections: Conduct routine inspections to detect problems at the earliest possible stage. Examine the components of the device box for signs of deterioration, corrosion or damage.
- Tighten Connections: Periodically assess all connections and fasten them where necessary so that they do not come loose with time.
- Clean Components: Ensure that the device box and its parts are kept clean at all times; no dust or debris should be allowed to settle on them. Use appropriate cleaning agents suitable for electrical parts.
- Seal Gaps: Close off any gaps or other openings in the device box in order to keep out moisture as well as prevent pests from gaining entry into it.
- Upgrade Old Parts: Replace outdated or worn-out elements with newer models that have better performance capabilities and higher reliability standards.
- Monitor Load: Watch closely the amount of current passing through various points within or connected to the device box; this should not exceed its rated capacity. Make necessary adjustments on loads so as not to overload it.
- Professional Servicing: It may be considered wise to arrange for professional servicing after some time has elapsed since installation, say once every six months, just to ensure everything is working fine as expected.
Repairing Damaged Covers and Boxes
- Assess the Damage: Start off by evaluating how far the damage has gone through the cover/box. Check for any cracks, splits or distortions that could compromise it.
- Clean the Surface: In order not to hinder the repair, ensure you clean up the damaged part from dust and other unwanted materials. You can use a soft brush or cloth with appropriate cleaning agents.
- Temporary Fixes: When there are little cracks in an item, you may want to use epoxy or silicone sealants as temporary fixes. Apply on that particular point then let it cure completely according to what is directed by its manufacturer.
- Replacement of Components: Where necessary such as when many parts have been destroyed and this affects structural stability or safety aspects; one should replace whole covers/boxes altogether while making sure that replacements are similar in every aspect with original ones used initially.
- Reinforcement Techniques: For boxes under continuous stress consider reinforcing repaired areas so they become stronger than before by adding extra support like metal brackets or plates which will enhance durability against harsh conditions.
- Preventative Measures: Take precautionary steps against future damages. Install guards around them; also move device boxes into less vulnerable places among others.
- Consult the Manufacturer: It is wise to follow specific guidelines supplied by manufacturers during repair procedures, but if need be, contact their support team for further assistance regarding fixing up different parts related to these device containers.
These stages offer a holistic approach towards dealing with covers and box harms, thus ensuring safety plus functionality continuity of electrical devices.
Reference Sources
Electrical conduit
Sustainability
Management
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is an FS Box, and what are its main uses?
A: An FS Box is a type of device box that primarily works with raceway systems for wire devices. It can act as a conductor-pulling box to help manage and protect electrical wiring. FS boxes are widely used in different industrial and commercial applications.
Q: What materials are FS Boxes made from?
A: Malleable iron, ferrally iron alloy, stainless steel, sheet steel, and non-metallic materials are some of the materials that can be utilized to make FS boxes. Depending on application requirements, each material has its own merits, such as robustness, corrosion resistance, or lightweightiness.
Q: How do FS Boxes improve electrical installations?
A: They offer the strength of protecting electrical connections, used as pull boxes for conductors, and safe enclosure provision, which ensures efficient management of wiring devices, thereby enhancing the power system reliability. This keeps safety intact.
Q: What is the role of gasketed covers for FS Boxes?
A: These items create a watertight seal around FS boxes, thus preventing moisture or dust from entering internal wirings or connections while at the same time keeping them safe from other environmental factors like rain. This feature is very important, especially when dealing with outdoor installations where there may be exposure to harsh weather conditions over long periods.
Q: Can FS Boxes accommodate different types of wiring systems?
A: Yes, they can. Fs boxes are designed to accommodate various conduit systems and fit different wiring devices. They come in different configurations and sizes, like type FSE or FD deep, depending on specific wiring requirements and applications.
Q: What does 1 gang FS Box mean?
A: One gang FS Box denotes a single device box that houses one electrical appliance like a switch or outlet. They are used in residential and commercial electrical installations to provide space for individual wiring devices.
Q: Can I use FS Boxes for heavy-duty industrial purposes?
A: Yes, FS Boxes are appropriate for heavy-duty industrial applications, especially those made of malleable iron and ferroalloy iron alloy. These materials have high impact resistance and durability, which makes them suitable for harsh industrial environments.
Q: What are some typical sizes and shapes of FS Boxes?
A: FS Boxes come in various sizes, such as L, W x H x D, etc., with specific dimensions to fit different uses. These boxes made of malleable iron are installed to withstand rugged conditions. They also have other configurations like L x W x H to meet various installation requirements.
Q: How do I choose the suitable FS Box for my application?
A: There are several things you need to consider when selecting an appropriate fs box, such as the type of wiring system, environmental conditions, and specific electrical devices that should be accommodated, among others. You should think about the material used in making it, its size, as well as configuration based on what your project requires. If need be, consult with a professional or follow manufacturer’s guidelines, e.g., fs.com can help in proper selection.
Q: Where can I buy FS Boxes from?
A: F.s boxes can be bought from different distributors, including fs.com or Crouse-Hinds, who stock varieties depending on the application you want them for with part descriptions attached alongside shipping options plus delivery time frames given, so shop at reputable places where quality is guaranteed along with customer care services also provided.
Post Views: 7,715




