Fiber optic technology has acquired the status of a standard in the field of telecommunications, given its capabilities for transferring a large amount of data input, which is essential in a global village. The connectors that enable seamless connections and signal integrity are central to this technology. In this case, attention moves to LC connectors, precisely, the Duplex LC connectors, which are practical and reliable, compact and versatile, and thus they find applicability in many networking situations. In this guide, we will examine the essential points of the Duplex LC connector as well as describe how this particular connector is implemented in various networking systems. It is worthwhile to read through these critical components to see how this connector complements the performance of fiber optic networks designed to achieve maximum systems performance and reliability.
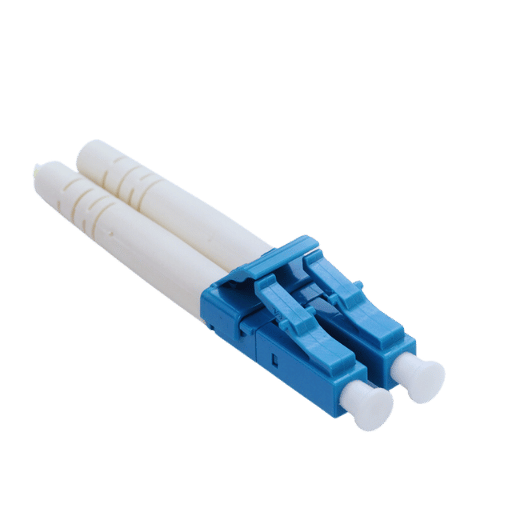

The Duplex LC fiber optic connector is known for its small size and push-pull latch. This consists of two connectors or fibers incorporated into a single housing unit which is economical enough to enable duplex communication; reciprocation and reception operating predominantly. The connector uses a 1.25mm tapered insert which guarantees accurate self alignment and low insertion loss. Such a small form factor is useful for high density applications, particularly in data centers and high end networking environments.
The Lucent Connector has distinct attributes which set it apart from other varieties of optical connectors. It is especially useful in systems where space and accuracy are more important because of its size and performance. Because it employs a ferrule with a diameter of 1.25 mm, which is barely a quarter the size of a conventional SC connector, the area needed to connect LCs in a connectorized solution is largely decreased. This shrinkage assists in the creation of high-density panel forms, rendering them crucial in data centers and telecommunication closets where efficient use of space is a requirement.
Key Specifications:
Within the LC connector, a push-pull functionality has been incorporated and this further prevents the disconnections from being loosened, while the connectors’ duplex orientation enables the fibers to transmit and receive signals in both directions at once. All these attributes work together to improve the performance of fiber optic networks and aid in the transfer of data, which is critical to meeting future telecommunication capabilities within a reasonable timeframe.
The best feature of the LC connector is it’s duplex configuration which serves as a distinguishing feature from simplex connectors. Simplex connectors on the other hand, are designed to only apply a single fiber, thus allowing a uni directional use, while the duplex LC connector supports two fibers thus providing for data sharing in both directions at the same instance. These two usages are the reasons why LC connectors are for high data loads and speeds. The below features highlight detailed differences and specifications between duplex LC and simplex connectors.
Fiber Capacity
Data Transmission
Space Efficiency
Applications
Cabling
These distinctions make LC duplex connectors a preferred choice in modern telecommunications, where efficiency, speed, and space-saving are critical technical requirements.
Modern telecommunication systems rely greatly on fiber optic infrastructure due to its bandwidth capacity and the ability to transmit information over long distances.
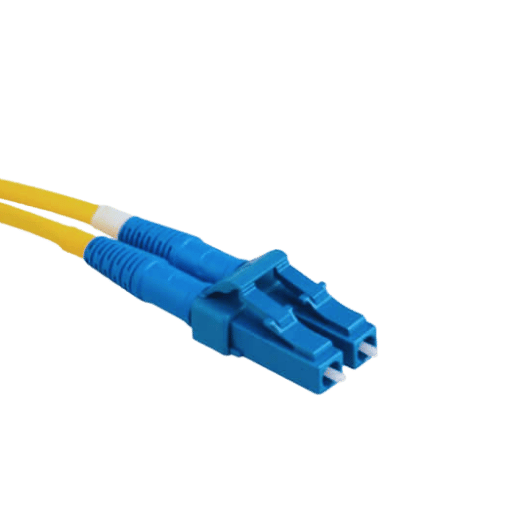
An LC connector is integral to the coupling of optical fibers and also to transferring light signals between fiber modules. LC connectors are small, which is an advantage in high-density networking as space can be utilized efficiently without any loss of performance. An LC connector’s push-pull configuration also alleviates concerns about connection security and avoids signal loss as well as reflection. The integration of a high degree of precision in the interconnect marginalizes the impact on data transmission even while reaching greater distances, which is critical for telecommunications and data networking.
Proper cable management ensures that the elements of any fiber optic system are correctly aligned resulting in minimal losses. Unfortunately, where there is poor alignment, there is an increased attenuation, reflection, and eventual degradation of the signal and quality of data transmitted. Correct orientation of connectors, LC fiber optic connectors, for instance, contributes towards better coupling of the light signals, which are very important for high integrity of signals over long distances in a network. Special and sophisticated equipment and alignment techniques are used to guarantee perfect positioning of the fibers, which minimizes performance degradation in high-speed telecommunication and data networks.
LC fiber optic connectors are designed to interconnect and couple optical fibers with a robust connection. This is accomplished using a push-pull technology which allows for the quick and easy insertion and removal of the connectors whilst maintaining the butt connectors’ alignment and minimizing insertion loss. Fiber optic connectors comprise two basic elements: the ferrule and the LSH connector, which contain the optical element. It is necessary that during the mating process, the connector’s ferrule components are mated to one another so that the light path is aligned. The effectiveness of the mechanism is also influenced by the quality of the materials of the ferrules and the accuracy of the connector housing. Furthermore, the mechanical backing of the LC connectors using a latch mechanism assists in anchoring the connectors in place and preventing disconnection in situations of high-density and high-performance networks.
Radio transmission systems have a different architecture than fiber optic communication systems and when comparing singlemode and multimode fiber optic cables it is necessary to know their properties and applications in order to ensure the most efficient operation of the network.
Core Size:
Transmission Distance:
Bandwidth Capacity:
Cost:
Light Source Technology:
By taking note of these differences, network planners can make the right choices so as to fit their intended requirements in terms of performance and connectivity which guarantees efficient and reliable data transmission systems.
Selecting between singlemode and multimode fiber optics should take into consideration the requirements of your application. In case your network requires transmission a great distance with bandwidth, singlemode fiber should be chosen as it is able to deal with large data rates and long distances with ease. This makes it suitable for telecommunication infrastructure and large network architectures. On the other hand, if your application targets shorter distances within buildings or campuses and is more cost-sensitive, then multimode fiber may be sufficient. Its relatively cheaper cost and ease of installation places it suitable for local area networks LANs and areas where there is minimal need for long-distance coverage of high performance. Think of these issues with respect to your project’s cost, distance, and performance targets so as to make the best possible choice.
The first advantage that makes it suitable for a given application of multimode fiber optic cables is its cost-effectiveness. It refers to the cables and transceivers used in its operation, which mainly consist of LED sources and not-based sources, which means higher expense than the case of singlemode fiber. This reduces the overall networking cost, which is more beneficial in short-range communication within data centers or within an enterprise environment. Second, multicore multimode fiber is significantly easier to install and terminate because of its larger core size, which, in turn, simplifies the handling process and alignment processes. In addition, it enables high data rates to be achieved over moderate distances, which makes it suitable for area networks. Although its distance is limited, multimode fiber constructed bandwidth is sufficient for a large number of commercial purposes, hence any data communication can be carried out efficiently in such limited environments.
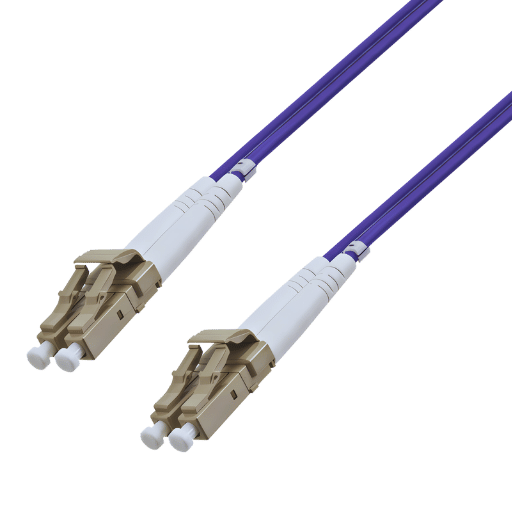

An LC Duplex configuration is a highly recognizable element of a network infrastructure because of its compact design and easy deployment. Congestion problems inherent in constructing new buildings or relocating them to better locations can be greatly eased by high connector density in patch panels and enclosures. This efficient use of space provides room for a larger number of connections within a single environment, minimizing the expansion of operational infrastructure and enhancing cable routing. Industry reports give evidence that data centers can bring a null deficit in deploying port density with data center overlay networks where all other interconnections are traditional MPX RXs. Moreover, the reduced volume occupies less material, and the installation is less expensive, which facilitates smooth network deployment. In addition, the Duplex LC builds in a reduced design that brings down the insertion loss, enabling it to function even in a hot room with all plugs tightened up.
Duplex LC configuration allows a substantial gain in data transmission since it utilizes separate optical fibers in both transmitting and receiving ends in a single connector, allowing throughput twice its simplex counterpart while allowing bi-directional communication over a single optical fiber link. Progress of fiber optic technologies greatly reduced the attenuation of Duplex LC connectors, which directly correlates to faster data speeds with less compromise in the signal quality. Because this capability allows a sufficient amount of bandwidth to increase and can be easily integrated with currently used advanced networks, this feature makes it an indispensable telecommunication infrastructure component.
Duplex LC connectors have competitive advantages over other media types and connectors with regard to cost efficiency and scalability. They facilitate better port density and lower the physical size ratios to available infrastructure which in turn reduces overall costs. Such an approach not only reduces material and installation costs but also energy and operating costs, which are important when dealing with large data centers. In terms of scaling out, the Duplex LC makes it possible to physically deploy more networks without having to make drastic changes to the existing one. These features correspond with the increasing requirements of supporting high data and connection density in telecommunication networks and allow the use of infrastructure that responds swiftly and timely to changes in technology requirements.
In order to offer the best service and lifetime for your network system, regular fiber optic connectors maintenance and care is fundamental. Regular maintenance practices should start with visual inspections for any damages or contamination. Cleaning must be carried out with solvent-free cloths and specialized equipment meant explicitly for fibers in order to avoid scratching or damaging the connector surfaces. Also, it is important to cover connectors against excessive force or bending effects, as these could deteriorate performance in the long term. Regular testing with an optical tester can assist in determining whether fiber optic losses have become excessive, enabling appropriate repair or change of components in order to maintain the effective running of the network.
When trying to solve basic problems associated with fiber optic connectors, always remember to apply a methodical approach. Start by inspecting the connector or the cable for any breaks, bends, or dirt that may be visible. Oftentimes, signal loss problems are a result of poor cleaning. Therefore, the connectors in concern must be thoroughly checked for any dust or dirt and cleaned using the appropriate tools and techniques. Another problem is related to the misalignment of the connectors, which can be fixed by reclipping them to make them fit together better. Make sure to confirm that all connections are attached securely and carry out the tests with an optical power measuring device to guarantee that the losses sustained in the signal remain within the determined level. Where there are problems, it may be necessary to change or reconfigure the whole fiber path and even consider environmental factors. This rational plan conforms to basic principles advocated and endorsed by experts and technology leaders in the field of fiber optics.
A: The duplex LC connectors consist of two connectors of separate ends that consist of two fibers combined into one bi-directional plug. These connectors are predominantly used as small form factor fiber optic connectors when space is more tightly constrained and are entirely suited for applications that call for duplex fiber optic communication. The connectors are available in different types, such as single-mode and multimode; therefore, depending on network requirements, a single cable of fusion connecting multiple connectors may be used.
A: This kit holds multiple tools that are essential for the purpose of terminating two-jacketed fibers, specifically 2mm jackets with the connectors; as a result this kit is classified as a duplex 2mm epoxy connector kit. Precision and durability are essential criteria and considering the use of duplex epoxy its tough bond makes it scope essential especially for strong reliable connections.
A: A duplex 2mm epoxy connector is suitable for applications requiring a sturdy lasting connection that is usually bonded with an epoxy making it easier to withstand tough environments while focusing on low loss and high ruggedness. Such advantages make it much better than other types of connectors particularly in terms of how well the signal does not get disrupted.
A: A duplex LC connector would work with a number of fiber patches most particularly single mode patch cord as well as multi mode patches like the OM1 and OM 3 patches and other such cable assemblies. Such connectors have been made to be able to facilitate better compatibility allowing for various types of fiber optic cable connections.
A: The multimode duplex 2mm epoxy connector is of utmost importance for 2mm optic fiber networks since it allows for increased performance range. Such connectors would be ideal for users that would want to maintain integrity of the information or signal when being transmitted over a short distance and are compatible with OM2 or OM3 multi mode fibers.
A: Yes, use of duplex LC connectors is feasible onto plenum-rated cable assemblies such as OFNP cables. Plenum-rated cables are intended for the installation in air-handling spaces and they have met rigorous requirements for fire safety, thus allowing the use of duplex LC connectors in such instances.
A: The uniboot design of LC connectors also offers cable reduction, as it is capable of accommodating two fibers under a single boot. This design facilitates the closure of the cable management, which makes it easy to accomplish the required connector’s polarity and decreases the connectors’ dimensions.
A: APC, or Angled Physical Contact connectors, improve the performance of duplex LC connections because the end face of the connector is angled, thus reducing back reflection over the duplex LC connection. This is quite significant in single-mode fiber optic systems, where signal loss should be avoided. Those connectors are used in several applications that require high return loss.
A: 900µm pigtails are used with duplex LC connectors to minimize splicing and installation. These pigtails are already terminated and, therefore, provide easier installation on the field and better management. The inclusion of a 900µm coating provides extra coverage for the fiber and increases the connection’s ruggedness.