Telecommunications and data transfer have been completely changed by fiber optic technology through faster and more reliable connections. There are different connectors at the heart of this technology, which links fiber optic cables to devices, thus ensuring that they function well and have weak signals. One of these types is called an SC (Subscriber Connector), which is widely used because it can be applied in many ways easily. This piece looks at fiber optic SC connectors in detail, including their designs, benefits, how they should be installed, and some tips for doing so correctly, among other things. Having understood what makes up an SC connector, people will know what choices to make regarding network infrastructure management and upkeep.
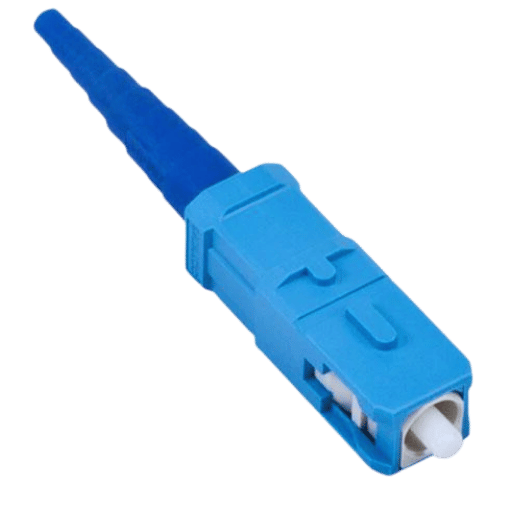

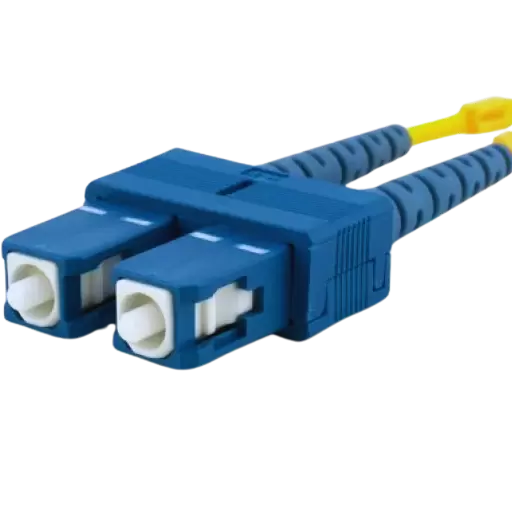
SC connector is a type of fiber optic connector that is rectangular in shape and has a push-pull feature. It works with a ceramic ferrule which aligns the optical fibers for efficient transmission of light. This component works well with both single-mode and multi-mode fibers, thus reducing signal loss and back-reflection. In addition, SC connectors have a locking mechanism to ensure tight connections even in harsh conditions where other types may fail due to vibrations or dust particles, etc. They are very convenient because they can be easily plugged or unplugged without using any special tools; hence, most people find them user-friendly whether at home or in office setups.
Although fiber optic LC connectors and SC connectors have similar uses in optical networks, they are different in terms of design, size, and application. The square shape of the SC connector is larger and typically has a 2.5mm ferrule which makes it ideal for environments with need for strong connections. Conversely, the LC connector is smaller with a compact design that uses a 1.25 mm ferrule thereby allowing for higher density applications within confined spaces.
Both connectors offer low values of insertion loss in as far as performance is concerned but usually sc connectors have slightly better characteristics because its larger ferrule size facilitates more accurate alignment of fibers than lc does. For instance, while sc connectors may have insertion loss values around 0.25 dBs, their counterparts can range from 0.2 to 0.3 dBs depending on the quality and installation practice adopted. Additionally, unlike the lc connector’s latch mechanism, which has been proven ineffective at times, especially when subjected to harsh conditions or environments where vibrations are common, the lock system employed by an sc connector provides better security during connection establishment.
Also, data applications are distinct; therefore, durability becomes necessary with long-haul networks thus making them suitable for use alongside telecommunication data centers appreciate high-density environments hence, should consider working closely together with LC connectors but not exclusively so if we take into account recent trends within modern-day networking industry where space saving measures have become important factor influencing decision making towards selecting appropriate types according to specific performance or environmental requirements among others that must be met.
SC connectors are used in many fiber optic applications because they are strong and reliable. In telecommunications, they are important for long-distance transmission systems. They have a low insertion loss and work very well which makes them perfect for backbone infrastructures that need stable data flow over long distances.
Furthermore, SC connectors are common in data centers. They have a larger size so they can be handled easily during installation or maintenance tasks; moreover their secure lock system guarantees stable connections which reduce downtime and other disturbances. Also, it is not rare to find them in local area networks (LANs) as well as metropolitan area networks (MANs) where durability is required due to high-speed data transfer demands with multiple endpoint connections involved.
Finally yet importantly also video & data broadcasting relies on sc-connectors for media settings based reliable signal transmission. Their performance coupled with durability ensures meeting the requirements set by current communication networks thus exemplifying versatility across industries using different technologies.

To successfully terminate SC connectors, you need to have the following tools:
The availability of such equipment makes it easier to terminate SC connectors within the shortest time possible and achieve successful installations.
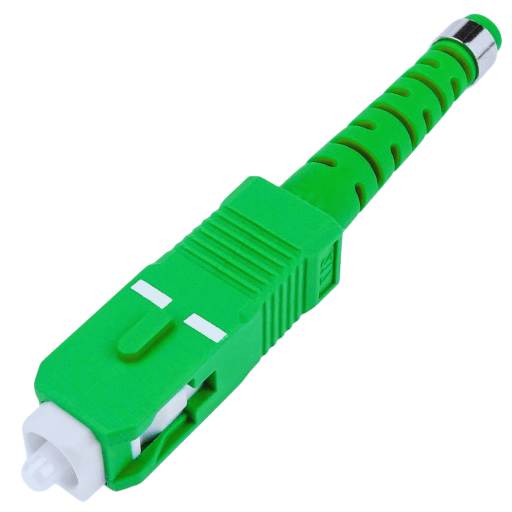

Singlemode SC connectors are made for long-haul communication and use only one light wave. The core of the single mode fiber optic cable is about 9 micrometers wide, which is smaller than that found in multi-mode cables. They can transmit data over longer distances without losing signal strength or getting attenuated, making them perfect for telecoms and data centers, among other applications. To minimize back reflection and maximize transmission efficiency, this type of connector has an end face that is accurately polished at an angle. Also it operates best at either 1310 nm or 1550 nm wavelengths – these being typical values for single mode fibers. This product works well with many devices because its design is standardized, thus allowing easy incorporation into any optical network setup.
Multimode SC connectors are designed for short to medium-range communication, using a larger optical fiber core, which has a typical diameter of 50 to 62.5 micrometers. This allows more than one light mode to move along at the same time in the connector, hence increasing its capacity for higher data transmission rates over shorter distances. They are widely used in local area networks (LANs) and within data centers that require high bandwidth. The multimode SC connector has a slightly angled end-face that helps reduce modal dispersion so as to improve signal quality as a whole. They usually operate at wavelengths of 850 nm and 1300 nm as per multimode fiber specifications. Their standardized design makes them compatible with many types of optical networking equipment.
To choose the right SC connector, you need to know what kind of application you’re using it for and what your bandwidth and distance requirements are. If you’re working with long-distance communications, singlemode SC connectors are recommended because they have very low signal loss and can transmit efficiently at either 1310 nm or 1550 nm wavelengths. They were designed for use in telecommunications applications and inter-building links. However, if your network spans only short to medium distances, then multimode SC connectors will be more appropriate since they can handle higher data rates at shorter ranges due to their larger core size which allows them to support multiple light paths simultaneously – this makes them suitable for use in places such as data centers or local area networks (LANs). You should consider these factors before making any decisions about which type of connector would work best, given that each one has its own advantages depending on the design specifications of the network being built along with its distance requirements as well as desired transmission rates.
It’s vital to clean and inspect SC fiber optic connectors to ensure that they work efficiently and prevent signal degradation. The steps below explain how you can clean and inspect them properly:
Visual Inspection: Use a microscope or a fiber optic inspection camera with high magnification to check the connector end-face. You need to look for things like dust, scratches, or fingerprints because these things can have a huge impact on the transmission of light. A good end-face must be uniformly polished and look shiny.
Cleaning Tools and Materials: Lint-free wipes, isopropyl alcohol (99% pure if possible), and an optical fiber cleaner are some appropriate cleaning tools you should use. Make sure that you don’t use any typical cleaning solutions which may leave residues behind.
Cleaning Process:
Re-inspection: After cleaning, inspect the end-face again under microscope to verify that no contaminants remain on it. If it still looks dirty then repeat cleaning steps until acceptable cleanliness level is achieved as per standards set in your organization or industry.
Documentation: Keep record about connector conditions including what kind of cleaning was done with time/date details etc.; such logs can help in tracking performance of different fiber optic links over time.
Frequency Recommendations: Depending upon the operating environment & usage frequency, regular inspections along with cleanings should be performed at specific intervals; for example, if there are many connections densely packed together or located at dusty places where a lot of debris may enter into them, then monthly inspection might be required, etc.
Following these steps will ensure the reliability and efficiency of data transmission within fiber optic networks by maintaining the integrity of SC connectors.
There are a few reasons why you might need to replace an SC connector:
To ensure that fiber optic networks remain reliable, the proactive replacement of SC connectors should never be underestimated since it can help avoid bigger problems. Hence, regular inspection and testing protocols should also be put in place to determine when they need to be replaced.
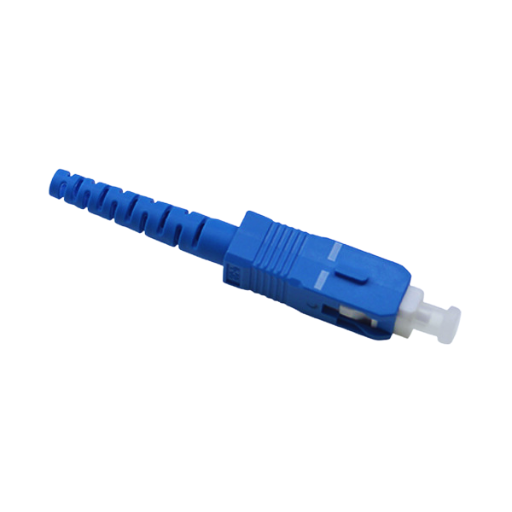

Simplex SC connectors are manufactured for individual fiber connections that only allow signal transmission in one direction. They are used in systems where two-way communication is not necessary, such as point-to-point links. Conversely, duplex SC connectors can hold two fibers to enable simultaneous transmit and receive paths, which makes it best suited for bidirectional communication systems, thereby enhancing faster data transfer rates and better efficiency between servers or switches in data centers, among others. Although the design of these connectors is similar but their usage varies depending on network setup requirements.
APC (angled physical connection) and UPC (ultra-physical connection) are two different ways of polishing SC connectors that affect their performance considerably. The APC connectors have an end-face ferrule with an 8-degree angle polished, which helps in cutting down on the reflection at the back, hence making them best suited for high-performance applications, especially in fiber optic networks where preservation of signal quality is key. Conversely, UP connectors are designed with a flat end face that enhances contact between mating surfaces to reduce insertion loss, though this comes at the cost of increasing back reflections as compared to APC connector types. Generally, whether to choose APC or UPC should be determined by the specific needs of the network since APC is more desirable when dealing with return losses, while UPC works better in places where back-reflections pose minimal threats.
Different designs are included in specialty SC connectors to satisfy different performance requirements in fiber optic networks. The ST (Straight Tip) connector is widely used due to its robustness and simplicity as a bayonet-style connector. It has a 2.5 mm ferrule which makes it suitable for use in areas that need strong connections like data networks and telecommunications.
The FC (Ferrule Connector) connector also uses a 2.5 mm ferrule but differs from others by having a screw-on mechanism that ensures stability under high vibrations where other types fail to provide secure connections. With this type of connectors, insertion losses are kept minimum hence signal integrity remains within required limits especially when dealing with very sensitive signals or working on environments such laboratories and industries among others.
MPO (Multi-Fiber Push-On) connectors are designed for handling many fibers at once through one port thereby greatly reducing cabling needs while simplifying cable management simultaneously where multiple connections can be made using only single connection point such as those found in data centers or telecommunication trunks which require higher density applications otherwise unachievable without sacrificing space efficiency. These connectors have quick deployment capability coupled with high-speed connectivity, thus becoming a preferable option for modern network infrastructures.
In conclusion, every type of specialty SC connector has unique features and benefits that make them suitable for particular uses within fiber optic systems; therefore, an appropriate choice between ST, FC, MPO etcetera should be informed by specific operational demands/constraints together with environmental considerations applicable during installation/implementation process.
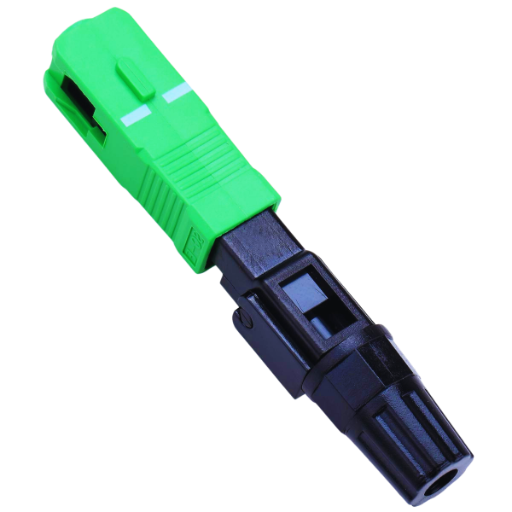

The push-pull coupling mechanism of SC connectors allows for easy and reliable connection and disconnection. It has been widely accepted in both single-mode and multimode applications, which makes it versatile and suitable for use in different environments. In data transmission, the ceramic ferrule ensures accurate alignment with minimal signal loss thereby improving performance. Furthermore, they are built specifically for high-density installations, which help save on space while setting up networks. These types of connectors are also resistant to harsh weather conditions and hence can be applied in various fields such as LANs and telecommunication systems, among others, where they may be exposed to environmental hazards frequently. All-in-all, this component offers a good trade-off between performance, simplicity, and robustness, thus making it an excellent choice for anyone who needs one.
LC connectors of small size and large capacity have been used extensively in current fiber optic systems. This is because they occupy much less space in fiber management units than SC connectors, thereby allowing for greater port density per rack unit, making them more suitable for applications where many connections are required, such as data centers or telecom networks.
To ensure a firm connection that cannot be accidentally pulled apart, LC connectors feature a locking mechanism. They also share with SC connectors the use of ceramic ferrules which enable accurate alignment of fibers hence leading to better signal integrity and lower insertion loss. It has been found out that insertion losses as low as 0.2 dB can be achieved by using LC connector which makes them good for high-performance networking.
Moreover, one does not need any special skills to handle or install LC connectors since they are designed with simplicity in mind. You only need to push its latch down before inserting it into the adapter and then release it when you want to pull it out, thus saving time during the installation process, especially when dealing with multiple connections. These devices come either as single mode or multimode types so that different needs can be met, ranging from home environments up to large-scale enterprise networks. Ultimately, what sets the lc connector apart from other types is its ability to provide both efficiency and versatility without compromising performance, hence becoming the preferred choice for most contemporary fiber-optic installations.
The use of ST (Straight Tip) connectors in various networking applications is common because they are durable and easy to handle. They have a bayonet-style coupling mechanism that enables quick connections which can be locked securely. This type of connectors lowers the risk of being accidentally disconnected by external forces, hence making them suitable for areas with lots of movement or vibration. Besides, ST connectors also adopt a ceramic ferrule like LC connectors do; this ensures accurate fiber alignment and enhances signal integrity while minimizing insertion loss which may be as low as 0.25 dB or 0.5 dB depending on the application.
Another feature that sets ST connectors apart from other types is their compatibility with multimode fiber optics which makes them perfect for use in local area networks (LANs) as well as video transmission systems. Moreover, these connectors have been designed to withstand tough conditions where reliability cannot be compromised due to their robust design. In addition to this, the simplicity involved during the installation process, together with maintenance works related to the ST connector, contributes towards reducing overall downtime experienced within any given system coupled with lowering associated costs for such maintenance activities too, thus making it cheaper than other types available in the market today. As a result, many people prefer using st connectors over any other type currently available since they offer high levels of reliability combined with good performance and are becoming widely used across different industries engaged in networking business.
A: SC Fiber Connector is actually the abbreviated term for Subscriber Connector. It is a standard type of connector used in fibre optic cables and it has simple push-pull mechanism that makes its insertion easy and removal easy. It is popularly used with both single mode and multi mode fibres.
A: An SC fiber connector terminates a fiber patch cable, creating quick and secure connections between different networking components such as switches, patch panels, network devices
A: A patch panel is a device that allows you to manage and organize your network of cables from optic fibres as well as their respective connectors. By use of these fibers and related panels, one can easily access an easier way of connecting or disconnecting the whole group from this particular line.
A : Yes ,SC Fiber Connectors are versatile with ability to support both Single mode fibers which are usually yellow jacketed while multicolor jackets like orange or aqua are employed for multimode ones.
A: In addition to being widely accepted by industry stakeholders, they have many other advantages including low insertions loss therefore making them reliable choice over various optical fibre applications. These benefits include low loss, high repeatability, easy handling among others.
A: There are many varieties of SC fiber connectors including simplex and duplex, which can come in packs such as a 10 pack for bulk installations. This gives one the chance to select depending on the requirements of his or her network.
A: They differ from LC ones that have a ferrule size of 1.25mm while SC ones have a bigger size of 2.5mm. When it comes to durability, ease of use and handling, SCs stand out. However, LCs accommodate more connections per square inch (density) and are thus suitable when space is limited unlike the former which is widely used for different optical cable networks.
A: An optical fiber connector adapter is an apparatus that helps join two separate fiber optic connectors together; hence it enables seamless connectivity between various fibers with diverse cables. These adapters are used by SCs to link with other types or extend their distances.
A: High-speed data transfer applications in data centers often prefer using this type of connector because it can transmit signals at very high rates. The Fiber to the Home (FTTH) application uses this component to provide residents with high-bandwidth internet services among others due its reliable performance characteristics and user-friendliness.
A: Yes they can be fitted over either 3 or 2 mm thick wires without any problem whatsoever but users must remember that also consider meshing them accurately with cables and other items so as not make them incompatible since some networks are wired in different configurations.