Due to their sturdy construction and multiple uses, DIN Rail systems have become increasingly important in contemporary electrical engineering. Known as the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) metal rails, these also aid the positioning of various industrial and automation components. The present article highlights the foremost varieties of DIN rails, their structural and size parameters, and the multiple ways such DIN rails and junction boxes can be used in various industries. The main features, which are of great importance for understanding the ways of using DIN Rail, are characterized. In this way, the paper’s authors provide enough information on how incorporating the DIN rails enhances the organization and performance within the technical and industrial environments.
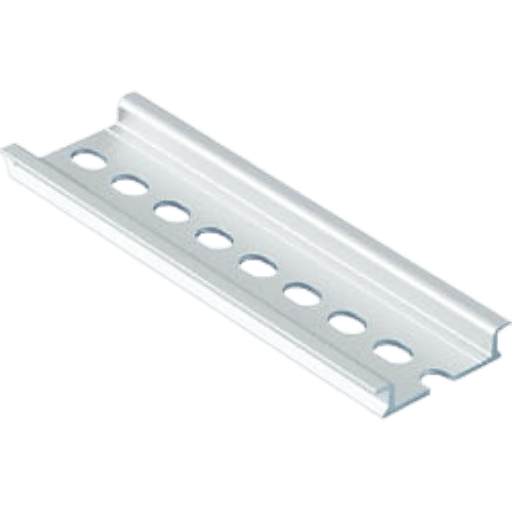

A DIN Rail refers to the standardized metal strip of a specific dimension that is usually used to install circuit breakers, terminal blocks, and other industrial control gears inside separate racks. These rails are usually made of cold-rolled carbon steel sheets, either zinc-plated or chromated, to prevent rust and corrosion. Such rails are built to protect and sustain the integration of electrical components. DIN Rails are crucial to the systematic arrangement of electrical systems, making it possible to combine electronic devices more rapidly and rearrange them and service circuits, too.
A DIN Rail is a metal bar manufactured to make it easy to assemble and hold various electric or mechanical parts. It is systematized by the German Institute for Standardization, which creates uniformity among multiple systems and assemblies. The primary function of a DIN Rail is to enable optimal arrangement and quick fitting of electronic components within control boards to improve the flexibility and scalability of the systems. Enhancing the effective arrangement and depreciation of the electrical network has reduced the time needed to install the systems and helped strengthen the efficiency of operation and maintenance of industrial and automation systems.
DIN Rails have gained pectoral arms application with electrical devices due to their versatility and efficiency. Most of the time, they are placed in enclosures called control panels and in the enclosures known as switchgear assemblies, where these are used to mount the circuit breakers, contactor units, and even relays. They also carry pen strips for wires that need to be connected, minimizing wirings out to ensure an orderly system with some complexities in terms of electric systems. In industrial automation, din Rails holds timers, programmable logic controllers (PLC), and other instruments to make the devices more accessible and troubleshootable. In addition, their flexibility makes it possible within a short time and relatively less cost to modify and expand electrical systems as the operations may change.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the EN 50022 standard are essential regulatory constitutions concerning the specifications of the DIN Rails. This is because their dimensions will be compatible in performance on a global scale. The IEC is responsible for creating international standards for electric and electronic equipment to facilitate rachet growth regarding its popularization and commercialization. In particular, the facilities en 50029 vilket definer matt och jarnvagsbroen for din rails, making it possible to fit different uses and manufacturers. Unfortunately, according to some, this is so the guidelines are closely adhered to that the interspersed components with the Riles remain operational, indicating the industry and approval requirements.

Mounting a DIN Rail requires proper tools and methods to guarantee effective and professional fastening. Basic tools for such an exercise include a measuring tape for guidance, a level to facilitate straightness, and a drill with suitable bits to form fixative holes. Furthermore, mounting plates or clips may be necessary depending on the particular sort of DIN Rail being installed and where it will be used. The method consists of defining drilling zones and making sure, in this case, the rail is horizontal before anchoring it. Any loading must consider all established manufacturer requirements regarding weight distribution and usage. These Manufacturer specifications must be respected if overload protection and system integrity are essential. The importance of these loading restrictions cannot be overemphasized, as compliance with the prescribed mounting practices enhances the safety of the users and makes possible later maintenance and extension of the electric power system.
Height also influences how much area can be filled by electrical and electronic fittings. Hence, the structural height of a DIN Rail is an important parameter. Usually, the heights of DIN Rails are 7.5 mm or 15 mm instead of the known types Miniature (Mini) and Standard, respectively. The determined height of the rail affects how the design and development of interconnecting components are done, which helps in how cross-sectional views of the electrical panels appear in terms of cascading accessible areas and space utilization when integrated within subjected enclosures. Thus, when purchasing a DIN rail, the height has to be factored in to accommodate the rising or falling devices that will be mounted or to meet the required technical specifications of the manufacturer. Such knowledge of these dimensions helps to plan accurately and better the available room that can be used for various electrical and control purposes and applications.
One major problem with DIN Rail mounting is ensuring it is securely and properly installed. This task requires proper tools and accurate measurements, as misalignment may result in unsatisfactory operation because of vibration, which may damage the components. The size and configuration of the DIN Rail are other major issues as they differ in significant proportions. Therefore, dependent devices need to be installed, and compatibility must be checked with the relevant guidelines of the respective manufacturer. These problems can be addressed by using adjustable mounting brackets for different rail sizes and applying pre-drilled holes or templates during drilling to eliminate the chances of going off standard. Moreover, adverse conditions like changes in humidity and temperature may interfere with the Definition of Insulation Resistance and the integrity of the rails and the attached components. Proper materials and proper equipment protection will help prevent any external conditions or damage to the electro-assembly, ensuring its effectiveness and longevity.

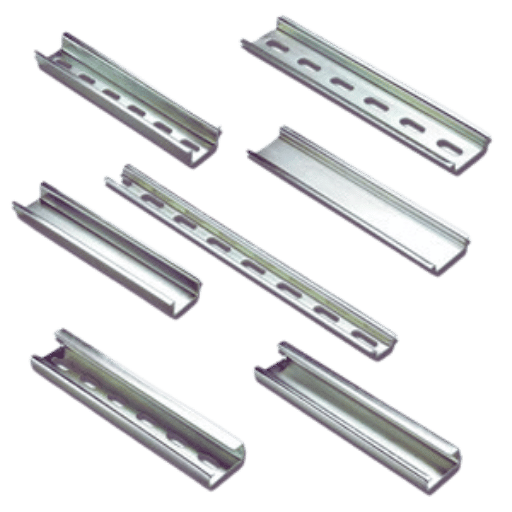
Also known as the top-hat rail, the TS35 DIN Rail is utilized in various applications in industries and commerce because of its widely accepted width of 35mm. It comes in a standard height of 7.5mm and another high version of 15mm, making it suitable for different supported and stable components. This rail type is famous for its fast installation and firm decent for electric and automation devices.
The miniature rail, or mini TS15, is used in areas where sufficient room is difficult to accommodate the apparatus. It only has a width of 15mm, making it perfect for fitting in a shallow but modular DIN-railed electrical product that requires some strong support. The TS15 rail is smaller in most dimensions, but that’s not a weakness. It is small but robust for secure component fitting.
The TS32 DIN rail is a C-channel, primarily 32mm in width. Its design is usually chosen for high-strength demands. That’s because Transformer TS 32 has a unique profile that is well suited for typical applications. This type is helpful in applications or operations with high dynamic forces, so you can’t expect it to break or get outerwear in such harsh places.
The selection between solid and slotted DIN rails, almost invariably, is directed by the requirement regarding weight, wiring convenience, and vibration resistance. Generally, slotted DIN rails contain several pre-machined holes that provide easy wiring and more flexibility for mounting components. Such a design reduces the rail’s overall weight, which can be an advantage in applications where the weight has to be minimized. On the other hand, solid DIN rails are far more rigid and can easily be used where sectioned applications subjected to vibration or ones that need strong support on heavier parts are being viewed. Solid rails allow that surface contact to be consistent, making the attached devices more durable and stable. These can also be made of such materials as galvanized steel plates and aluminum, all of which have design corrosion to include long-lasting uses under different environmental conditions.
The G-type DIN rails, with a G-shaped cross section, usually find applications when strong support and alignment are required for heavy machinery or components. G-type rails and out-of-plant connectors are commonly used in industries focusing on heavy electrical and automation components, such as manufacturing and industrial systems control. Due to its strength and stability, G-type rails are also highly valued as they can withstand harsh ergonomic conditions involving mechanical stress and vibrations, especially for applications demanding broad support from edge to edge.
In contrast, the standard DIN rails, otherwise seen as Top Hat rails, are very common and not specific to one type of application. Their shape makes it easy to install or remove mounted components for quick and complete wiring of panels. These rails are widely used in automation, building control systems, and consumer electronic devices, making them very efficient in space management and improving modularity due to standardization. Top Hat rails are meant for lighter parts, which are likely to change or be replaced often and can, therefore, be used in very active configurations, particularly with jumper connections.
The impact of DIN rail terminal blocks on the functions of industrial control systems is significant as they make them much more accessible and improve the wiring. With the industrial’s best practices, it is easy to join the control panel’s parts with terminal mounting, raising, arranging electric wires, and connectivity of many electrical devices and parts. As mentioned and observed, rail systems are pretty modular, giving the user the advantage of tailoring the system according to their specifications, especially in the future, without having to cause a massive redesign of the MAT. Moreover, using universal DIN rail terminal blocks also eliminates extra time wasted on wiring since it allows connection to various electrical equipment and automation tools. Such improvements in the systems’ design and functioning lower the general time of inactivating a system because of breakdowns and also costs in maintenance, which, in return, increases productivity as far as the industrial control systems are concerned.
RoHS compliance plays a crucial role in the safety and environmental protection of electronic parts and electronic systems, particularly for the searches for relevant, compliant products. RoHS signaling as ‘Restriction of Hazardous Substances’ is a legal framework for manufacturers that limits the use of particular hazardous elements present in the electronics like lead, mercury, cadmium, and others among flame retardants. By complying with the RoHS standards, the manufacturers may go a long way in minimizing the impact of electronic waste on the environment and the health of the users of the products. This compliance assures customers that their products do not contain materials that are harmful to health and the environment and helps in the strategies set out to protect the environment. In addition, implementing RoHS-compliant parts helps industries comply with laws in the strategic markets, earn consumers’ confidence, and achieve corporate accountability.
Circuit breakers and power supplies are consolidated in the DIN rail systems to enhance the safety and practicality of the structure. While operating digital devices, it is critical to provide a reliable operational voltage that is always low. The procedure of incorporating these devices is usually mounting and replacing the locking of these devices on the DIN rails, thus creating sanity and ease of maintenance. The primary function of an automatic circuit breaker is to protect the electricity supply network by automatically cutting off the electricity supply when specific parameters are exceeded or when a fault occurs, thereby preventing damage to equipment and injury to personnel. Due to technological progress, most supplies today provide overvoltage protection, while most circuit breakers are now made with the ability to be monitored remotely by users. Such developments enhance the effective and safe operation of electrical systems in industries and buildings to meet safety standards and promote the efficient use of the systems.
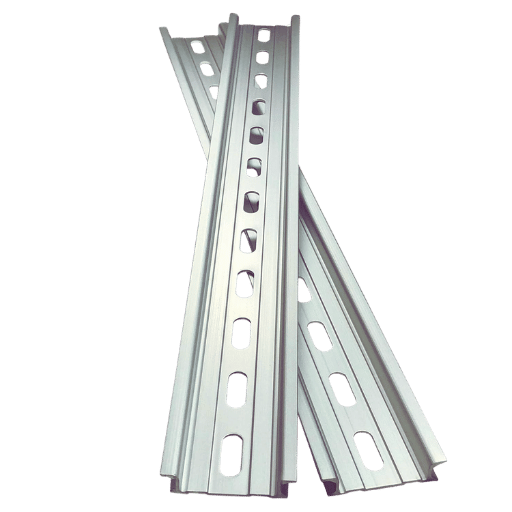
The commonly used DIN rail, which has a width of 35mm, is quite popular due to its flexibility and usability in multiple fields. To begin with, standardized dimensions enable the relatively quick installation of many electronic parts, helping achieve the desired integration and consider future growth. Secondly, 35mm is a good working width as it offers sound support and stability, essential in ensuring safe connections during operational use. This helps reduce the mechanical strains and vibrations, improving the components’ lifespan. Finally, using the 35mm standard is preferable as it conforms to specific organization policies, enhancing compliance with electrical standards and making the process of purchase and maintenance easier based on the ample availability of compatible parts.
This standard value of 35mm width in the DIN rail has also been evaluated in comparison with the 7.5mm and 15mm variants, as seen from several perspectives concerning usability and versatility in application. Though smaller and more casual, the 7.5mm and 15mm DIN rails are meant to be used in an enclosed area, where a light load is needed, or where space is at a premium. It does not have adequate support, which may be required for heavy-duty uses, but it has benefits in situations where space use is vital. On the other hand, the 35mm DIN rail is constructed with a robust structure that can withstand greater/heavier components. The size variation also affects the machine’s compatibility. The 35mm version is used with other equipment in the industry more often than the 15mm counterpart because it has an industry-universal attachment. The combination of these metrics contributes, and contractors using the 35mm sized DIN rails tend to undertake a complete industrial project application where stability and the ability to grow in the future are necessary.
The international body in charge of setting standards for electrical and electronic systems, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), has also defined the specifications for DIN rails. Such measures promote performance ceilings regarding safety, reliability, and efficiency, which are crucial for industrial components. Compliance with IEC standards, especially IEC 60715, which pertains explicitly to DIN rails, ensures product compatibility and interoperability amongst various manufacturers’ products. This certification enables easier global trading and design reusability while ensuring that the components achieve elaborate performance characteristics. Products within the regulations undergo multiple tests and quality assurance measures, making them suitable for complex applications requiring high performance. Therefore, IEC certification not only shows the observance of international standards but also guarantees the end user the safety and reliability of the product.
In my opinion, the contribution of DIN rails in holding motor controllers and relays is invaluable in maximizing the available space and achieving proper and efficient installations. As per the best sources, DIN rails offer a stable base for the placement of these components to be easily incorporated within the automation system. The design made possible through DIN rails allows for quick change or improvement of parts, which is beneficial since it allows for flexibility within the system and decreases the period of inactivity. Moreover, such standardized fixing devices enable the correct and stable operation of motor controllers and relays from various manufacturers, increasing the system’s safety and efficiency within industrial settings.
When connecting with electrical components, installing DIN rails proves valuable in ensuring that the electrical system configurations are systematically arranged. As per the learning from the prominent research institutions, I comprehend that DIN rail systems are a standard provision for efficiently and conveniently mounting various electrical devices, including terminal blocks, circuit breaker units, and connectors. This type of standardization is such that it lessens the wiring tasks, making the systems easier to manage and extend. Furthermore, the ease of changing and upgrading components made possible using DIN rails promotes flexibility and dependability in changing industrial environments. I have also learned that by using DIN rails, all electrical work can be kept orderly and in good reach, and all directives to the industry are followed, thus improving the entire system’s performance.
Regarding the electric system configuration in industrial and commercial establishments, DIN rail enclosures can be beneficial as they eliminate wasted space occupied by various cluttered and unorganized components by providing shrunk and orderly cover for these elements. The simple fuselage configuration used in these enclosures allows for many arrangements of the electrical equipment, thus ensuring full utilization of the available physical space. These enclosures have additional benefits: they often have self-adhesive devices that can hold and arrange the different components. This reduces the clutter and avoids the risk of wiring shock, considering the harsh edge-to-edge width while holding the device. It helps in tangle-free cable routing, which is necessary for the device sub-assemblies and frequent access for repairs in the system and the overall devices operating properly about safety requirements.
A: A DIN rail refers to a bending machine industry standard complicated rail in which facial loads are mounted in a skirting cabinet or elsewhere, and a supportive structure is employed. Din rails are 35mm in proper width and serve primarily to accommodate small devices like commercial switching circuit breakers, mains or comms power transformers, terminal connectors, and various programmable machines called PLCs. It keeps needless flourishes down, enabling better distribution and in-order position of diverse electrical instruments.
A: Broadly classified, the main types of DIN rails in present use include: 1. Top-hat rail (TS35): 35 mm wide, available in heights of 7.5 mm and 15 mm 2. C-rail: These come in sizes C20, C30, C40, and C50, with C30 having the most take-up area 3. G-rail: This is a shallow and less popular option that requires no penetration 4. Slotted DIN rail: It has slots, hence allowing flexibility in mounting components.
A: Slotted type of DIN rail has cut-outs or indents known as slots, which are spaced at intervals along the length of the rail. On the other hand, a Nonslotted DIN rail is blank. The slotted type is better because it imbues more provision for improved mounts for attachments with slotted channels, caters to heavier devices, and also aids in managing cables and wires. The non-slotted type is mainly used for standard applications and is cheaper than the latter.
A: Most components, if not all, which are meant to be mounted on DIN rails, come with a snap feature. To attach, the upper side of the component is clipped into the upper edge of the rail, and the lower part is pushed until a snapping sound is heard. Phoenix Contact and several other devices by Mean Well are designed to make it easy to snap onto the din rails. If you want to detach the wiring net from the rail, you must first unscrew the locking system and pull it away from the rail with a bit of force.
A: Zinc nominal steel is the most commonly used material for DIN rails due to its corrosion resistance and durability. Similarly, Polycase is listed among different companies that have some aluminum DIN rails, which are best suited for lightweight applications. High-class STAINLESS STEEL DIN rails are also available, suitable for uphill places that require high corrosion resistance.
A: It is possible to use DIN rails for such purposes. Some DIN rails have electric current transferring, electric current distributing, and grounding functions and are made of a busbar for those functions. Still, it should be noted that even when it is attempted to use the rail as a ground bus, it is essential to have correct connections to the ground and that the bolts are tight on all components to ensure that there is no loss of the ground.
A: DIN is an abbreviation for “Deutsches Institut für Normung,” the German Institute of Standardization. This organization established the norms for the said DIN rails, which later expanded globally for industries and electricity.
A: Some of the relatively common mistakes that pertain to DIN rail installations include: 1. Components that are supposed to be secure, becoming loose after vibrations, or poor installation Matrix type technology 2. Placing too many rails, cars, or busbars leads to heat build-up within the enclosure 5. static fragility, not catering to heavy, desktop-based components 4. Graffiti, in terms of excessive advertising 6. Furthermore, materials expose corrosion-resistant properties, sheaths, or liners that may not withstand hostile environments if adequately fortified. Regular maintenance and adequate installation procedures can reduce the occurrence of these instances.