In the world we live in today, connectivity is vital. This means that networking infrastructure has to be solid and reliable. Direct burial Ethernet cables are essential to outdoor and underground network installations as they are tough enough to withstand harsh environmental conditions. This article aims at giving you all the information you need when choosing the correct direct burial Ethernet cable for your needs. We shall look at various factors such as types of wires available, materials used in their construction, and performance specifications. Whether setting up a residential network or working on a large-scale commercial project, understanding these aspects will enable them to make informed decisions, resulting in better performance and longer life span for their networks.

Direct burial Ethernet cables are created for installation underground without additional conduit protection. They’re designed to endure severe weather conditions like moisture, high temperatures, and even physical abuse. The different types of this cable are differentiated by their performance levels and construction standards; for example, there are cat5e, cat6, or cat6a, which all vary in data speed transmission rates per second (Mbps), frequency ranges covered among other features such as shielding capabilities where higher values indicate better performance. The type chosen should be based on what you need it for, i.e., the distance between devices involved in the connection setup process, the desired speed at which information travels through the network connection setup process, and environmental conditions surrounding these connections, among others.
What distinguishes direct burial ethernet cables from regular ones is how they are built and where they are meant to be used. Direct burial Ethernet cables are designed specifically for being buried in the ground with no additional conduit protection around them. They have a strong outer jacket that can resist UV rays, moisture, temperature changes, and other things that happen outside the world. Sometimes these types of wires also contain gel-filled or water-blocking tape so as not to let any water inside it. On the contrary, an ordinary ethernet cable is used indoors where there is a controlled environment; therefore, it does not need such enhanced protective features for burying under ground level. Hence, such a type of wire cannot be used outside or underground because it may easily get damaged by external factors associated with nature.
There are many benefits to using Ethernet cables that can be directly buried, specifically in outdoor or underground settings where environmental factors present significant challenges. These wires were created to withstand harsh conditions and last long enough for your network performance to remain steady. Some advantages are:
By choosing carefully among direct burial ethernet cable options based on specific environmental needs and desired performance levels, organizations can create strong, resilient networks that last forever.
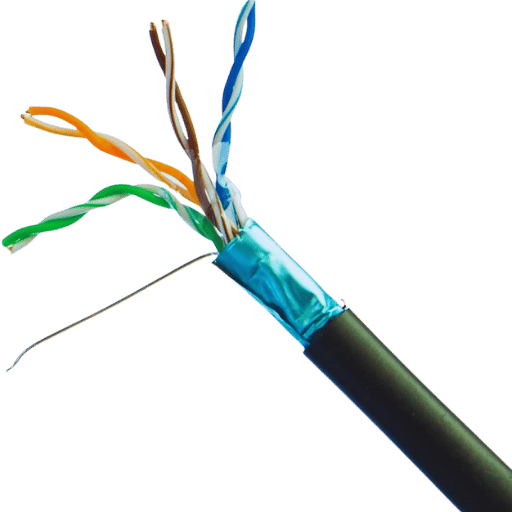
To select between Cat5e and Cat6 cables for direct burial applications, it is important to understand their performance differences. Here are some comparisons based on different technical metrics:
Data Transfer Rates:
Bandwidth Capacity:
Crosstalk and Interference:
Maximum Distance:
Future-Proofing:
By examining these performance metrics, businesses can select the Ethernet cable type most suitable for their needs, achieving optimal network performance and durability.
When looking at the cost of Cat 5e as opposed to Cat 6 cables, it’s important to think about what you’re paying for and how that investment will pay off over time. In general, the manufacturing process is cheaper for category five enhanced cables than sixes because they are less complexly built. This can be attractive when working on a project with budgetary restrictions or if top speeds aren’t necessary within certain environments. Nevertheless, even though they may seem more expensive at first glance, Cat Six cable offers improved performance levels compared to its predecessor, along with lower levels of crosstalk interference and more future-proofing potential. Consequently, this upfront expenditure could save money over the long term by eliminating upgrade needs in addition to providing better network reliability under heavy signal loss conditions, but such decisions must always reflect organizational requirements and financial limitations.
To make your network future-proof, be prepared for new technology and more bandwidth.
By doing these things, companies will be able to keep their networks strong enough to handle any future requirements without having too much cost involved through complete overhaul, which may lead to inefficient operations over long periods.

The American Wire Gauge (AWG) rating is a very important specification to consider when selecting Ethernet cables, especially for direct burial applications. The AWG rating determines the thickness of the copper conductors within the cable, which affects signal transmission quality, durability, and overall performance.
By choosing Ethernet cables that have been rated as such by appropriate means, organizations enable themselves to realize reliable connection points throughout their systems’ networking capabilities while also ensuring resilience against both physical and environmental stress, thereby optimizing investments made toward these infrastructure components.
While picking out between these two types of cables, it is important to take into account the particular needs of network environment.
In conclusion, what determines if one should go for UTP or Shielded Ethernet cable depends on the conditions of the environment as well as the need to control noticeable noise for maintaining signal integrity.
The resistance of UV rays is very important when choosing external cables. These cables are exposed to the sun, which may lead to material breakdowns as time elapses. The radiation from the sun can make non-UV-resistant cable jackets weak, brittle, and eventually break, affecting such cables’ performance and durability. For this reason, outdoor cables must be made using materials that have resistance to UV or have coatings protecting them from harmful ultraviolet rays so that their life span can be prolonged. This will still enable a wire to retain its electrical and mechanical properties even if it stays under direct sunlight for long hours. Using outdoor cables with high UV resistance helps organizations avoid frequent upkeep activities, enhancing continuity in network connectivity and reducing operational costs over time.

To properly evaluate how well a direct burial ethernet cable can resist weathering, you must take into account many external factors that may affect its durability and performance. Such elements include but are not limited to humidity levels, fluctuations in temperature, types of soil chemicals present as well as mechanical stresses that could be exerted upon them.
Moisture and Water Ingress
Any ethernet cable designed to be buried directly must be highly resistant to moisture. Water entry would degrade signals, causing short circuits, among other problems. These cables usually have gel-filled or water-blocking tape between their layers, serving as barriers against dampness.
Temperature Variability
Outdoor environments experience extreme heat and cold; hence, cables need materials able to tolerate these shifts without becoming brittle or losing their shape permanently, even after repeated flexing. An example is using polyethylene (PE) for outer jackets because it has excellent thermal properties.
Chemical Resistance
Cable jackets used in outdoor environments should be able to withstand exposure to various types of soil chemicals, which can eat away at them over time. This means they must have wide-ranging resistance against acids, bases, and other corrosive substances commonly found in soils worldwide.
Mechanical Stresses
Direct burial ethernet cables are prone to mechanical stresses, such as being run over by heavy vehicles during construction activities or accidentally hit by sharp gardening tools. Therefore, they are usually armored with steel wire mesh surrounding an additional layer made of sturdy plastic material so that they can resist such physical pressures without breaking easily.
Data and Testing Results
Recent tests indicate that direct burial ethernet cables have better performance and share low values on water absorption rates, which is coupled with the ability to maintain electrical characteristics when exposed continuously under wet conditions. For example, according to an IEEE report, gel-filled cables only allowed 0.1% water entry, which is far below the industry-acceptable limit of 1%.
Also, through temperature cycle testing, it was discovered that those containing polyethylene jackets can withstand wide ranges between minus forty degrees Celsius and seventy degrees Celsius without significant mechanical or electrical damage occurring to them throughout these extreme temperature variations. Furthermore, other tests revealed that they can resist 10% sulphuric acid concentration levels along with 20% sodium hydroxide concentrations without affecting jacket material integrity.
By considering these factors together with performance data, enterprises will be able to choose whether direct burial ethernet cables are suitable for their particular environmental conditions, thus ensuring strong stable networks over time.
One of the things that make direct burial Ethernet cables robust and durable is the High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) jacket material. Firstly, HDPE is moisture resistant; this is important as it maintains cable functionality under wetness. Secondly, its chemical resistance is very high, which makes these wires impenetrable by a wide array of substances such as acids and bases, thereby safeguarding against rusting or decomposition of internal components. To add on that, HDPE possesses great toughness, meaning it can stand up to heavy mechanical strains like being squeezed or struck without losing any part of its structural strength at all. With an operational temperature range spanning from negative forty degrees Celsius to seventy degrees Celsius, materials with such a wide working temp are always reliable in different climates but not limited there. Therefore, one may say that the lack of them would render many cables designed for use over long periods useless, especially under adverse conditions where they have proved themselves most useful before now.
To survive different environmental stresses, an outdoor-rated cable must follow certain rules. Robust jacket materials are used in designing these cables, like UV-resistant PVC and HDPE, that can protect them from being destroyed by direct exposure to the sun, moisture, or extreme temperatures. Besides the facts mentioned earlier, it is also worth noting that such types of cables usually have various kinds of weatherproofing. For instance, tapes or water-blocking gel might stop water from entering them altogether. Another essential attribute is their high tensile strength and physical damage resistance, which allows them to withstand mechanical stress such as bending, crushing, and abrasion. Additionally, they should meet industry standards like UL 444 for communications cables so that people can be assured they will perform better than expected when used outdoors and meet recommended performance levels set for this kind of application area. What makes these cables really strong and useful in harsh environments is a combination of all the abovementioned qualities.

To maintain signal fidelity during installation, follow these recommended practices:

Direct burial Ethernet cables are mostly found in homes. They are used to create a strong and quick network between buildings or different parts of land without using conduits. They can be used to connect houses with garages, set up outdoor security cameras or improve Wi-Fi coverage through outside mounted access points. These cables have an ability to hold up under various environmental conditions including wetness, dirt and temperature fluctuations thereby guaranteeing their efficiency over a long period of time.
Direct burial Ethernet cables are used in business and industrial sectors to create strong and consistent communication networks outside over large spaces. They are typically used to link different buildings within a compound, connect outdoor surveillance systems or set up networks at far-flung construction sites. In addition, they can be used for interconnecting devices in factories as well as commercial outdoor Wi-Fi hotspots. Their rugged design guarantees reliability even in unfavorable conditions hence can be relied upon to keep connectedness intact throughout various difficult environments.
To integrate direct burial Ethernet cables with current network infrastructure, it is important that you do so in a way that will ensure seamless connectivity and optimum performance. You should start by choosing a cable type that is compatible with your current network’s specifications; for example, Category 5e, 6 or 6a can be used. Use high quality connectors to terminate the cables correctly and follow standard industry wiring such as TIA/EIA-568-B.1 or ISO/IEC 11801 configurations.
Before you start laying them down however, ensure to conduct an environmental scan which will help identify any possible challenges like soil composition, moisture levels or even things like sources of interference. Carry out correct trenching methods and consider using additional protection such as conduit to enhance durability where necessary. Once they are all set up you’ll need to test the network connection points – this ensures signals integrity while at the same time giving opportunity for troubleshooting using Network Cable Testers if need be.
These steps are designed in such a way that if followed correctly one can seamlessly incorporate direct burial Ethernet cables onto their existing networks thus making them reliable and efficient across both old and new components of the system.
A: An outdoor direct burial Ethernet cable can be buried underground without additional conduit protection. It is commonly UV-resistant and built to handle extreme weather conditions, ensuring dependable network connections.
A: Compared to Cat5e outdoor cables, Cat6 outdoor Ethernet cables have higher performance capabilities. These cables support faster data transfer rates and bandwidths, hence making them more suitable for larger network systems, whereas Cat5e is enough for basic home or small business networking needs.
A: Yes, they are; this makes them appropriate for outside installations, too, because they can withstand being exposed to sunlight continuously over long periods of time without being damaged by it.
A: They provide better conductivity and durability than copper-clad alternatives; not only do they enhance signal integrity, but they also resist physical damage better, thus making them perfect for outdoor and direct burial applications.
A: No, you should not. Patch cords are generally not meant to be buried directly or used outdoors. Instead, it is advisable that you employ cables specifically rated for this purpose, such as cat5e or cat6 outdoor-rated ethernet cables designed to withstand harsh conditions.
A: Outdoor Ethernet cables can be run up to 100 meters (328 feet) for Cat6 and Cat5e cables. Signal quality decreases after this distance, which can affect network performance.
A: Direct burial rating means the cable can be buried underground without further protection, such as a conduit. It is made to withstand moisture, soil acidity, and other conditions found underground so that it lasts longer and works better.
A: A 4-pair outdoor ethernet cable uses four twisted pairs of conductors; this increases the speed at which data travels while reducing crosstalk and electromagnetic interference, thus ensuring reliable, fast network connections.
A: When purchasing a 1000 ft ethernet cable for outdoor use, consider whether it is UV resistant, direct burial rated, or what kind of conductors are used. Solid bare copper is preferred over anything else because of its performance benefits depending on the category (Cat5e or Cat6).
A: HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) Ethernet cables are chemically resistant, moisture resistant, and physically strong; hence, they are best suited for use outdoors, where they may need to be buried directly into the ground. Their robust construction ensures reliability even under harsh environments.